Maternal and Child Health
Specific objectivesAt the end of this lecture you will be able to:
• Define maternal and child health care
• Identify importance of such services
• Enumerate its main elements
• Specify each elements
Pregnancy and childbirth are two very important life change events for the mother, newborn and the family. The health of women and children has always been an important social goal of all societies.
Mother and Child always regarded as a Single Entity.
Why??????Health of the child and the mother are closely linked;
Infection during pregnancy (TORCH infections) ---congenital defects.Some specific health interventions jointly protect pregnant women and their babies –e.g. Inj T.T., Iron & Folic acid
At childbirth, both mother and child are at risk for complications.
After birth, the newborn is solely dependent on mother for breastfeeding, care and development.
The postpartum care of the mother is inseparable from newborn care, immunization and family planning advice.
Mothers and children are both vulnerable groups of the community. Women in the childbearing period (15-49 years) constitute about 25% of the population. Children on the other hand constitute about 40% to 45% of the population in developing countries. This group is characterized by relative high mortality and morbidity rates.
Rationale for MCH care
Each year > 200 million women become pregnant.> 50 million experience acute pregnancy related complications.
15 million develop long-term disabilities.
585,000 die annually.
At least 20% of the burden of disease in children below the age of 5 is related to poor maternal health and nutrition status.
