د.منى
\
radiology L2
Radiology of thyroid
The major function of thyroid is secretion of thyroid hormones that regulate the normal growth and
development of each small cells in the body
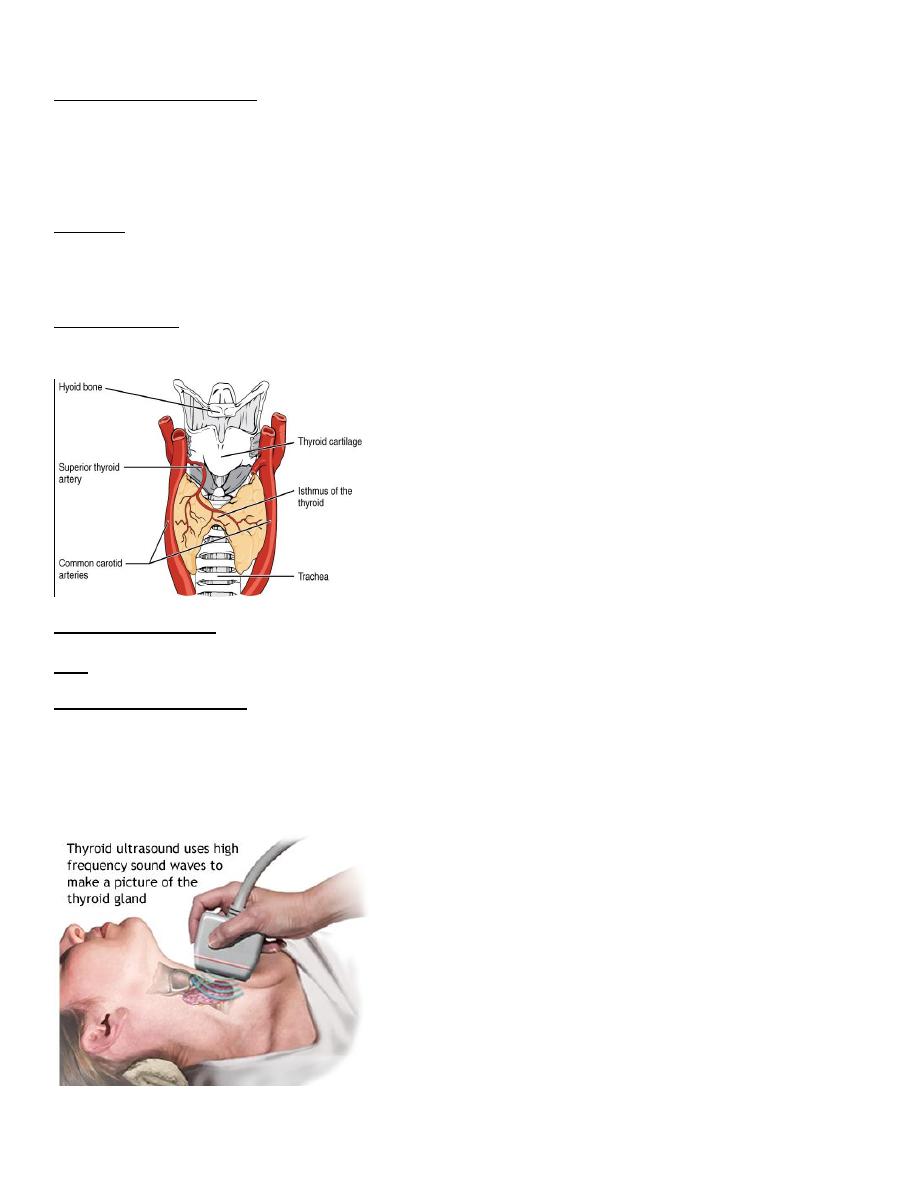
Anatomy :
Location :
Two lobes and isthmus in between and its lies in and encircling the trachea from both sides and the anterior
part and leading the posterior part of trachea is free
