Symptoms
Pain: diffuse or localized (eg lateral epicondyle of the humerus in tendinitis).Referred pain from cervical spine.
Stiffness:
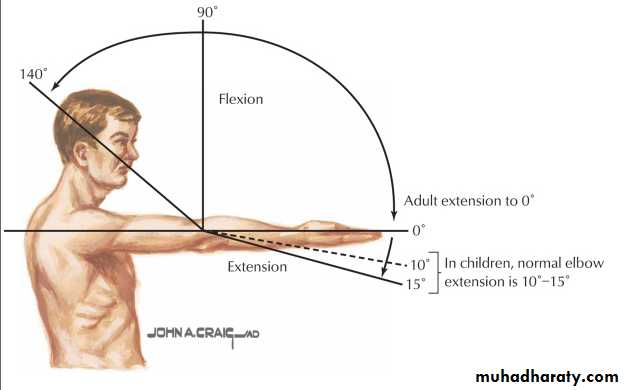
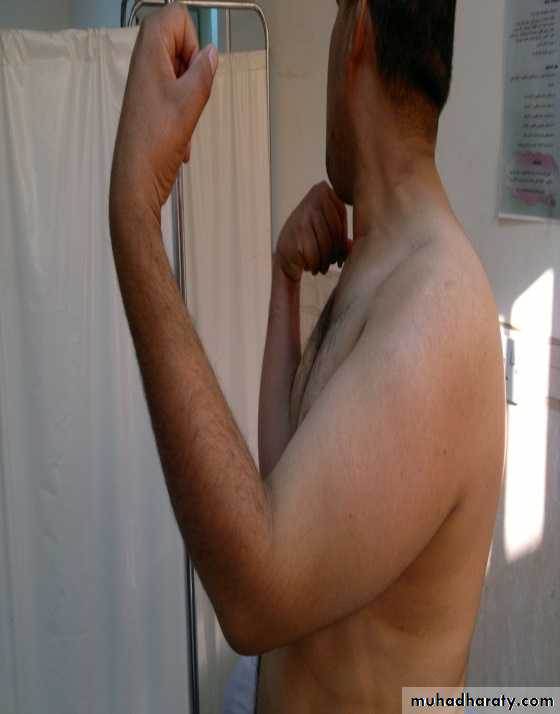
Limited flexion; cannot reach the mouth.
Limited extension; cannot reach the perineum.
Deformity: eg.
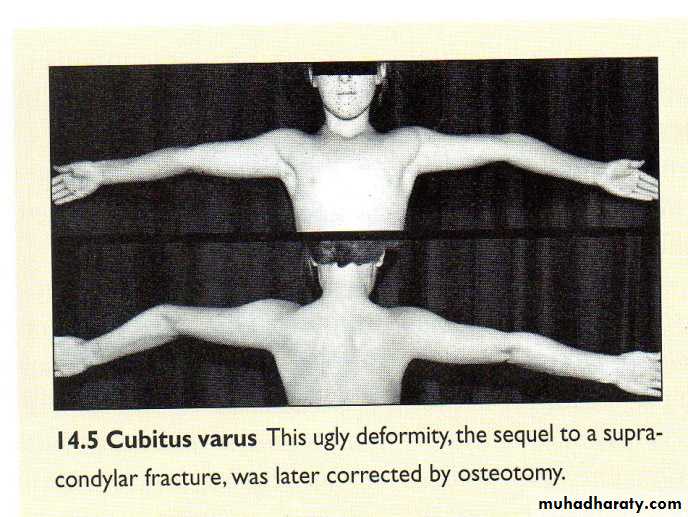
Malunited supracondylar fractures; cubitus varus, cubitus valgus.
Rheumatoid arthritis.
Signs
Expose both upper limbs.
Examine from front and behind.
Also examine neck shoulders and hands.
Look:
Skin; scars, sinuses,
Deformity; cubitus varus, cubitus valgus,..
Rheumatoid nodule
Feel
Warmth.Nodules; rheumatoid arthritits, bursitis,…
Tender points; eg, over lateral epicondyle in tennis elbow.
Move
Assess:Flexion/extension.
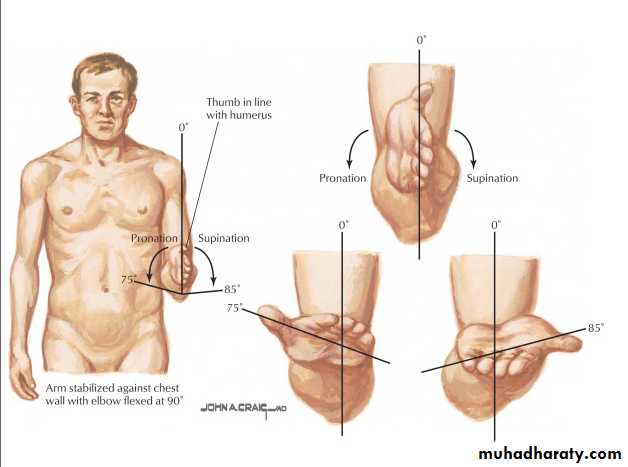
Pronation/supination.