Inappropriate management of labor is responsible for about 75% of 7.5 million annual perinatal deaths.
[Reproductive Health is one of the most neglected health problems in the world. Interventions are available, but policies are inappropriate.]
Rationale
Maternal and Child Health care (MCH)MCH refers to the promotive, preventive, curative and rehabilitative health care for mothers and children, child health, family planning, school health, handicapped children, adolescence and health aspects of children in special setting such as day care.
Elements of MCH
Care before conception (pre-marital care )Ante-natal (pre-natal) care
Intra natal care
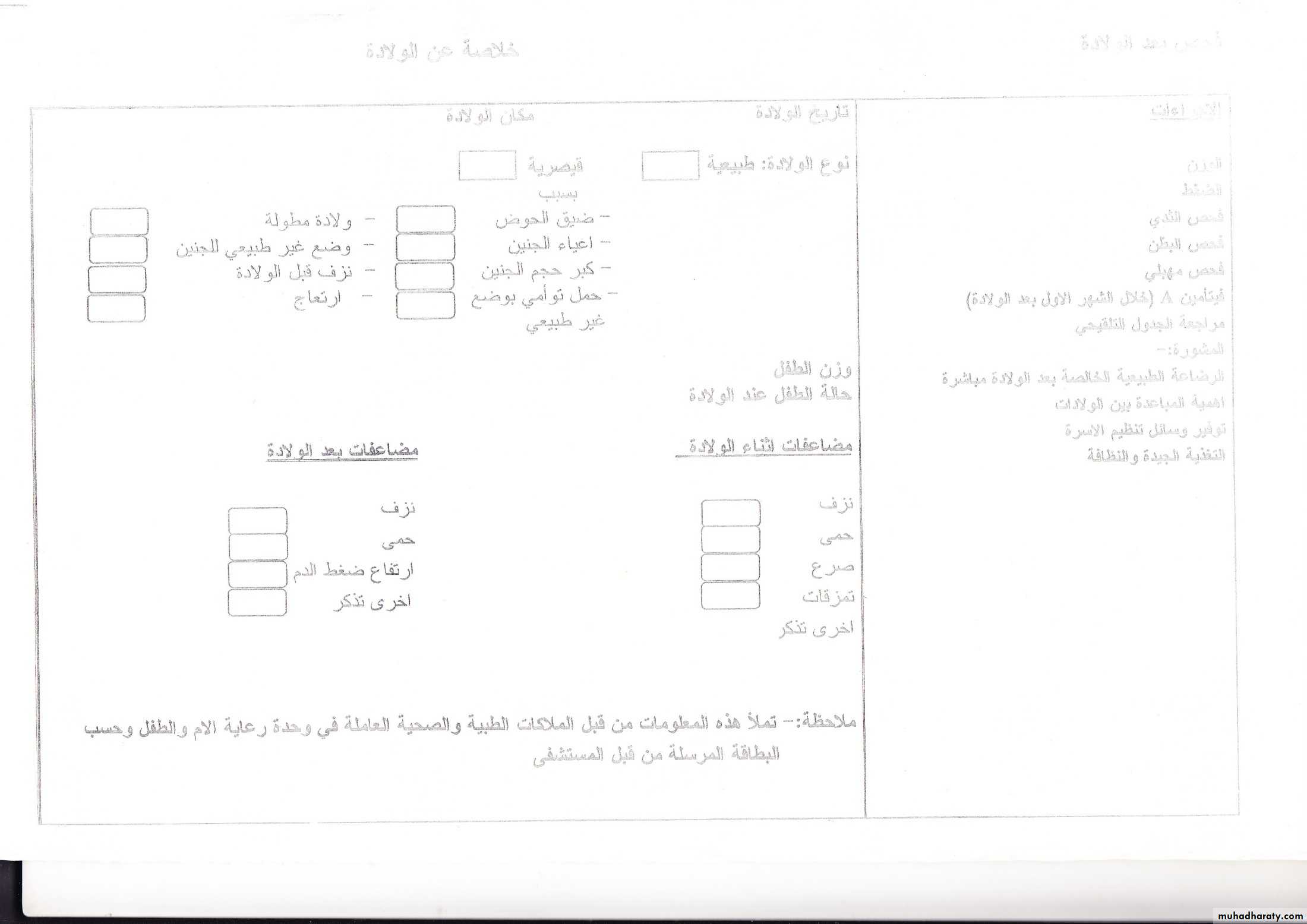
Post-natal care
Care of new born
Child health care
1-4 maternal care
5-6 child health care (young child clinic)
Maternal Health Care
MHC
MHC
Preconceptional
CarePostnatal
Care
Intra-natal
Care
Antenatal
Care
Including
PremaritalCare
Preconceptional Care
It is a care of female before conception.It is continued care from birth, through stages of growth and development, and until the time of conception and pregnancy, so as to prepare the female for normal child bearing and delivery in the future.
Components of Preconceptional Care:
Health promotion and prevention of health hazards specially those of particular risk to pregnancy.Regular health appraisal for early case detection and management, and prevention of sequel or complications.
Health education of young girls e.g. determinants and requirement of health, family health, family planning…..
Premarital care (for both partners).
Premarital CareIt includes:
Premarital counseling
