PREPROSTHETIC SURGERYDR. SALWAN AL-HAMDANIB.D.S.MSC.PROSTH
Preprosthetic SurgeryObjectives:
1. To understand the anatomy and physiology
of the edentulous status including alveolaratrophy and its associated pathoses
2. To diagnose conditions that can be improved
by preprosthetic surgical procedures3. To treatment plan, design and execute
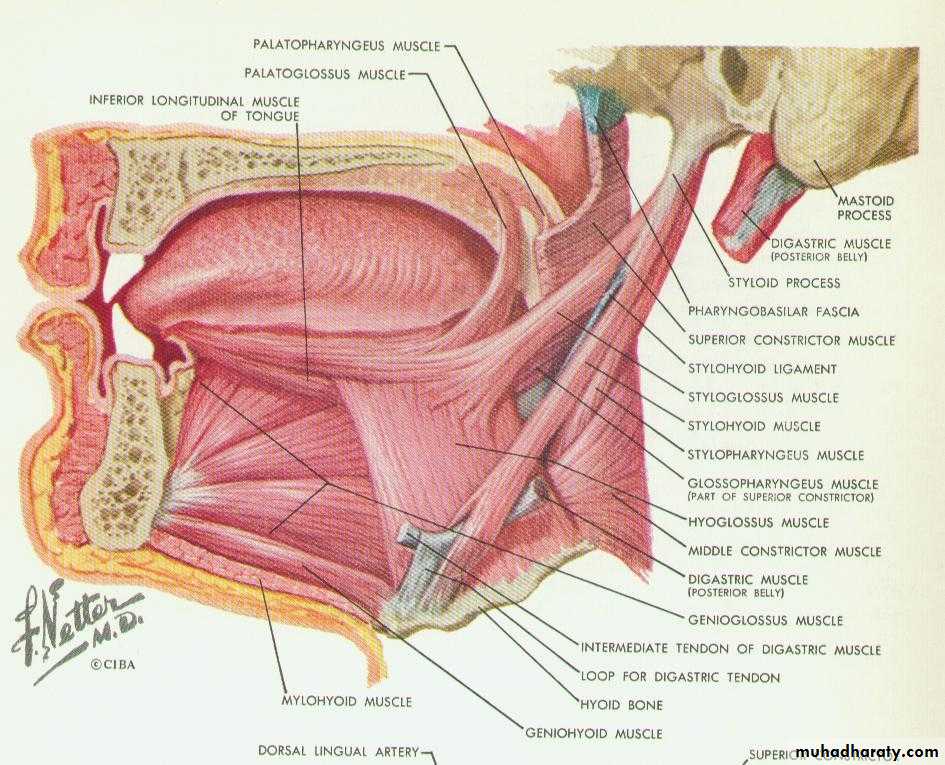
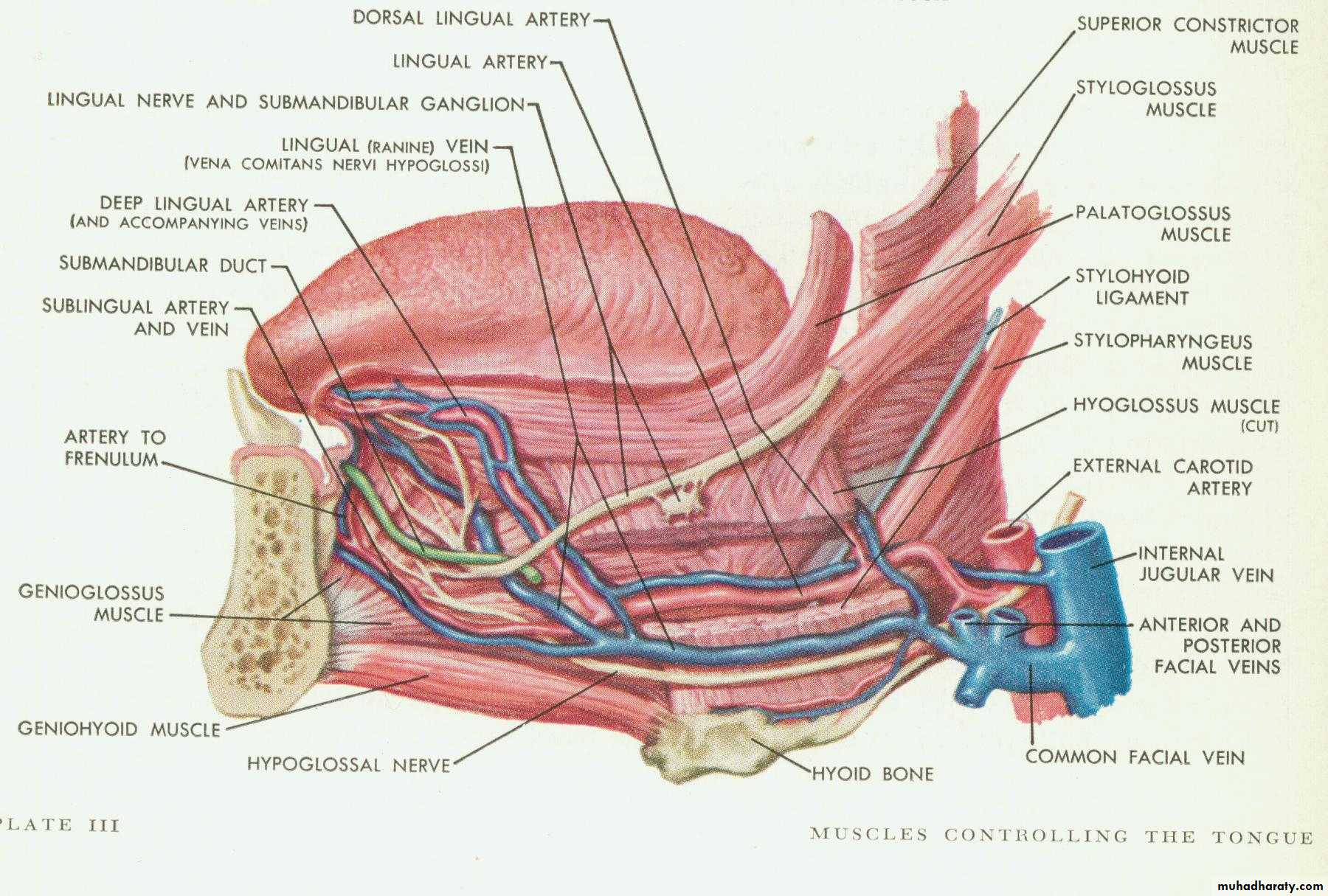
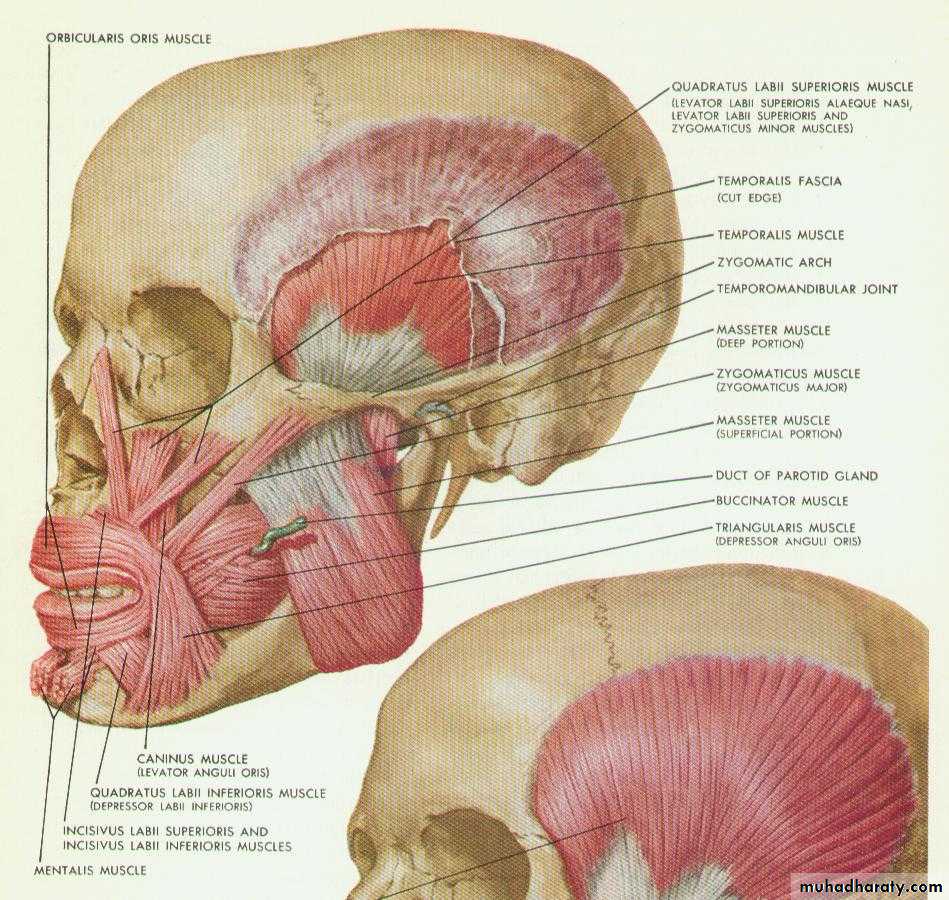
preprosthetic surgical proceduresFactors that impact on fit: anatomy
1. Bone quantity
2. Bone contour
3. Muscle attachments
4. Gingiva (mucosa)
1. Bone quantity
2. Bone contour
3. Muscle attachments4. Gingiva (mucosa)
Factors that impact on fit: physiology
1. Gingiva (mucosa)2. Lip / tongue habits
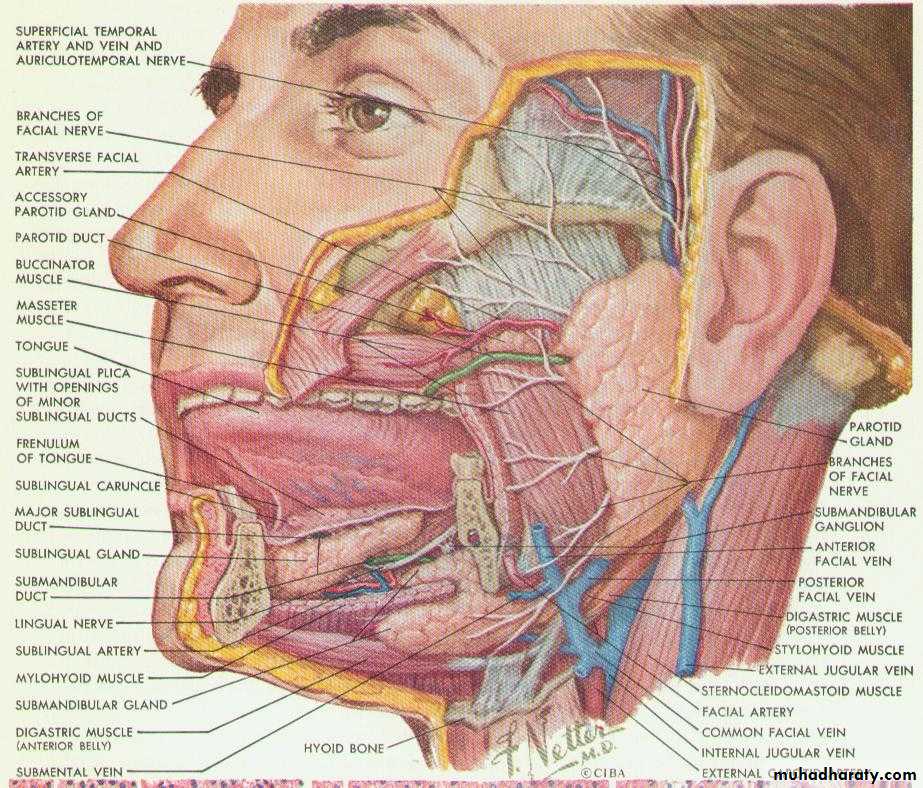
3. Salivary function
4. TMJ / muscle function
1. Gingiva,. mucosa