General examination
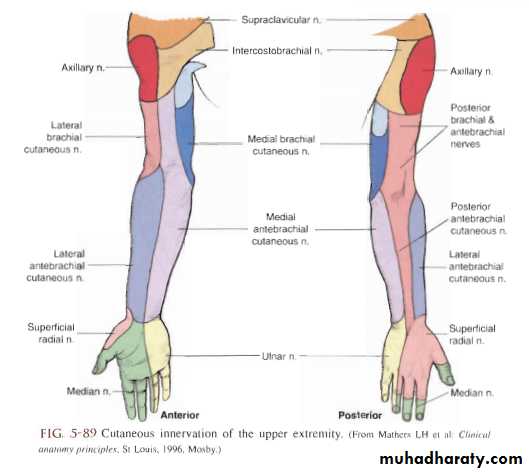
Examine the neck and shoulders for referred pain.Examine the hand for nerve dysfuncion
.
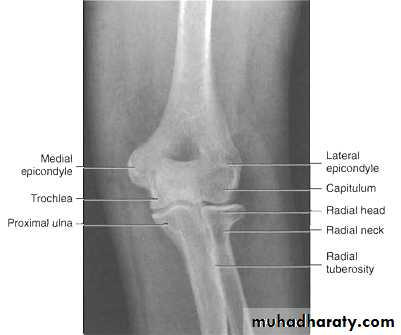
Radiological assessment
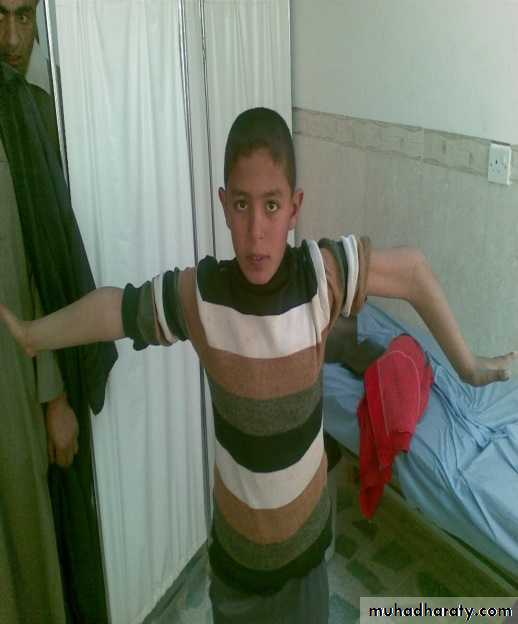
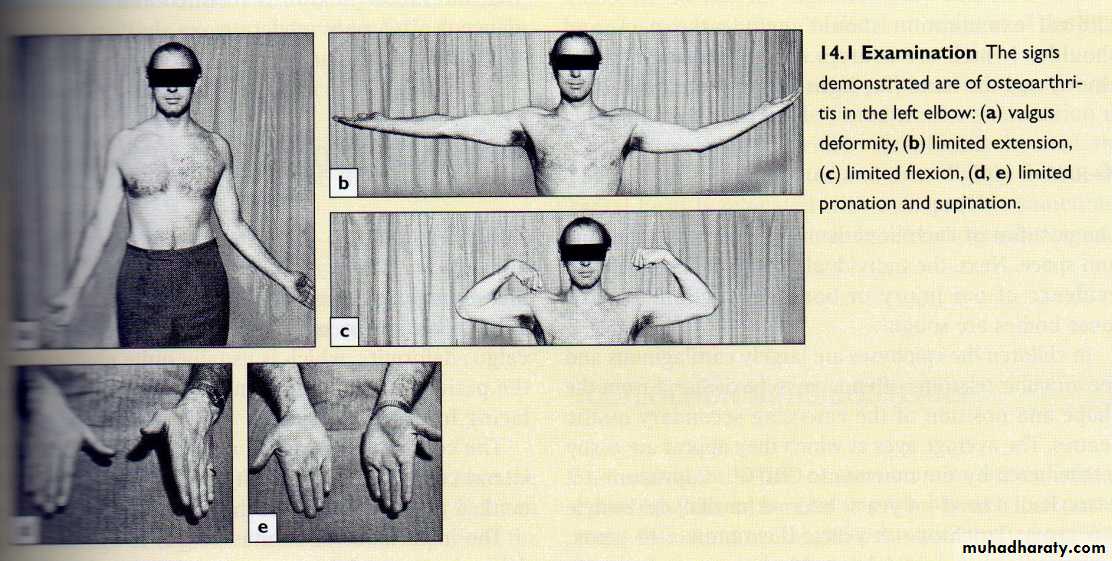
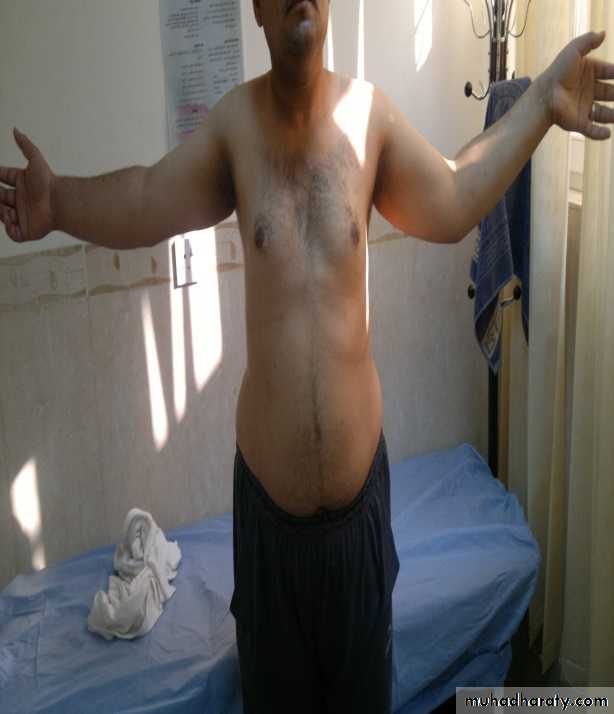
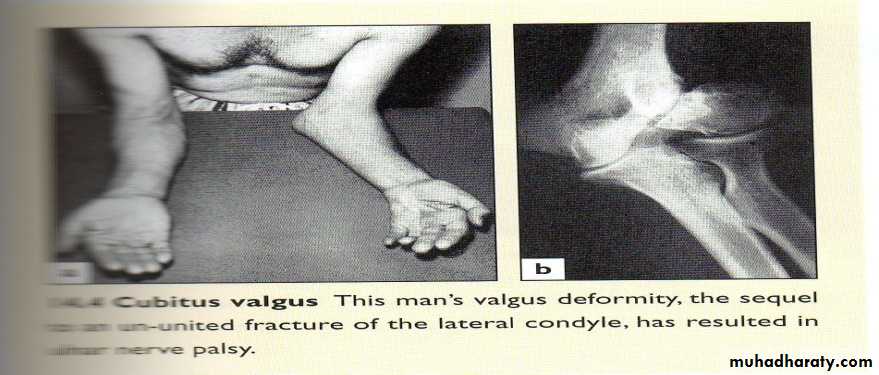
Cubitus valgus
Normally the elbows are in 10-15° valgus (carrying angle). More than this is cubitus valgus.best examined with the arms on the sides of the trunk and the palms facing forwards.
