1
Fifth stage
Surgery-Ortho
Lec-10
د.يقضان
29/10/2015
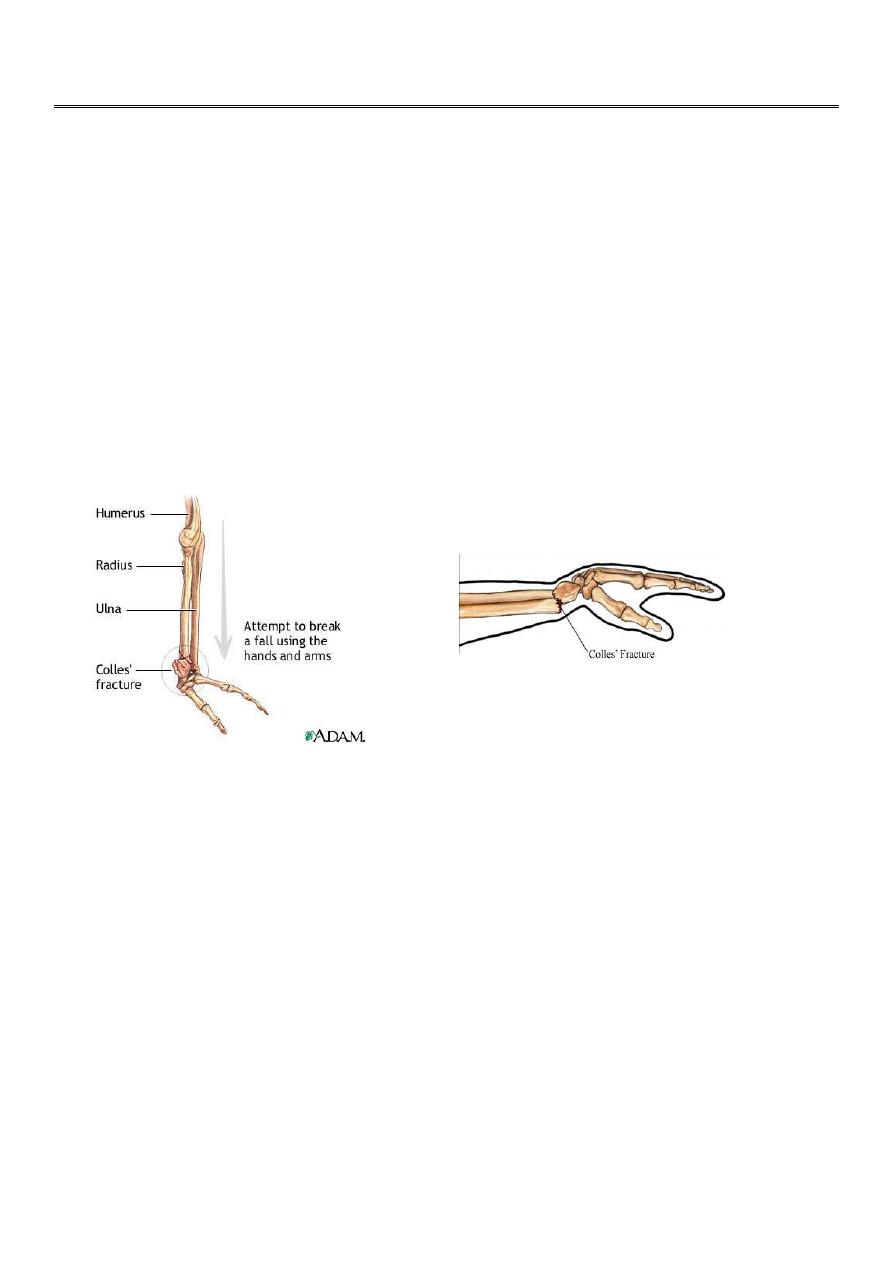
Fractures of the distal radius
Colles` fracture
This fracture is described by Ibraham colles` in 1814
.