2. Lip / tongue habits
3. Salivary function
4. TMJ/ muscle
function
Parotid
SubmandibularFactors that impact on fit: pathoses
1. Hard tissue2. Soft tissue
1. Hard tissue
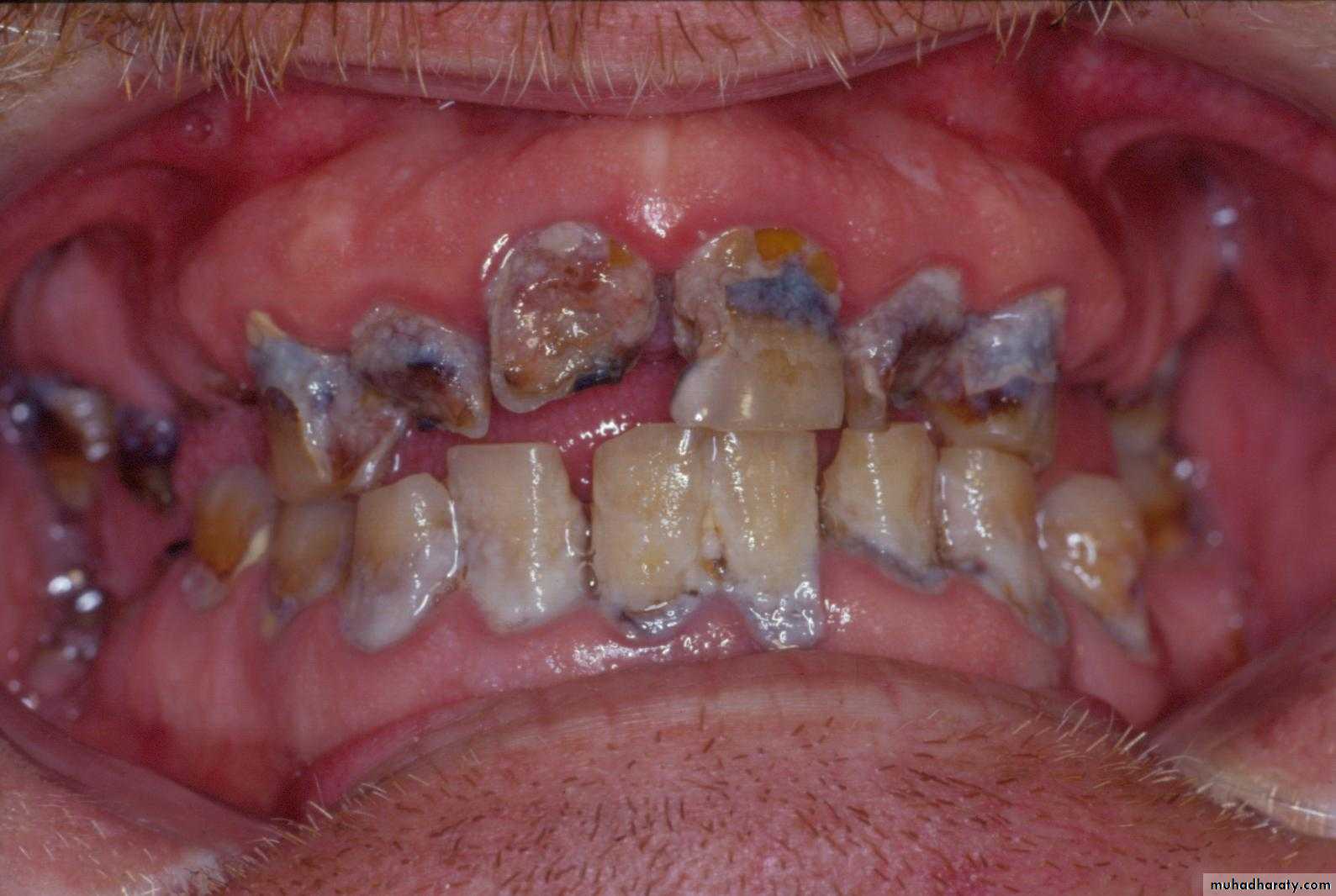
a. Dental cariesb. Periodontal disease
c. Infection
d. Cysts and tumours
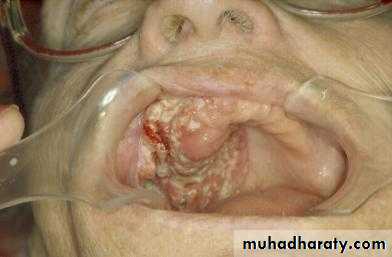
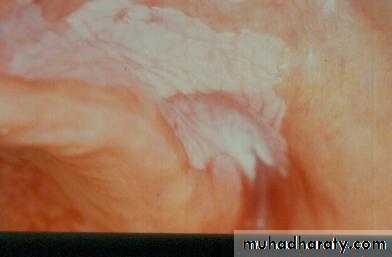
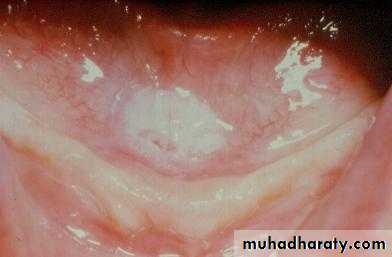
1. Soft tissue
a. Ulceration
b. Hyperplasia
c. Dysplasia
d. Carcinoma
a
b
c
d
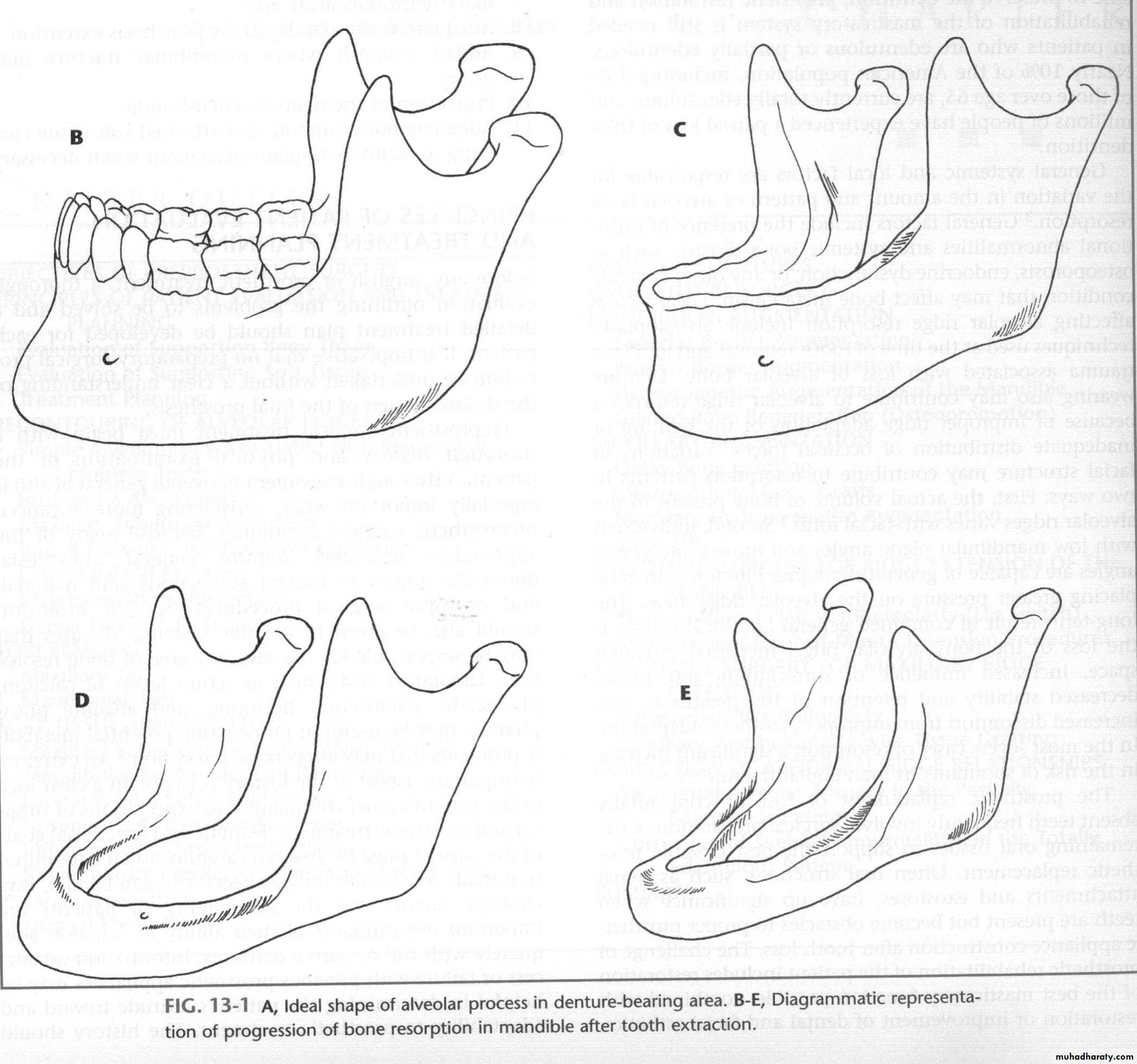
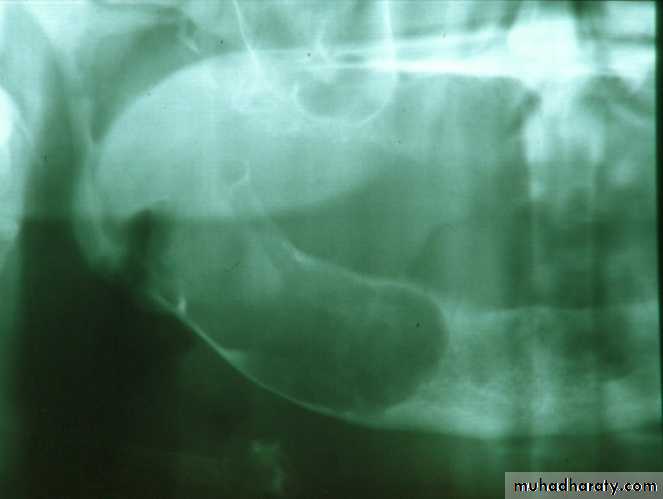
Factors that impact on fit: atrophy
• Atrophy• a. Decreasing bone
b. Increasing soft tissue
Factors that impact on fit: atrophy
1. Atrophya. Decreasing bone
b. Increasing soft tissue
Factors that impact on fit: atrophy
1. Atrophy: accelerated by inflammationa. Infection
b. Poorly fitting dentures … friction
