VITAMINS
Organic compounds required in the diet in
small amount to perform specific
biological functions for the maintenance
of optimum growth and health
.
Classification
:
Fat soluble Vit A,D, E, K
.
Water Soluble vit B, C
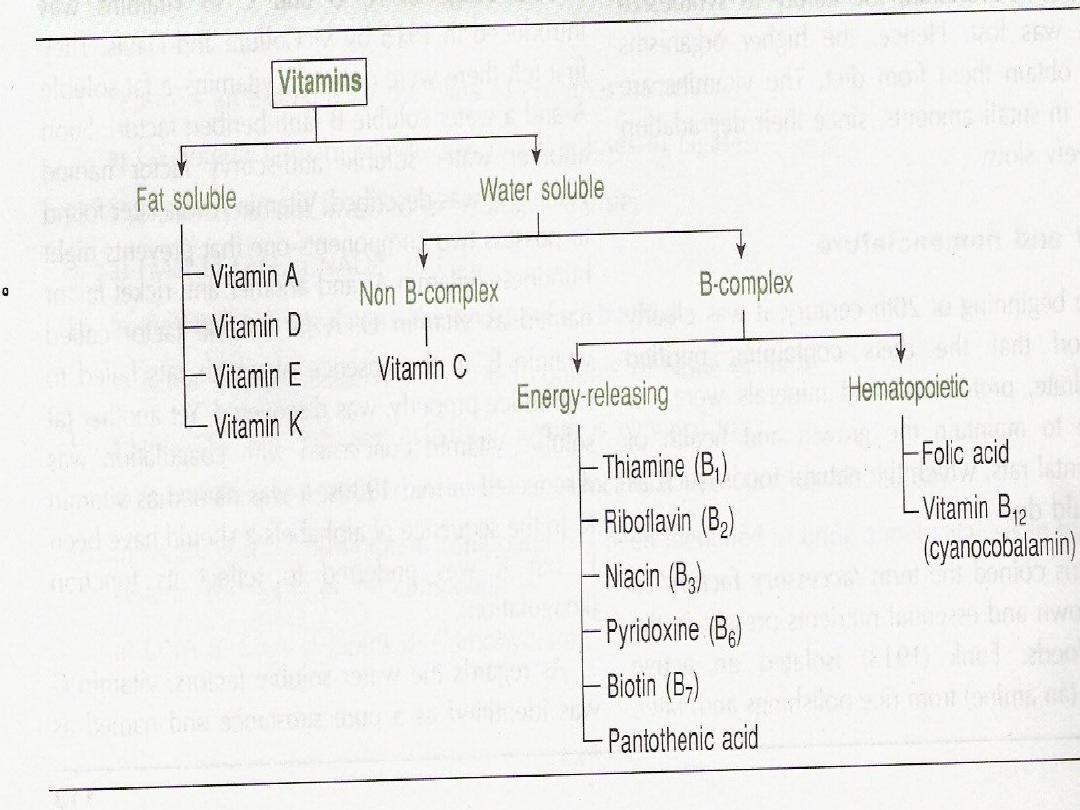

Fat soluble vit are solule in fat ,oil and in
fat solvents like alcohol, acetone
,
In general fat S. Vit. are stored in liver and
excreted through the bile , and excess
consumption of these vit particularly A
and D lead to accumulation and toxic
effect
Hypervitaminosis

Water soluble vit. are readily excreted in
urine and they are relatively less toxic
.
Water soluble vit are not stored in the body
(except vit B12
).
Generally vit deficiency are multiple rather
than single deficiency
.

