Pediatric surgeryClinical practice
DR. Bassam Al-Abbasiالصور من الدكتورالشرح من كتابة الطلاب
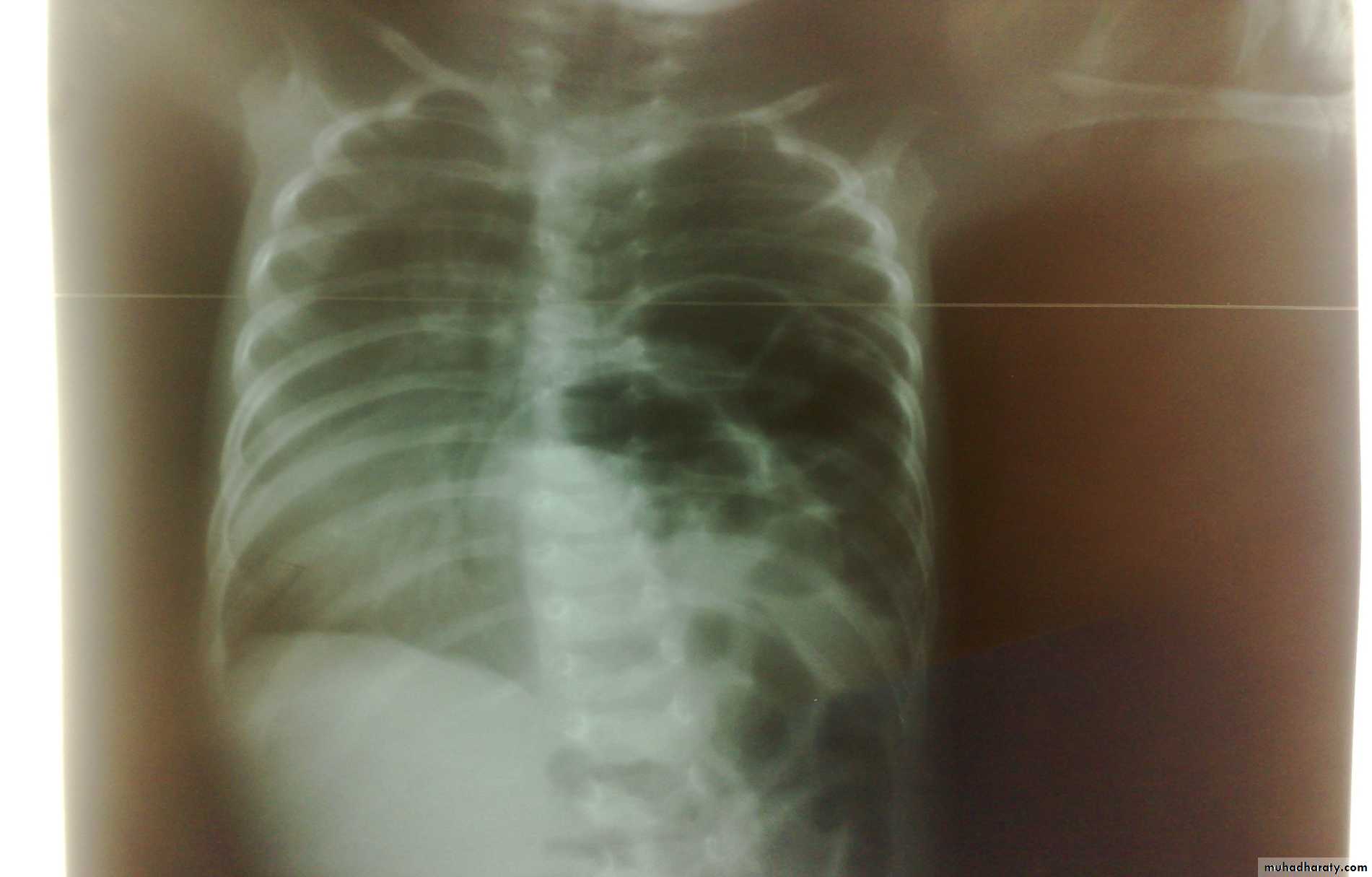
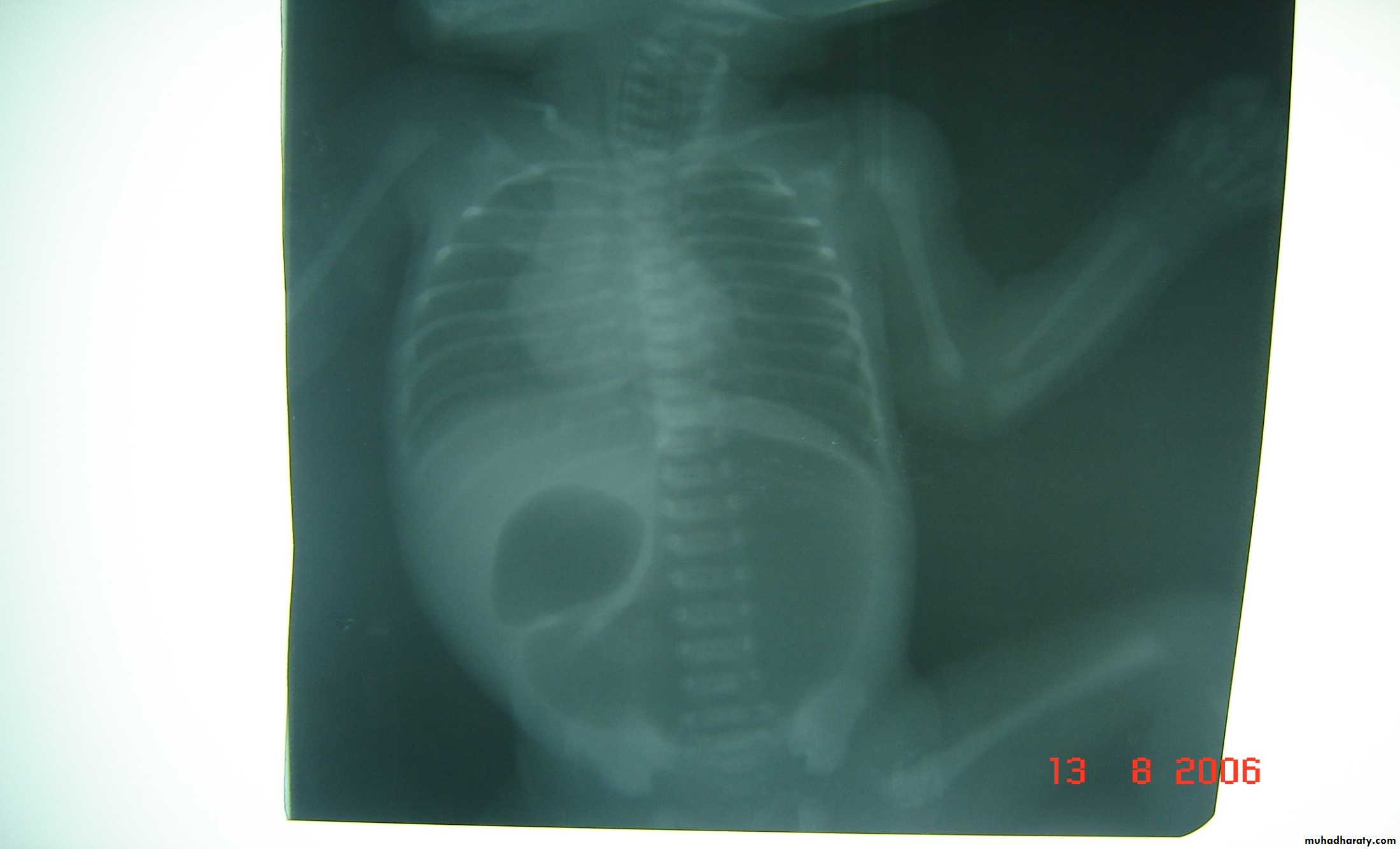
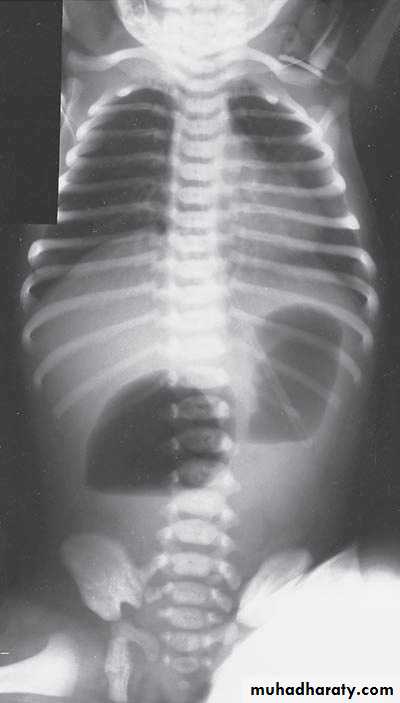
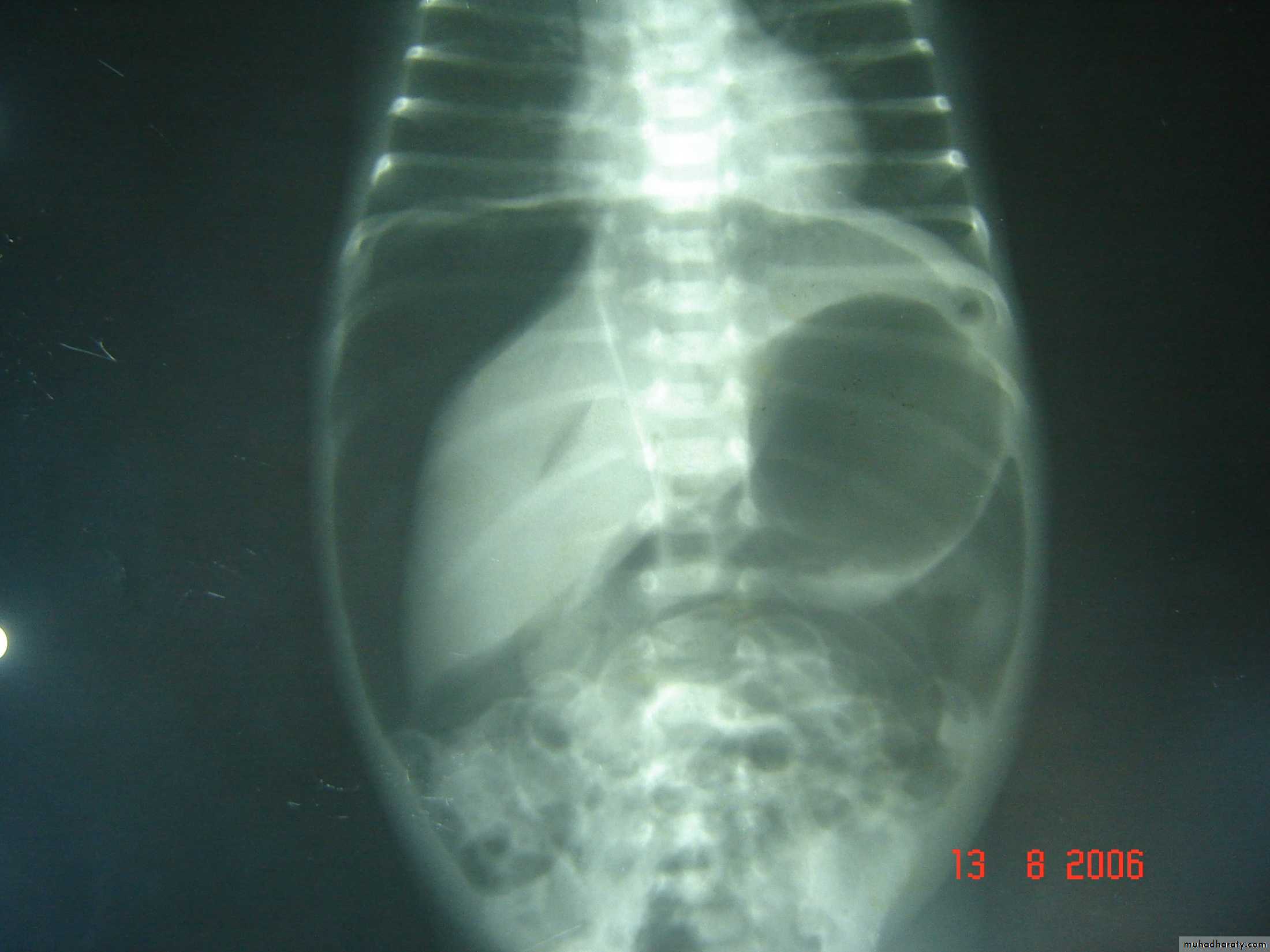
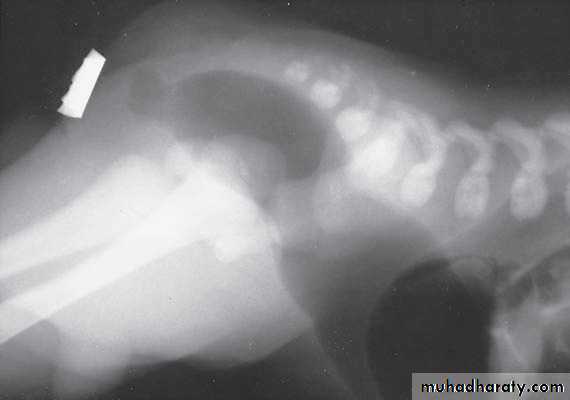
Respiratory Distress in the NewbornFirst photo:
Diagnosis: eventration of diaphragmDescription: mild dextrocardia – recurrent chest infection – diaphragm is present
mild distress - 7 months age baby – less number of intestinal loops in the chest
there is lung tissue in the chest - Paradoxical movement of the diaphragm.
Treatment: plication of the hemi-diaphragm (through thoracic approach).
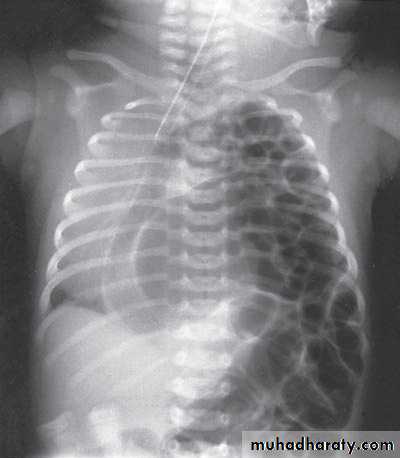
Second photo:
Diagnosis: congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Description: more dextrocardia – diaphragm not present – there is nasogastric tube
severe distress – very tired - 1 day age baby – more number of intestinal loops in
the chest - there is no lung tissue in the chest.
Treatment: pull the intestine ad close the hernia (through abdominal approach).
