1
Fifth stage
Practical pediatric
كتابة الطالب
23/11/2015
Cardiovascular system
Vasculitis:
Inflammation of BVs, it causes:
1. thickening
2. narrowing
3. scarring
These changes restrict blood flow, resulting in organ and tissue damage.
One of them Henoch-Schonlein purpura:-Inflammation of BVs in kidneys,skin &
intestine.
The exact cause of HSP is not known.
Many cases. Approximately two-thirds of the cases of HSP occur days after symptoms
of an upper respiratory tract infection develop.
Some experts also say that HSP is associated with the colder weather of fall and winter.
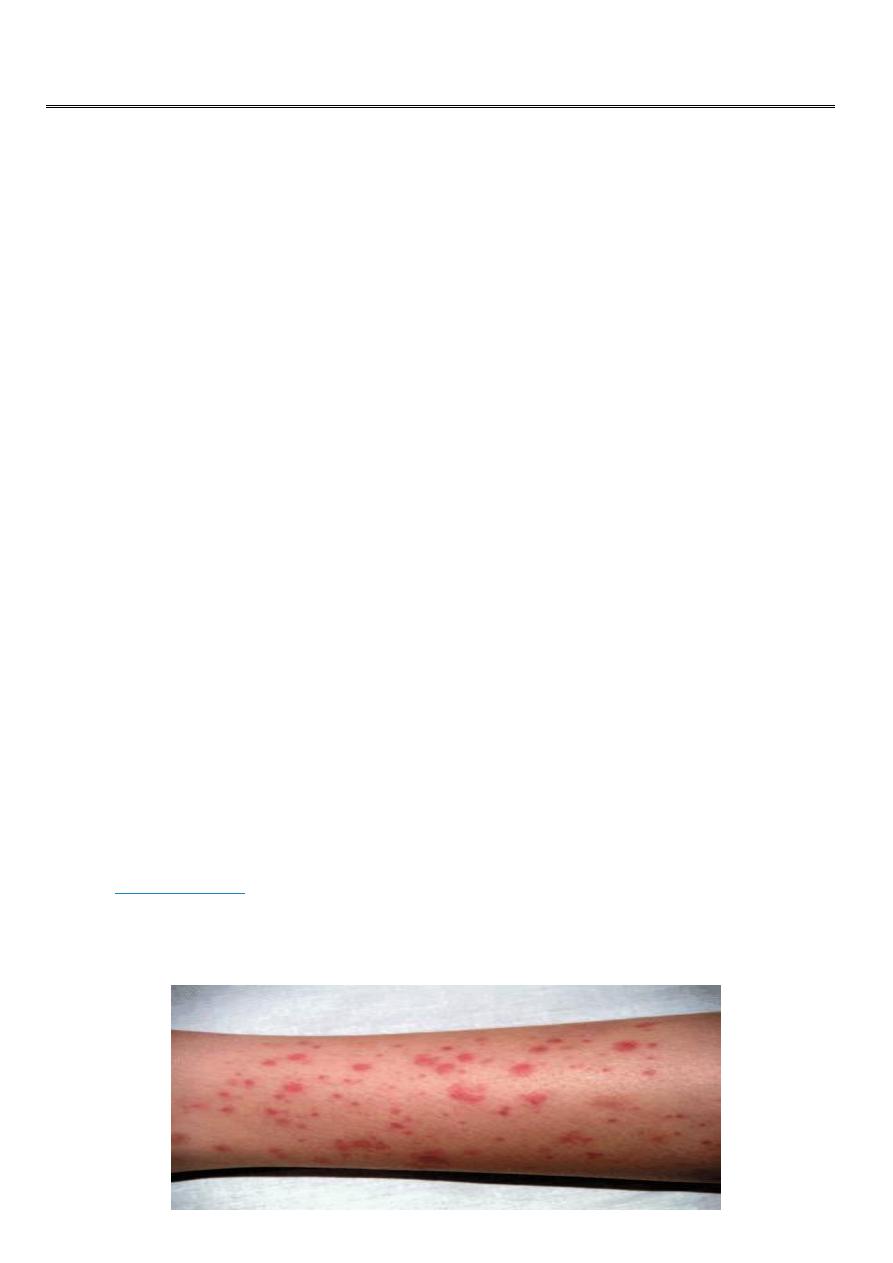
Symptoms:-
1.
: appears in all patients, The initial appearance may resemble
, with small red
spots or bumps on the lower legs, buttocks,
, and elbows. But these change to
. The rash usually affects both sides of the body equally and
does not turn pale on pressing.
2.
3.
swelling
4.
(blood in urine)as mostly due to nephritic syndrome or nephritic.
6.