c. Habits … clenching / bruxism
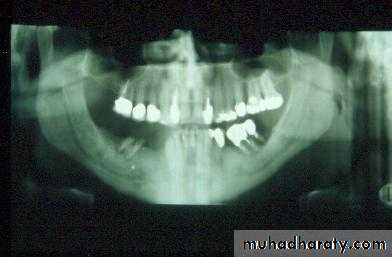
Procedures designed to optimize the retention, support, stability and comfort of prostheses by the selective modification of soft and hard tissues
Preprosthetic Surgery
Indications: compromized retention, support, stability or comfort of prostheses due to suboptimal hard or soft tissue anatomy or pathoses
Preprosthetic Surgery
Preprosthetic Surgery
Procedures span a spectrum from verysimple to quite complex:
a. extractions and alveolar osteotomy
b. removal of pathosesc. gingivoplasty and frenectomy
d. tuberosity reduction
e. alveoplasty and torus removal
f. vestibuloplasty with soft tissue graft
g. bone grafting???
h. orthognathic surgery
Preprosthetic Surgery
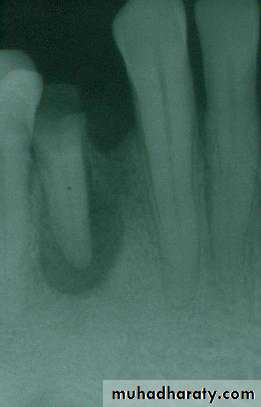
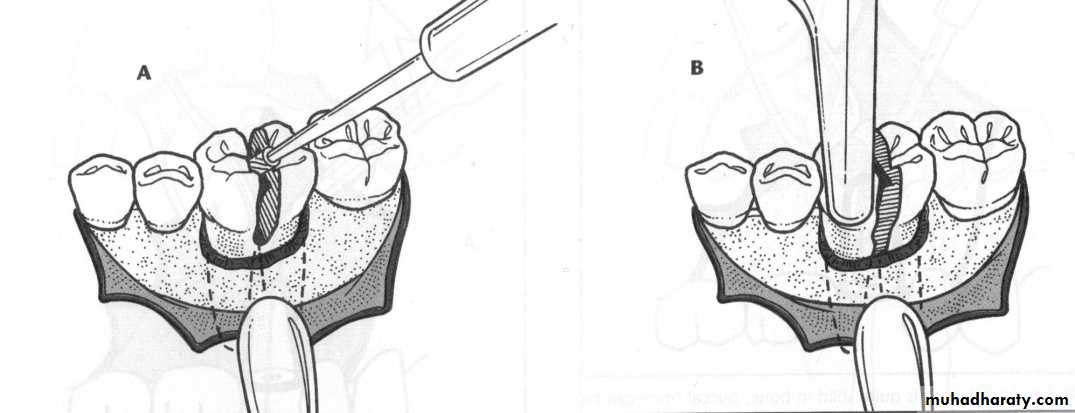
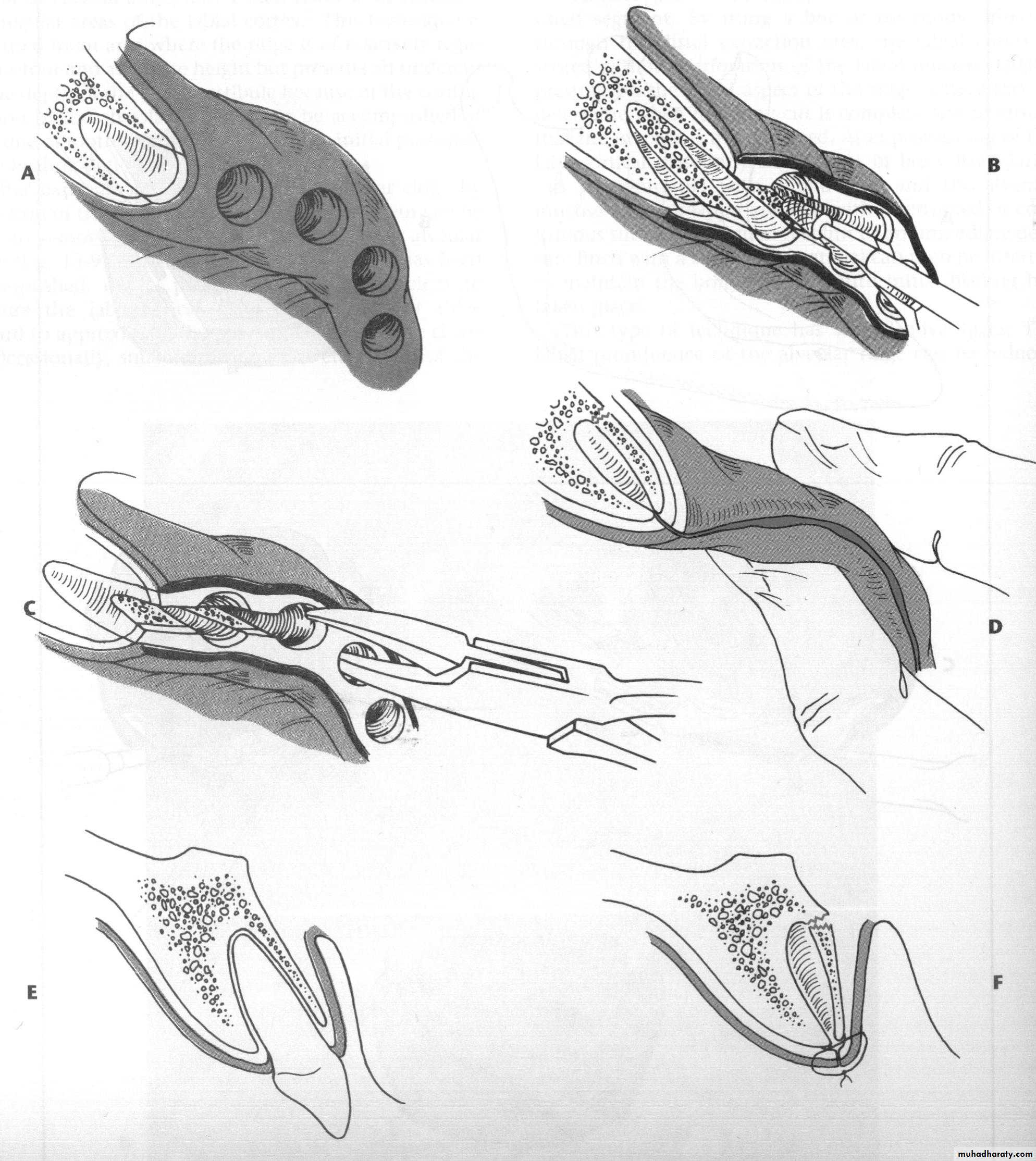