Scaphoid abdomen
Subcostal incision
content
Defect=sac
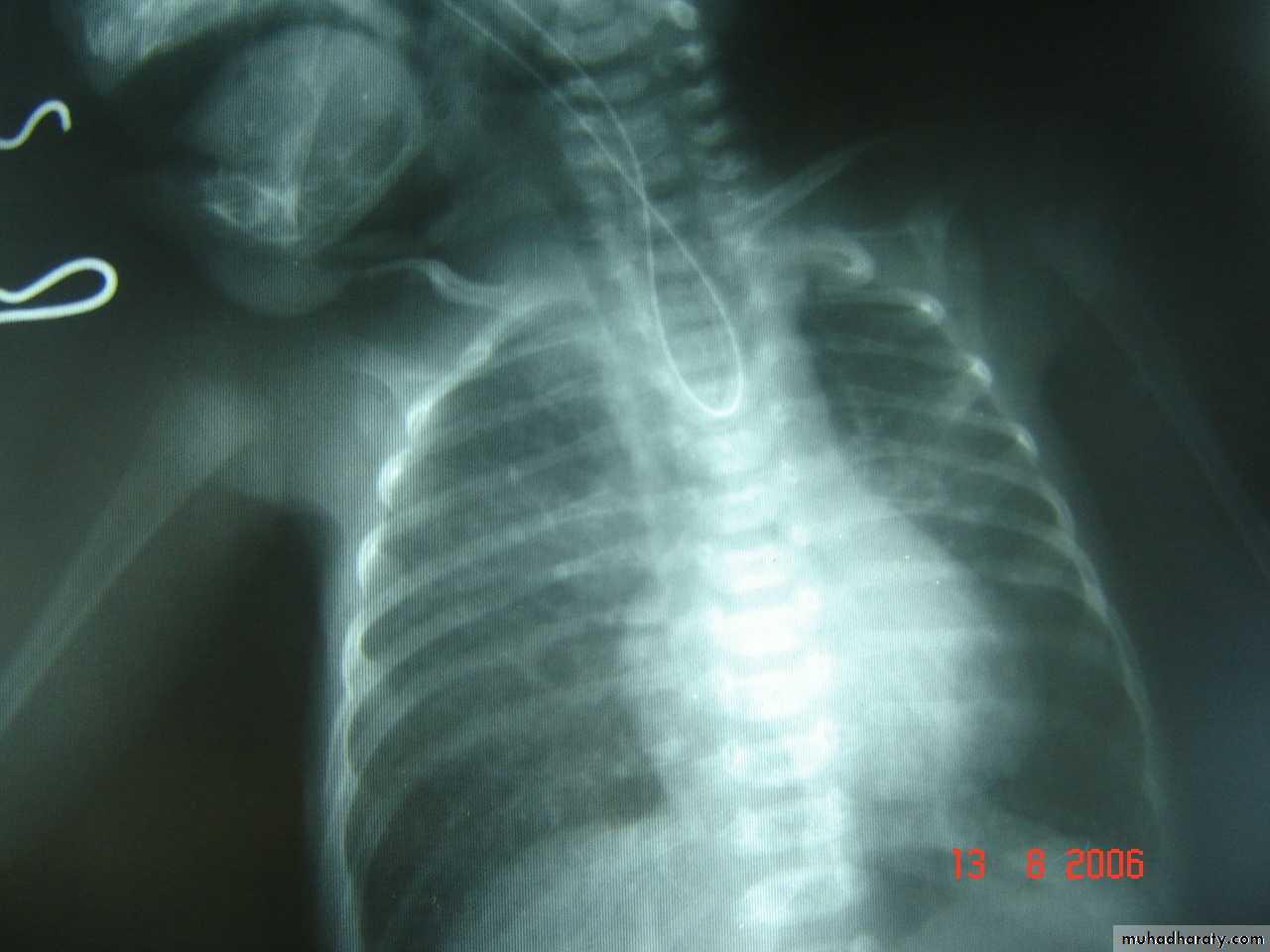
Oesophageal Atresia and Tracheo-Oesophageal Fistula,
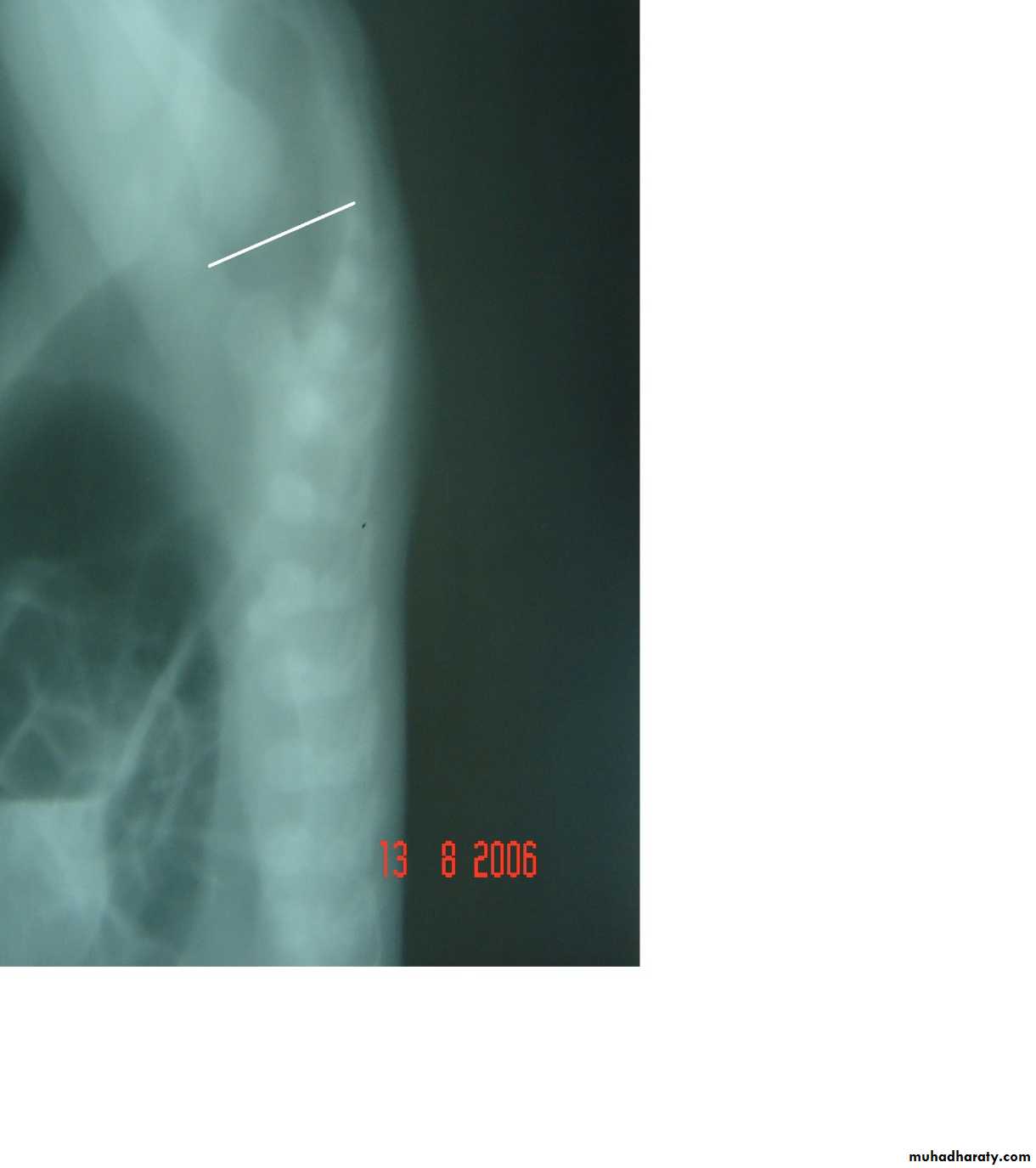
First photo:
Diagnosis: pure atresiaDescription: radiolucent abdomen (no gases) + failure of nasogastric tube passage.
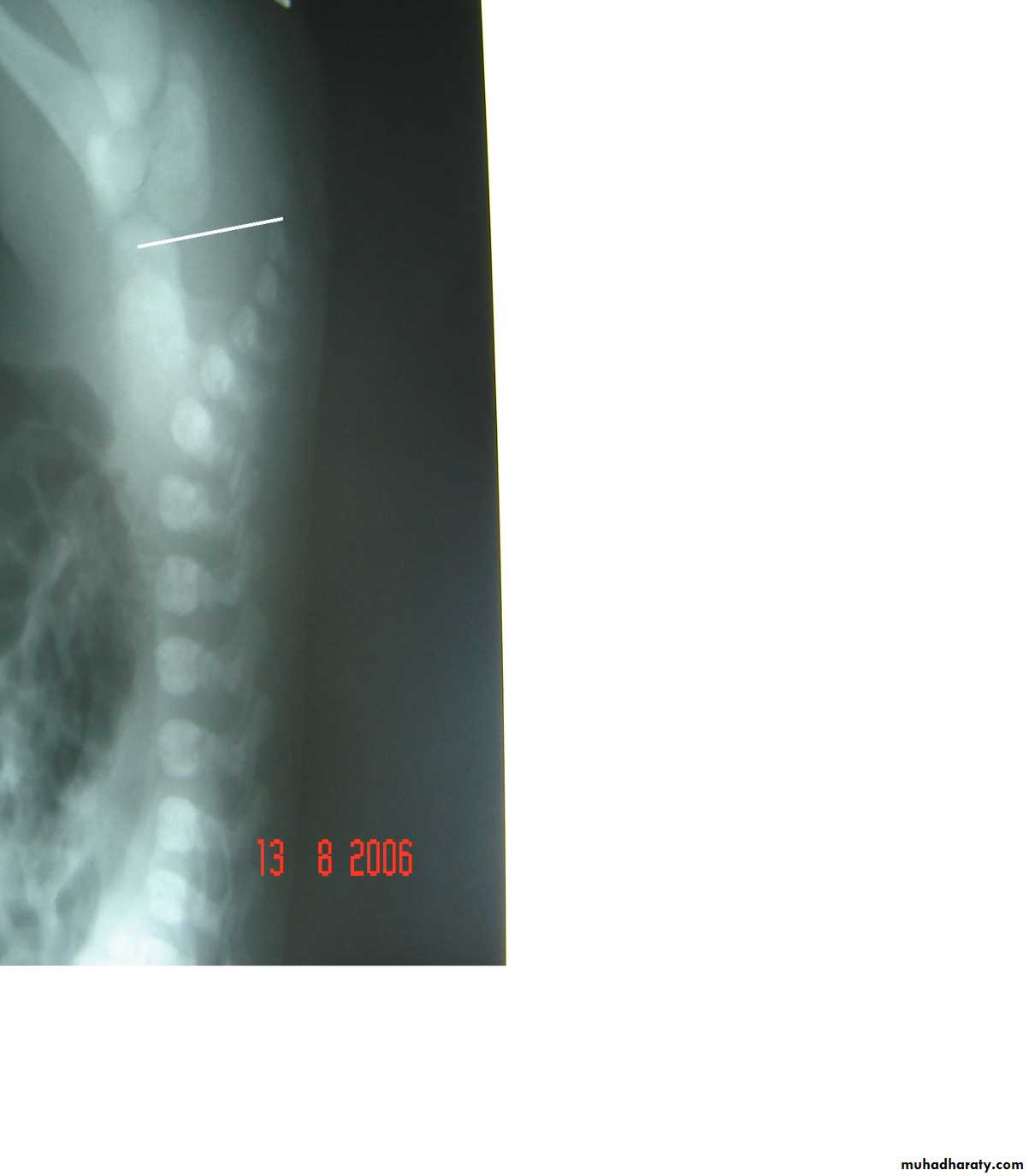
Second photo:
Diagnosis: TEF (with fistula)
Description: pass of gases to the abdomen + failure of nasogastric tube passage.
Diagnosis: TEF (atresia with fistula)
Benefits of X-ray:1- to see the failure of nasogastric tube passage.
