1
4th stage
نسائية
Lec-6
د.اسماء
14/12/2015
Ultrasound Basics in Obstetrics
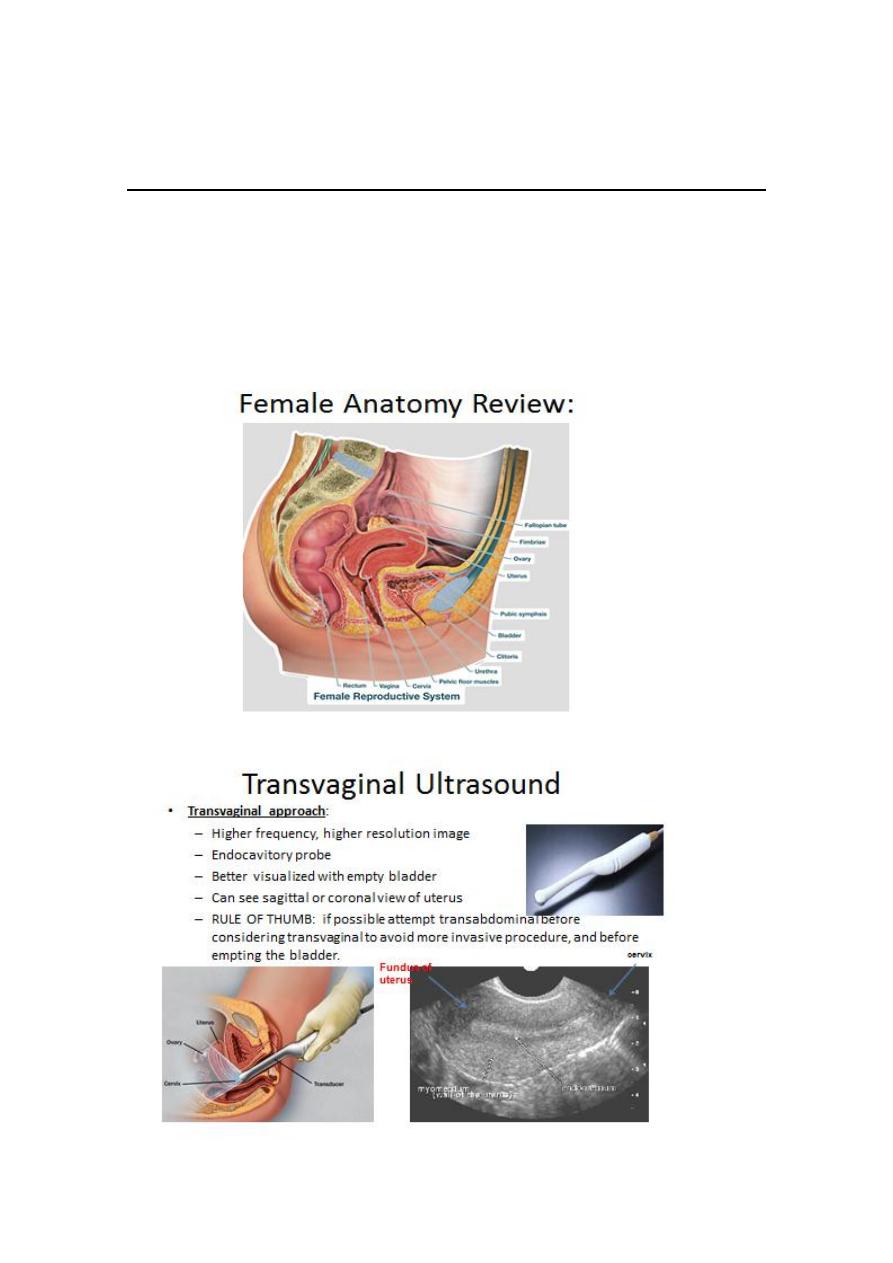