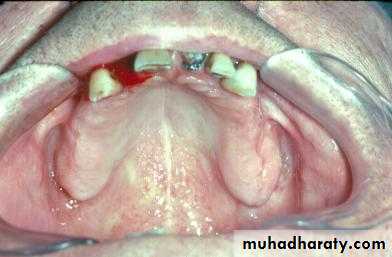
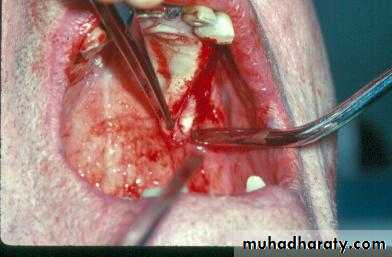
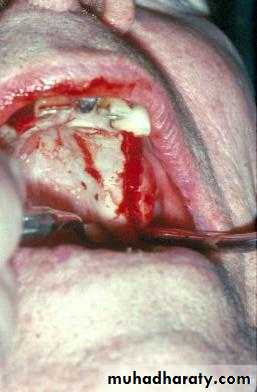
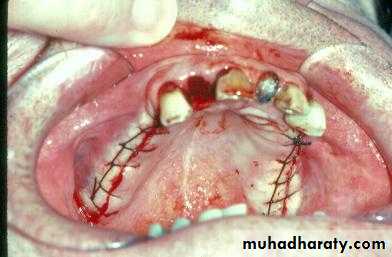
a. Extractions for caries, periodontal disease, infection, etc.
a. Extractions…flap, bone removal, section
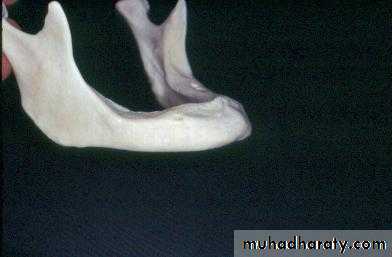
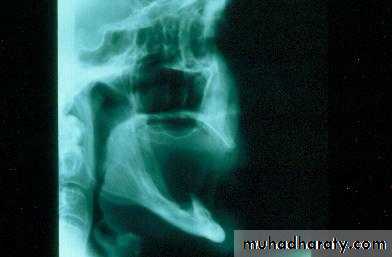
a. Extractions and alveolar osteotomy …
removal of proclined incisors andosteotomy of labial plate of bone
Preprosthetic Surgery
a. Extractions &
and alveolar
osteotomy …
removal of
proclined incisors
and osteotomy
of labial plate of
bone
Preprosthetic Surgery
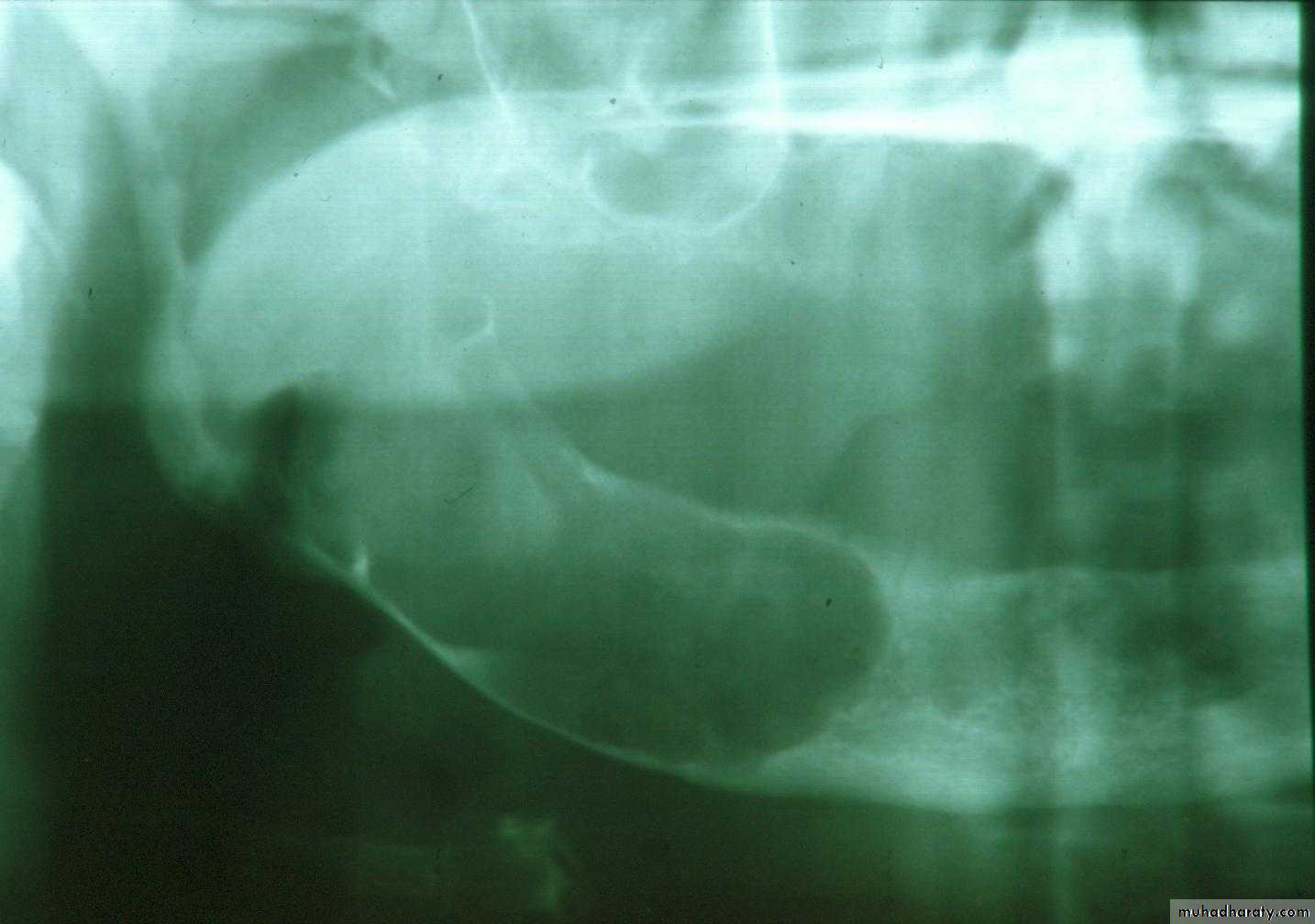
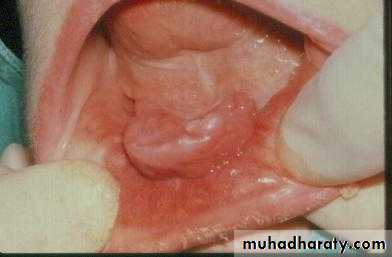
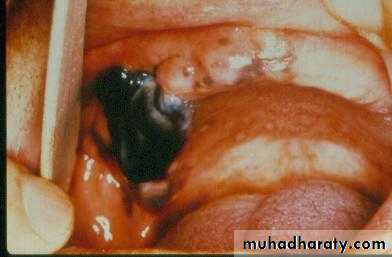
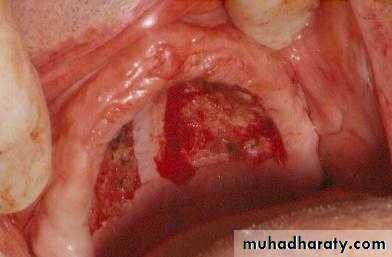
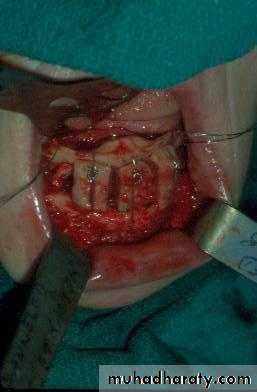
b. Removal of pathoses…cystic, traumatic, hyper-plastic, dysplastic, etc.