2- to determine the type of TEF
3- to check the condition of the lung
4- diagnose the associated anomalies (aortic arch – vertebra – ribs)
5- to measure the length of the defect (1-2-3 cm or more)
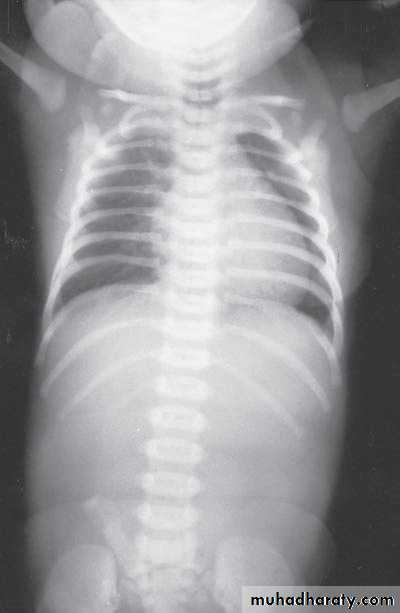
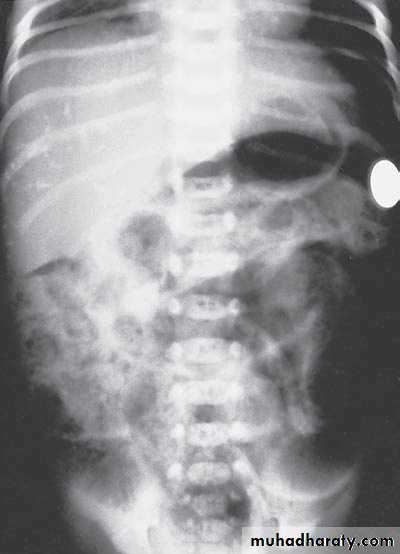
Bowel Obstruction
Diagnosis:
first photo upper bowel obstruction // second photo lower bowel obstructionDescription:
double bubble signCauses of obstruction in the first photo:
1- duodenal obstruction2- duodenal atrasia
3- annular pancreas
4- mal-roation of bowel
Cardinal symptoms of bowel obstruction (first photo):
1- mild abdominal distention (epigastric distention)2- failure if pass of meconium
3- bile stain vomiting
Note:
In pediatric we cannot say small or large bowel obstruction but we say upper
or lower bowel obstruction
غير مطلوب
N.E.Cغير مطلوب
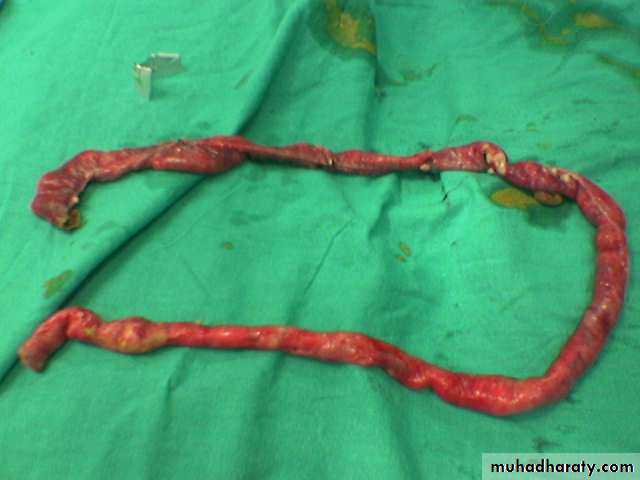
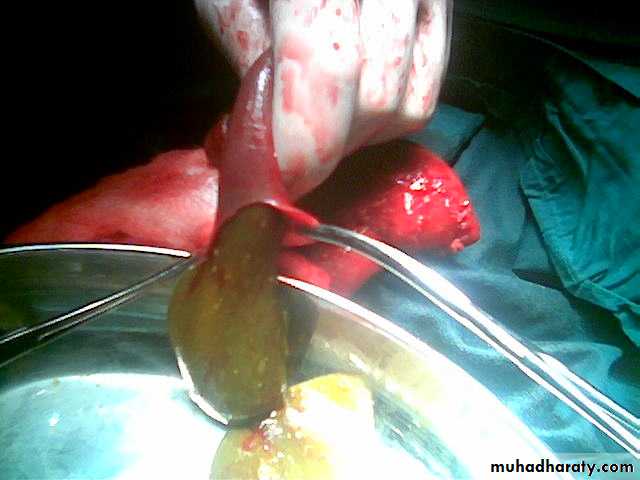
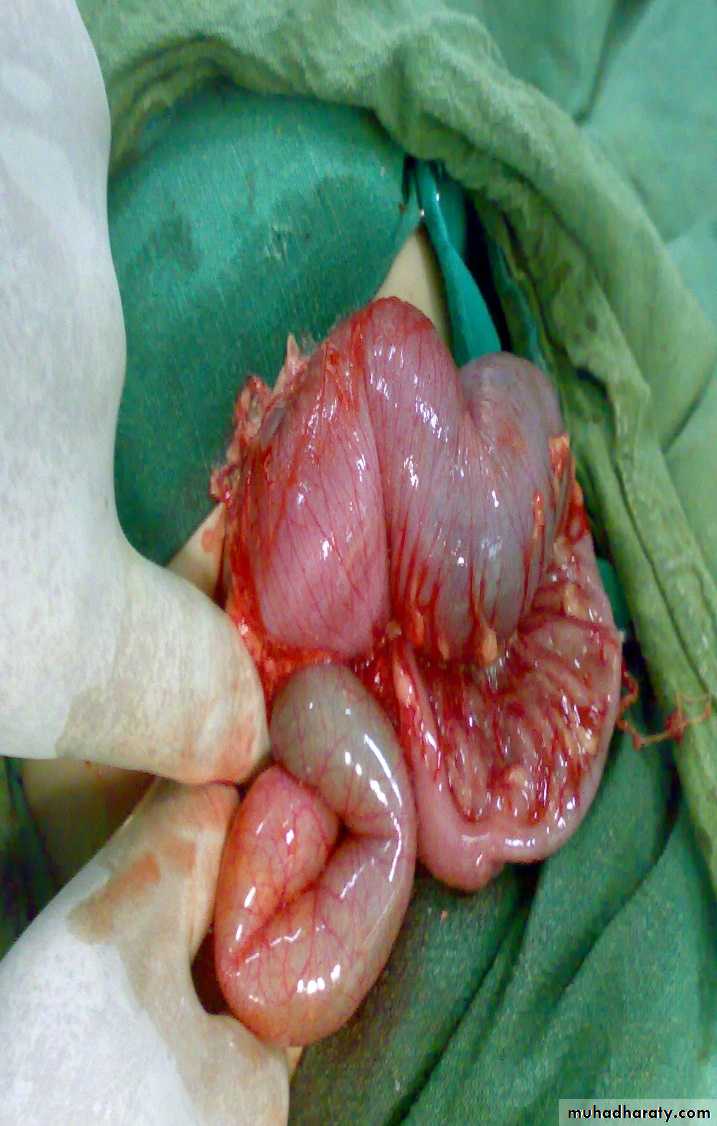
Meconium ileus+atresiaDescription:
• Thick sticky meconium in the ileum.• Signs of abdominal onstruction
• Abdominal duffy (مثل العجبي) mass
• No A/F level in x-ray
• Causes: cystic fibrosis
• Treatment: surgery by excision and re-anastomosis
• Before sugary do gasrtographine enema it could treat the condition
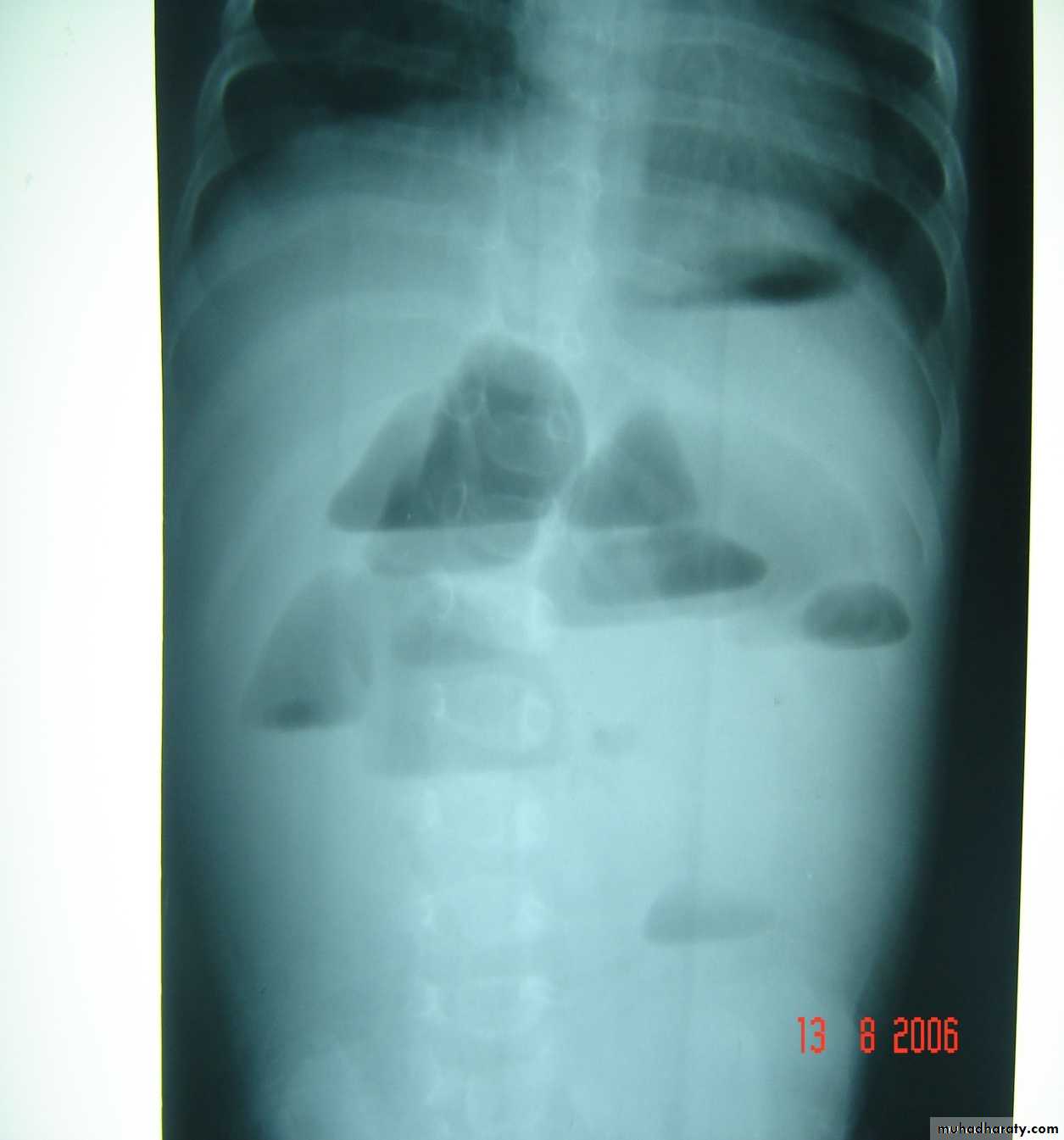
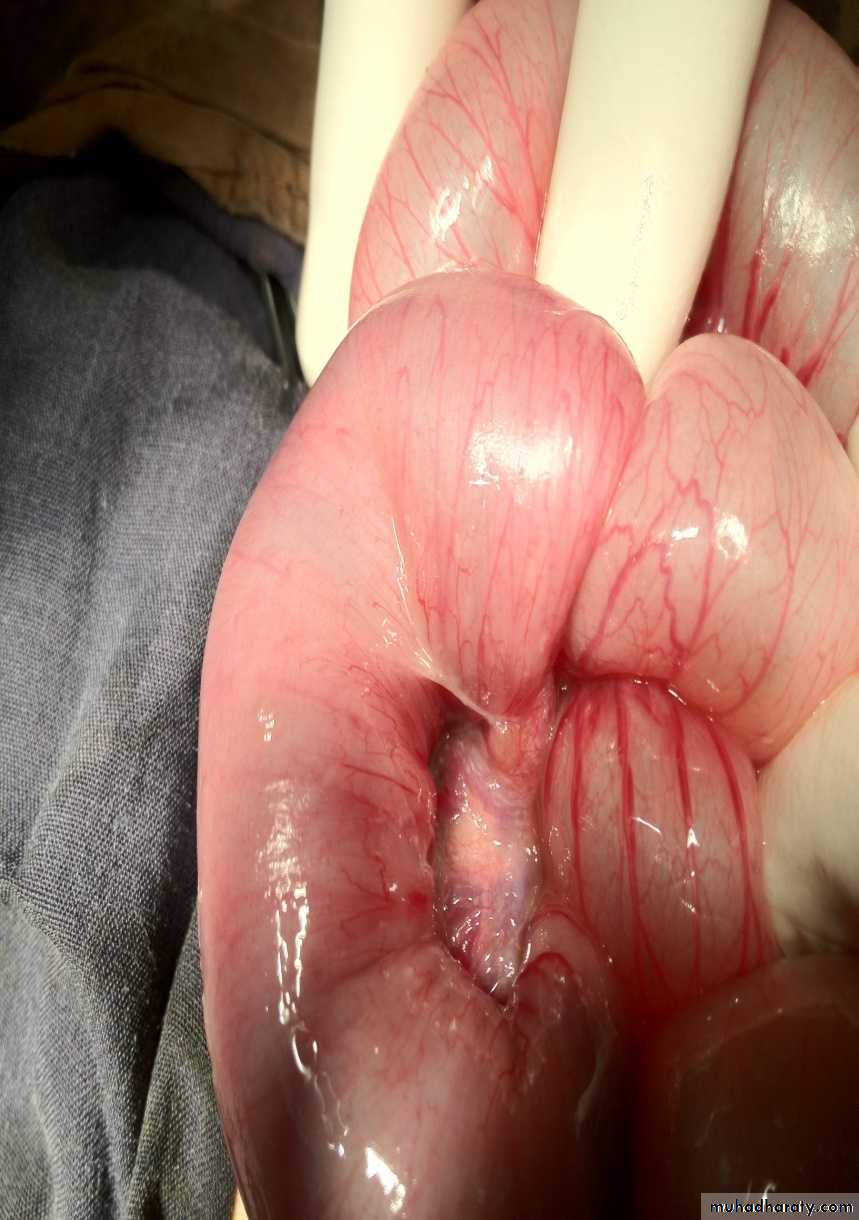
Description:
• Small bowel atresia• X-ray show multiple A/F level
• Treated by surgery resection with end to end anastomosis
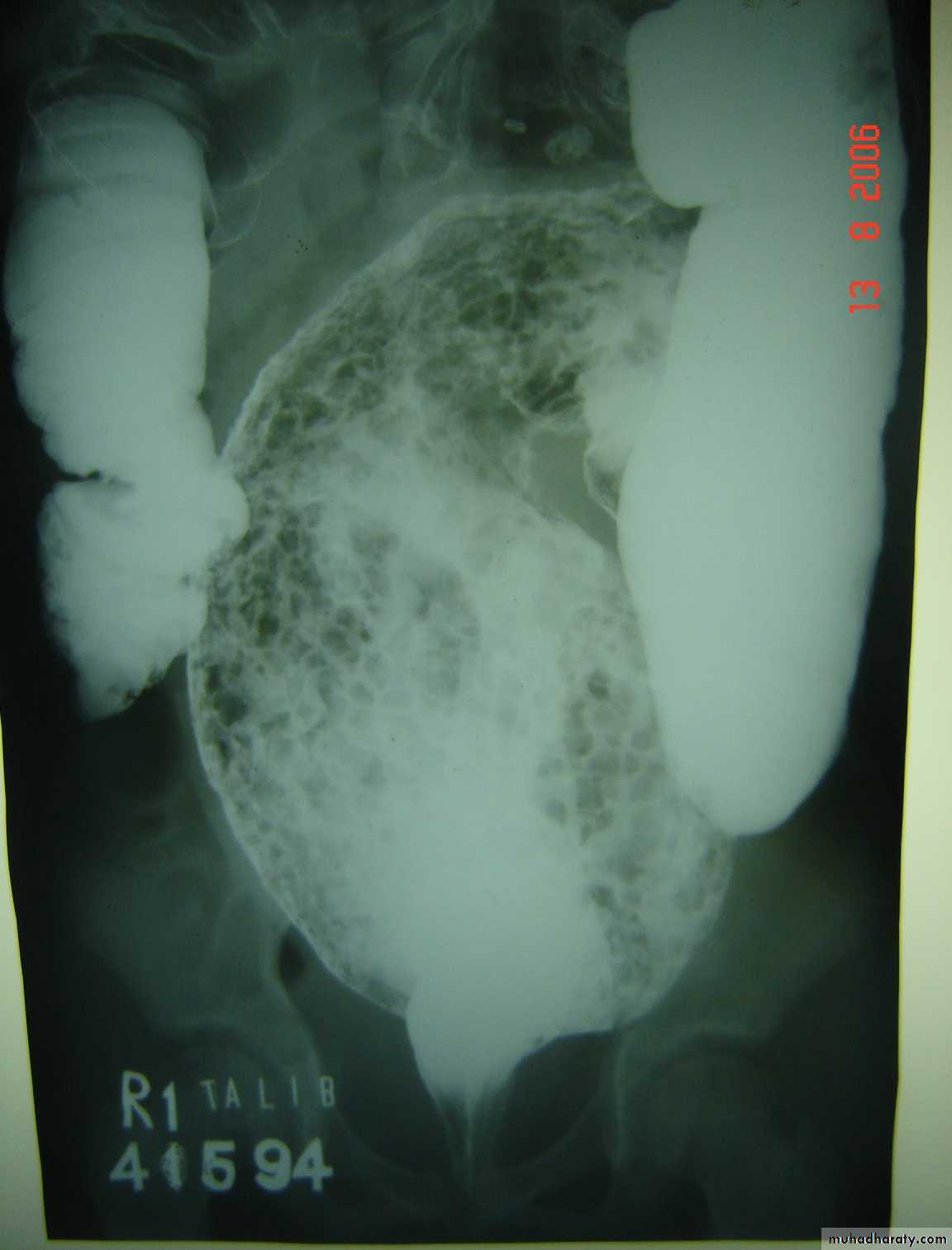
Hirschprungs disease
Description:
• Two years old child• Fist photo: Ba-enema test show dilatation of the sigmoid and narrowing of
• Recto-sigmoid junction and filled with material.