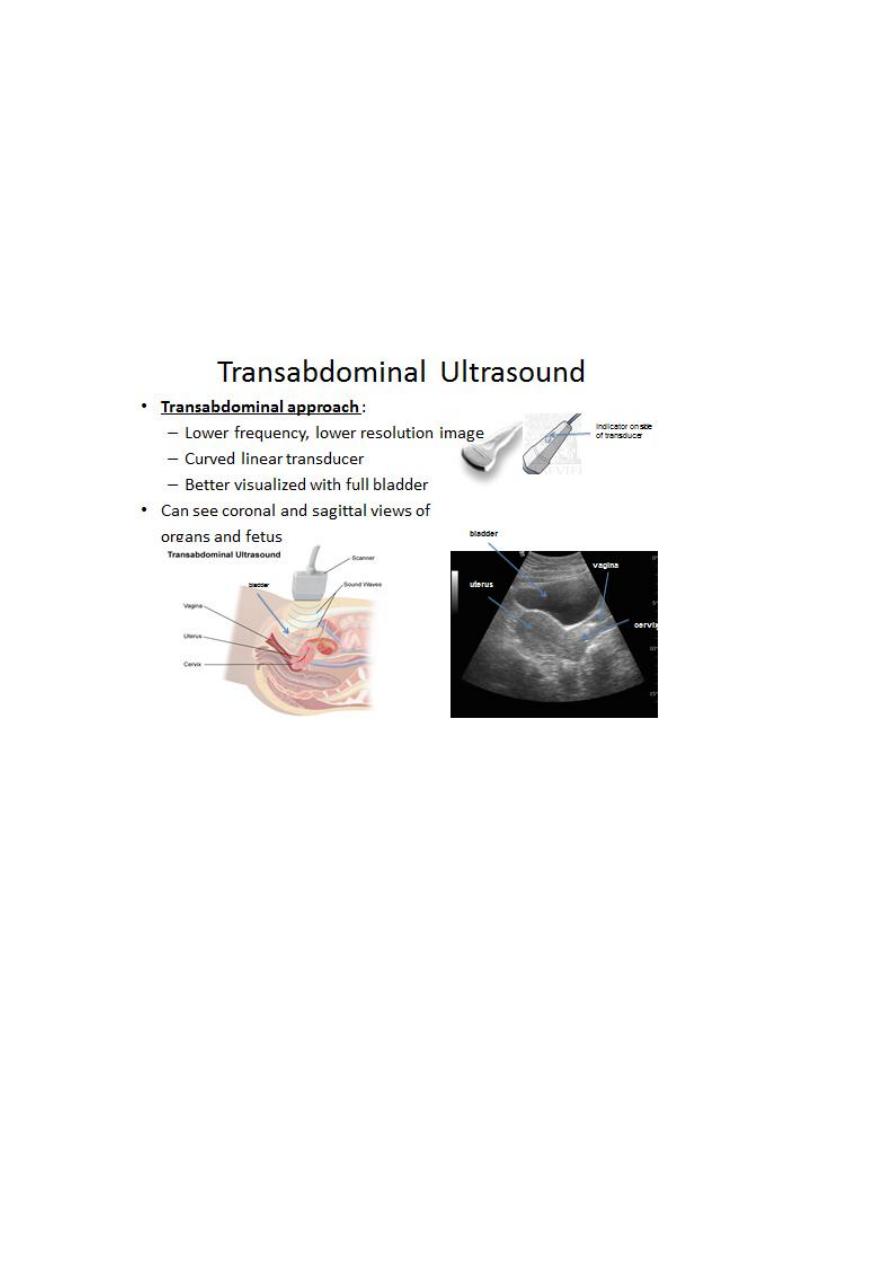
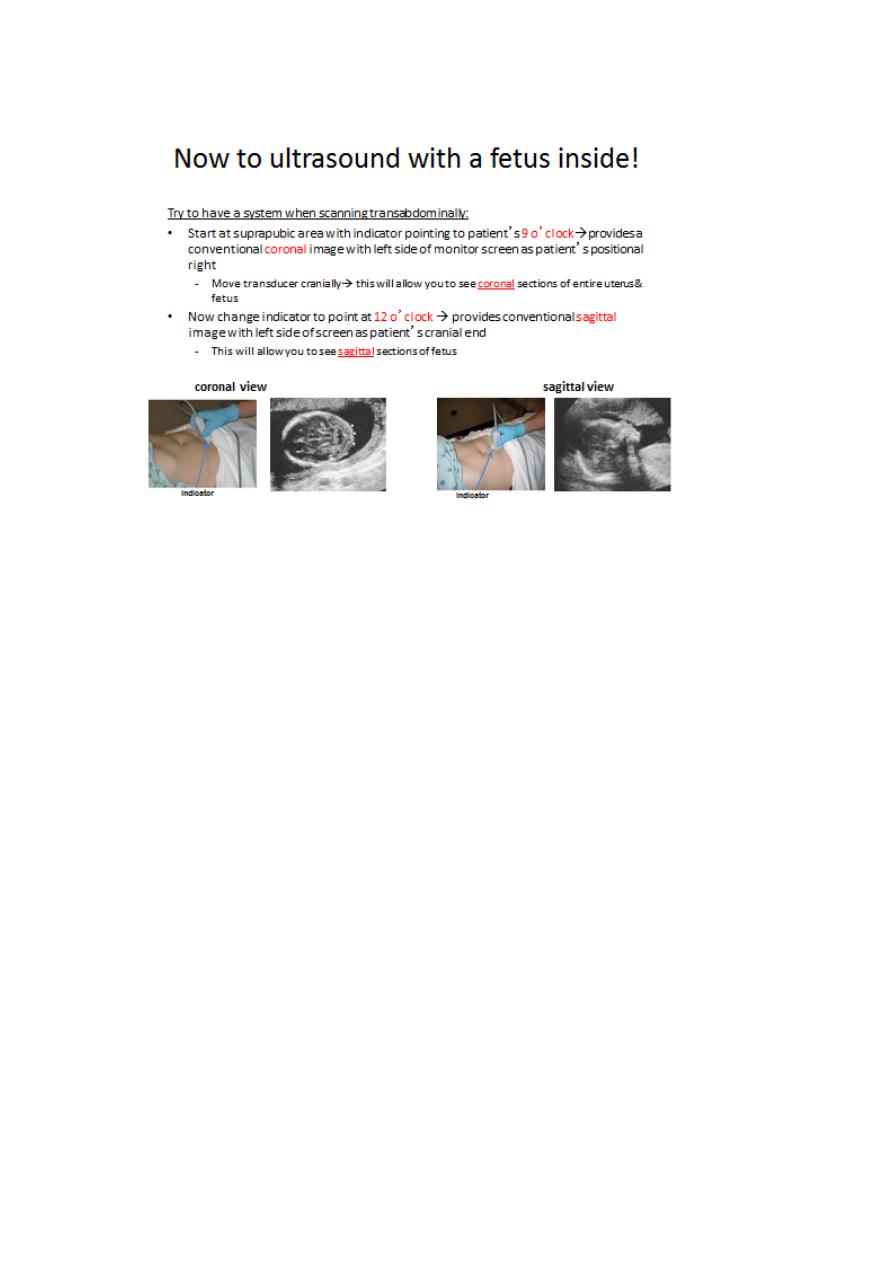
Obstetric transvaginal and transabdominal US plays apivotal role
in obstetric care, many women nundergoUS examination without
no adverse effect on the fetus.