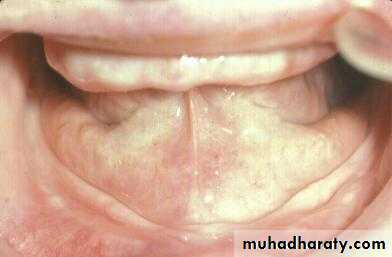
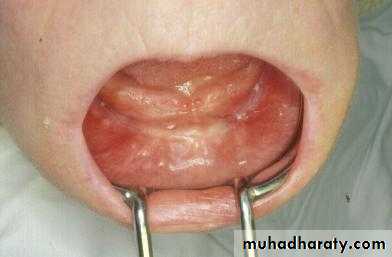
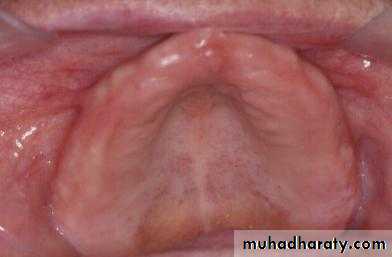
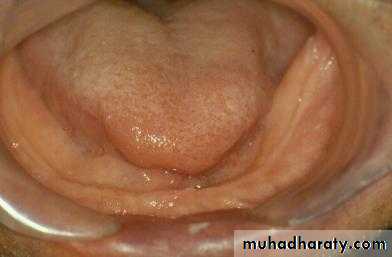
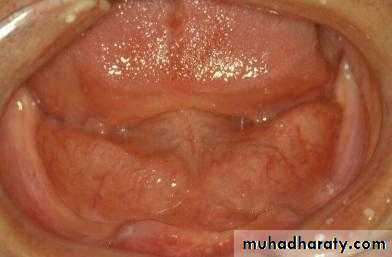
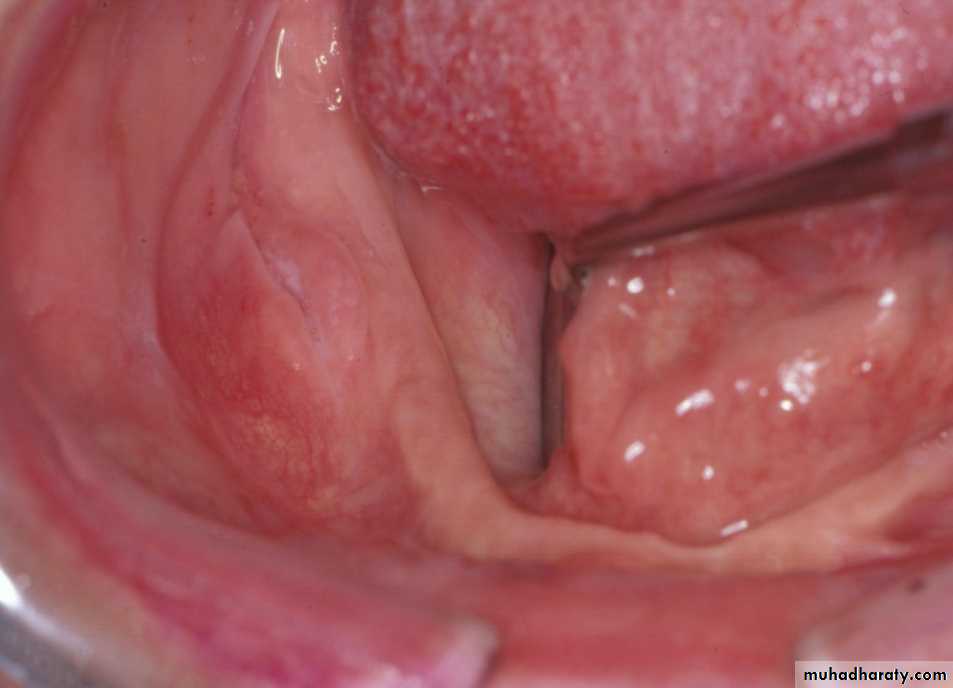
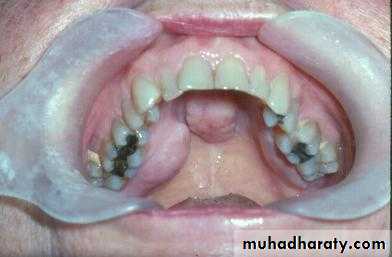
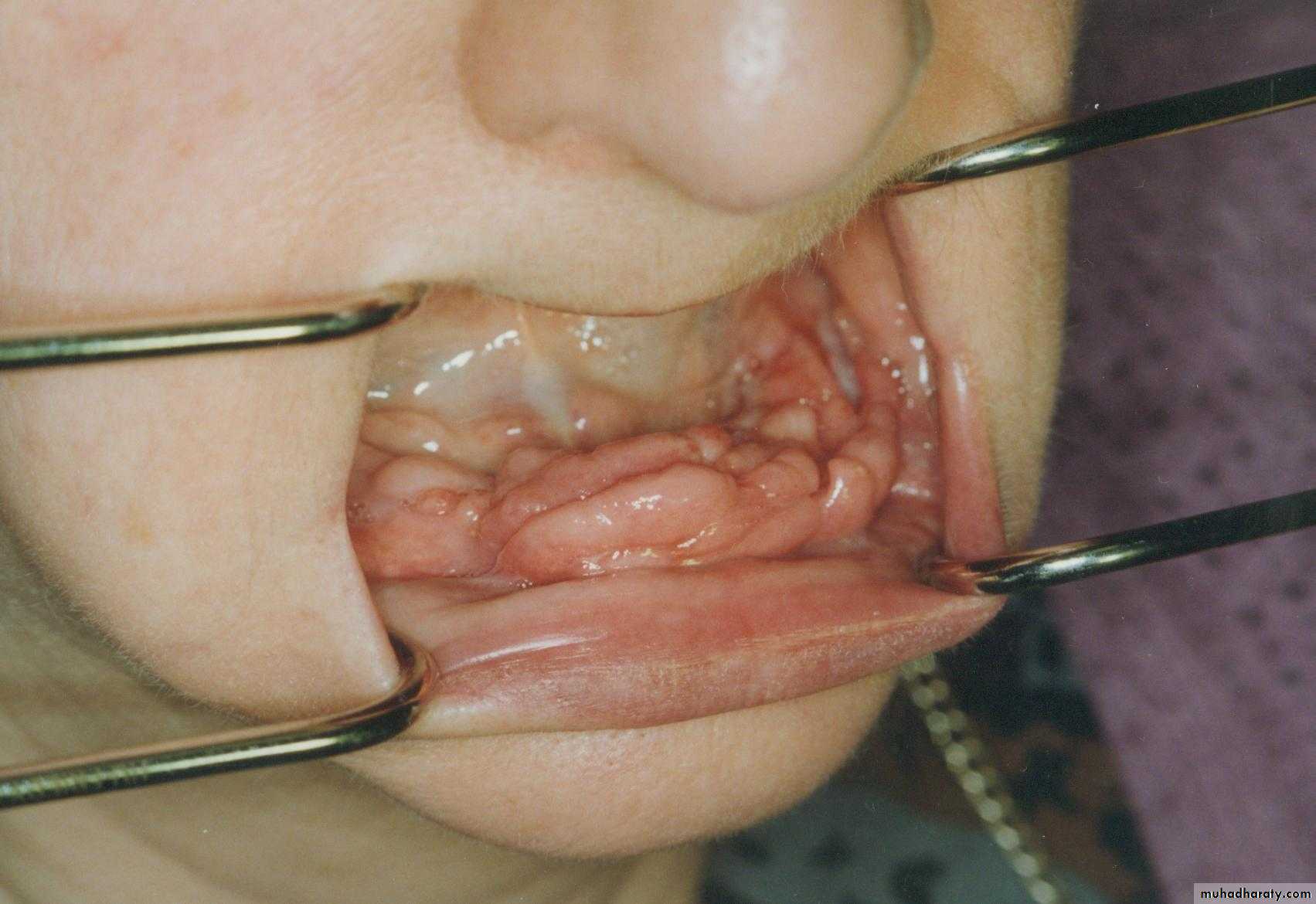
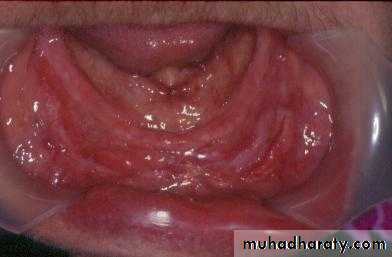
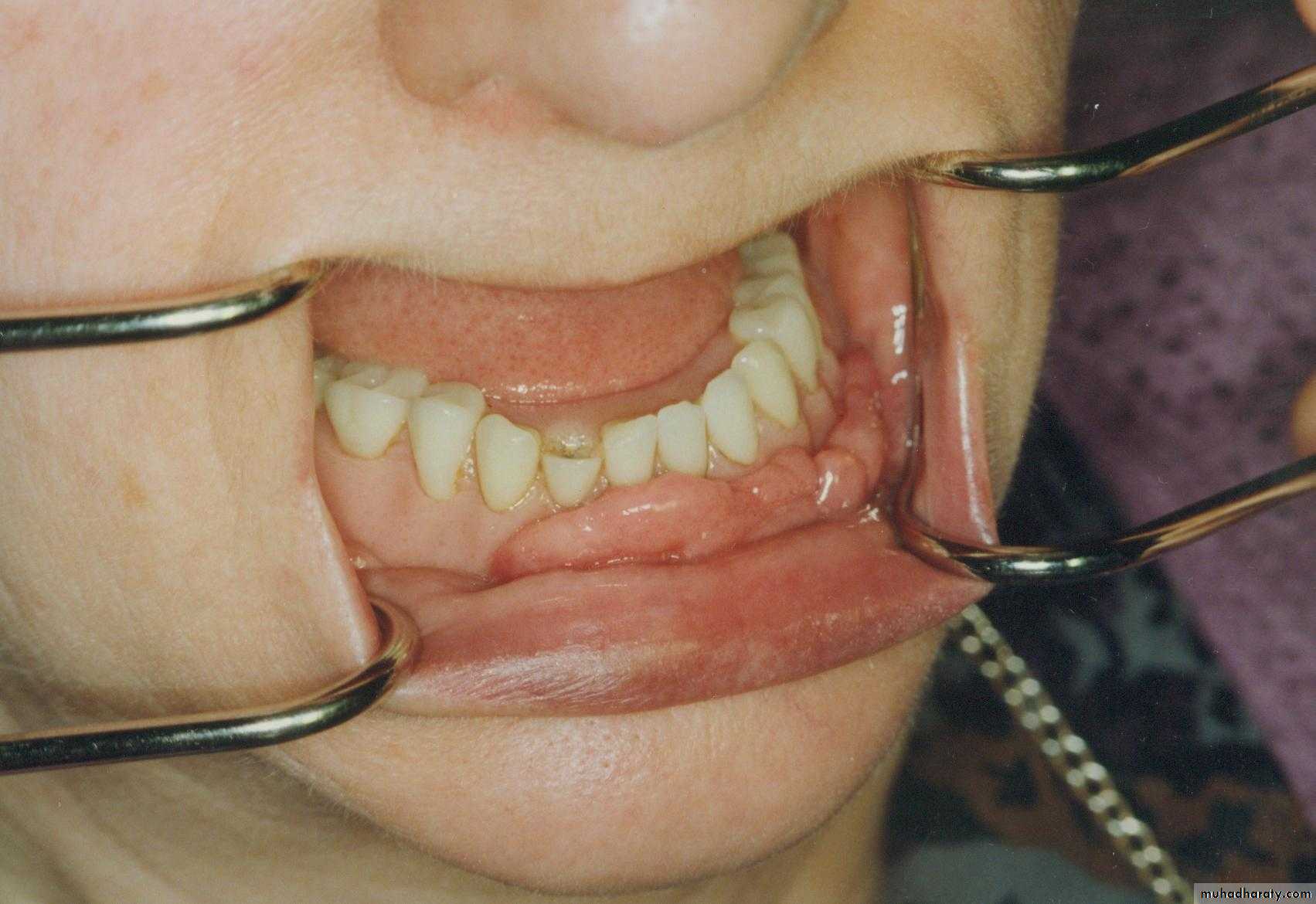