) may cause a bowel blockage
Before these symptoms begin, patients may have two to three weeks of fever,
and muscular aches and pains.
2
Note:
purpura is palpable
We must send for urinalysis to check for proteinuria.
in hyperinflated chest
size of liver is normal but displacement of liver downward.
Ibuprofen induce bleeding.
CVS exam:
1. is the patient looks well?
2. pale?
3. cyanosed?
4. regular respiration?
5. dysmorphic?
6. vital signs?
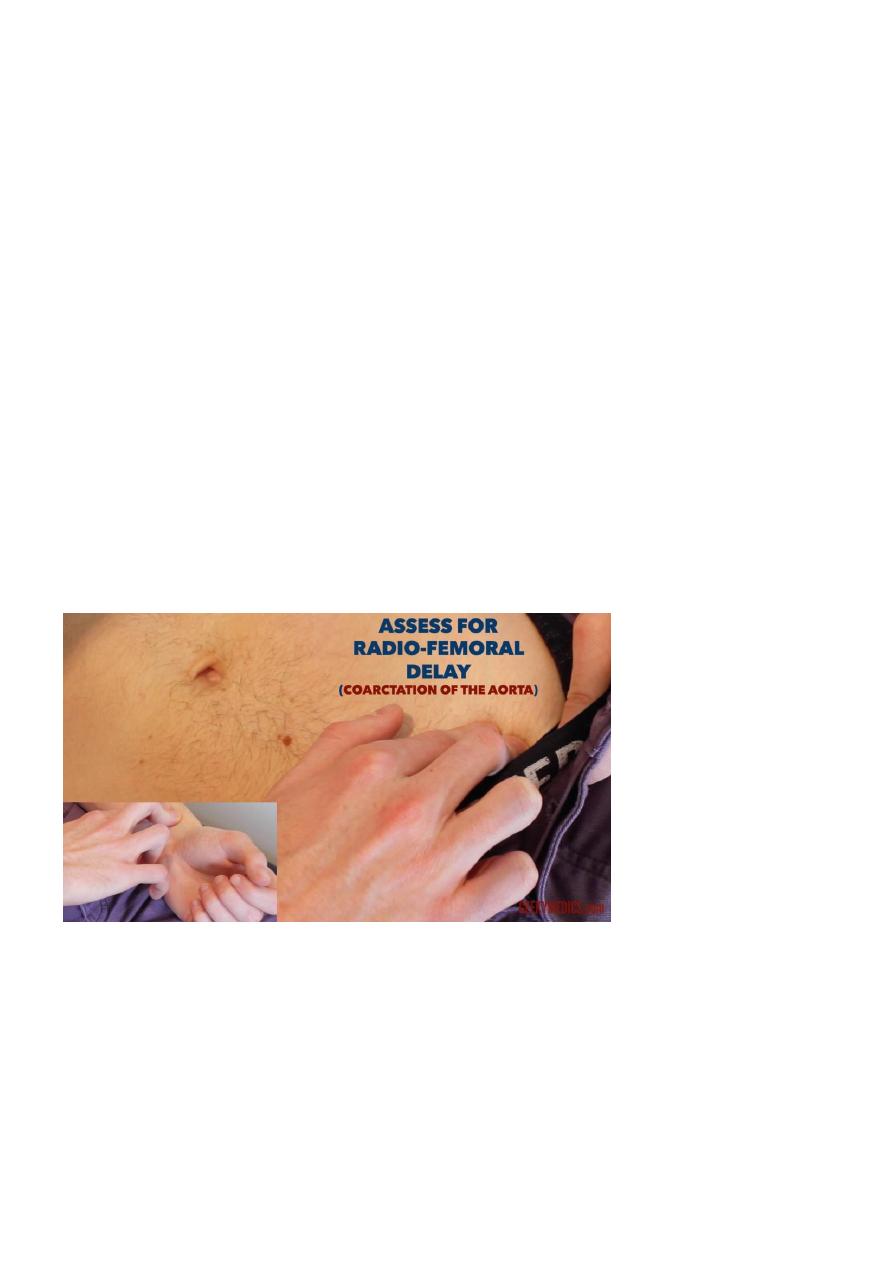
P.R:either from brachial artery or by auscultation(H.R)
In older childrenfrom radial artery.
Don't miss the radiofemoral delay as this indicate (coarctation of aorta).
7. growth parameters(very important).
8. clubbing
9. splinter hemorrhage.
10. janewaylesions
11. osler's nodes.
12. sacral edema(in those yet not able to walk).
13. pulse oximetry.
14. capillary refill(details in the last session)
15. hydration status?
3
Precordium examination:
--Try to do auscultation firstly as the inflan/child is quiet,percussion of precordium is NOT
routinely done,as it will NOT clarifly the dullness of precordium as it is barrel shape usually
in infant.