2
It’s used in early pregnancy before 16 weeks because of close
proximity of the intravaginal probe allowing better resolution of
the pelvic organ ,uterus and pregnancy
3
The Report and Criteria for Assessment
1. Record if transabdominal and/or transvaginal scan performed.
2. Clinical history and indication for examination. LMP or EDD by dates.
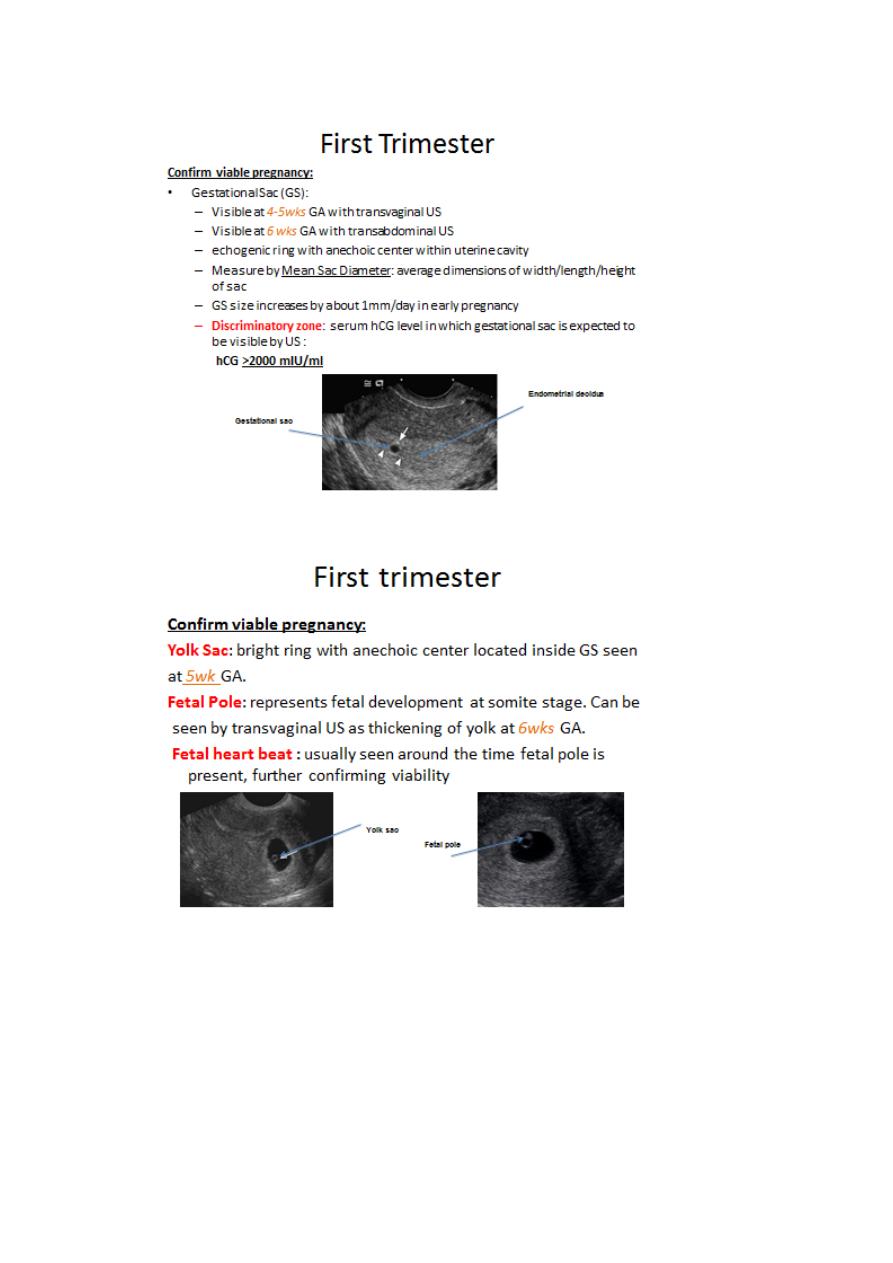
3. Dating: If a fetal pole is present, the CRL used for gestational age
calculation is recorded. If no fetal pole is present, the mean gestational
sac diameter is used to assess gestational age. Presence or absence of a
yolk sac should be noted when a fetus is not seen. Calculate EDD by
Ultrasound if more than 4 days different from EDD by dates , ultrasound
in 7 days may be recommended .
4. Fetal Viability: Transvaginal Scanning is recommended in all
pregnancies of <8
weeks gestation if no fetal heart motion can be recorded
transabdominally:
If the above criteria are not present, i.e. pregnancy is < 6 weeks
gestation, a repeat
ultrasound in 7 days may be recommended in the report. If fetal
viability is confirmed but PV bleeding persists or worsens, reassessment
may be indicated.