The blood supply
The major blood supply is the superior thyroid artery which is branch from the external carotid artery
Imaging technique :
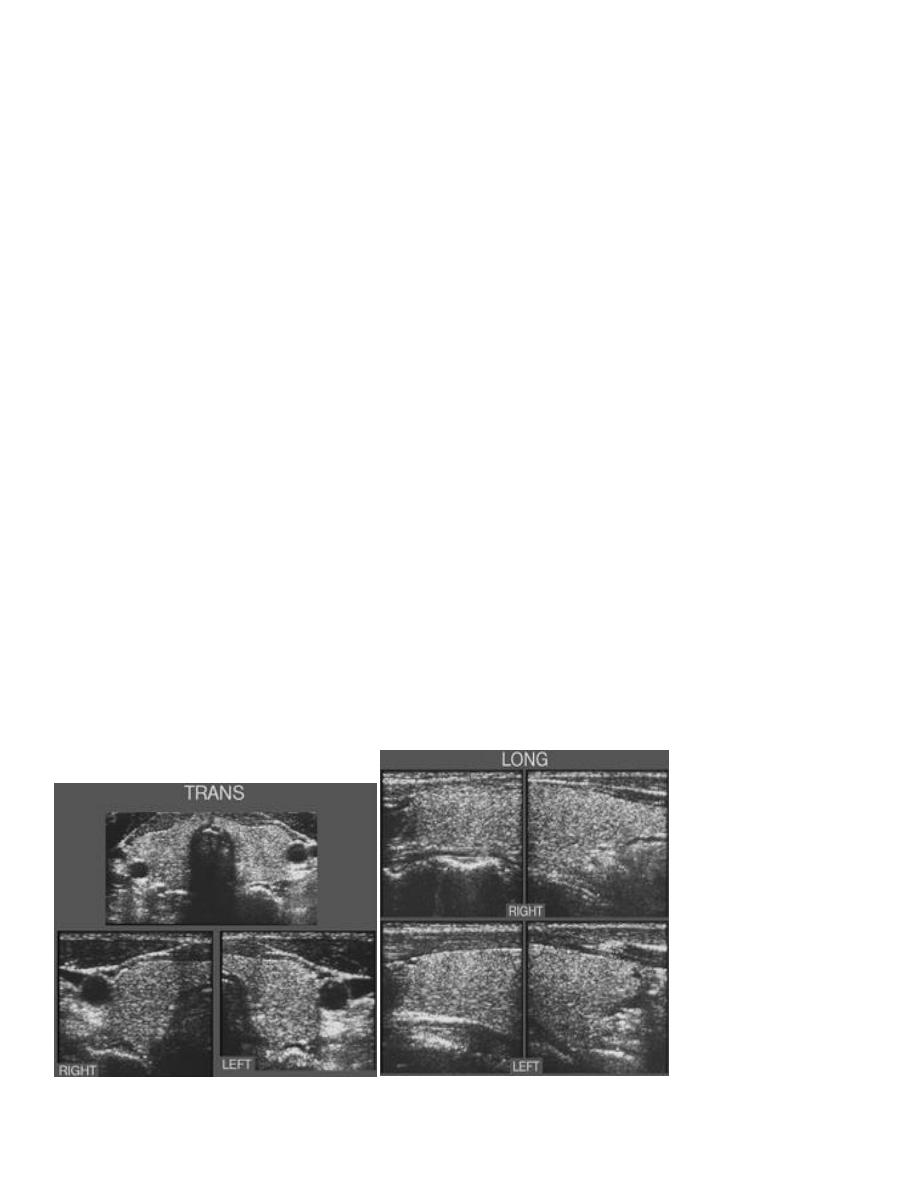
US :
Measurement of thyroid :
- Using a linear probe that used for any superficial structures
- Assume it in a full extension position when lying in supine position
** it’s the initial imaging to the thyroid
د.منى
\
radiology L2
• Non ionizing radiation