Premarital immunization ( e.g. Tetanus toxoid)
Premarital examination:
History taking (thalasemia, sickle cell anemia, hemophilia, mental retardation, congenital anomalieas, TB, STDs…..etc.)
Genetic counseling
Systemic medical examination
Investigations (Serology for syphilis +HIV; Rh + ABO group; MCV, MCH, PCV; and HBs antigen)
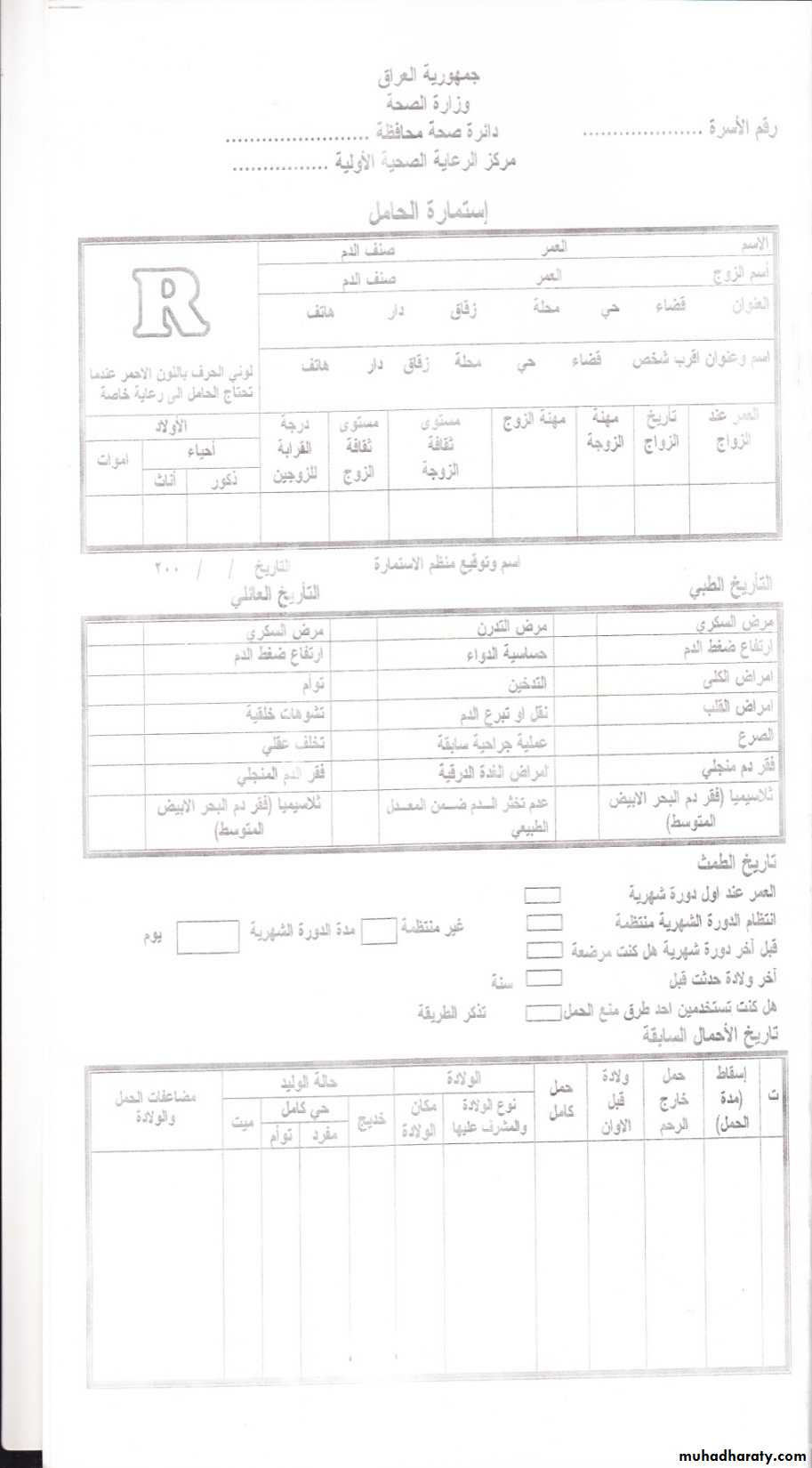
Antenatal care
Antenatal care refers to the health care provided to a pregnant woman throughout pregnancy until labor.
Basically, its a screening program intended to detect complications early; provide health education and implement effective health promotive and preventive interventions
Objectives
Overall- reduce maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortalityTimely detection and management of complications
Ensure the birth of a healthy child
Ensure the health of the mother
Provide essential health education to the mother including information on the danger signs of pregnancy
Antenatal care
Components of Antenatal (Prenatal) Care
Registration: During the booking visit, and record keepingMedical examination and investigations; for both the booking visit and continuing visits.
Health education
Immunization
Supplementations
Clinical services
Social services (outreach services).
Antenatal care
Schedule for Antenatal Visits
The first visit or initial visit should be made as early is pregnancy as possible.
Return Visits:
Once every month till 28 w.
Once every 2 weeks till the 36 w
Once every week, till labor.
(i.e. Nulliparous with an uncomplicated pregnancy, a schedule of 10 appointments and for Parous with an uncomplicated pregnancy, a schedule of 7 appointments).