4
5. Ectopic Pregnancy: Uterine cavity appearance, ovarian appearance
and site of corpus luteum, presence, size and site of the suspected
ectopic, presence of peritoneal fluid including under the diaphragm.
Correlation with quantitative b HCG recommended.
6. Multiple Pregnancies: Chorionicity should be reported and is most
accurately assessed during the 1st trimester. Two completely separate
gestational sacs confirm a dichorionic twin pregnancy. The CRL and
FHR of each twin should be stated.
If there is only one gestational sac, the pregnancy is monochorionic and
in these cases, the yolk sac and amnion should be clearly assessed.
If there are two separate yolk sacs and a separating amnionic
membrane, the pregnancy is mono-chorionic/diamniotic.
If there is only one gestational sac with only one yolk sac, and a single
amniotic cavity,the pregnancy is monochorionic/monoamniotic.
7. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: A molar pregnancy is suspected in
the presence of
cystic hydropic change to placental tissue.
8. Uterine and adnexal Masses – Describe the dimension, nature and
location of the mass. Presence of free fluid.
5

6
Other measurement parameters used to estimate gestational age
Biparietal diameter
Femur length
Abdominal circumference
The various parameters can be used in a specificequation providing
estimated fetal weight (EFW)
First Trimester:
Thickened Nuchal Tanslucency (NT):
One of the parameters used in sequential screening (SS) for
Down’s syndrome in first trimester
SS: Pregnancy associated plasma protein levels, hCG levels, NT