• Clear out the nature of a nodule ,,weather cystic or solid
• Readily available method
• But it is not able to differentiate benign from malignant nodule ,how ever the majority of thyroid
nodules are benign
• Ultrasound aid for a needle guided biopsy
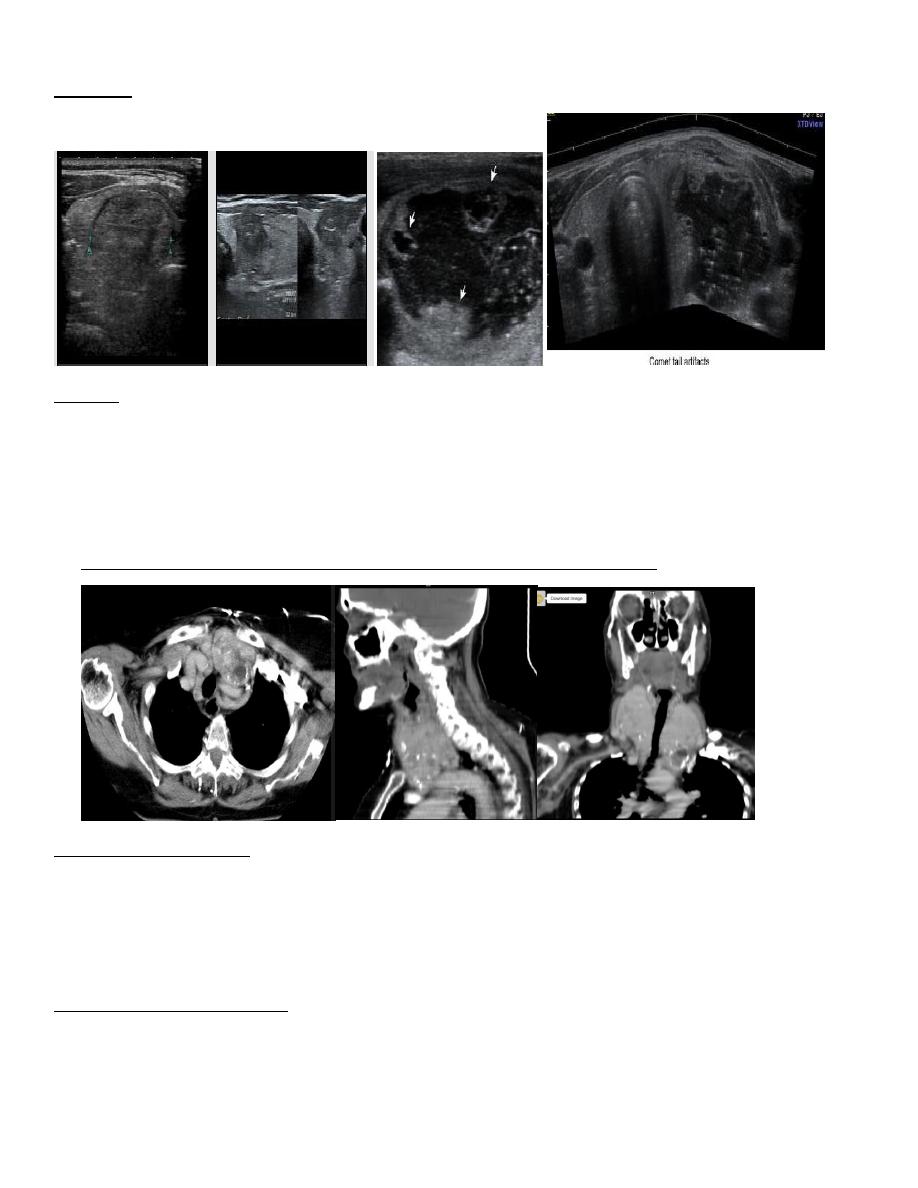
• Son graphic features favoring benign lesion: large cystic component, hyper echoic nodule and coma tail
artifact.