Vit A
:
Water soluble vit. ,stable at
high temp, cannot synthesize in
the body,must be supplied by
diet
.
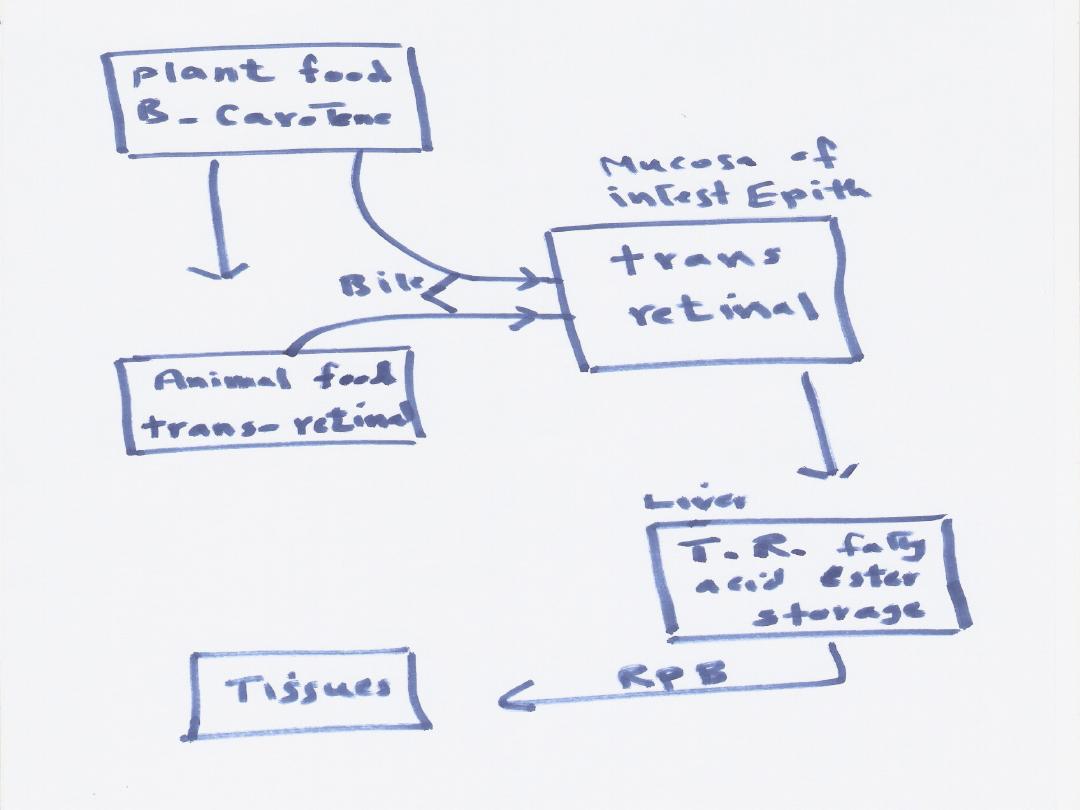
Sources: vit, pro vit
.
Pro vit: (B- carotene
)
B-Carotene: it is part of the
pigment of green and yelow
vegetables
.
After absorption from the gut it
will be converted into active
form

It is more important that vit
B- carotene can be converted into 2
molecules of vit A in the intestinal mucosa
.
Carots
………
Retinal molecules Retinol(alcohol
form
)
Retinol absorbed from intest mucose then
esterified with fatty acid and transported to
the liver.Retinol is then transport to the blood
stream in associatation with Retinol binding
protein(RBP
).
Intest
mucose,Reduction
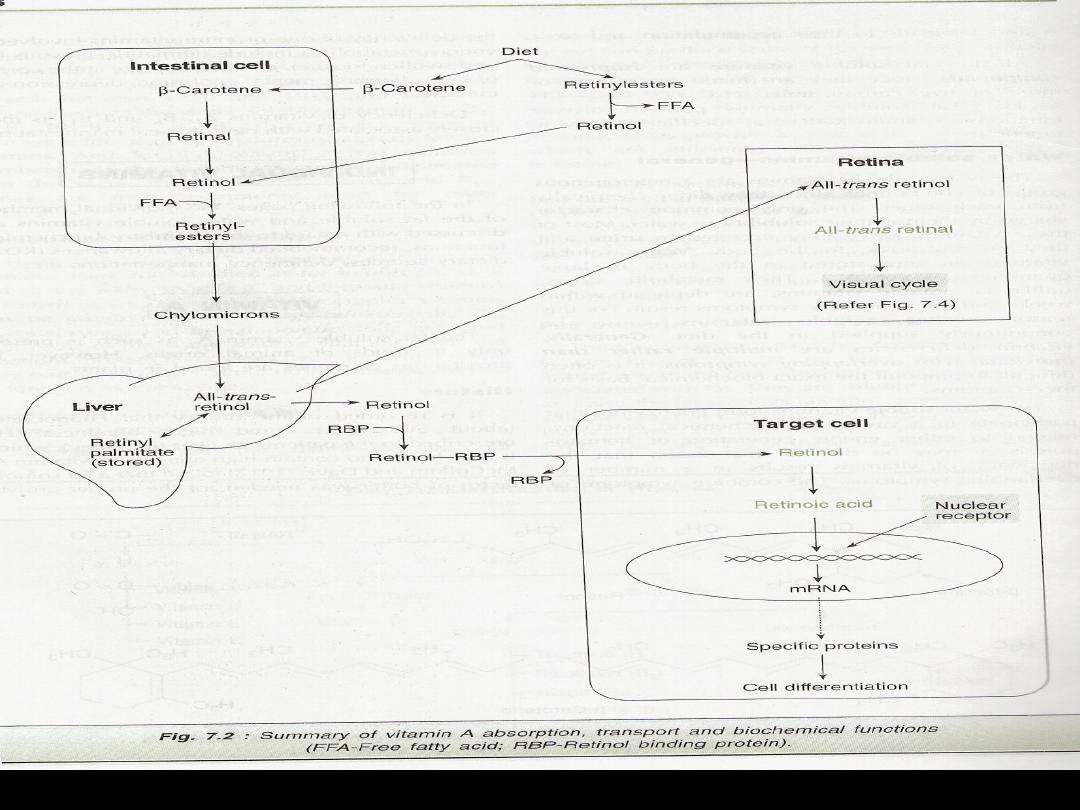
Schematic
presentation of
metabolic pathways
of retinol (VitA
)