--Exposure from the neck to the umbilicus
Inspection:
1. chest deformity:pectus carinatum,pectus excavatum.
2. dilated veins.
3. visible apex beat(pulsation).
4. scar:
Infra-clavicular scar
Pacemaker
Sub-mammary
mitral valvotomy
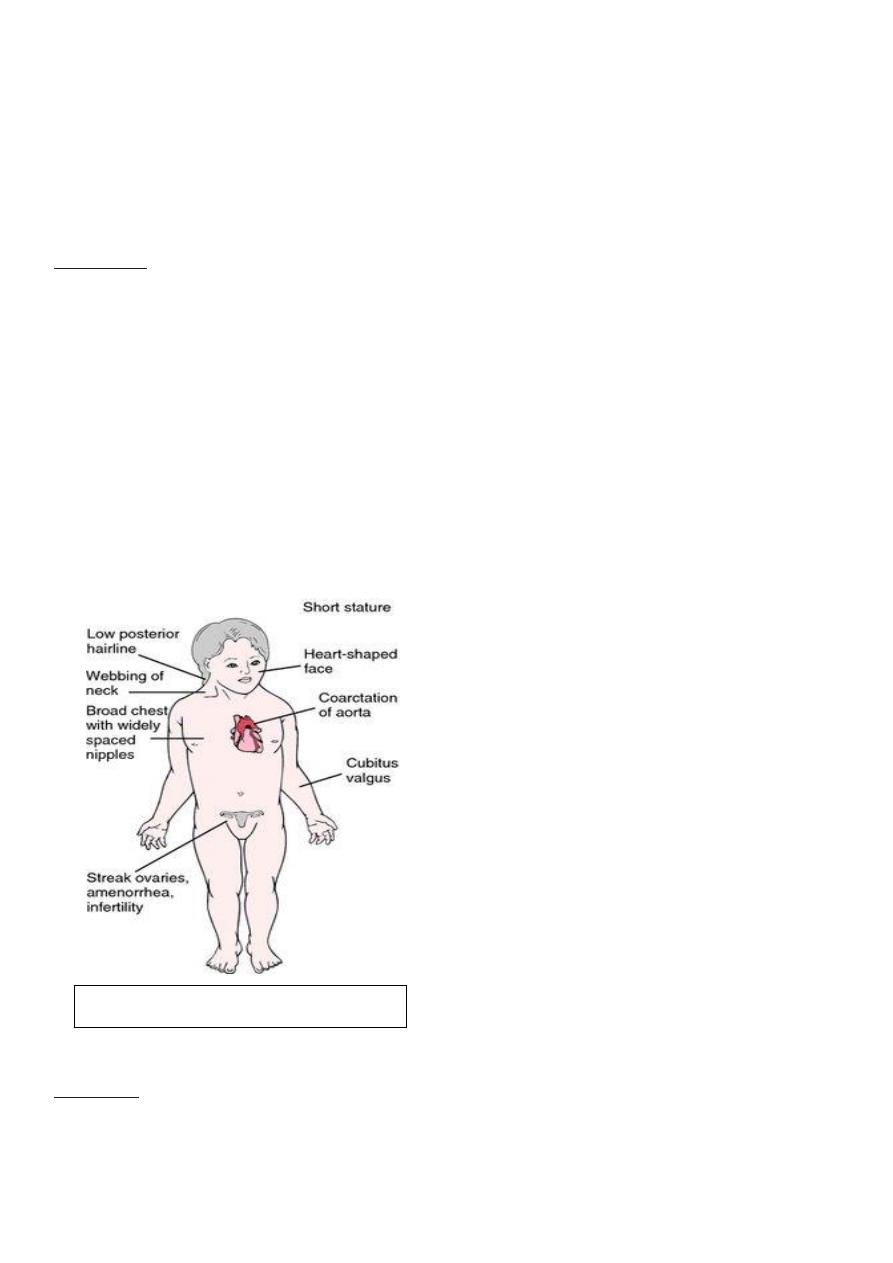
5. nipple are widely spaced ,or in their normal position((widely spaced nipple indicate
Turner syndrome: a condition in which a female is partly or completely missing an X
chromosome))
6. 6-chest movement with respiration:symmetrical or NOT?
Palpation:
1-apex beat (4
th
-5
th
intercostal space in MCL):-is the most lateral & inferior cardiac impulse
can be felt.
Features of Turner syndrome

4
Is thers is associated thrill(palpable murmer),parasternal heave which indicates right
ventricular hypertrophy :when we place our hand near the sternum,our palm will be elevated
with the pulsation accordingly).
2-tracheal position?shift present or NOT?