Antenatal care
During the firs visitA: Conformation of pregnancy,(then)
B: Assessment
• Assessment
• History• Examination
• Investigation
Antenatal care
Initial visit- History
Present pregnancy-Accurate dating of gestational age
Any symptoms – minor or major complaints
Fetal movement perception
ANC details – investigations and interventions if the mother is referred from other facilities
Presence of any of the danger signs
Past obstetric history
Details of any obstetric complications in previous pregnancies
Family history
Any familial medical conditions
Family history of congenital anomalies; multifetal gestations and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy
Personal history
History of medical illnesses
History of smoking, alcohol intake and habitual drugs use
18
Antenatal care
Medical and surgical history:
Chronic condition such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and renal disease can affect the outcome of the pregnancy and must be investigated.
Prior operation, allergies, and medications should be documented.
Accidents involving injury of the bony pelvis
Menstrual history
Antenatal care
Initial visit- Physical Examination
Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temp.) and anthropometry (weight and height)Detailed physical exam for medical or surgical illnesses
• Skin pallor, yellowish discoloration ….etc.
• Breast abnormality
• Heart abnormality
• Chest
• Teeth caries
• Legs varicosity +edema
20
Antenatal care
Abdominal exam
• Fundal height by symphysis-fundal height measurement by the tape method
• Fetal heart auscultation after 10th week by Doppler or 20th week by fetal heart stethoscope
• Fetal presentation after the 28th week but malpresentations abnormal after the 34th week
Pelvic examination
• Evaluation of bony pelvis for symmetry
• Examination of vaginal discharge or bleeding
Antenatal care
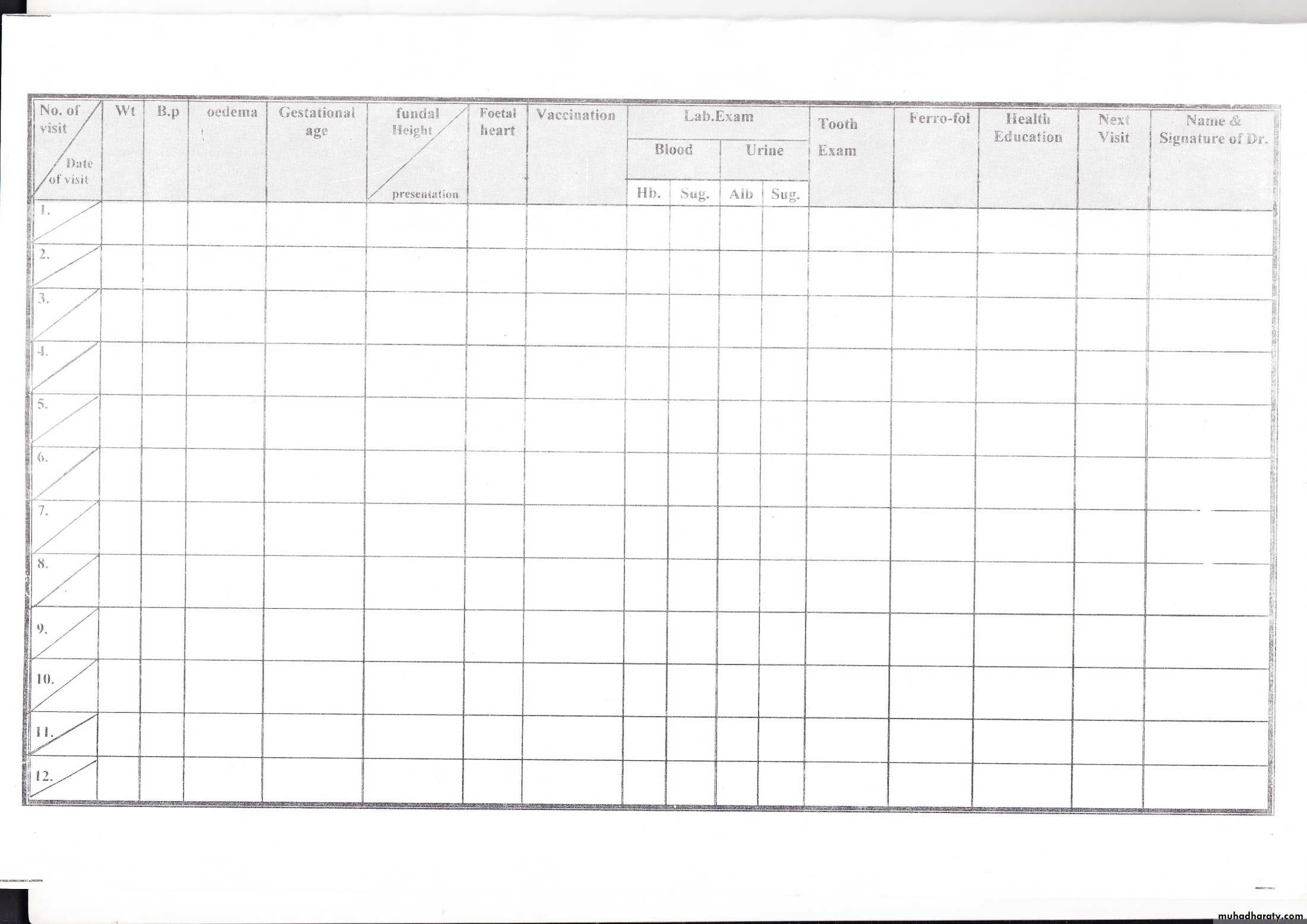
Subsequent visits – ActivitiesHistory
Follow up on previous complaints
Any new complaints since last visits
Development of any of the danger symptoms
Fetal movements history
Physical examination
Brief detailed exam including the vital signs, anthropometry and general examination