Biochemical Functions
:
1
support the growth and the integrity of
Epith. T. ,skin eyes, bronchus& testis
.
In Eye absence or reduced vit A may lead to
replacement of normal Epith. tissue by
keratinized tissue which are more susceptible
to invasion by microorganism
Xerophthalmia progress to blindness
.
2
Mediating vision as a constituent of the
pigment called rhodopsin
.
3
Anti-carcinogenic effect
4
Antioxidant effect
.

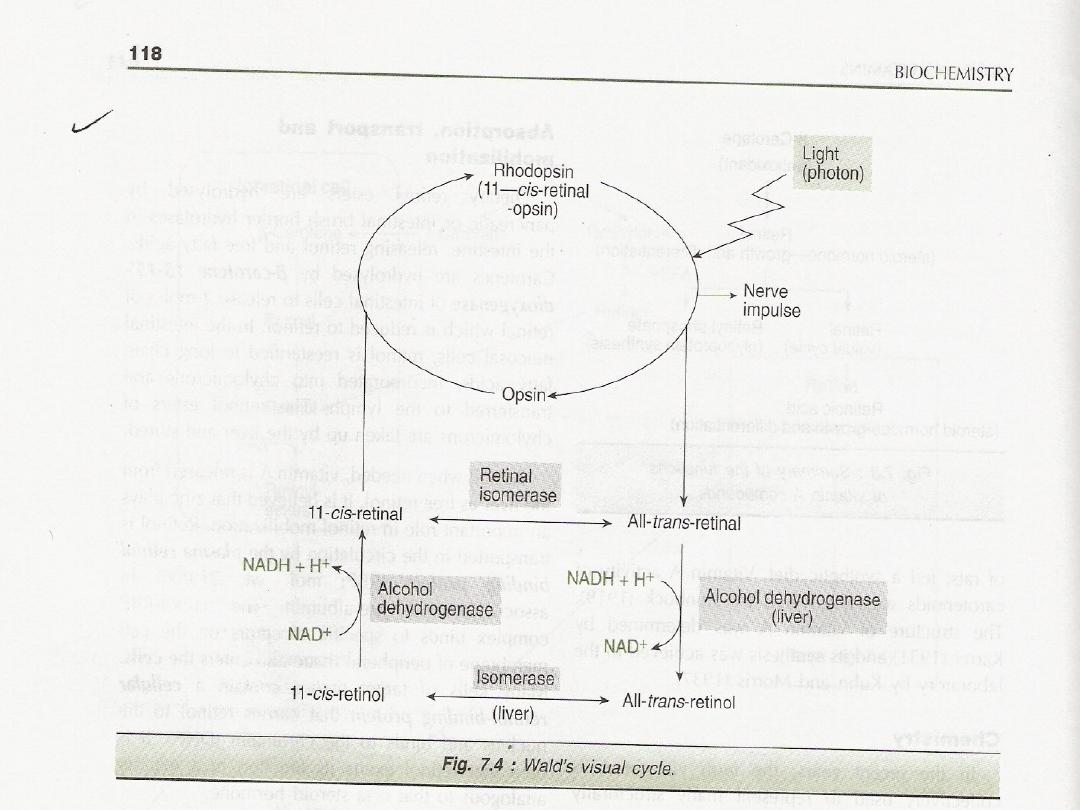

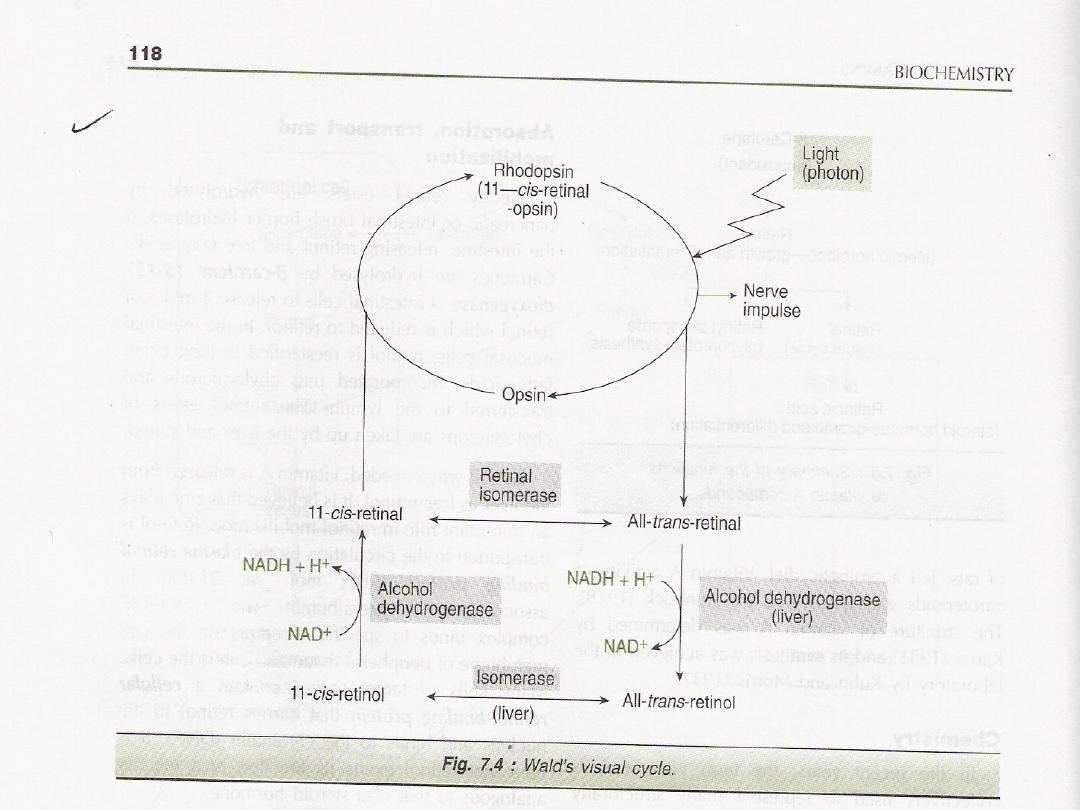
Effect of Vit A on vision
:
Rhodopsin Rods, cones
1
Rhodopsin on exposure to light is
isomerized through several steps t form
trans-retinal and by spontinous hydrolysis
to form opsin
.
2
The trans retinal is immedately
isomerized by an enzyme retinal isomerase
in the pigment of the retina to cis retinal
.

3
cis retinal bind to opsin spontaneously to