• Son graphic features favoring malignant lesion: hypo echoic nodule, micro calcification, taller than it is
wide and local invasive to surrounding structures
*** vascularity of thyroid lesions not guiding us to the nature of malignant or benign
Differentiate the malignant from benign nodules
Malignant benign
-Have infiltrative border - have clear cut border
-Have depth more than -have transverse diameter
Transverse diameter rather than depth
-Have microcalcifiactions -no
-Solid mass - more in cystic compartment
-No comma cell - have comma cell
Normal US
د.منى
\
radiology L2
Diseased
CT scan
- Used to assess the huge thyroid gland ( size )
- Any retrosternal extension through thoracic in let to lung so cause dyspnea and respiratory distress
- Can assess that the retrosternal extension is lying in the anterior or posterior compartment i=of the
chest
- Also see the related structures
*** neither US nor CT scan can differentiate the lesion is malignant or benign
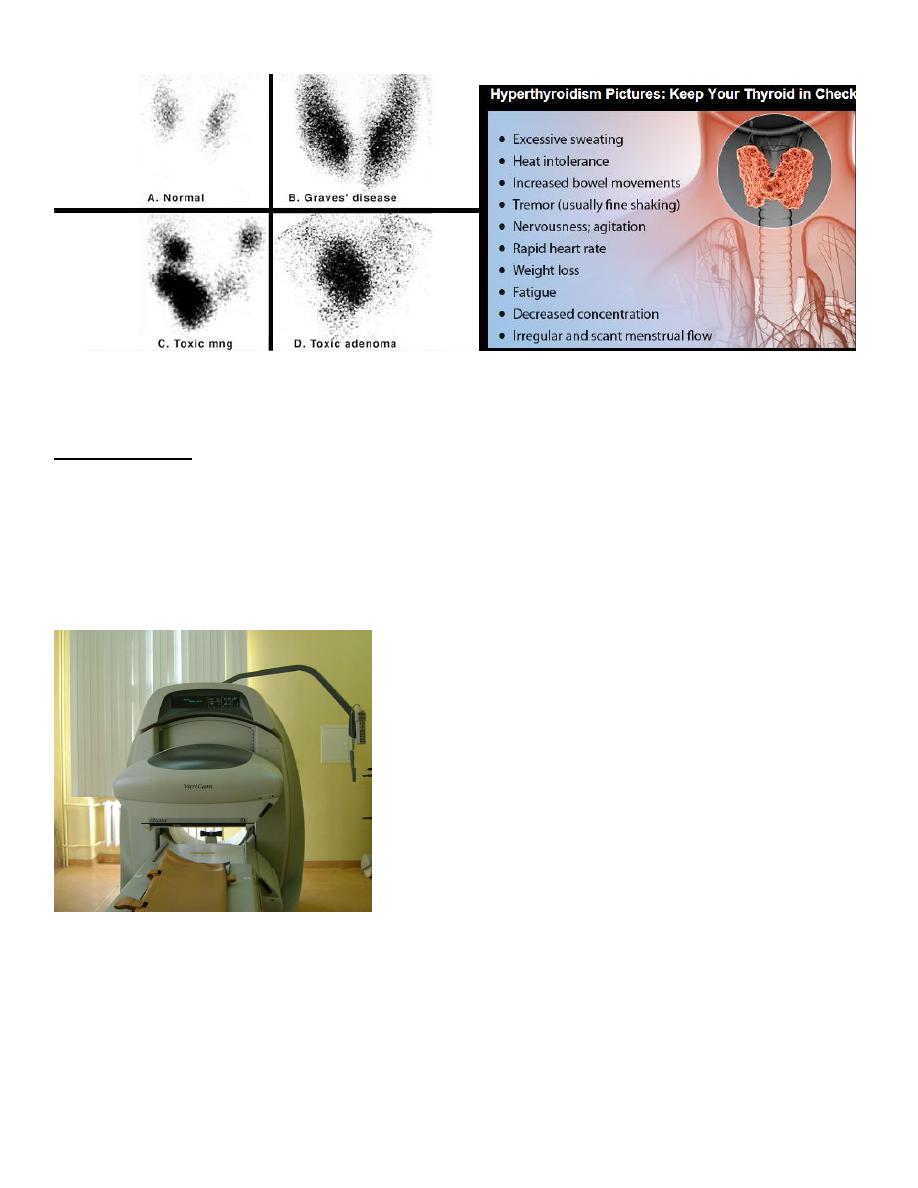
Radioisotope scanning
Push a particles that stained with iodine , inject into vascular system and reach thyroid and picked up by it so
can differentiate if the lesion is malignant or benign
Whenever there is increase intake it raised the possibility to benign lesion but low uptake it goes with
malignant Tu.
**It’s the best imaging modality
- Enlarge graves … more intake
- Toxic adenoma and goiter ,, its go with benign
د.منى
\
radiology L2
Gamma camera
It’s a radio isotope for whole body
Indications :
1. Distant metastasis
2. Boney metastasis , whole body
3. Lymph node ( small mesenteric )
Imedullary and papillary Ca. of thyroid ( more aggressive ) cause military metastasis to lung and reach the skull
than cerebral and reach the parenchyma
Cause of military lung metastasis ( military metastasis of axial CT scan lung window