thickness
Measured during 11-14 wks gestational age
Seen on sagittal image as increased subcutaneous non-septated
fluid in posterior fetal neck
Measurement >3mm usually considered abnormal, however exact
cut off measurements are dependent on maternal age/gestational
age
Detection rate of screening for Down’s Syndrome in first
trimester:
7
-sequential screening with NT: 82-87%
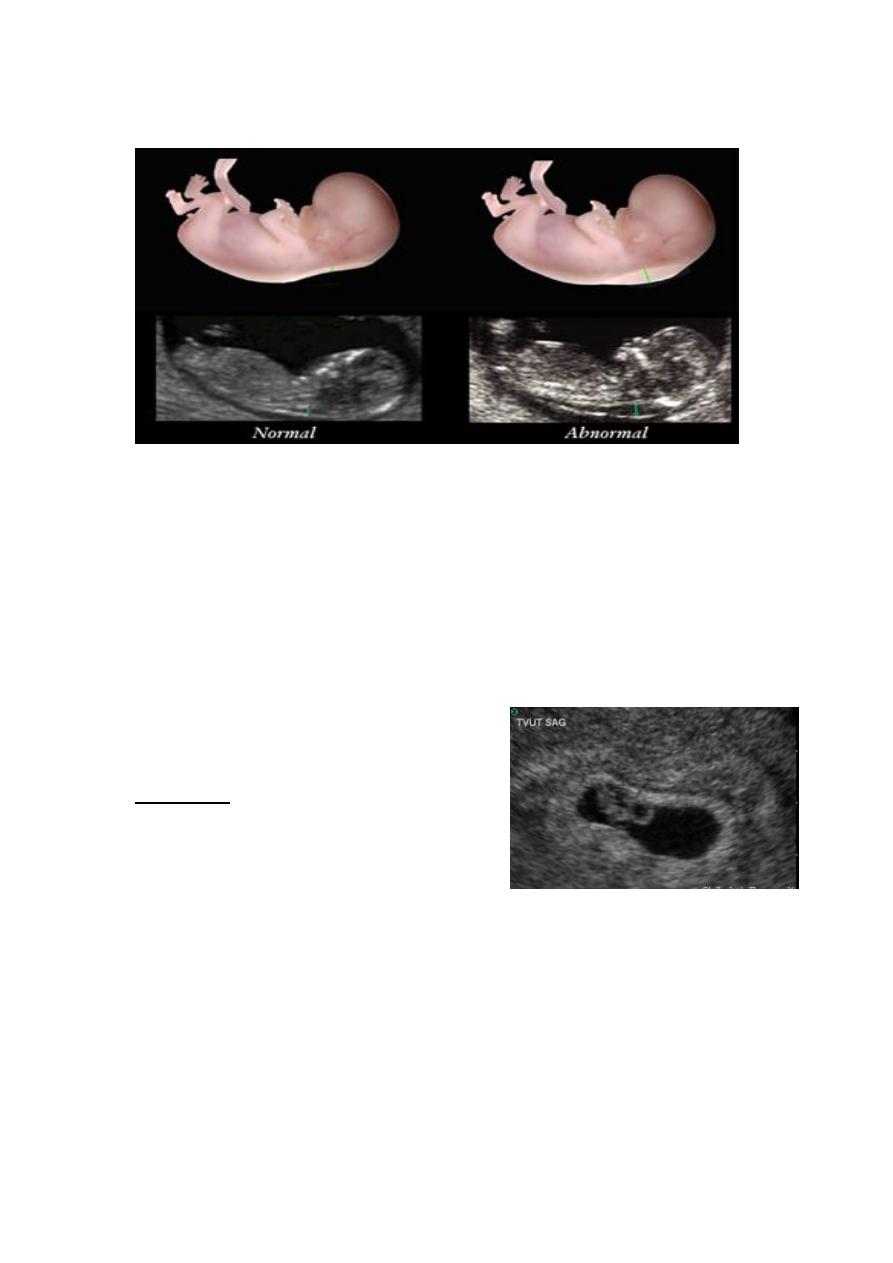
Case 1
A 23 year old G1P0 comes in to the clinic to confirm her pregnancy
status. Based on her last menstrual period (LMP) she is 8 wks 2days
pregnant. She took a home pregnancy test yesterday which was positive.
To confirm her pregnancy you do the following:
Repeat urine hCG test: Positive
Transvaginal ultrasound:
US findings: Gestational sac and CRL
measuring at
7wks gestational age
- There was a detectable
heartbeat
Question: Is this a normal pregnancy?
8
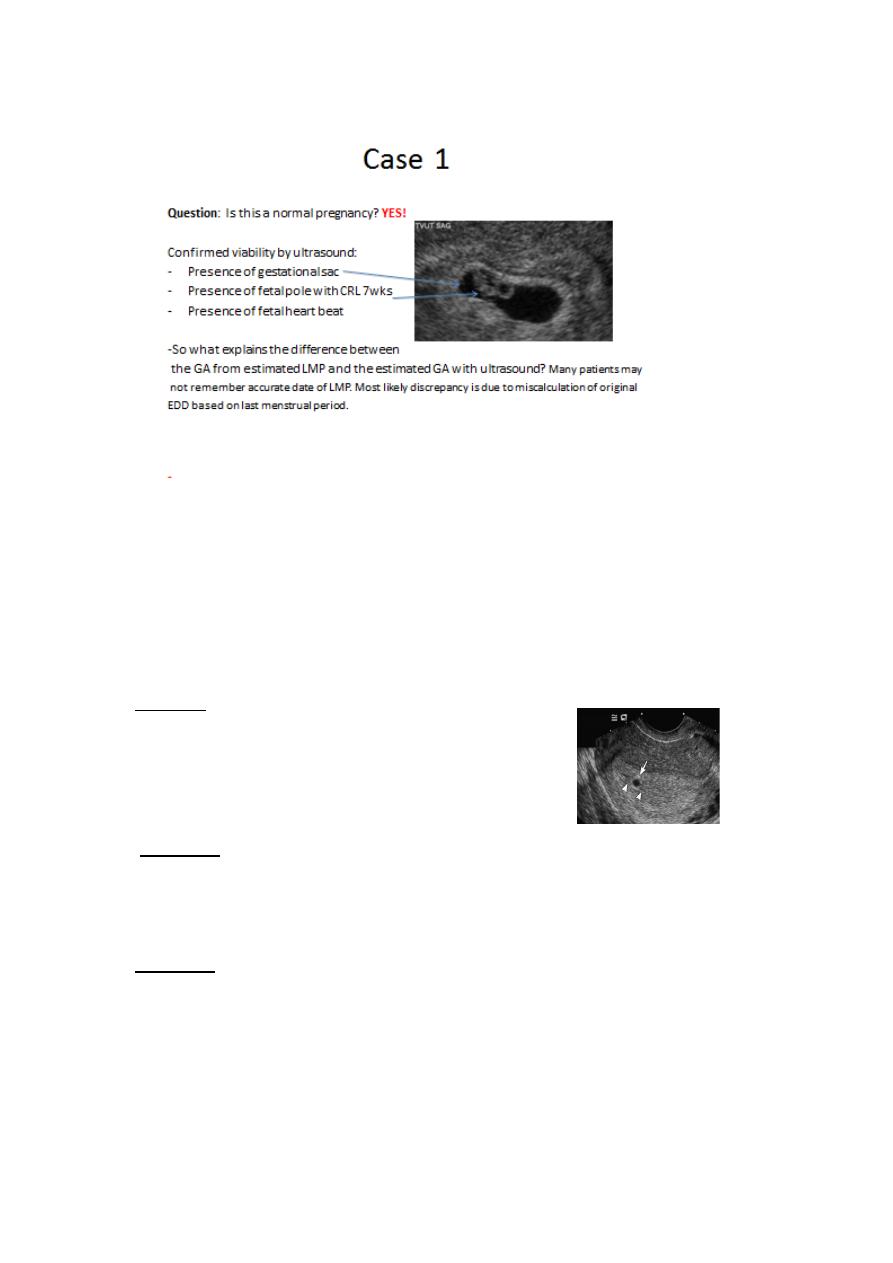
Case 2
A 28 y/o G1P0 comes in for her first prenatal visit. Patient has been
reliably tacking her menstrual cycle for the past year. Based on her LMP,
her estimated EDD suggests she is 9 wks pregnant. She reports
pregnancy has been uncomplicated. Upon ultrasound you see:
Findings:
-
Echogenic getational sac with in uterine
cavity,
GS measuring 5wks
Question: Is this a normal ultrasound finding?
Case 2
Question: Is this a normal ultrasound finding? NO!!!
-
This case is suggestive of a Missed Spontaneous Abortion with a
non-viable gestational sac
-
At 9wks GA expected ultrasound findings include:
-
yolk sac, embryo, fetal heart beat