form rhodopsin and this complete the visual
cycle
.
4
some of the trans-retinal my be reduced to
trans –retinol and temporarily stored in the
pigment epith cells of the retina
.
5This trans retinal along with trans retionl
from food or from that stored in the liver
must be converted to cis retinal
.

6
This cis retinal can combine with opsin to
form rhodopsin
.
See the diagram
Deficiency
:
1
nightblinfness 2 Xerophthalmia&
keratomalcia
.
3Increase risk of developing cancer

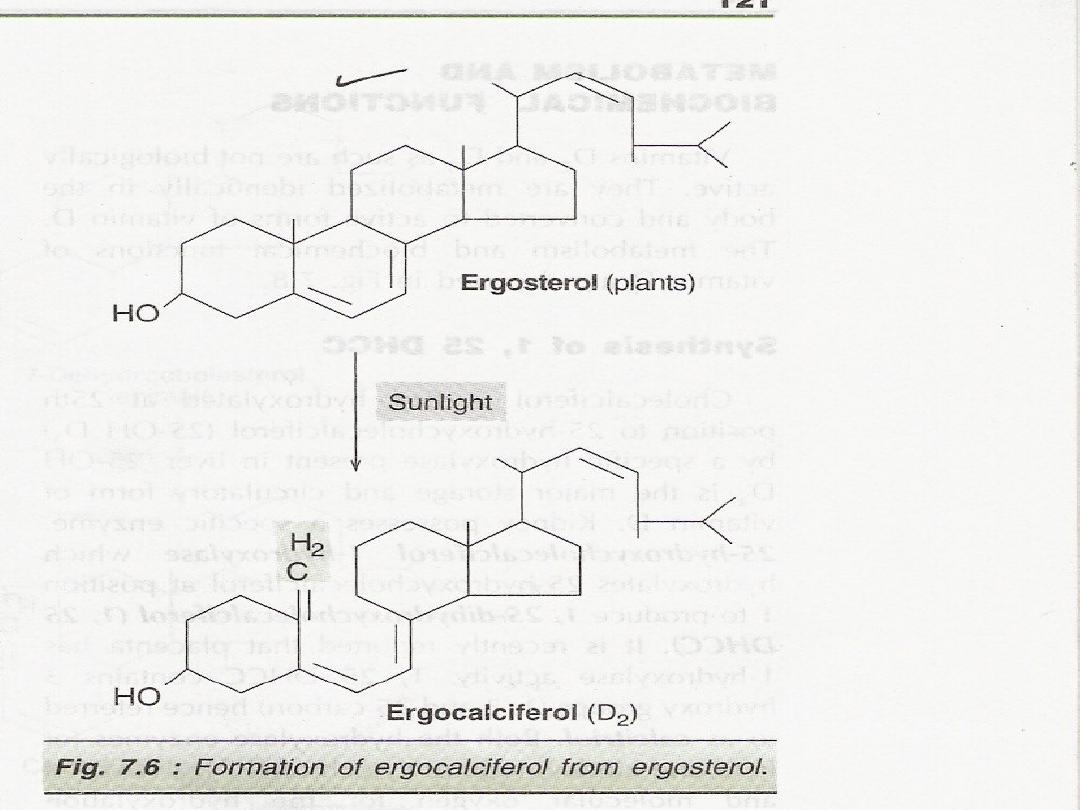
Vit D ( Antirachitic vit
)
It is now considered a a hormone rather than vit
It is a derivative of 7 dehydrocholesterol
.
(
pro-vitD) when subjected to light acquired the
physiological property of curing and preventing
richet
.
Vit D is asteroid prohormone by various metabolic
changes in the body they give rise to a hormone
(
calcitriol
)