It is a transverse fracture of the distal end of the radius with posterior displacement of the
distal fragment.
It is the most common of all fractures in the human being ; mainly in old osteoporotic
people , but it occur in all age groups
.
It is occur due to fall on out stretched hands
Clinically :
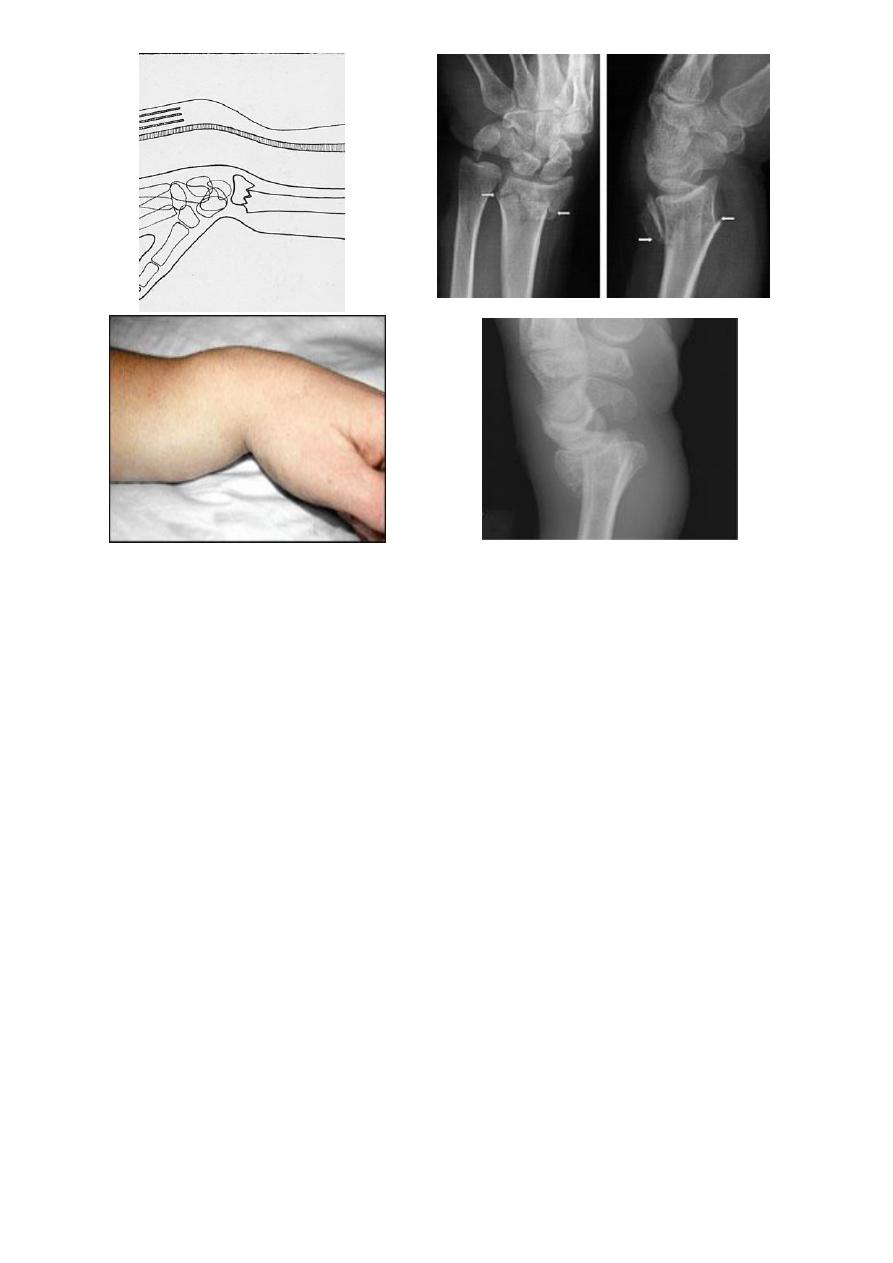
The deformity of this fracture called dinner – fork deformity .