1. Follicular or papillary ca.
2. Malignant melanoma
3. Breast carcinoma
د.منى
\
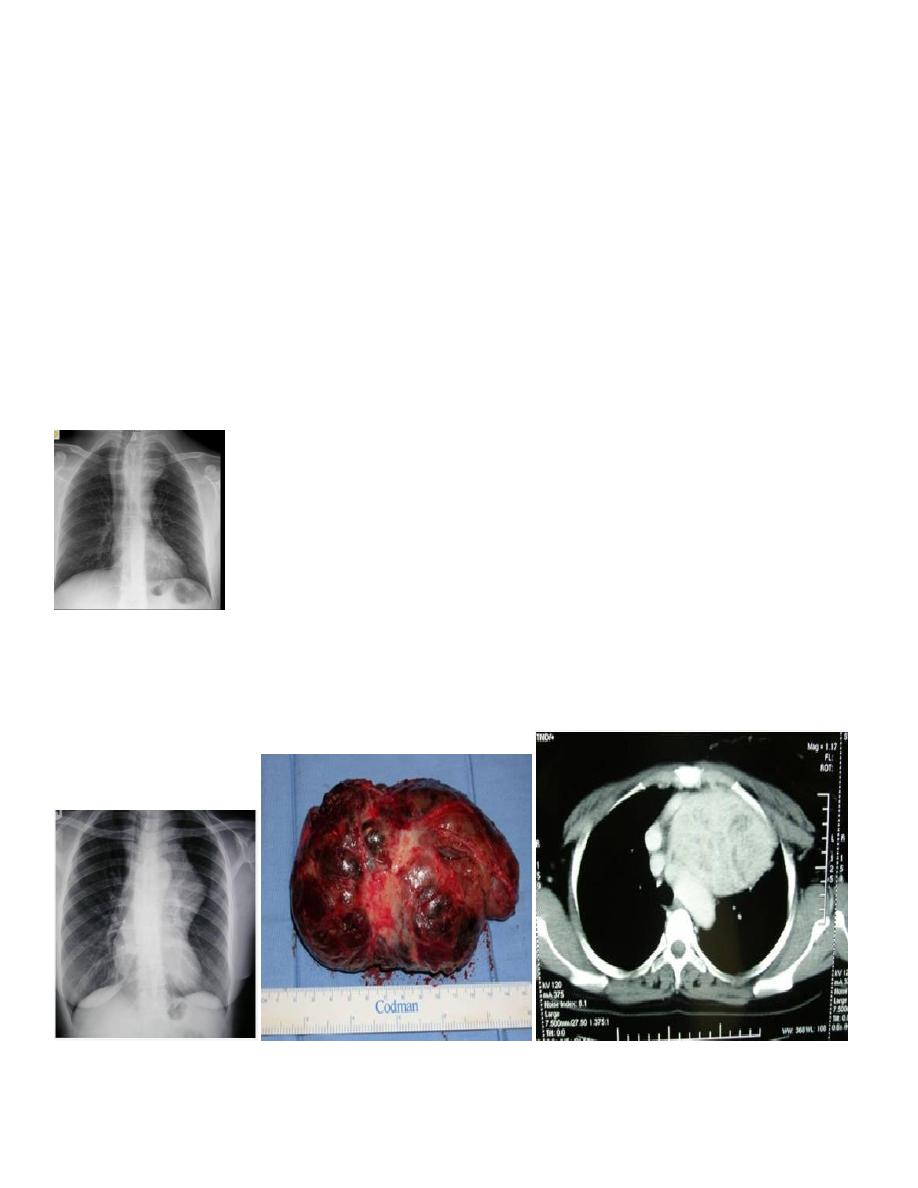
radiology L2
Here on of the presenting feature of retrosternal extension is dyspnea and palpitation
Advance case
Displacing the trachea into right side
Compressing the lung apex into thoracic inlet by enlarged retrosternal extension
It’s a superior mediational mass and cause widening in the upper mediastinum
Causes of superior mediastinal mass :
1. Mediastinal lymphadenopathy ( more common ) from infection ( EBV or CMV ) sarcoidosis or T.B.
2. Retrosternal extension of thyroid
3. Vascular cause ( aneurysmal dilatation of aorta or bronchus )
4. Thymus : infection , thymma , lymphoma
Neglected thyroid mass
Reach the middle mediastinum ,Trachea extensively displaced to right side ,The mass is extra pulmonary
If it intra pulmonary it cause loos of aeration ,Borders of heart still intact also aortic arch
Noor Rahman