Metabolism;vit D from sun exposure or from
diet after absorption from the intestine
,transported in the lymphatics then
circulate in the blood to bind to certain type
of protein calledvitD binding protein
Vit D takn by the liverto be hydroxylated in
position 25 by enzyme vitD 25 hydroxylase
.
In the kidney another hydroxylation at
position 1 1 hydroxylase enzyme
.
Resulting in a compound called
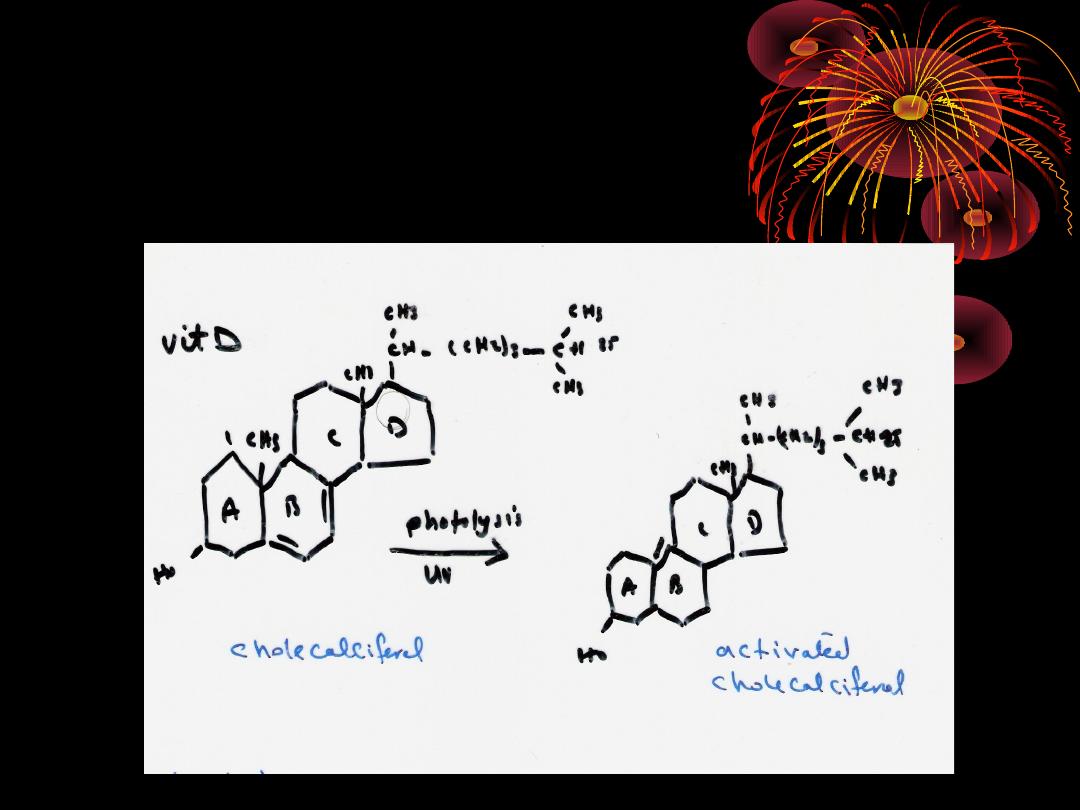
1,25
dihydroxycholecalciferol (active form
)
Calcitriol
.
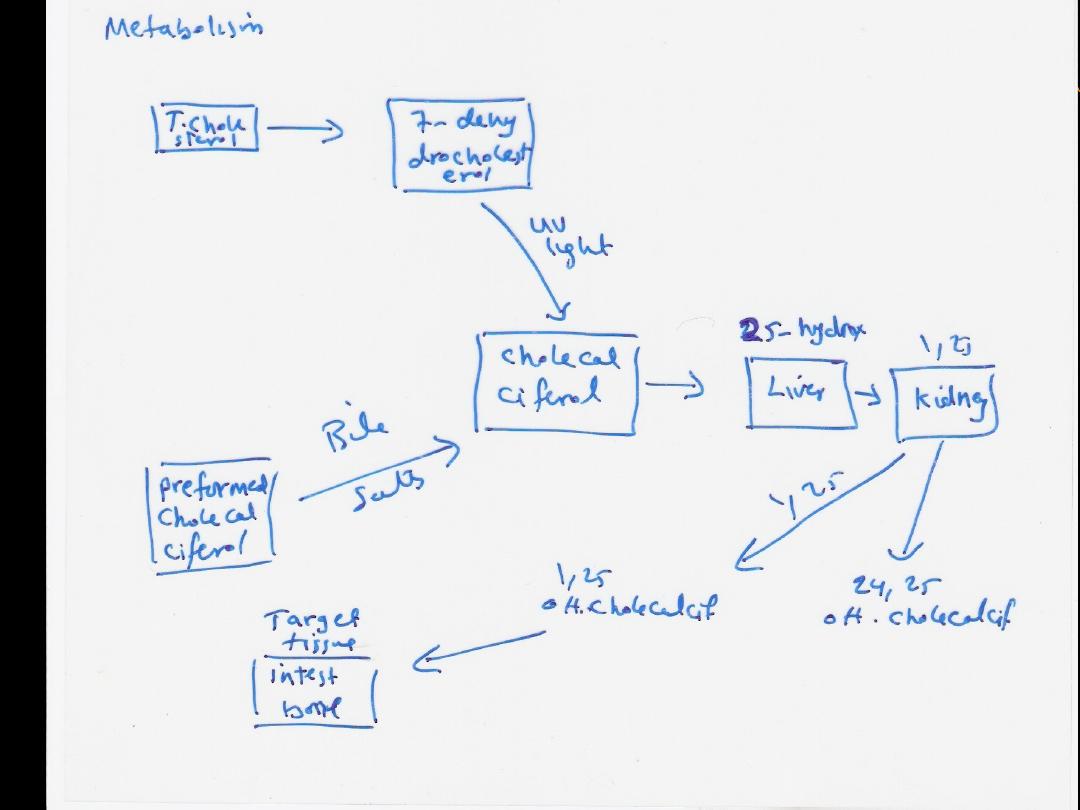
Metabolic pathway of
Vit D
.
Synthesis of 1,25
dihydroxycholecalcife
rol(active vit D
)