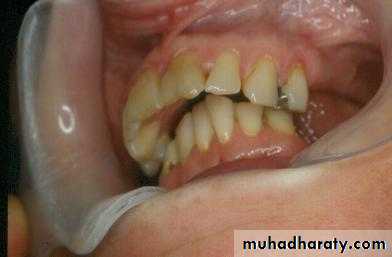
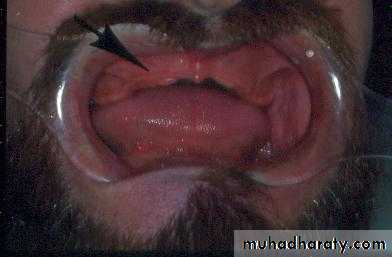
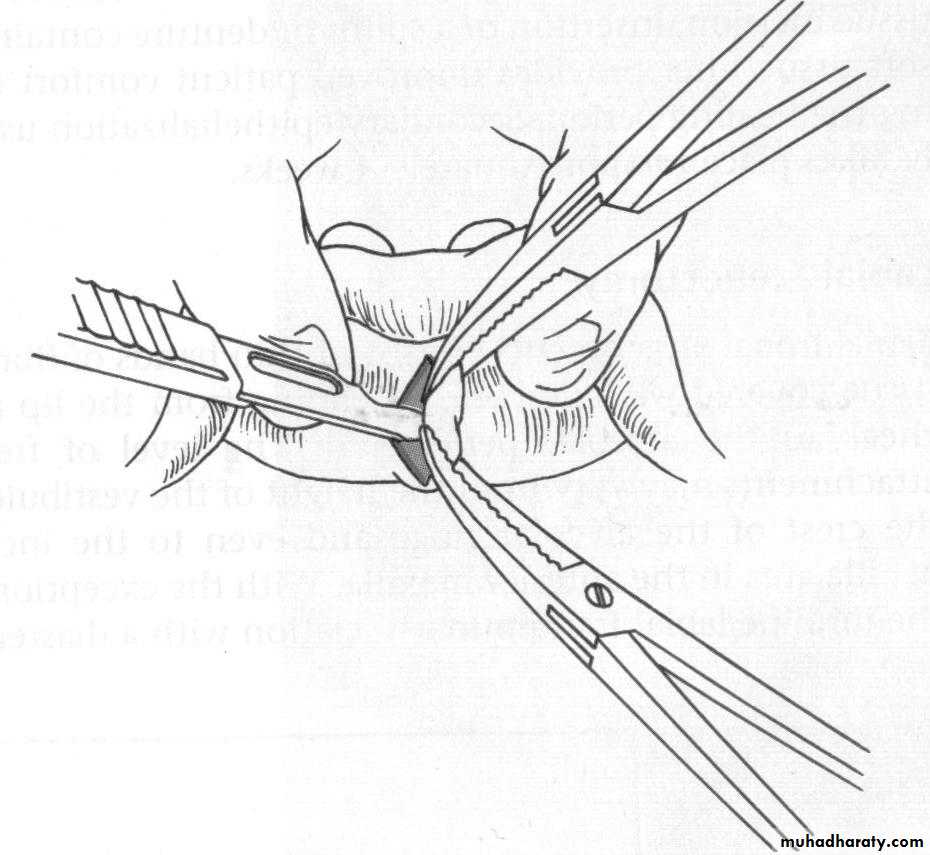
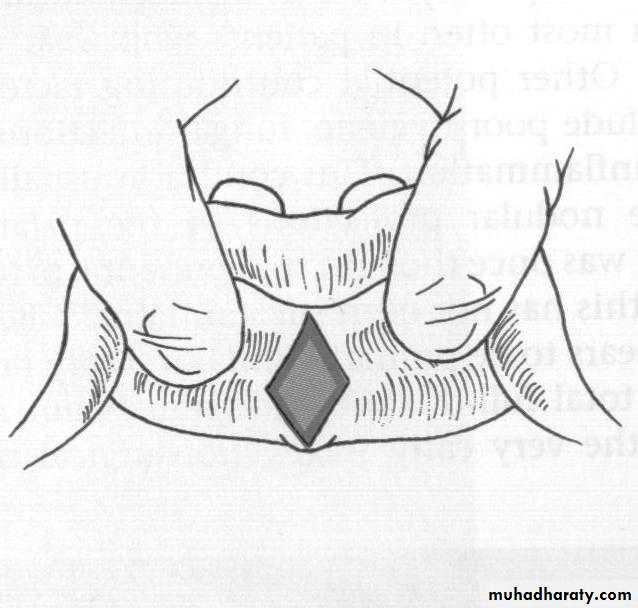
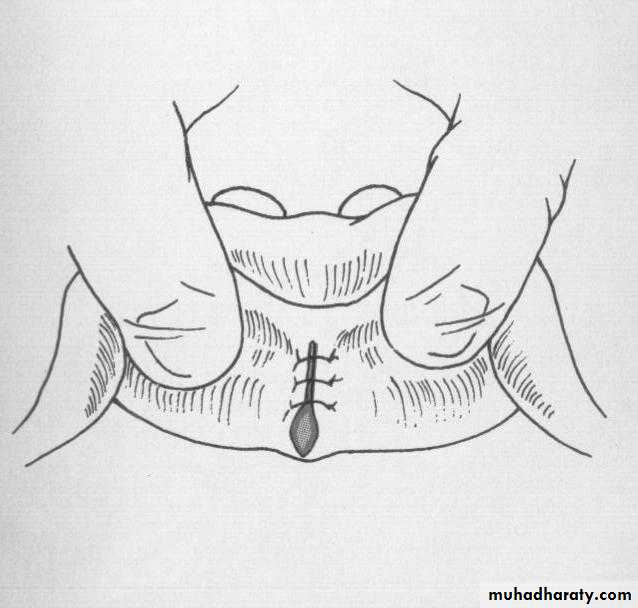
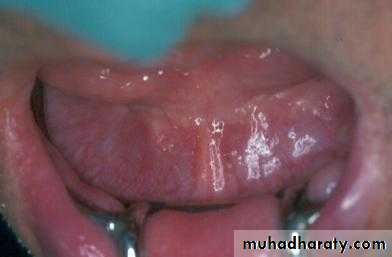
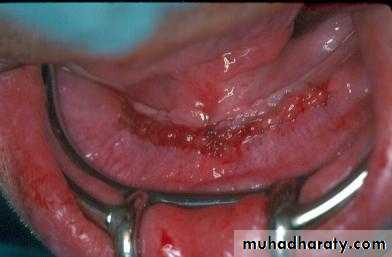
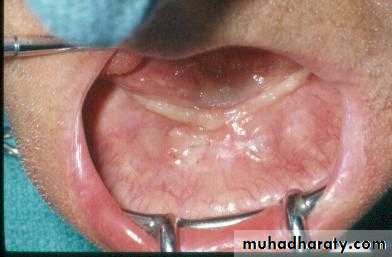
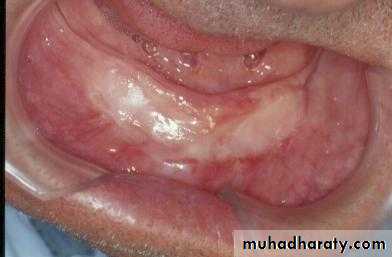