9
-
CRL of embryo measuring close to 8wks GA
Approximately 50% of early 1st trimester spontaneous abortions
are attributed to chromosomal abnormalities. Most common is a
non-viable trisomy.
In comparison, 2
nd
trimester abortions are less likely due to
chromosomal abnormalities.
Case 3
A 24 y/o female G0P0 comes in to the ED with acute onset of right lower
quadrant abdominal pain that started late last night. She is sexually
active and unclear of LMP . She reports that she had vaginal spotting this
week which is unusual because she usually does not spot between
periods. Sexual history is significant for chlamydia/gonorrhea 2 years ago
that was appropriately treated with antibiotics.
Physical Exam: She is afebrile, tender to palpation to RLQ with palpable
right adnexal mass.
What initial test should be done in the ED?
-
Pelvic ultrasound imaging
-
Urine hCG levels

11
Case 3
This case is most likely a Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy!
Further workup:
- In normal intrauterine pregnancy, serum hCG levels should increase
about 60% in 48hrs
-
Doing a 48hr serum hCG test that shows <60% increase may
further suggest abnormal pregnancy
Does this patient have any risk factors for an ectopic pregnancy?
Patient’s h/o of chlamydia/gonorrhea puts her at increase risk of
developing tubal ectopic pregnancy. This is found to be especially
true if past infection was an ascending infection that caused
inflammation of fallopian tubes that resolved with scarring of
fallopian tube. This may increase risk of fertilized egg getting stuck
in tube.