Functions
:
1
It regulates calcium,po4 metabolism
through the active form of vitD ,ie it increase
the absorption of calcium po4, from the
intestinal mucose
.
2
.
It infleunce the handeling of phosphate by
the kidney
.
Decrease vitD lead to decrease in the
excretion of phosphate
.
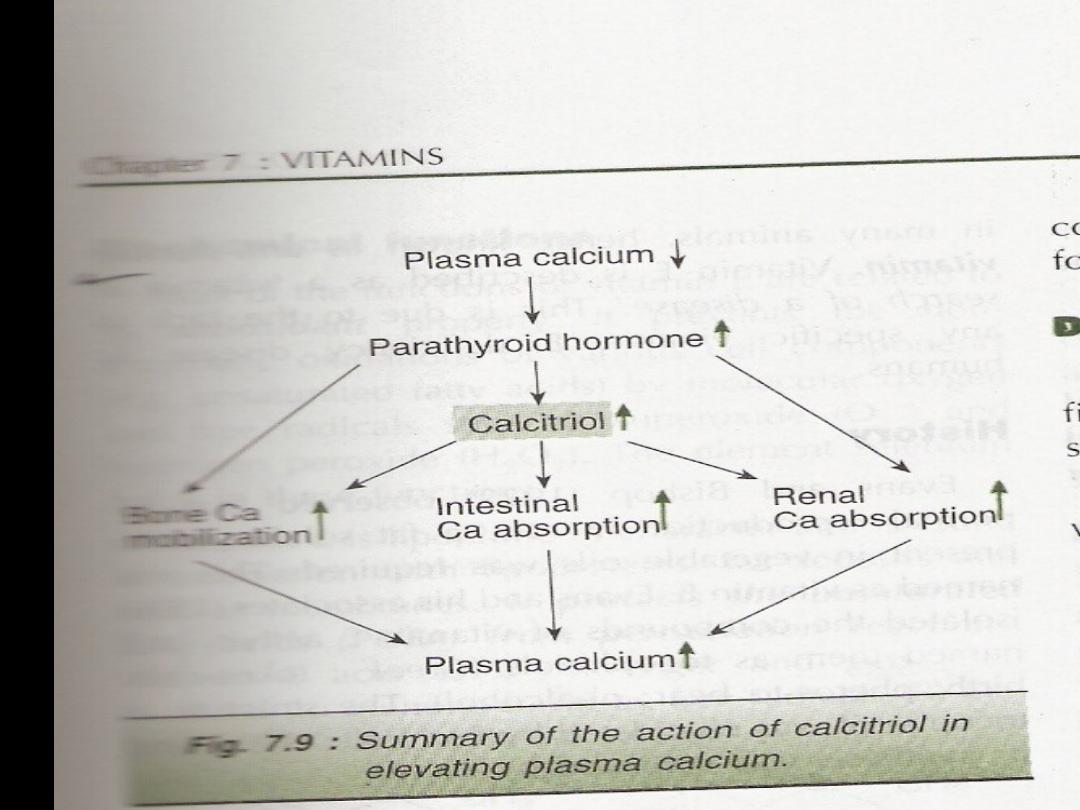
3
1,25
dihydroxy cholecalciferol increase
bone resorpton producing rise in calcium ,
this is mediated through parathyroid horone