Cause; non-union of lateral condyle of the humerus.
Complication; delayed ulnar nerve palsy.Cubitus varus
Obvious when elbows extended and arms elevated.
Cause; malunion of supracondylar fracture.
Treatment; wedge osteotomy of the lower humerus.
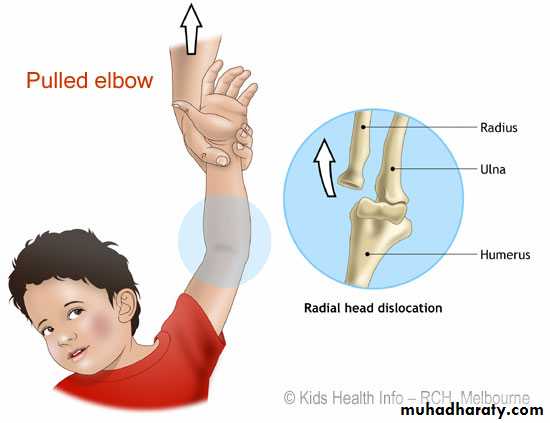
Pulled elbow
Downward dislocation of the head of radius from the annular ligament.Cause; fairly common, the child is jerked by the arm.
Clinical features:
pain and inability to use the arm.
Arm held with the elbow extended and forearm pronated.
X-ray: normal but made to exclude fractures.
