forth stage
surgeryLec-
د
29/11/2015
RENAL FAILURE & TRANSPLANTATIONRenal Failure
Reduced clearance of certain solutes principally excreted by the kidney
The most common indicators are urea & creatinine
RF could be acute or chronic
Causes of end stage renal failure:
-DM 36%
- Hypertensive nephrosclerosis 30%
- chronic glomerulonephritis 24%
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease 12%
-chronic pyelonephritis
In pediatric age group ( <18 year ) congenital causes predominate like cong. hypoplasia.
Treatment of end stage CRF:
Treatment is by
hemodialysis,
peritoneal dialysis,
or renal transplantation
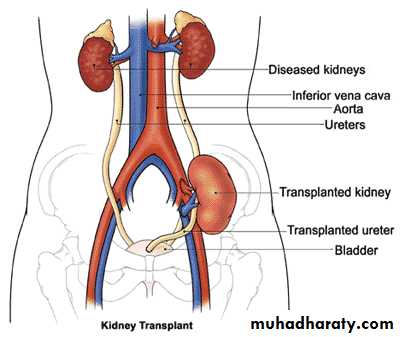
Renal transplantation
Renal Transplantation is the treatment of choice & the most cost effective treatment for end stage renal failure.
The upper age limit for renal transplantation is
70 year of age in average
DONER
RECEPIENTrecepient evaluation:
Cardiac statusMalignant diseases: waiting time :
1 – 2 year for low metastatic potential
5 – 6 year for high risk tumors
Infections
GIT diseases like peptic ulcer
GU abnormalities : MCUG , URODYNAMIC study
Pretransplant bilateral native kidney nephrectomy:
Seldom requiredIndications:
Pyelonephritis
Medically uncontrolled renin mediated hypertension
Malignant disease
Nephrotic syndrome
Extremely large polycystic kidney
Types of donors for renal transplantation
Living related donors :
Allograft half life is 10 year longer than cadaveric renal donation
Living unrelated donors
Cadaveric donors.
Contraindications for renal transplantation
Active infections including AIDSActive malignant diseases
*the donor is always left with the better kidney
*Left kidney is prefered due to longer renal vein
Investigations & HLA tissue matching
Tissue matching is performed for HLA –A,B,&DR antigen that are found on the 6th chromosome
ABO blood grouping & cross matchin
Types of rejections
Hyperacute rejectionAcute rejection
Chronic rejection
Hyperacute rejection
- incidence 1/1000
-analogous to blood transfusion reaction ,
occurs immediately
,preformed Ab against HLA expressed on donor renal vascular endothlium
-occurs as soon as blood flow to the donor kidney is established
-treatment : immediate transplant removal
Acute rejection
occurs between 1st week- 1 month
occurs in 25 – 55% of patient
Diffrential diagnosis :
ATN , ureteral obst, drugs toxisity
Clinically : febrile , tenderness over the graft
impaired renal function,decrease urine output.
Diagnosis : renal biopsy
treatment.. by steroids & immunosuppressants
Chronic rejection
Defined as a gradual progressive loss of renal function that cannot be attributed to another cu.there is no definitive treatment for this type of rejection
retransplantation to be considered
Immunosupression
Focused on preventing & reversing acute rejectionAgents used in 3 ways
induction :
immediately after Tx like Azathioprine & steroids
maintenance :
initiated once creatinine in normalised like Azathioprine & steroids, cyclosporin A
treatment of acute rejection like steroids
Complications of renal transplantation:
Technical
Delayed transplant renal artery stenosis
Anastamotic leak
Anastamotic or ureteral stricture
Ureteral obstruction
Ureterovesical disruption
Lymphocele
Non technical
Infections
Cancers:
lymphoma , Kaposi sarcoma