• The cause is problem in the ganglia
Presentation:
• Neonate delay to pass meconium – intestinal obstruction
• Old child chronic constipation – complications like enterocolitis (diarrhea)
and perforation
Treatment:
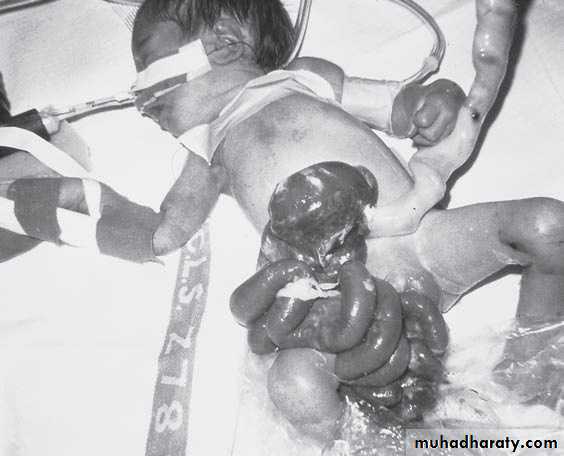
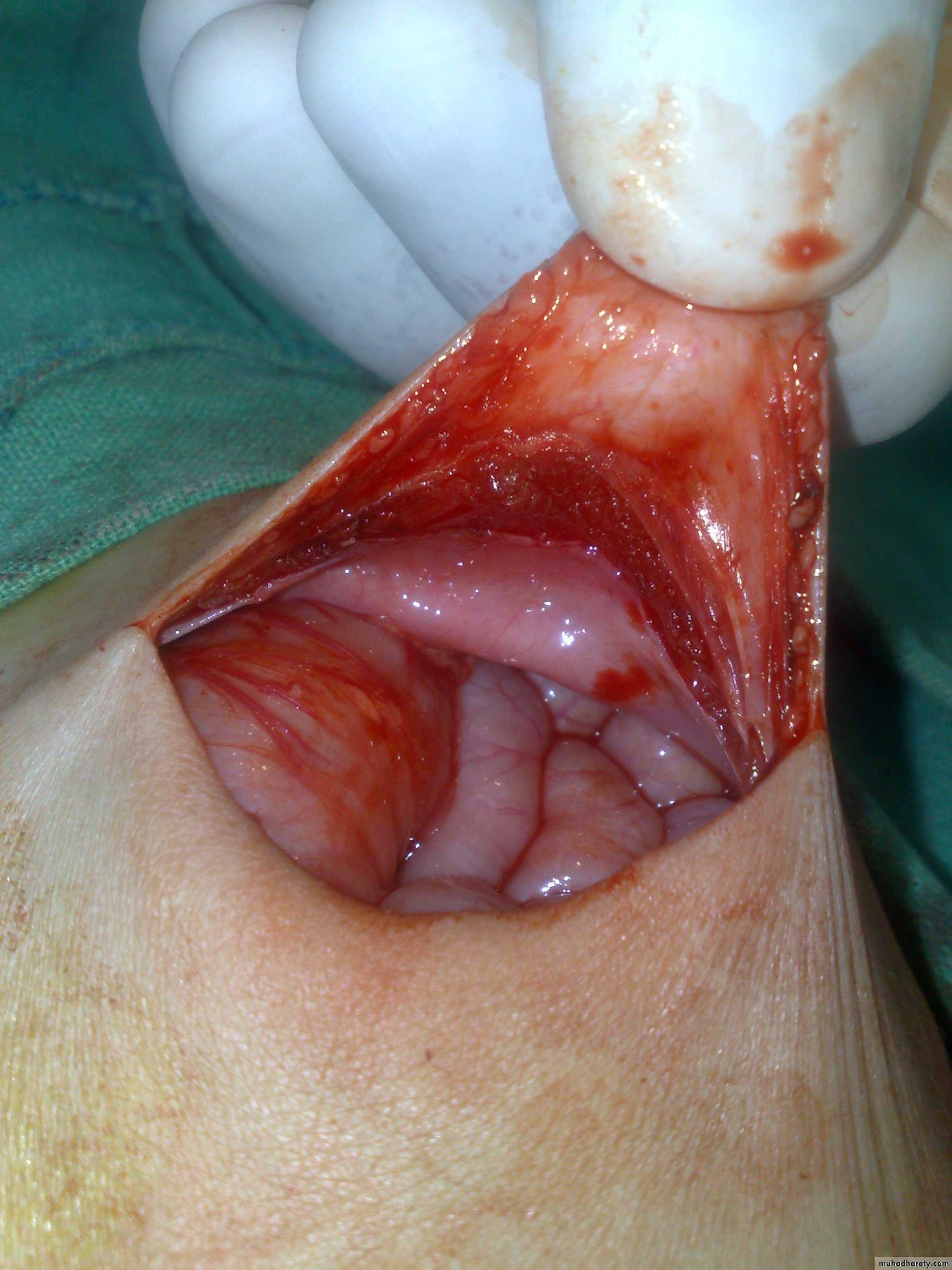
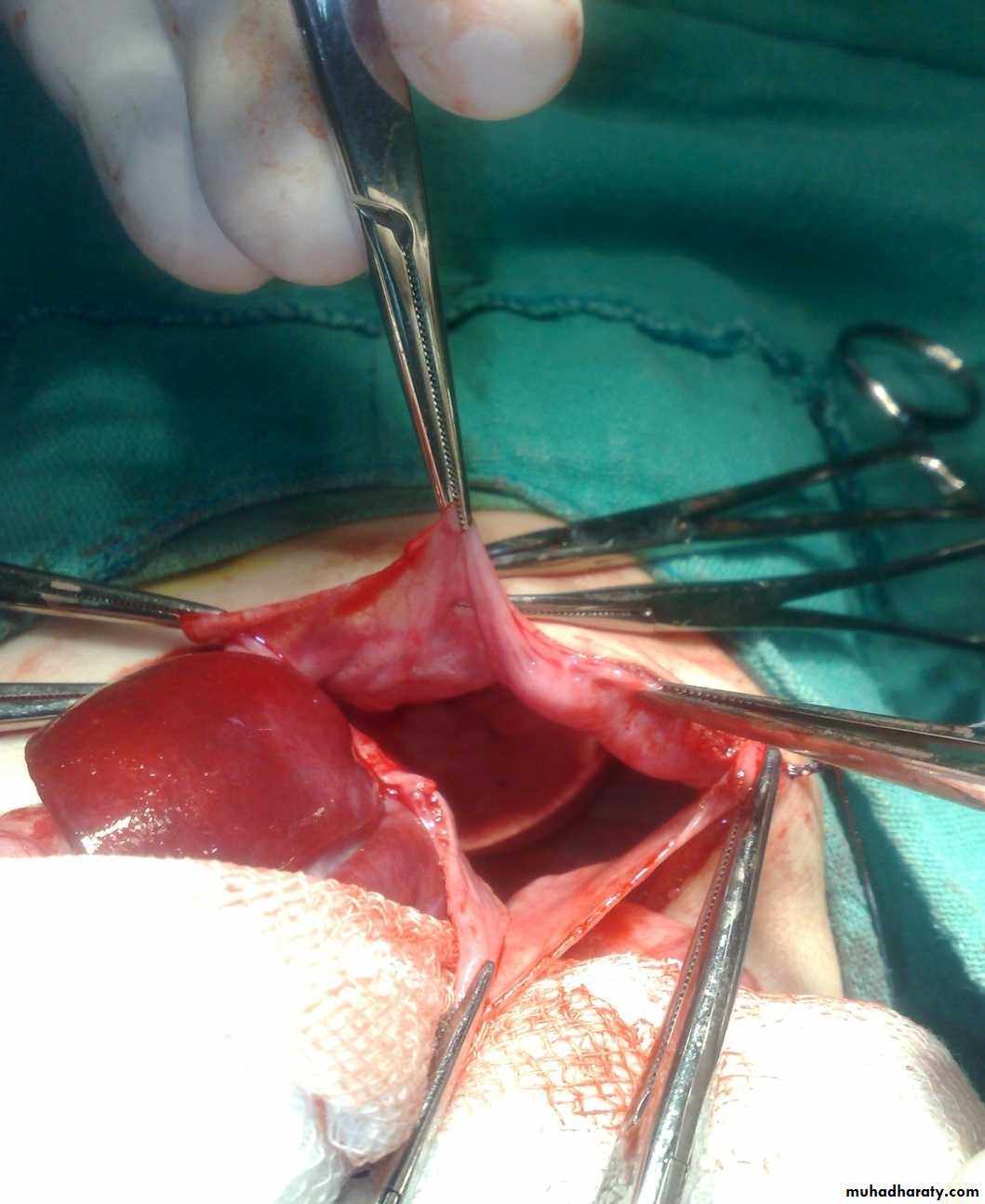
Surgery called pull-throughAbdominal Wall Defects
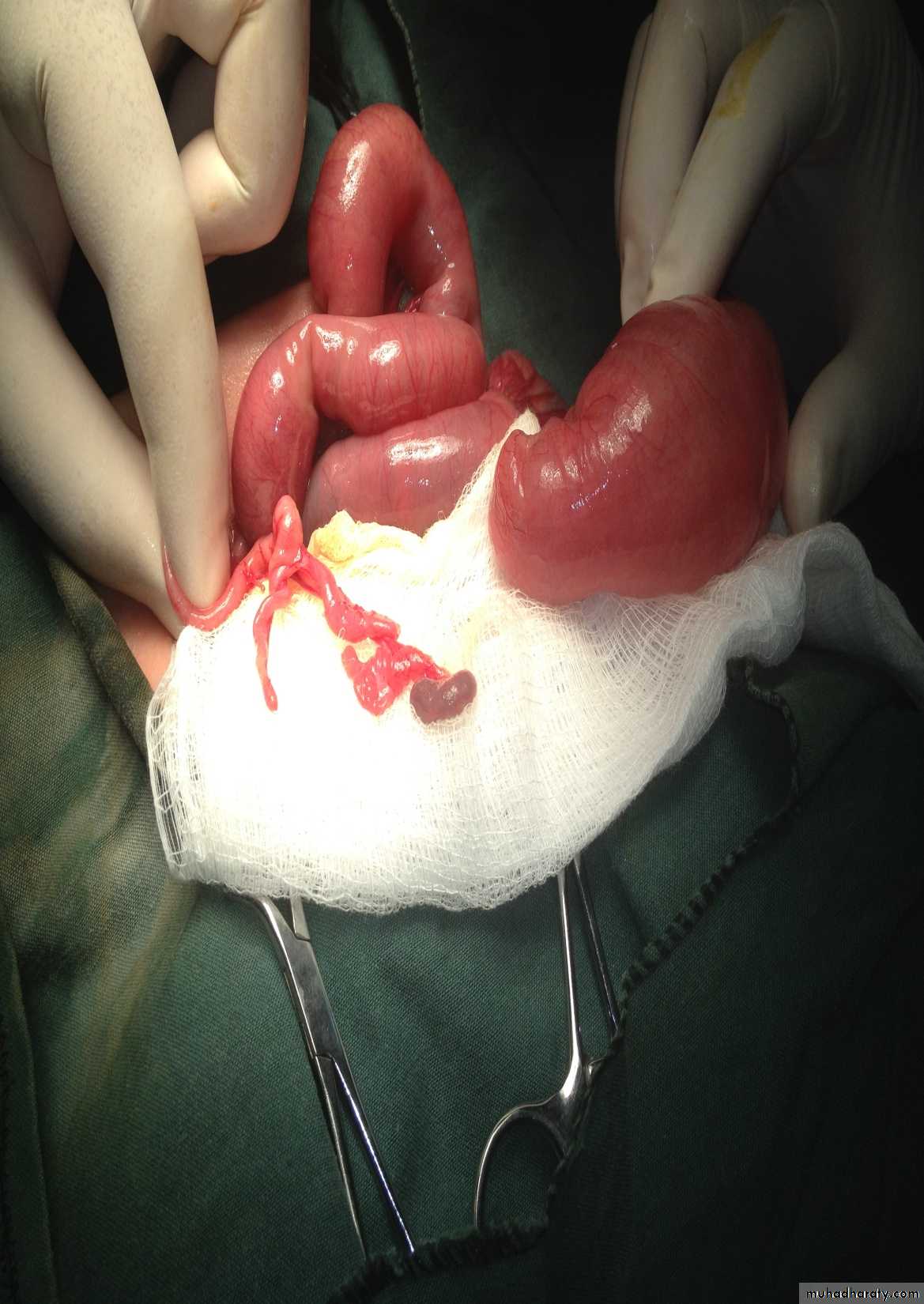
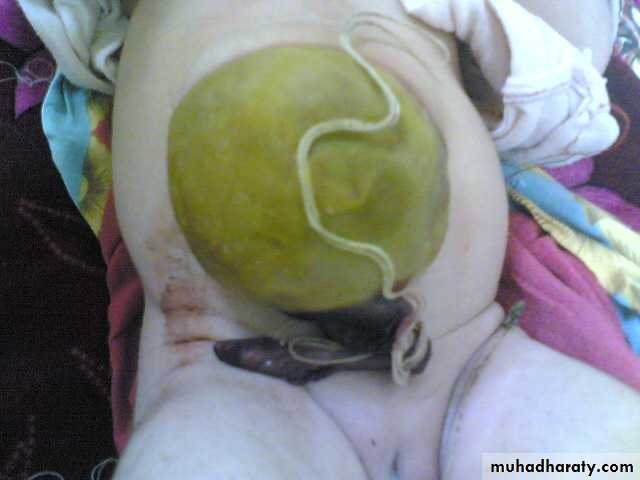
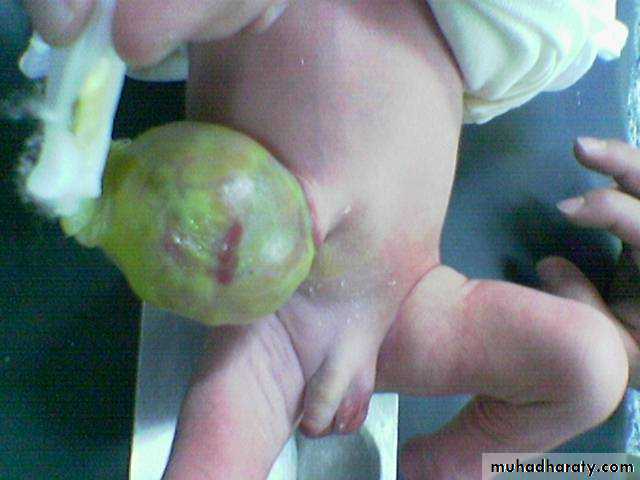
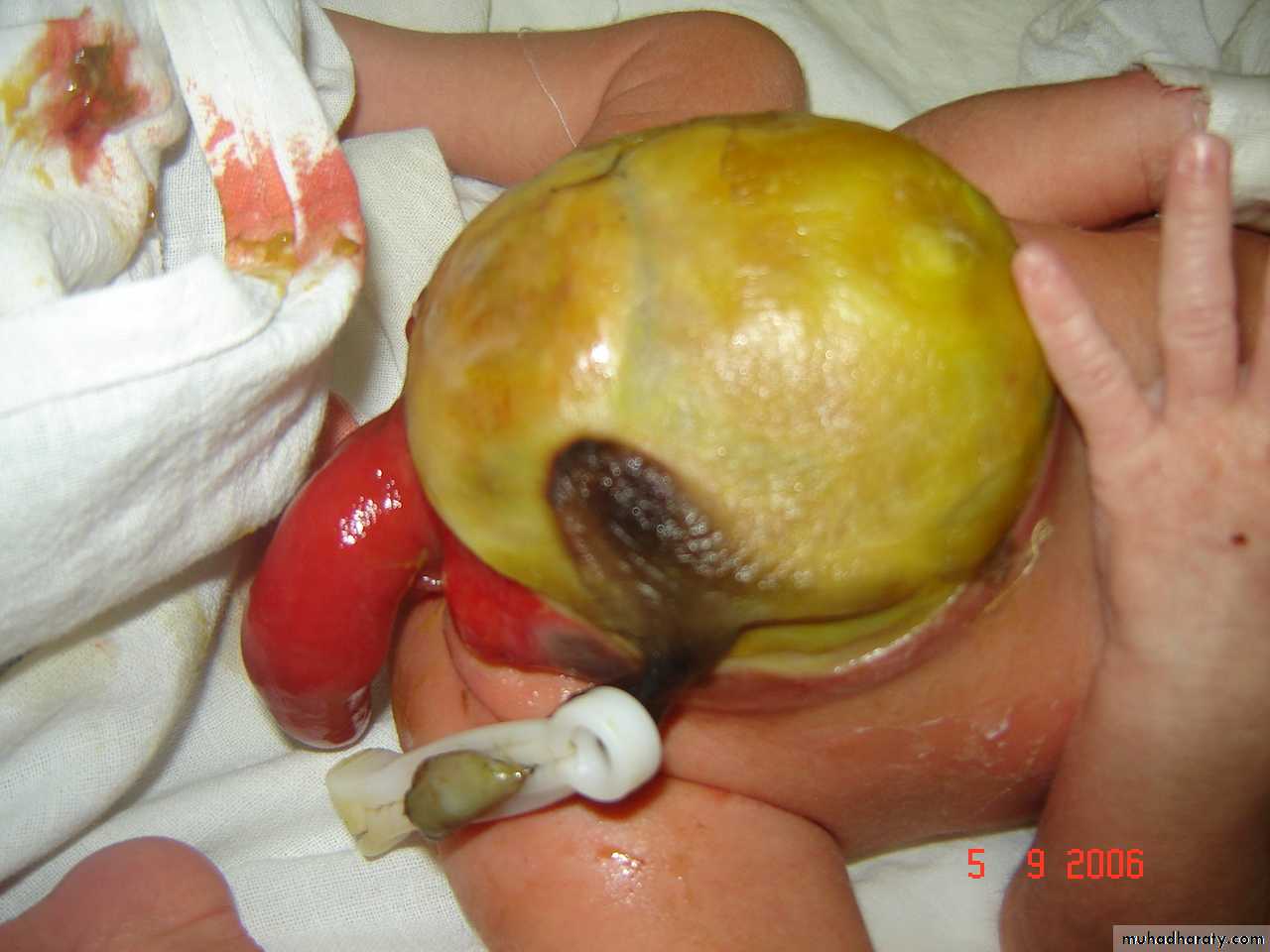
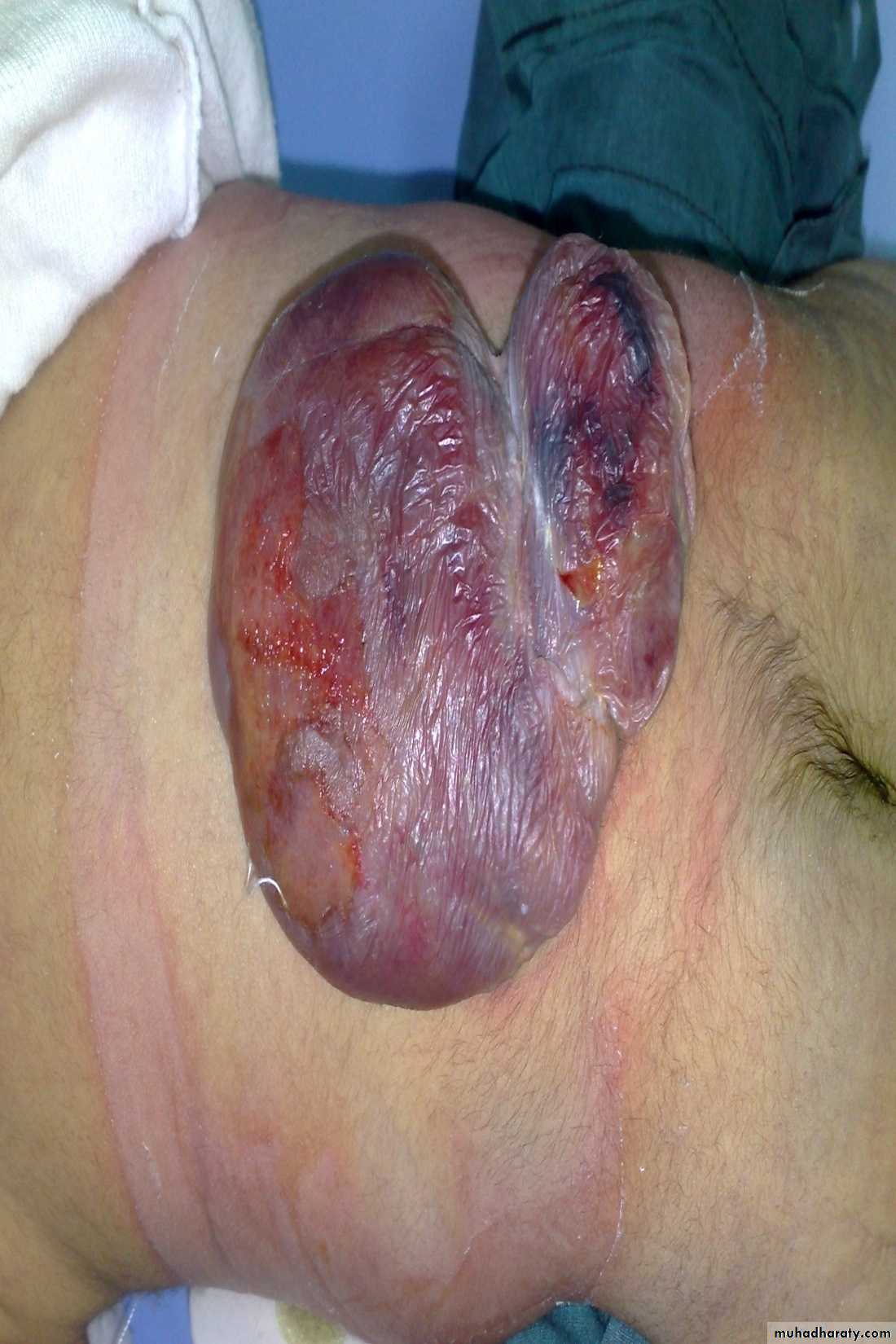