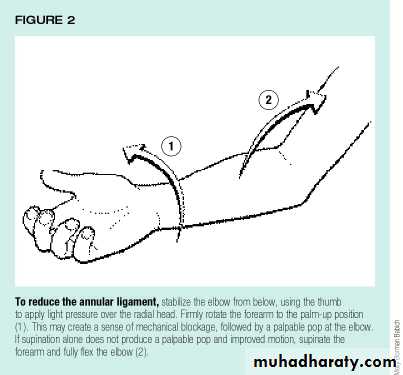
Treatment: reduce by flexion and supination of the forearm.
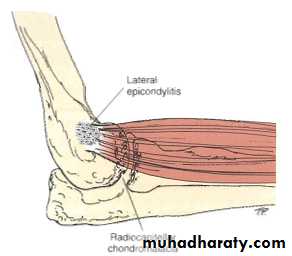
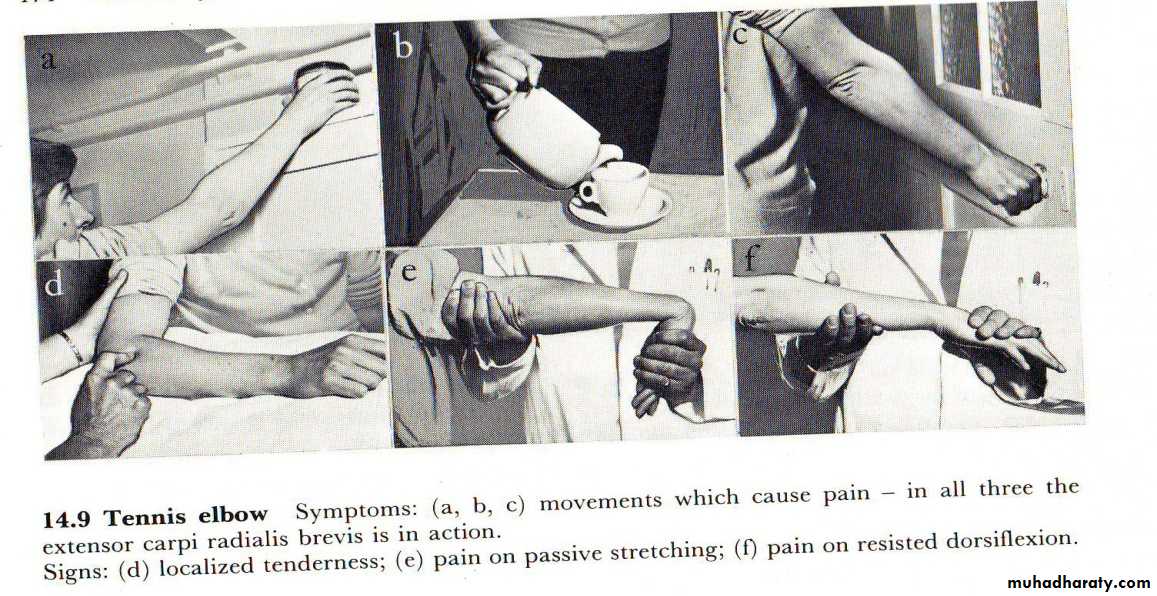
Overuse syndromes:1-Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)
Pain and tenderness over the lateral epicondyle of the humerus (common extensor origin).Cause: forceful repetitive extension of the wrist leading to chronic tendinitis.
Clinical features
30-40 years.
Pain on lifting with forearm pronated.
Localized tenderness over the lateral epicondyle.
\
Treatment
Restrict aggravating activities.
Injection of corticosteroid with local anesthetic in the tender area.
Surgical detachment of extensor origin from lateral epicondyle.
Medial epicondylitis(Golfer’s elbow)
Tendinitis of the common flexor origin over the medial epicondyle.
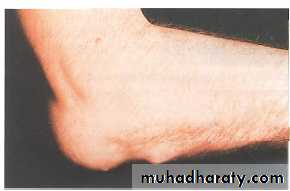
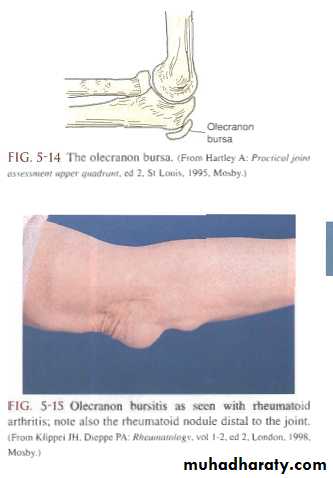
Olecranon Bursitis
Traumatic: continued pressure or friction (student’s elbow).
Non-traumatic: gout, rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment: large bursa needs excision.