Auscultation:
Comment on 1
st
heart sound, 2
nd
heart sound(loud,split), murmer present or NOT? systolic or
diastolic?
Lower back auscultation for:
a.pulmnary crepitation
b.Coarctation of aorta(the murmer radiate to the back).
*if u heard bowel sound in chestdiaphragmatic hernia.
Causes of absent apex beat
1. obesity
2. thick chest wall
3. pericardial effusion
4. dextrocardia(always search for situs inversus with it)
Murmur grades:
G1: fairly heard
G2: heard without difficulty
G3: there is thrill
G4: loud murmur
G5: heard without stethoscope
5
Heart failure causes in neonate (non cardiac):
1. Anemia
2. Hypoglycemia
3. Diabetic ketoacidosis
4. Hypothyroidism
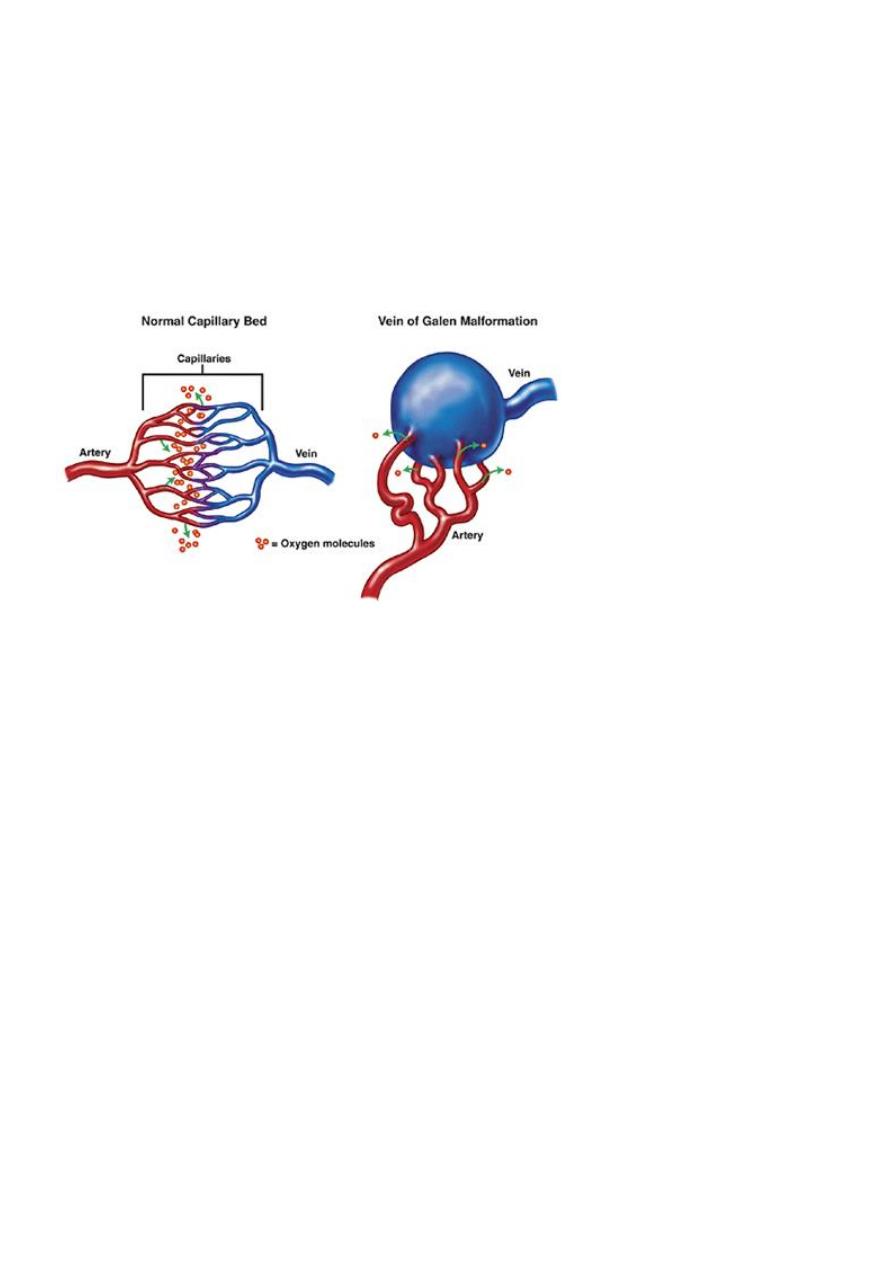
5. Arteriovenous fistula:-auscultate the fontannelle as there is vein of Galen will produce
murmer(connection between venous & arterial circulation shunting of blood which
progressively produce heart failure).
6. Renal failure(renal artery stenosis:renal bruit)