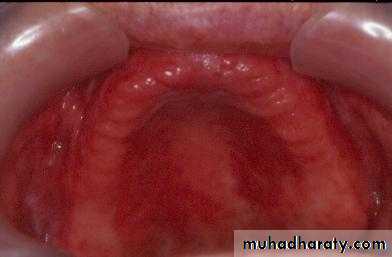
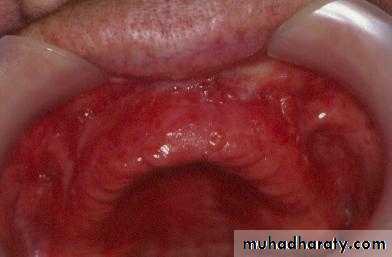
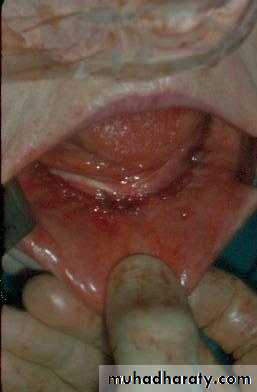
Preprosthetic Surgeryc. Gingivoplasty or frenectomy for flabby ridge tissue or high frena that interfere with support or retention
Gingivoplasty
Preprosthetic Surgery
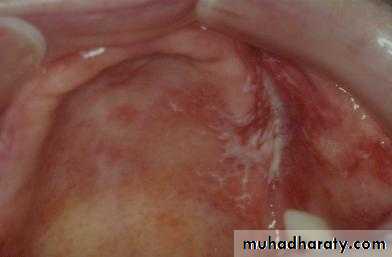
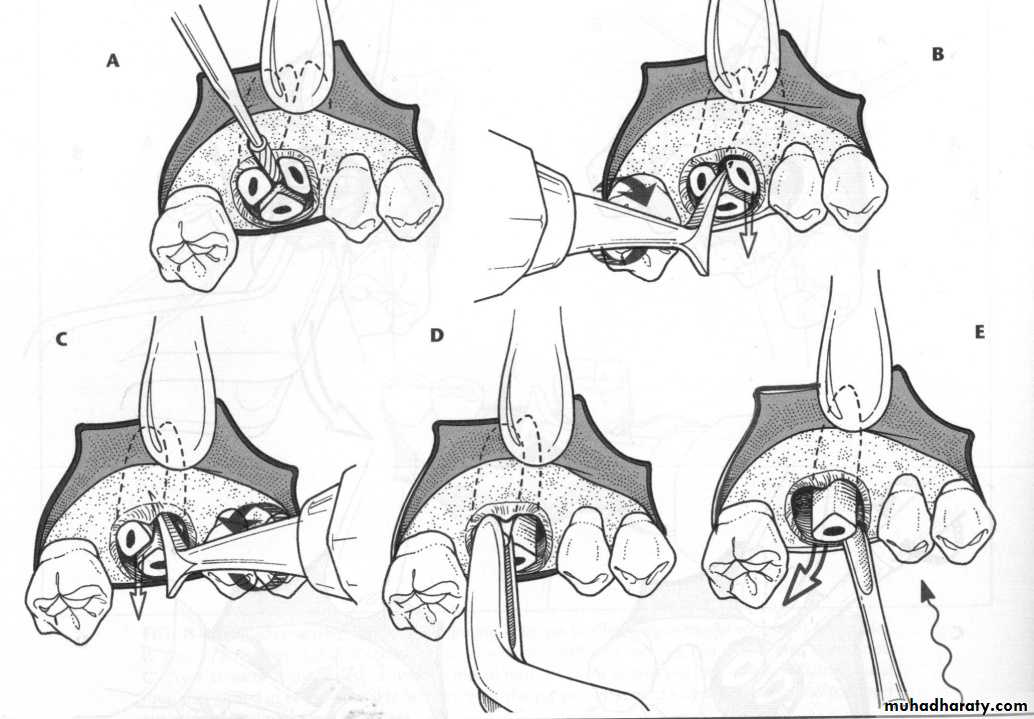
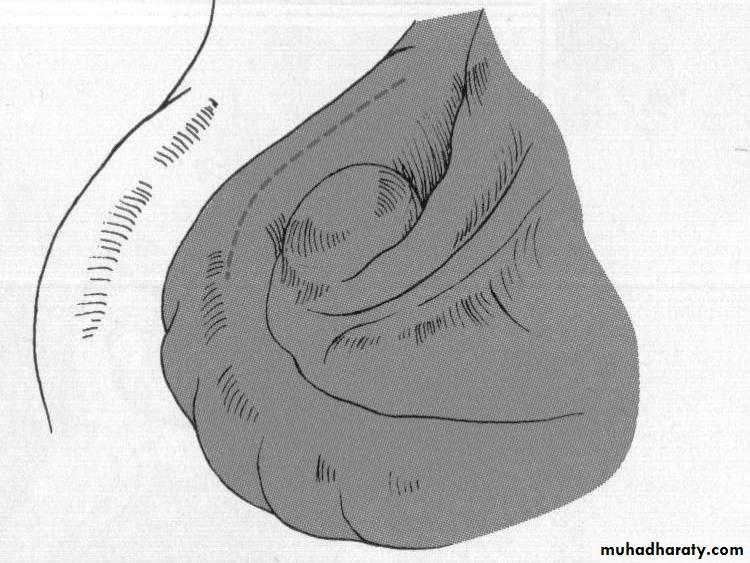