Common risk factors for tubal ectopic pregnancy includes:
chlamydia/gonorrhea
pelvic inflammatory disease of tubal ligation
11
12
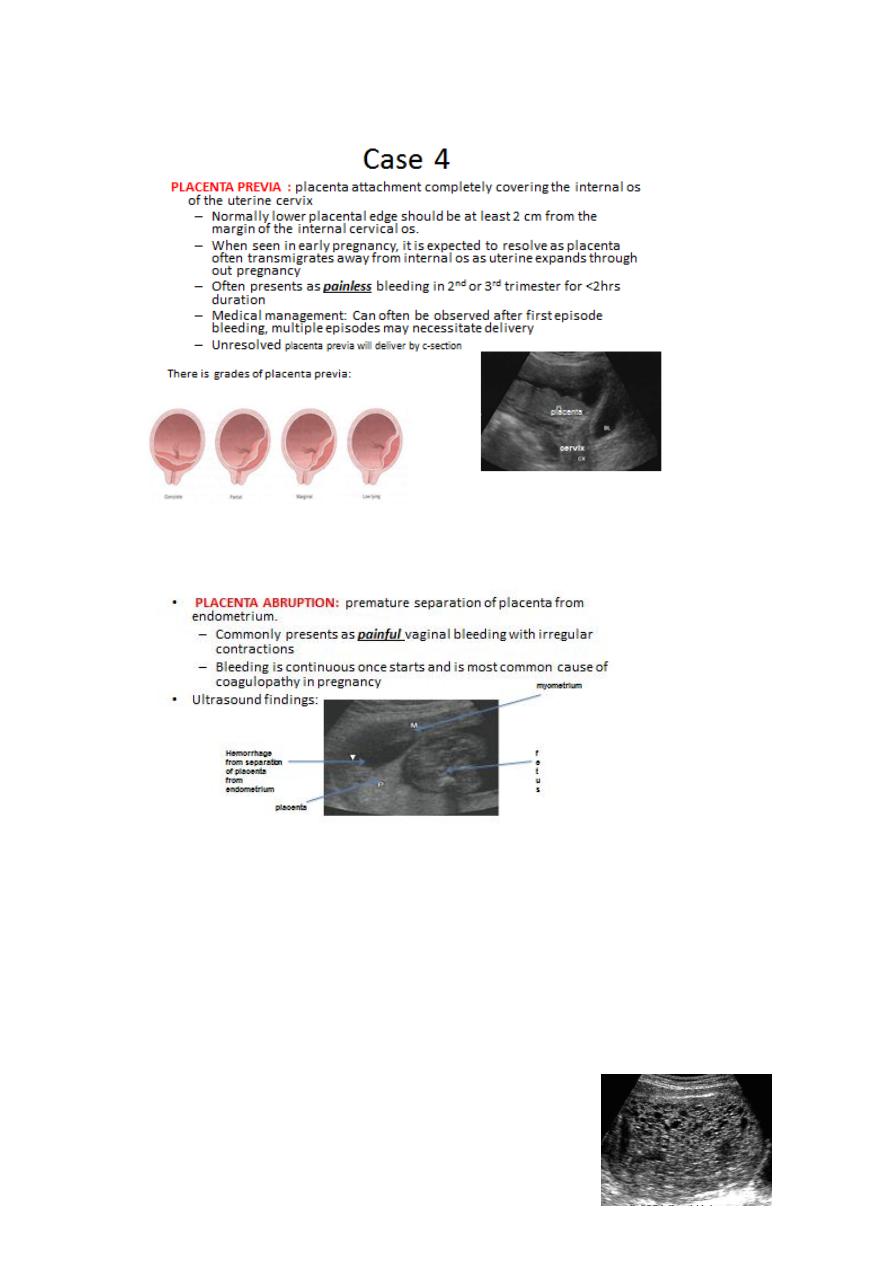
Case 5
25 y/o G1P0 at 14wks GA dated by LMP comes in for her first prenatal
care, Pregnancy was confirmed by multiple urine pregnancy test 7 wks
ago.
-
Pregnancy has been complicated with recent
vaginal bleeding with out pain.

13
-
Uterus larger than expeceted for a 14wk pregnancy.
QUESTION:
How would you describe this finding with in the uterine cavity?