Diagnosis: omphalocele
Description:• Huge dilatation
• Central umbilicus
• Liver present
Treatment:
It is no emergency condition• Cover
• Incubation
• Give fluid
• Use silo bag
غير مطلوب
غير مطلوب
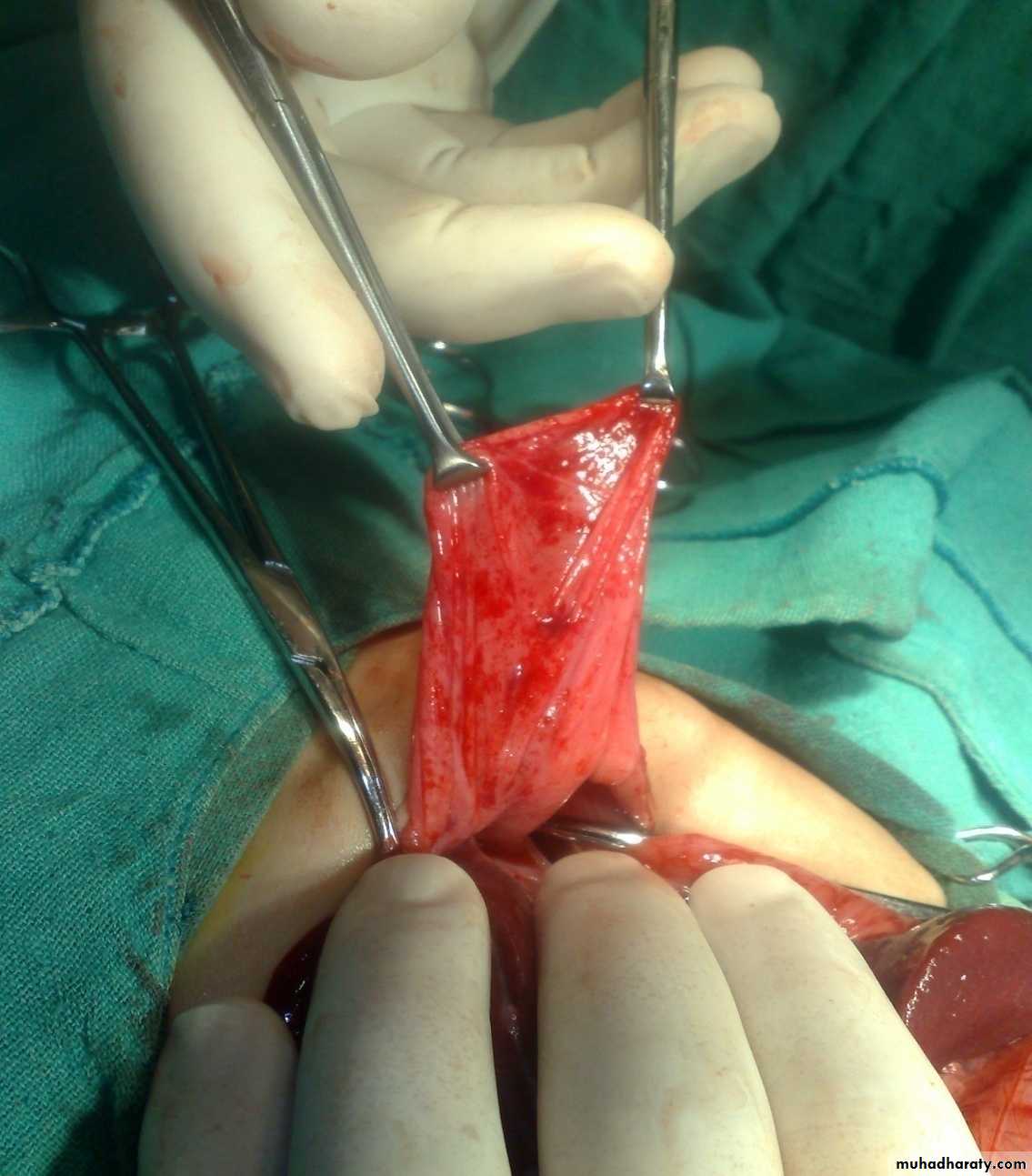
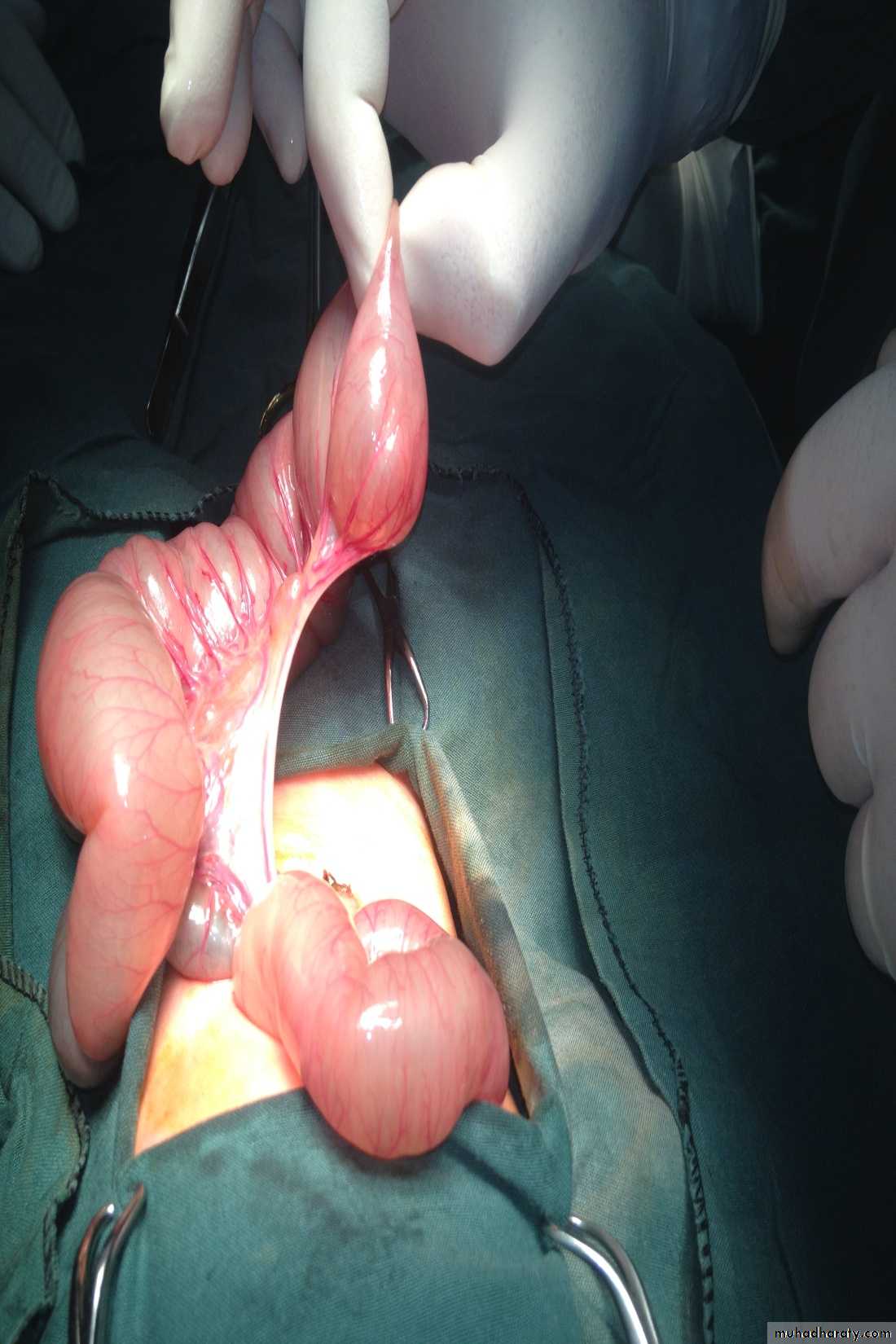
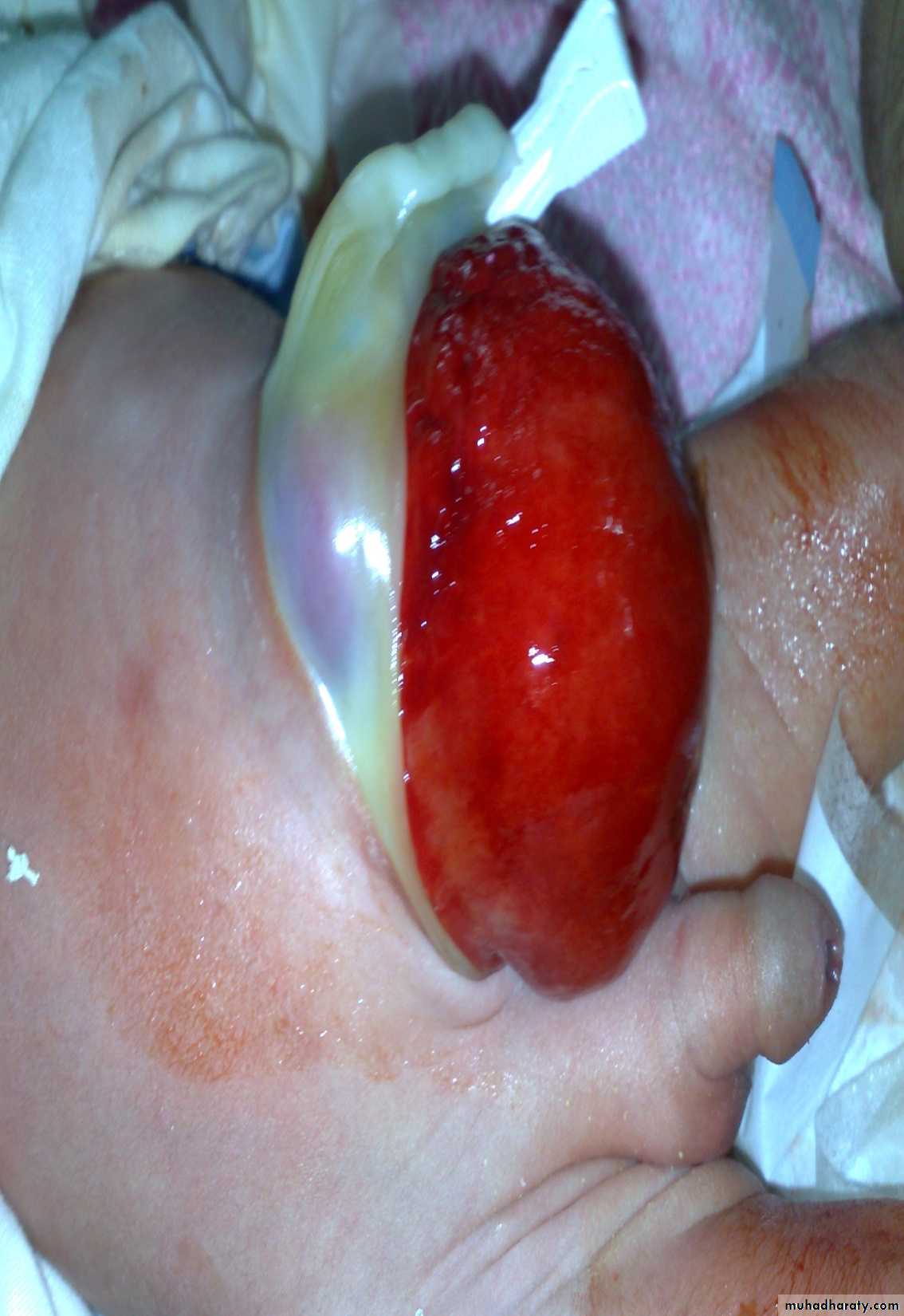
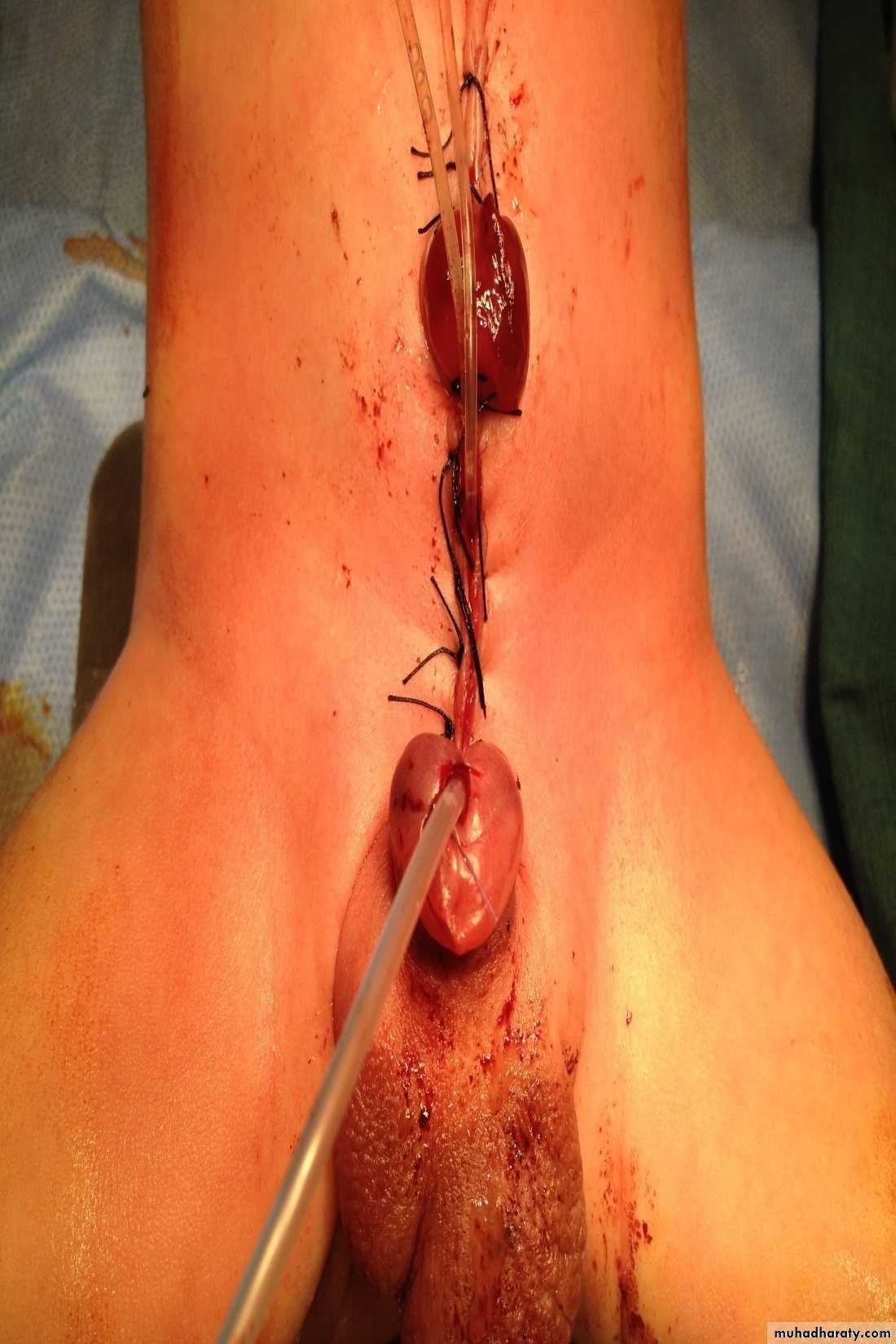
First photo:
Diagnosis: gastroschisisDescription:
• No sac
• Right to the umbilicus
• Associated anomalies are less
Treatment:
It is emergency condition• Reduction
• Close the defect
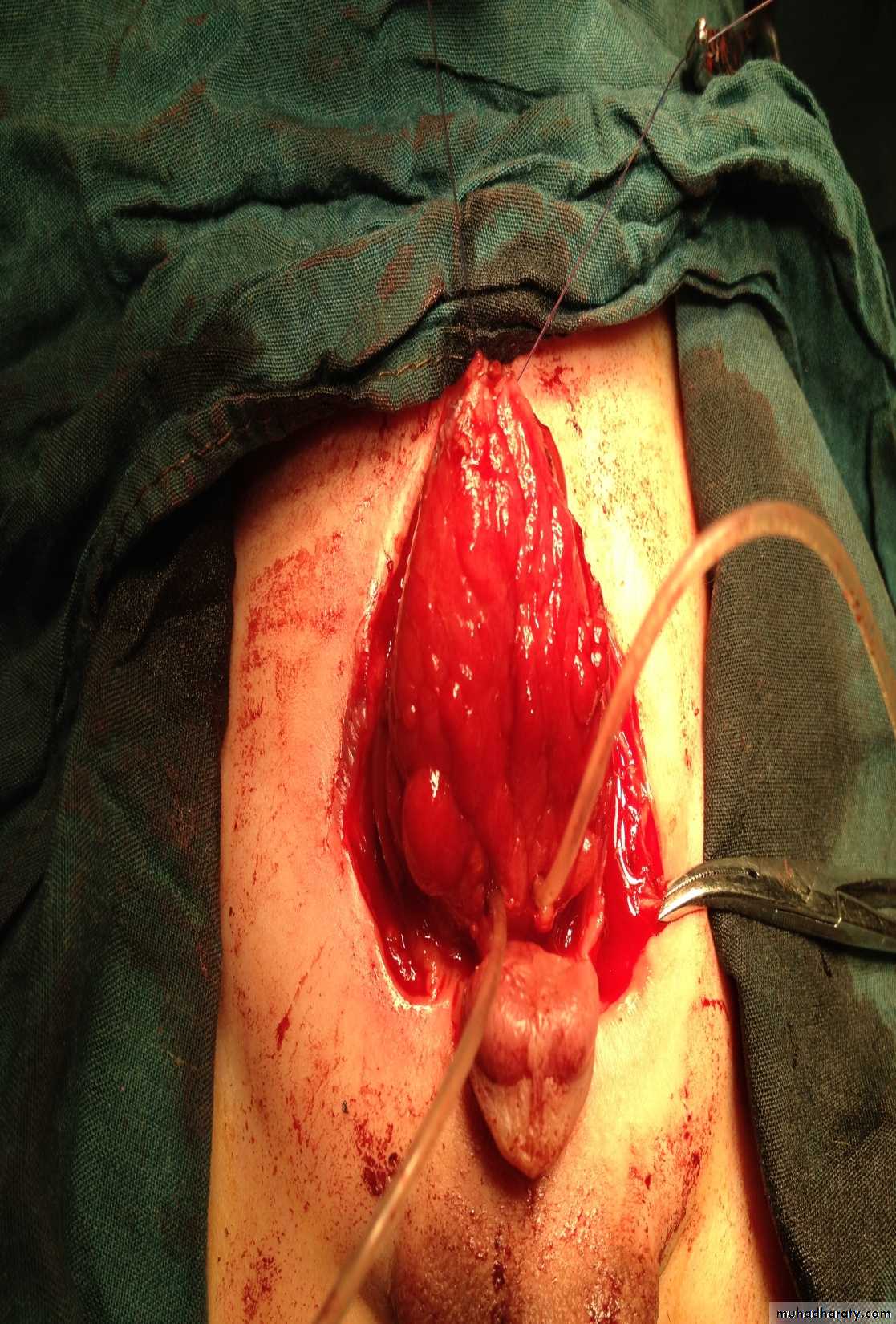
Second photo:
Diagnosis: meningomeylocele
Note:
It is associated with hydrocephalusand paralysis of lower limbs
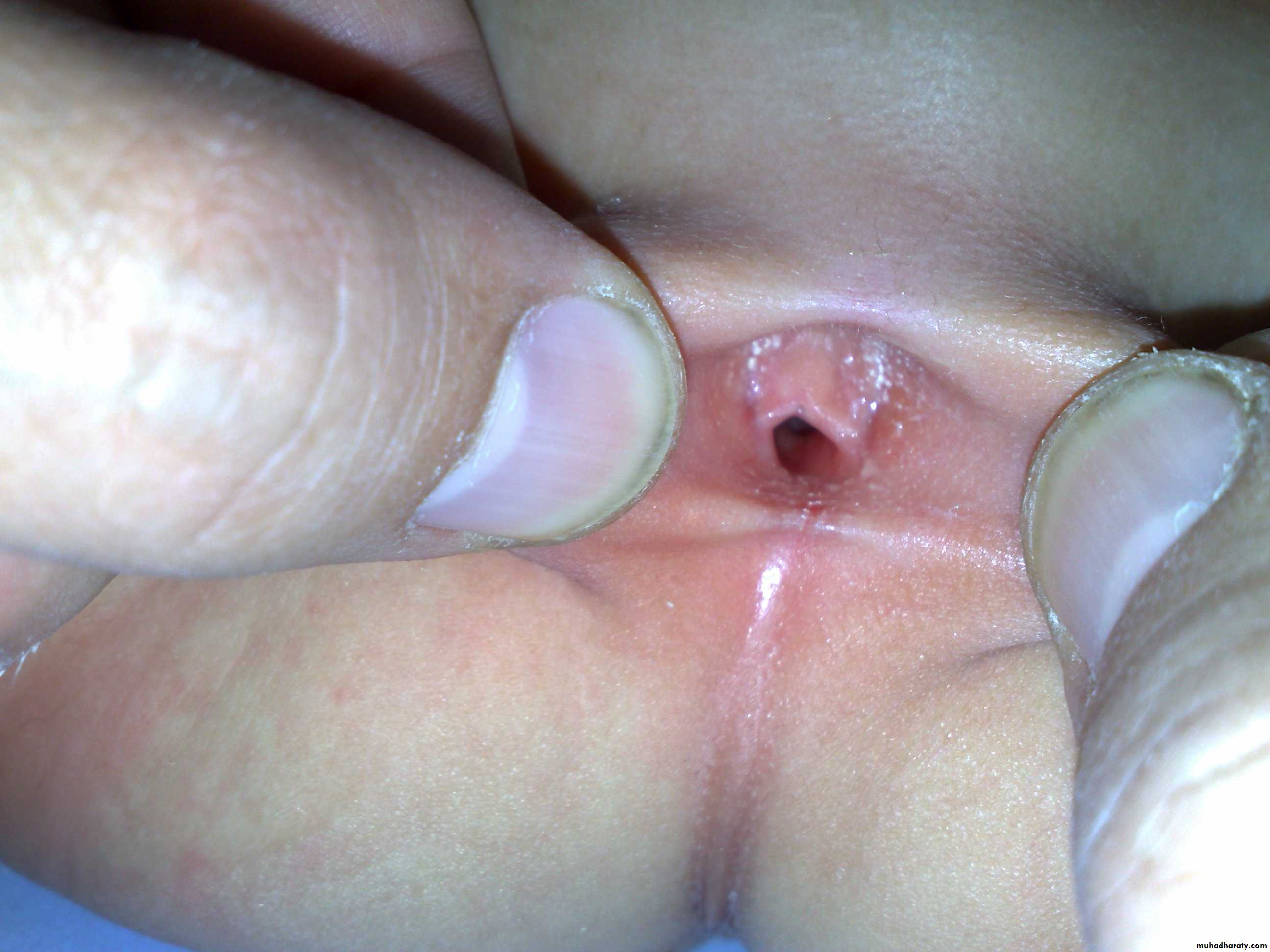
Anorectal Anomalies
First and second photos:
Lateral invertogrampubococcygeal line
It is low type
Third photo:
Supine type of view
Low type
Anal dimplePass of meconium through the urethra
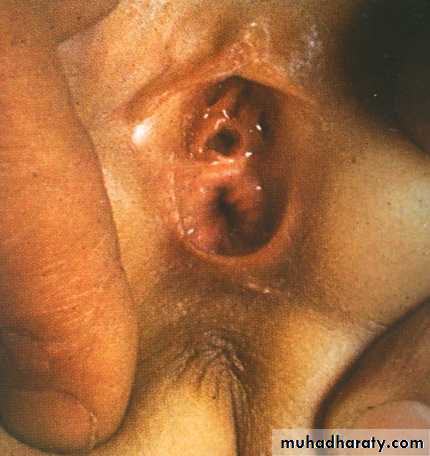
High typeSubcutaneous meconium – cutaneous fistula – low type
Cloaca
High typeVestibular type
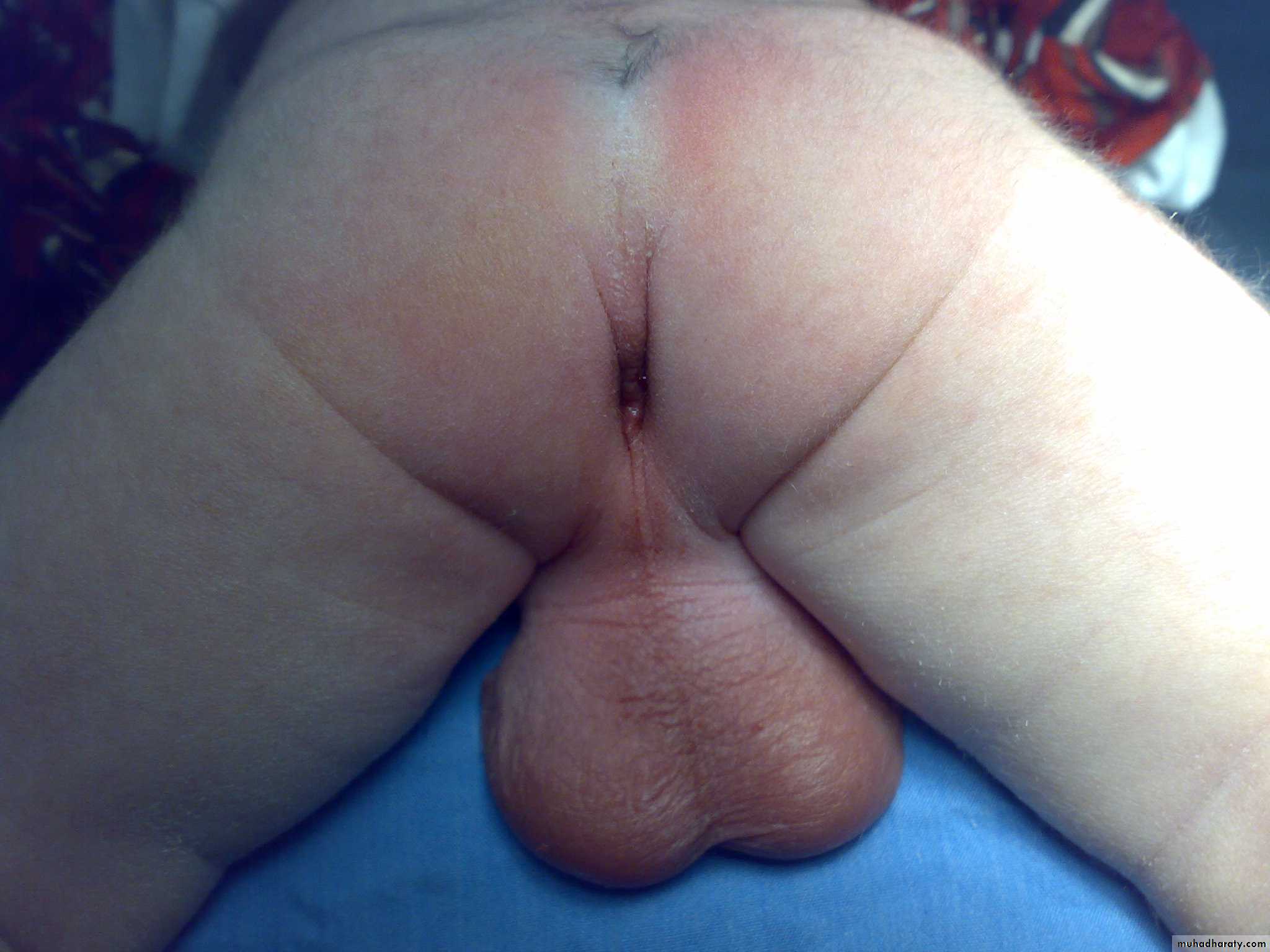
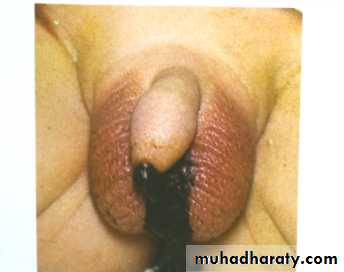
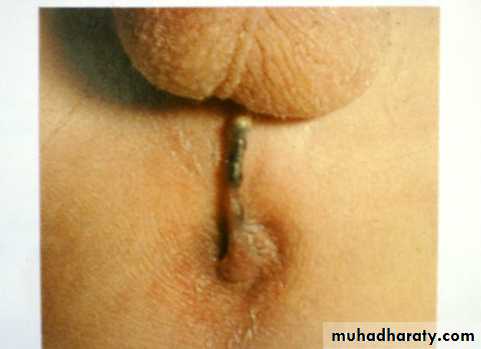
Disorders of Sexual DevelopmentFirst photo:
Diagnosis: proximal hypospadiasDescription:
• Severe type• Psychological problems
• Infection (UTI)
• Sterility
• Retrograde ejaculation
Treatment:
• By surgery• At first year
Second photo:
Diagnosis: distal hypospadias
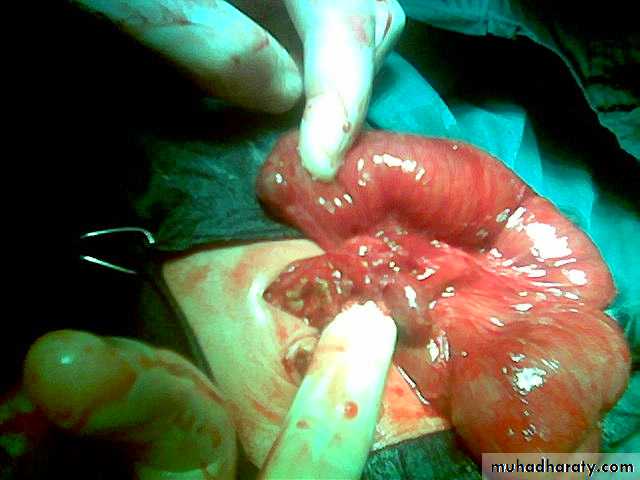
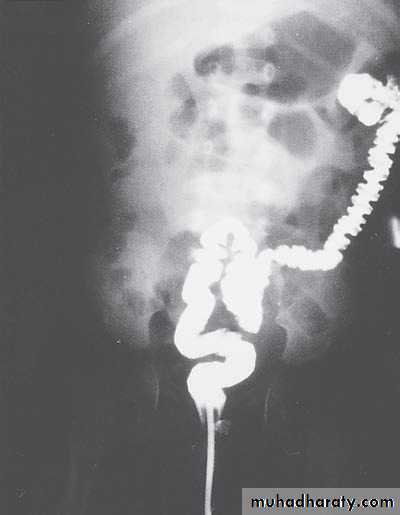
Intussusception
First photo:
Presentation:• Pull leg to abdomen
• Severe screaming
• Red current jelly stool
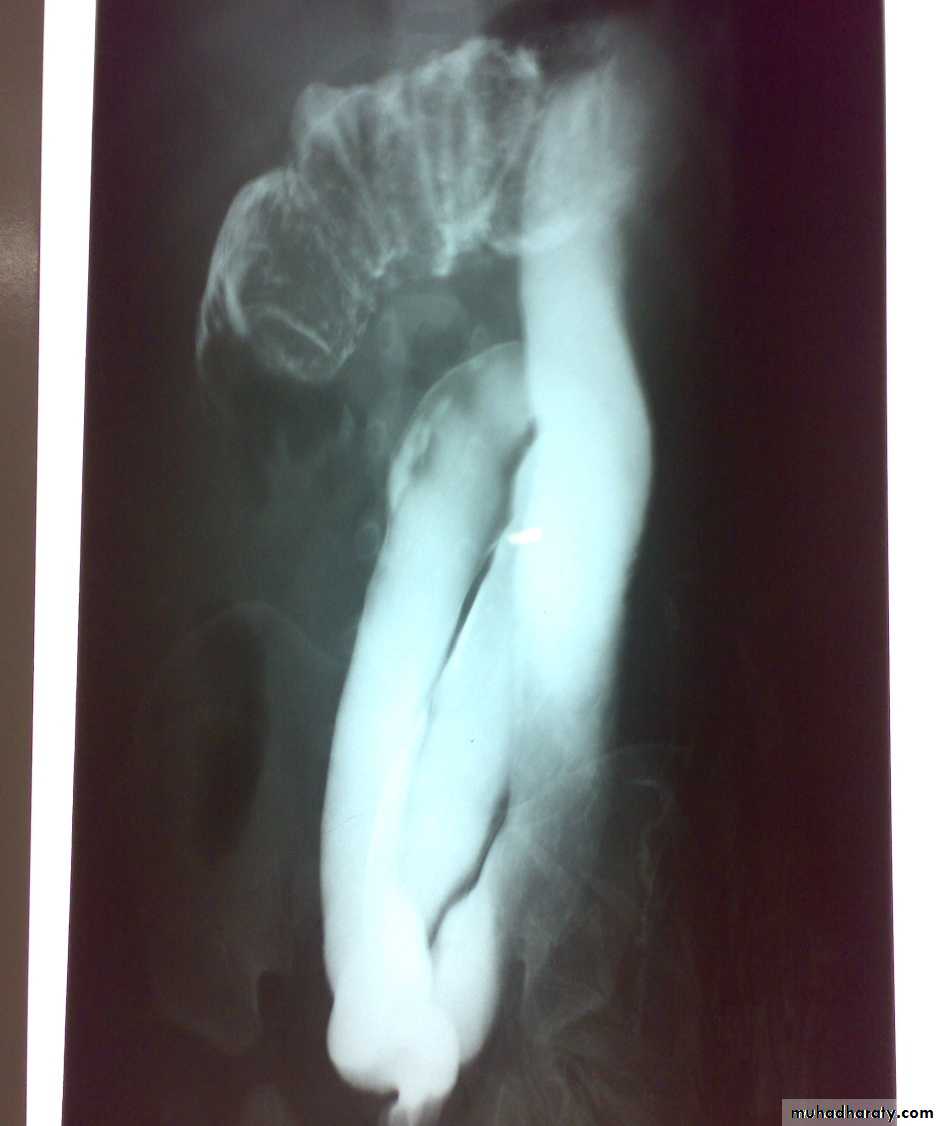
Second photo:
• Ba-enema exam spring cord sign• Could do hydrostatic reduction during Ba enema test
• Other method is pneumatic reduction by air