The patient also has the sign and symptoms of any other fracture like pain , tenderness ,
loss of function , swelling …..etc .
X-ray :
there is transverse fracture of the radius at the cortico – cancellous junction , and the distal
fragment is displaced posteriorly ; some time it is severely comminuted or crushed .
2
Treatment :
It must be reduced under general anesthesia, the reduction will be by traction on the hand
in the length of the bone , the distal fragment then pushed into place by pressing on the
dorsum while manipulating the wrist into flexion , ulnar deviation and pronation
Then put back slab and check by x-ray . The back slab from below elbow to the neck of the
metacarpals .Extreme pronation , flexion and ulnar deviation must be avoided ; 20` in each
direction is adequate .
Shoulder and fingers exercise then started .After 7-10 days remove the slab and do full
p.o.p. . The fracture usually unite in 6 weeks
Complication :
early :
1-vascular damage radial artery (rare) .
2- nerve damage median nerve (rare) .
Late:
1- malunion : it is common due to unreduced fracture or due to redislpacement .
2- delayed union and non union .
3
3-stiffness of the wrist ,fingers, elbow and shoulder
4-tendon rupture of extensor polices longus .
5- sudeck`s dystrophy (localized sympathetic over activity).
6-carpal- tunnel syndrome .
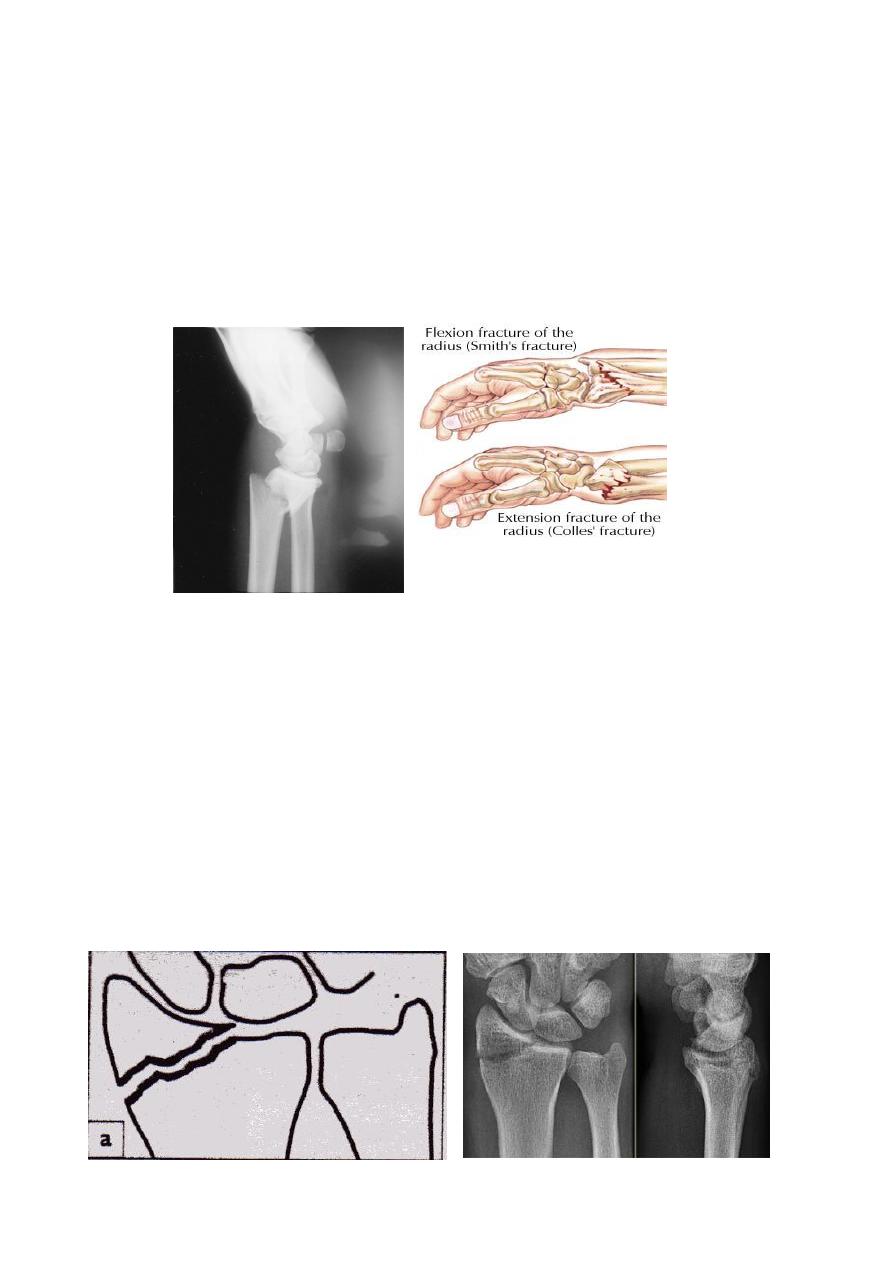
Smith fracture
: it is the same as colles` fracture but the distal segment is displaced
anteriorly .
Radial styloid process fracture
:
Here the fracture line extend from the articular surface of the radius laterally .
Treatment :
If there is displacement , the fracture should be reduced by manipulation under
anesthesia , then back slab below elbow tell the neck of the metacarpal ; imperfect
reduction will lead to osteoarthritis , so if the fracture not reduced perfectly by
manipulation then open reduction and fixation by screw or k wire .
4
BARTON`S FRACTURE
It is intra articular fracture of the lower end of the radius with subluxation of the wrist joint
It is of two types :
1. volar Barton's`: called true Barton fracture and it associated with volar subluxation
of the carpus . The fracture line run obliquely across the volar lip of the radius into
the wrist joint . The distal segment isplaced anteriorly carrying the carpus with it .