Under the condition of hypocalcemia there is
increase secretion in of PTH which in turn
stimulate the synthesis of 1,25 Di OH chole
In the kidney .this mobilize calcium from the
bone lead to rise in calcium and this high
calcium supress the PTH through feedback
mechnism. Suppress further 1,25
.

Deficiency
:
Occur due to inadequate exposure to sun
light or inadequate intake as in
pregnancy and lactation
.
Ricket infant&children
Osteomalcia Adult

Vit E :α tocopherol
:
Found in animal and plant fat and oil, fat
soluble vit stable to heat and acid
.
Sources: plant and animal tissues, cotton
seed oil,corn oil,soyabean oil,sunflower
oil,fish ,Egg
,…..
Functions
:
1
Biological Antioxidants
:
2
Vit E along with Vit C important in
preventing damage to lung tissuefrom
oxidant in air
.

3
It prevents the oxidation of various
compound particularly fat
.
4
Vit E may play a role in the
development of anemia in infant
( macrocytic anemia
).
5
Antisterility effect
.
Vit.E has a sparing action on vit A
.
Def 6 : sterilty Damage to the liver&
lung tissues. Rancidity of oil
Anemia in infant
.

Vit.K: (Antihemorrhagic vit
.)
Fat soluble vit.,green vegetables, cabbage,
cauriflower,spinach,cheese,dairy product
.
It also synthesized by the microrganism
(intestinal flora
)
3
forms Menadione K3
MenaquinoneK2
PhylloquinoneK1
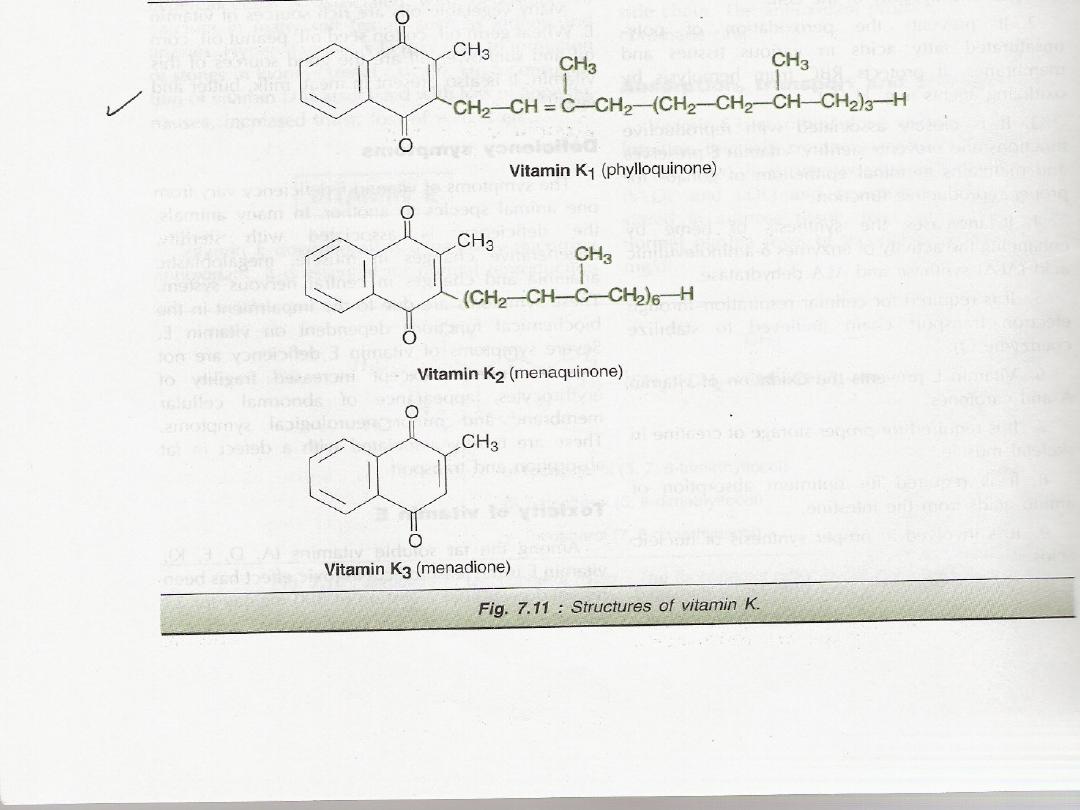