Third photo:
• Sausage massIn this video we see that the surgeon pull not push the intestine
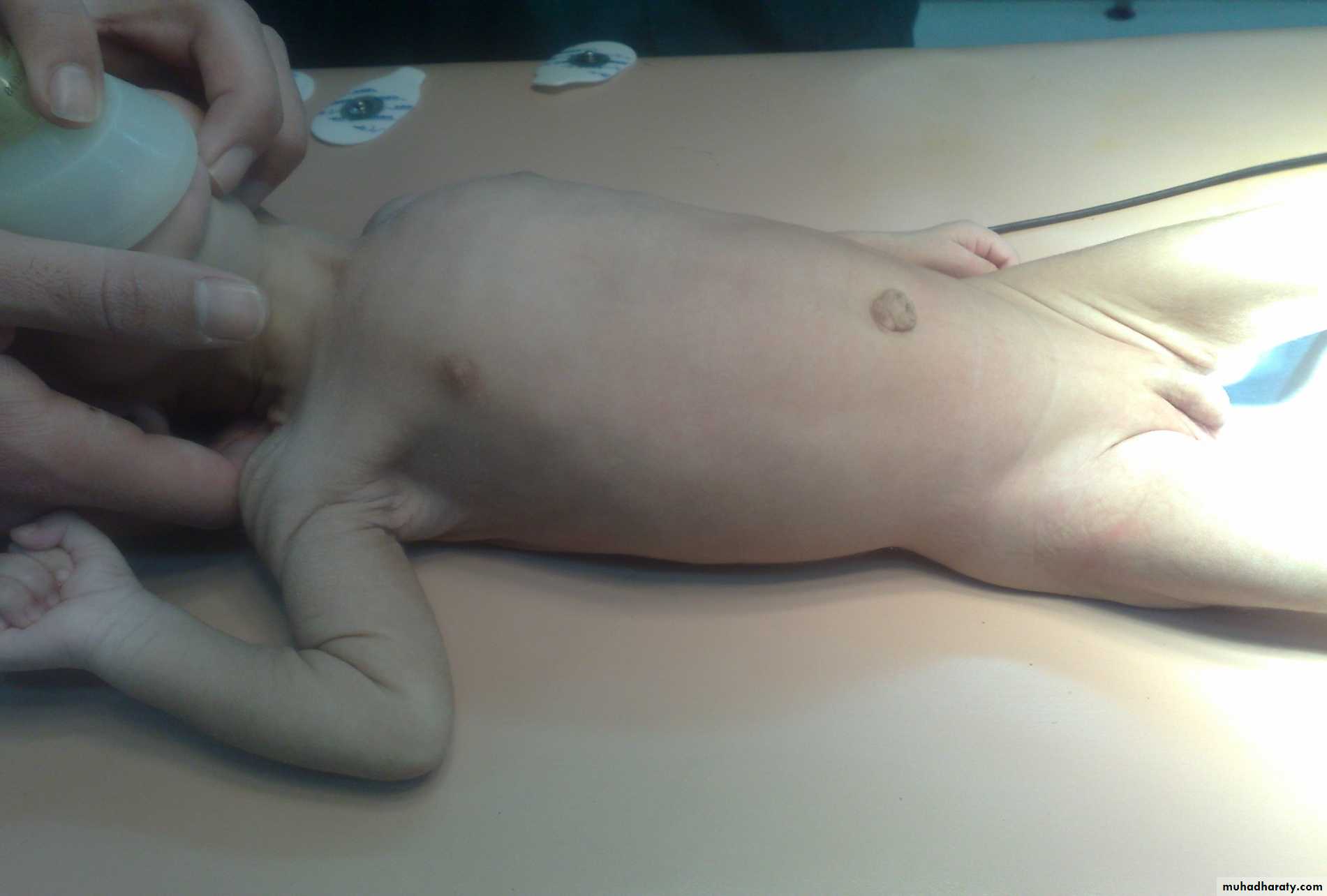
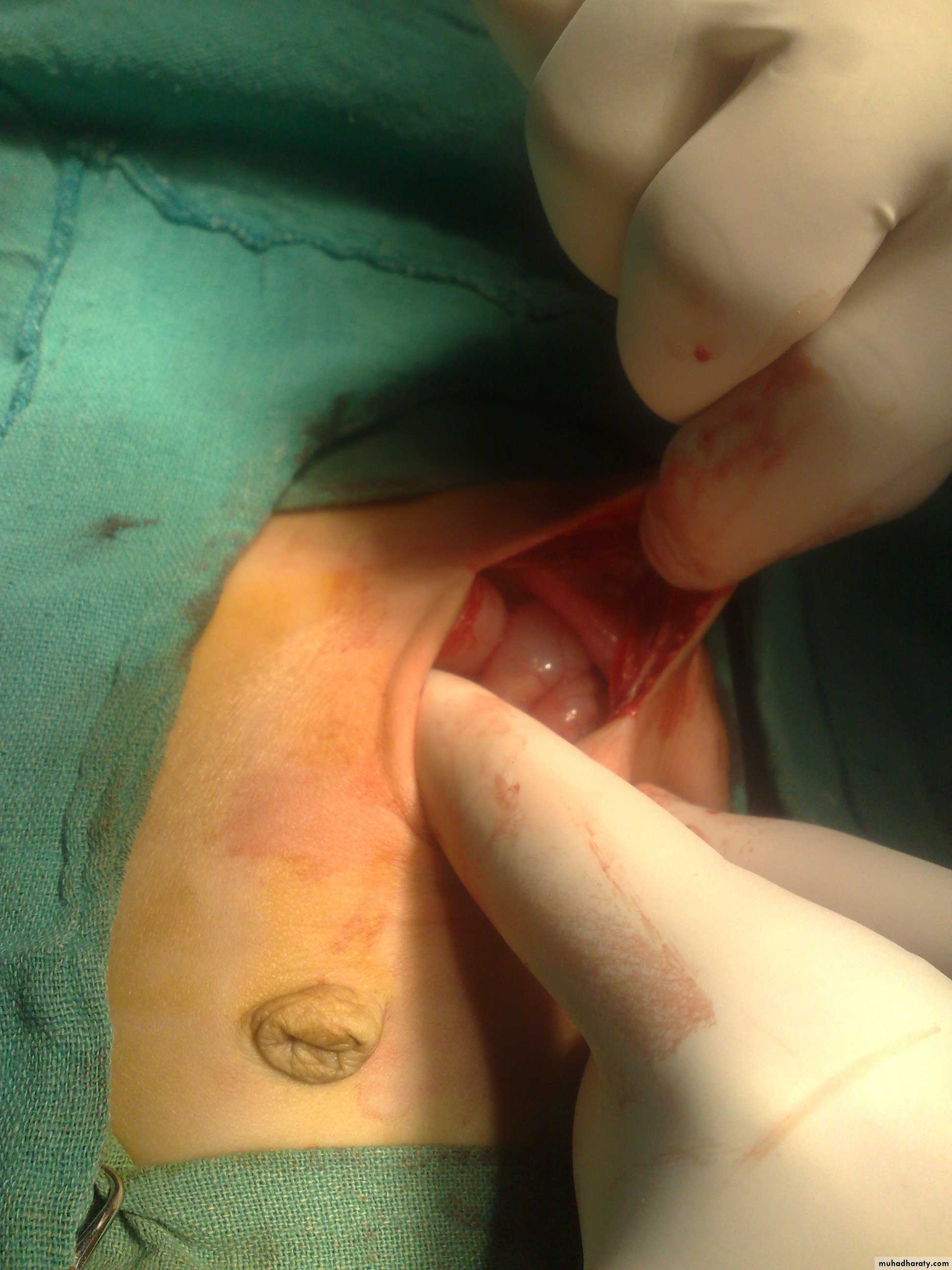
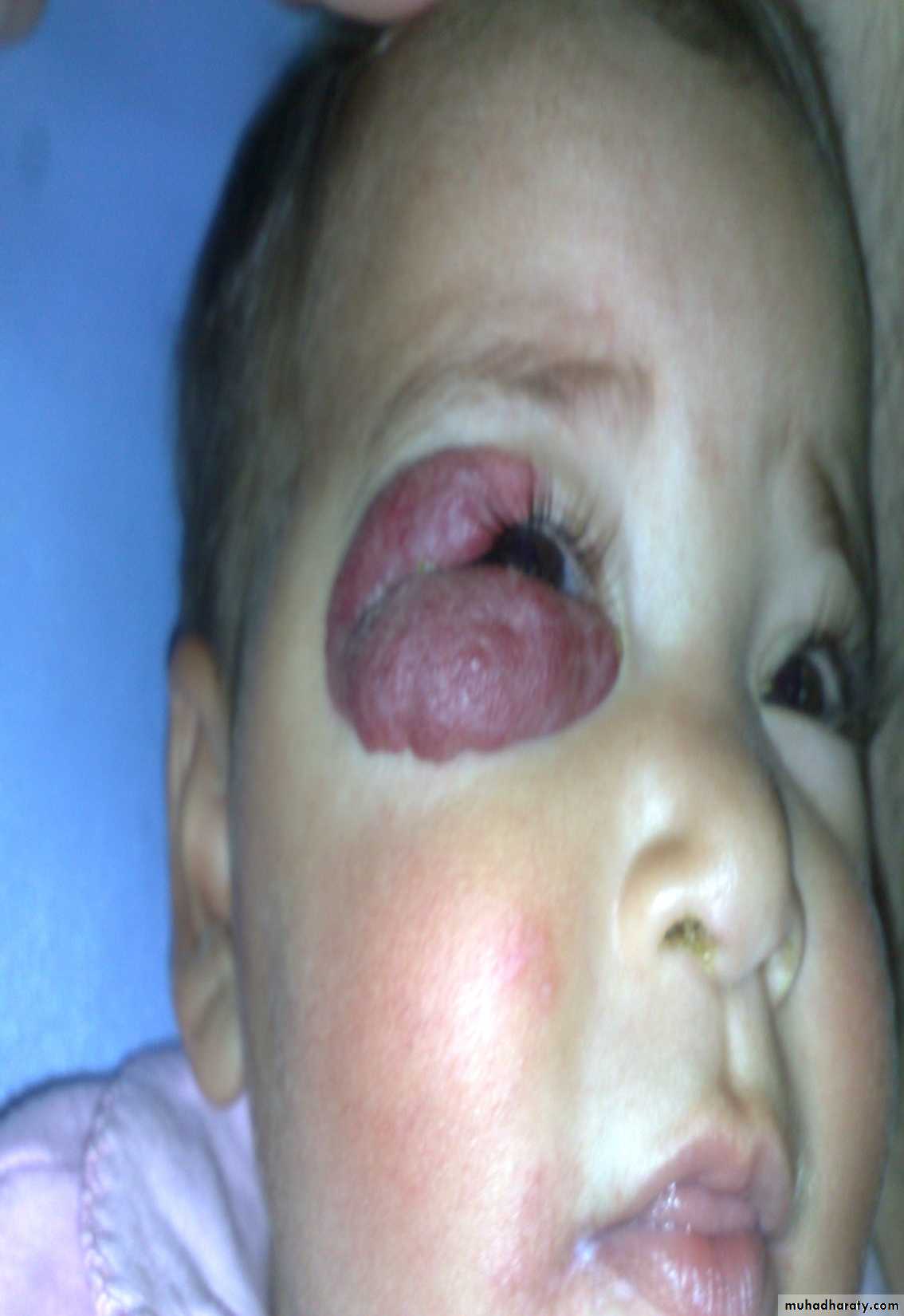
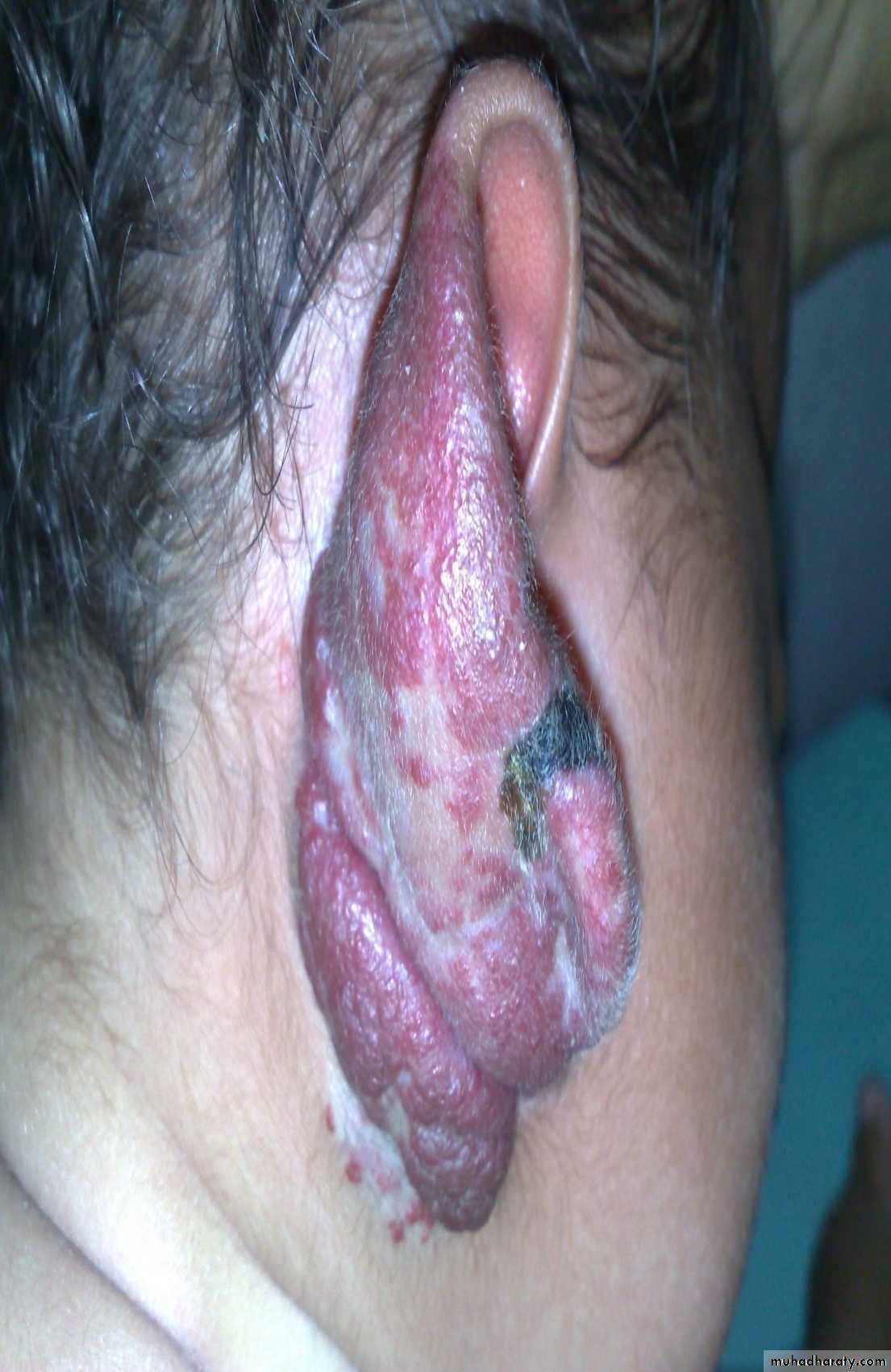
Diagnosis: hemangioma
Typical history: the condition start as small red point then within few monthsit become larger and after one or two years it may resolve spontaneously
Complications:
• Bleeding• Ulceration
• Pressure may affect vision or hearing
• Bleeding tendency in huge hemangioma
Treatment:
• Spontaneous resolve
• Surgery