Treatment : the fracture easily reduced but it is unstable so it can easily redisplaced
so the treatment will be by open reduction and fixation by special plate called
Buttress plate .
2. dorsal Barton`s: it is the reverse of the volar one .
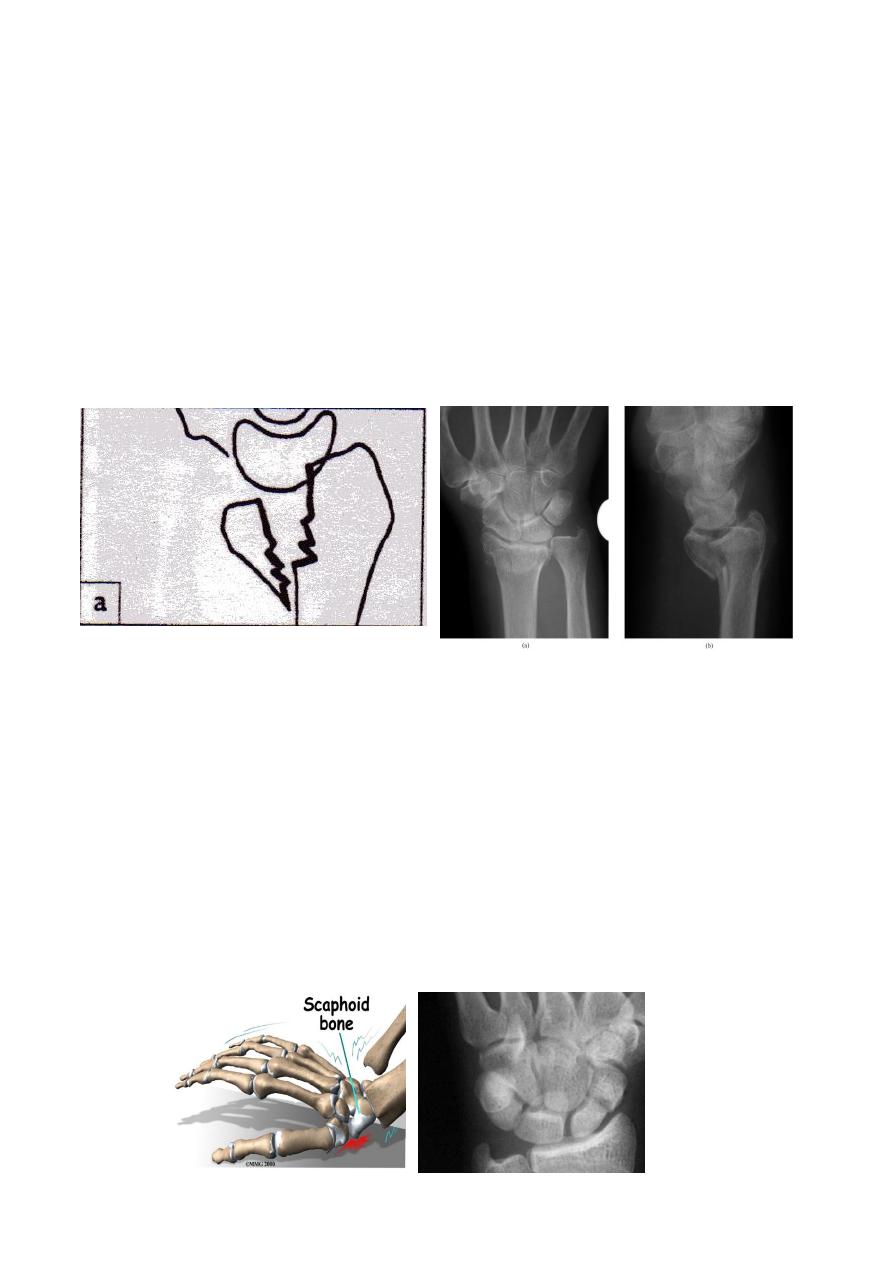
Fracture scaphoid bone
Clinically
: there is fullness and tenderness in the anatomical snuff box ; other diagnostic
sign is that, proximal pressure along the axis of the thumb is painful
X-ray :
a-p , lateral and oblique views are all essentials .
Some time recent fracture show it self only in oblique view .
Usually the fracture is transverse and through the narrowest part of the bone (the waist) ,
but it could be in the proximal pole or in the tubercle ; few weeks after injury the fracture
will be more obvious
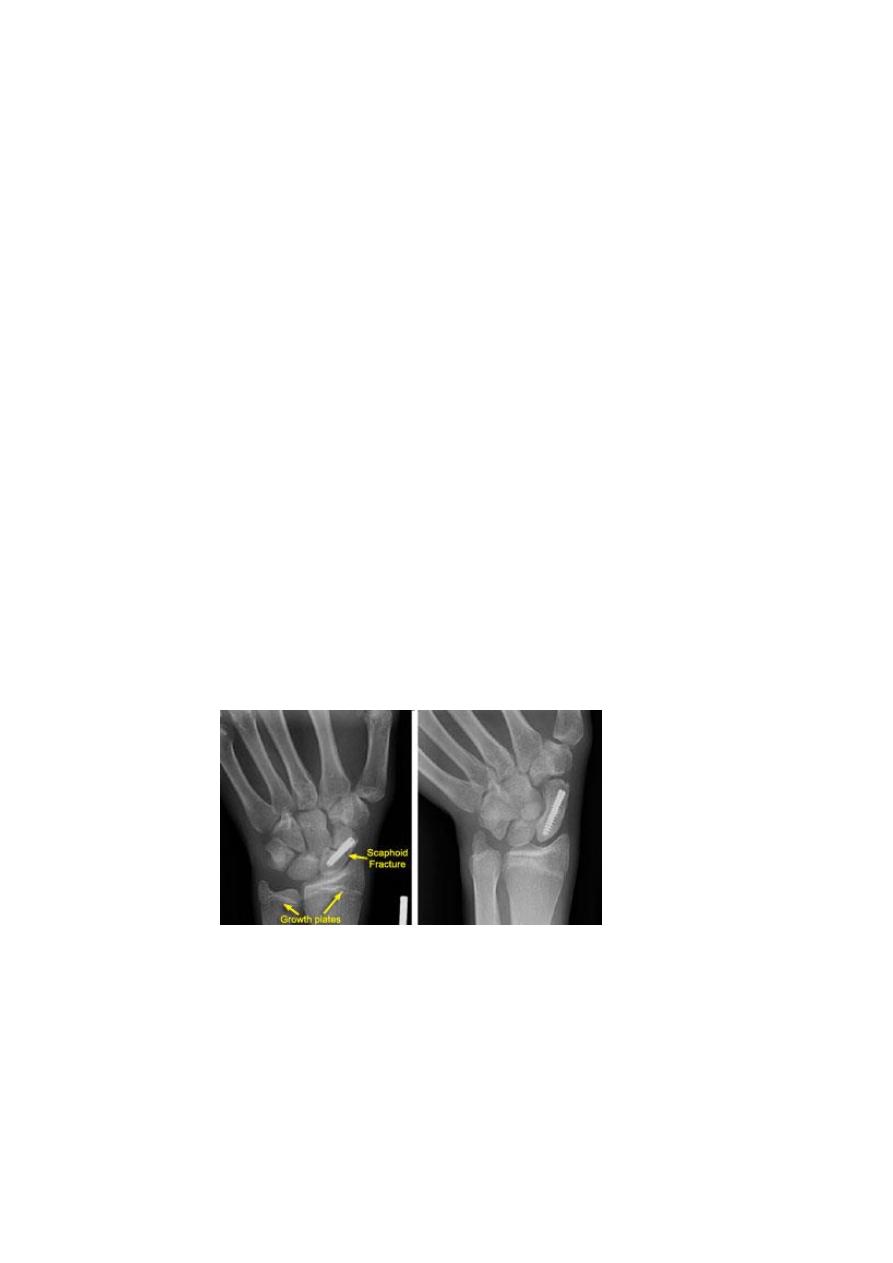
5
If union is delayed , cavitation appear on either side of the fracture
.
In old ununited fracture there will be sclerosis at the edge and the appearance will be as
there is extra carpal bone
.
Sclerosis of the proximal fragment is path gnomonic of avascular necrosis of the proximal
fragment .
Treatment :
Undisplaced fracture
: conservative treatment by p.o.p. cast in 90% of the cases
will heal ; the cast will be applied from upper forearm to just short of the
metacarpophalangeal joint of the fingers but it should incorporating the proximal
phalanx of the thumb ; the wrist is held in dorsiflexion and the thumb forward in (
GLASS HOLDING ) position and it should be retained for 6 weeks .
After 6 weeks the p.o.p. removed and the wrist examined clinically and radiologically
, if there is no tenderness and the x-ray show sign of healing , the wrist is left free If
there is local tenderness or the fracture is still visible in x-ray , the p.o.p. is reapplied
for further 6 weeks and after that either the wrist become painless and the fracture
healed so the p.o.p. removed or the x-ray show sign of delayed healing then we
should do fixation and bone grafting .
Displaced fracture
: treatment by open reduction and fixation by compression
screw .
Complication
1- avascular necrosis : the proximal fragment may die especially with proximal pole
fracture , it will appear dense on x-ray .
Treatment : by excision of the proximal fragment .
2- non union : after 3 months if fracture not united it will be obvious that the fracture will
not unite at all .