Adequacy of weight gain since last visit
Adequacy of fundal growth since last visit
Presence of fetal heart beat
Presence of other findings such as generalized edema
22
Antenatal care
Diagnostic work-up during antenatal care
Diagnostic procedure
Gestational age
Hemoglobin/hematocrit determination
Initial visit; repeat at 28-32 weeks
ABO and RH typing
Initial visit
VDRL
Initial visit; repeat at 28 weeks if negative
Urinalysis
At each visit to detect protein, sugar &ketone
Urine culture and sensitivity
Initial visit to detect asymptomatic bacteriuria
Indirect Coomb’s test
Initial visit
Serum alpha-fetoprotein test
16-18 weeks
Routine ultrasonography
16-18 weeks
Screening test for gestational diabetes
24-28 weeks
Pap smear
Initial visit
Cervical smear gram stain and culture
Initial visit
HBsAg; HIV tests
Initial visit
23
Antenatal care
Immunization
Active immunization by tetanus toxoid 5 doses.first dose at the beginning of the second trimester
2nd dose after one month
1st booster after 6months
2nd booster after one year
3rd booster after one year
Antenatal care
SupplementationProvision of supplements including; folic acid and ferrous tablets.
Psychological support
Antenatal care
Health Education:
Follow up:Advice the mother to follow up according to the schedule of antenatal care that mentioned before,
OR to follow up immediately if any danger sings appears, describe the important of follow up to the mother.
Antenatal care
Danger signs of pregnancy
• Vaginal bleeding including spotting.• Persistent abdominal pain.
• Sever & persistent vomiting.
• Sudden gush of fluid from vagina.
• Absence or decrease fetal movement.
• Sever headache.
• Edema of hands, face, legs & feet.
• Fever above 100 F( greater than 37.7C).
• Dizziness, blurred vision, double vision & spots before eyes.
• Painful urination.
Antenatal care
Health Education (topics)
Physiological changes during pregnancy
Weight gain
Fresh air and sunshine
Rest and sleep
Diet
Daily activities
Exercises and relaxation
Hygiene
Teeth
Bladder and bowel
Sexual counseling
Smoking :
MedicationsInfection
Irradiation
Occupational and environmental hazards
Travel
Breast care
Minor discomforts
Signs of Potential Complications
Antenatal care
THANK YOU