Absorption
:
Require bile salts for its absorption
.
Deficiency occurs if bile is prevented from
entering the intestine
.
Sterilization of bowel
…………
Prolonged administration of antibiotics
.

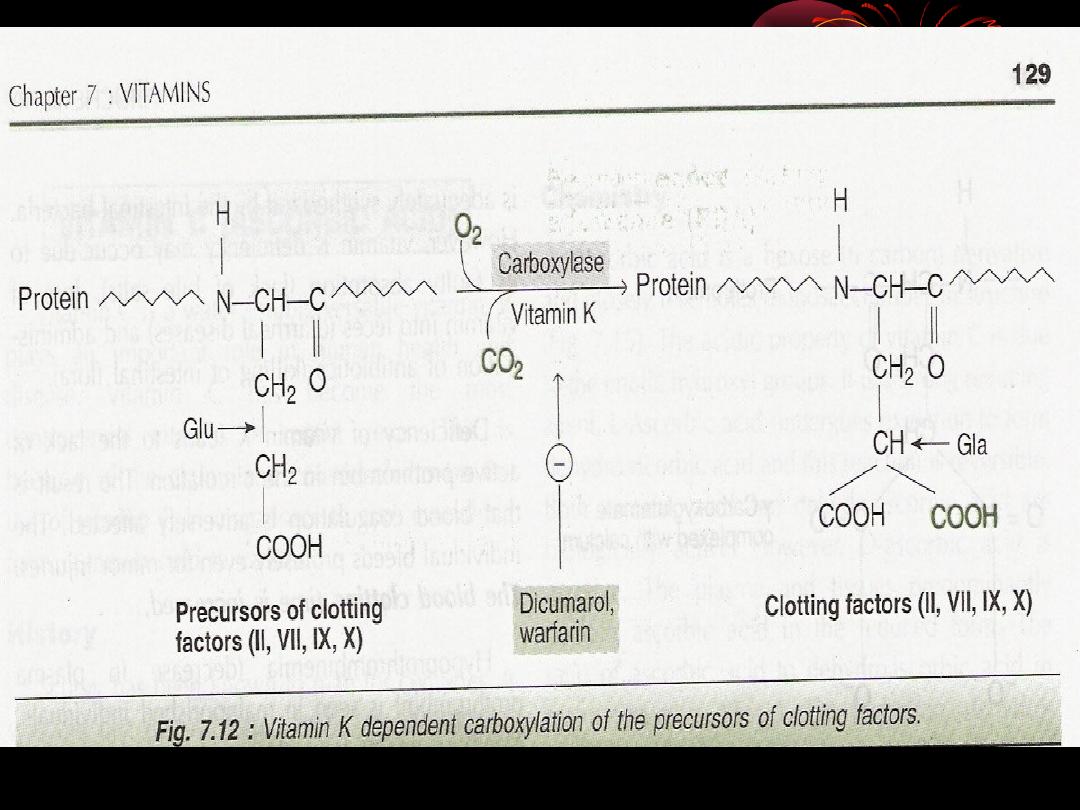
Functions
:
1
vit k has been shown to be involved in the
maintenance of normal level of blood clotting
factor
II VII IX X
.
2
It catalyze the synthesis of prothrombin in
the liver
.
Absence of vit k , hypo prothrombinemia
occurs and blood clotting time is prolonged
.
3
.
Anti dote to some drugs(warfarin
).