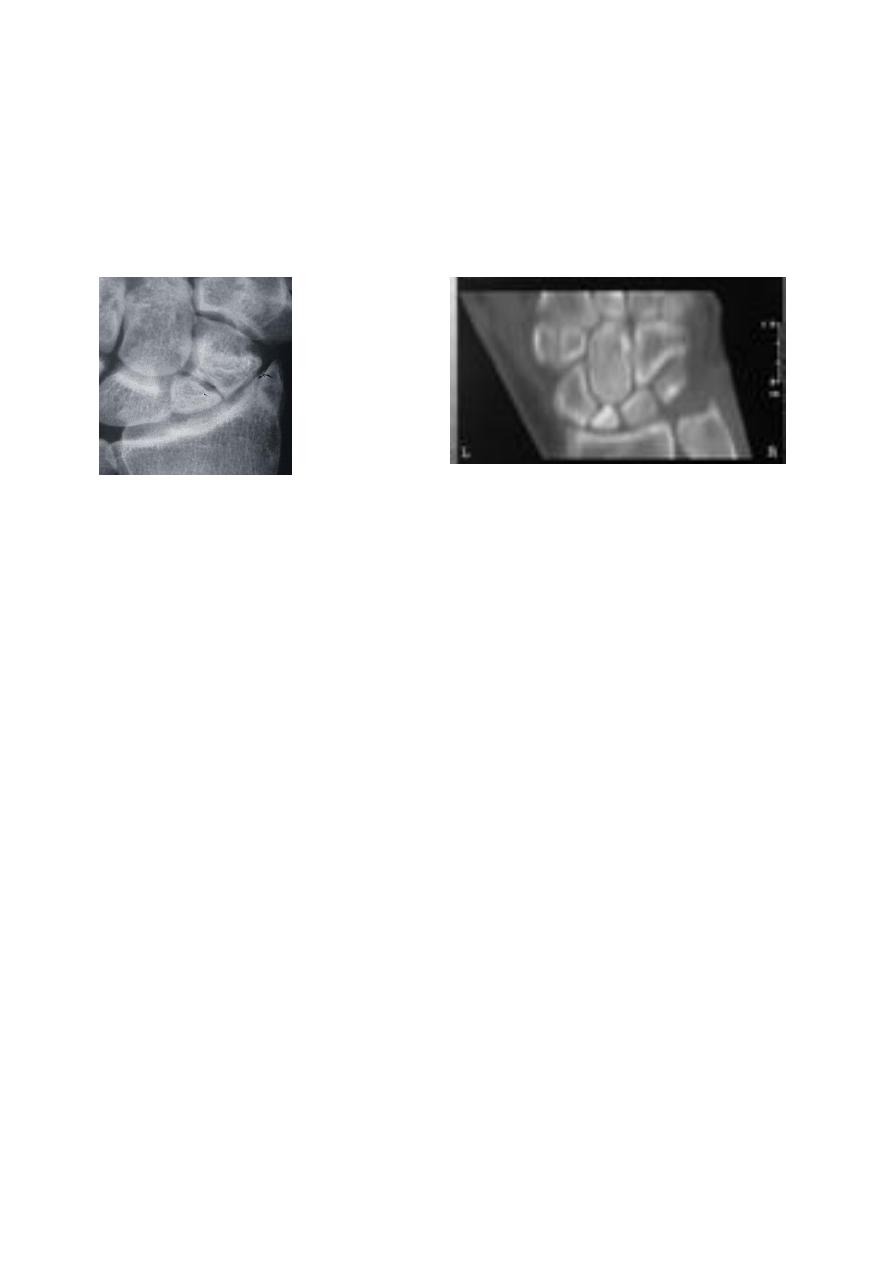
6
Treatment :in old people and in those who are completely asymptomatic , non union may
be left untreated .
In young patients treatment by fixation and bone grafting .
If the graft fail then do excision of the scaphoid and fusion of the carpel bones .
non union fracture scaphoid Avascular necrosis of proximal segment of scaphoid frac.
3- osteoarthritis : non union and avascular necrosis may lead to secondary osteoarthritis .