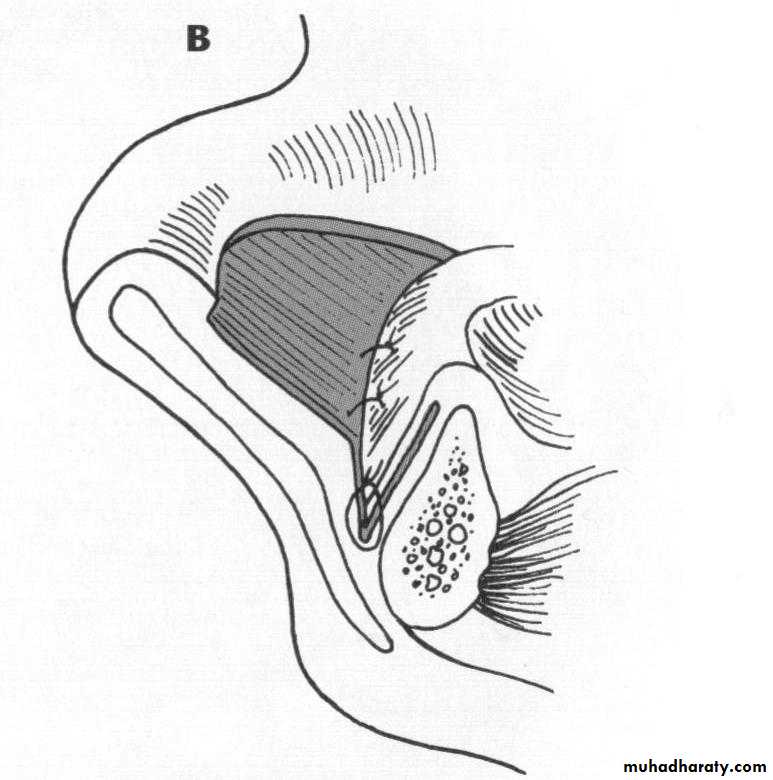
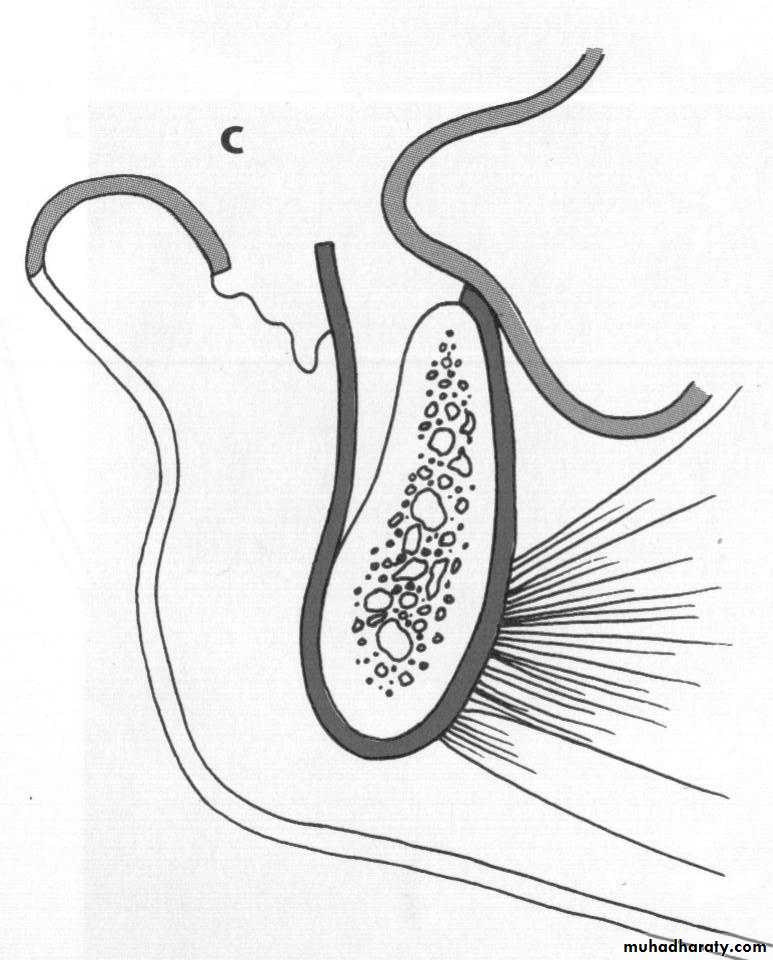
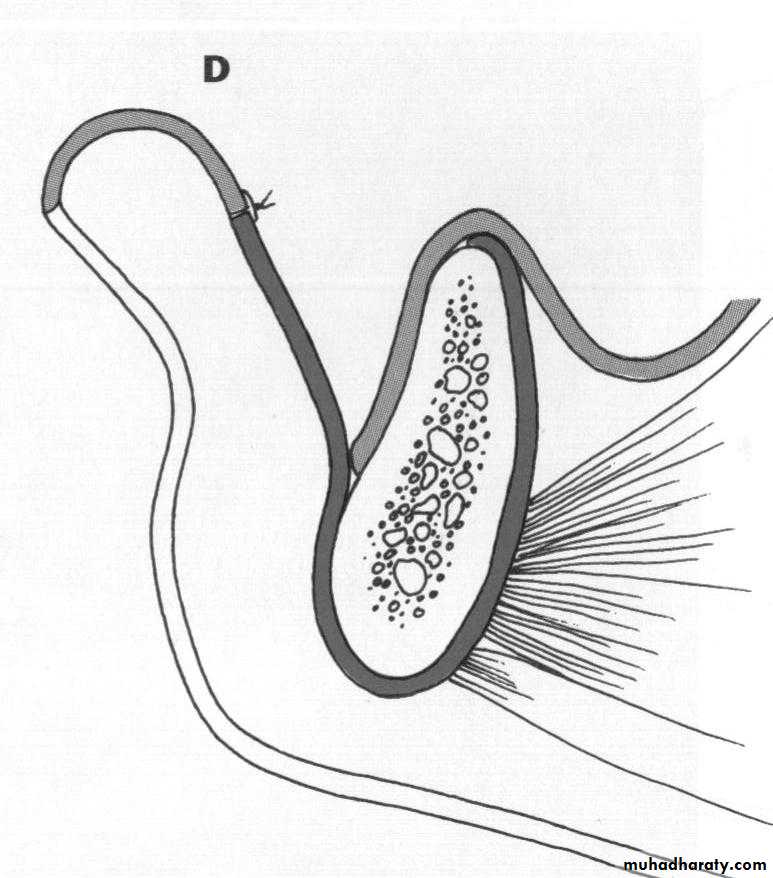
c. Frenectomy1
2
4
3
Preprosthetic Surgery
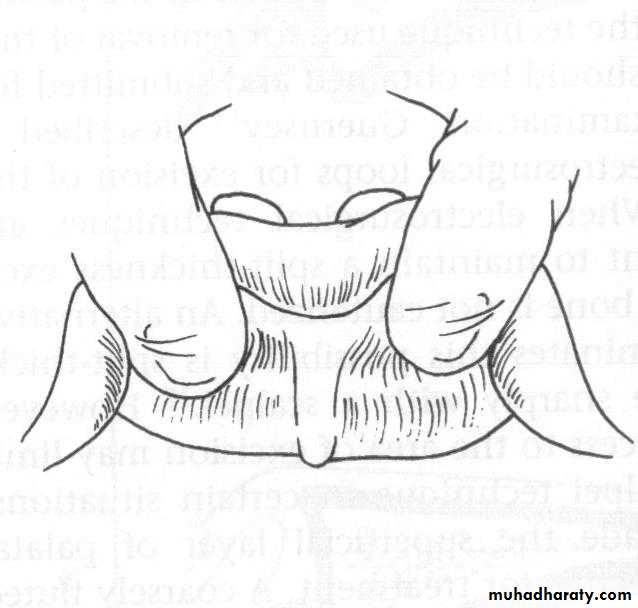
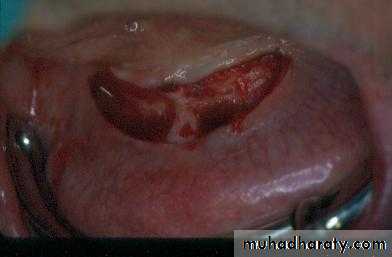
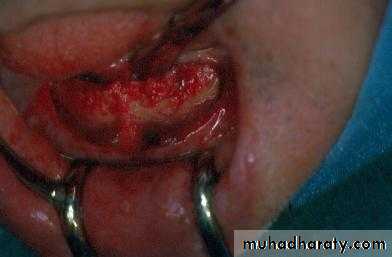
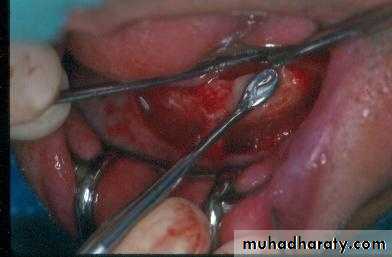
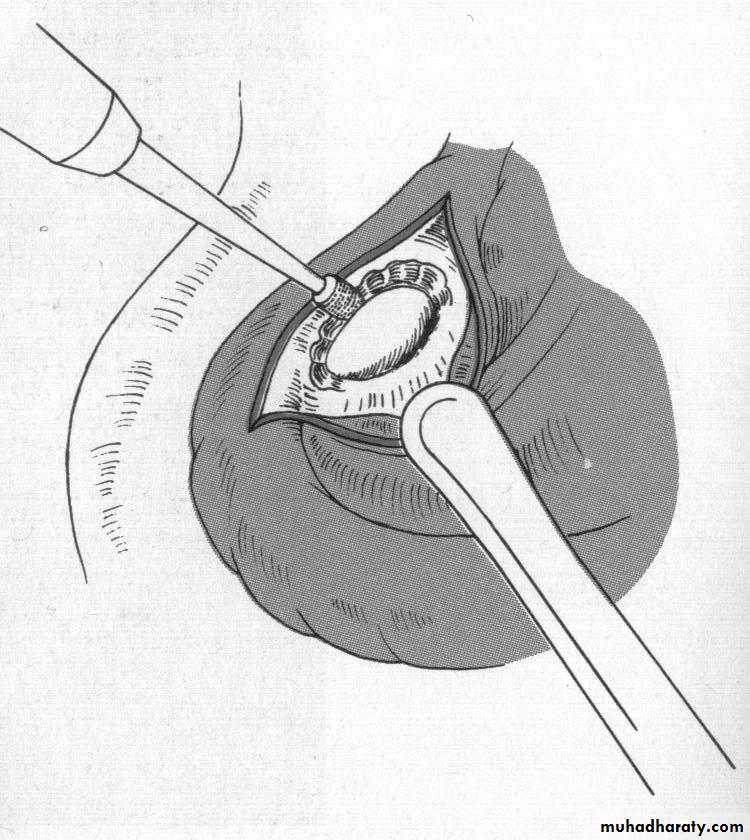
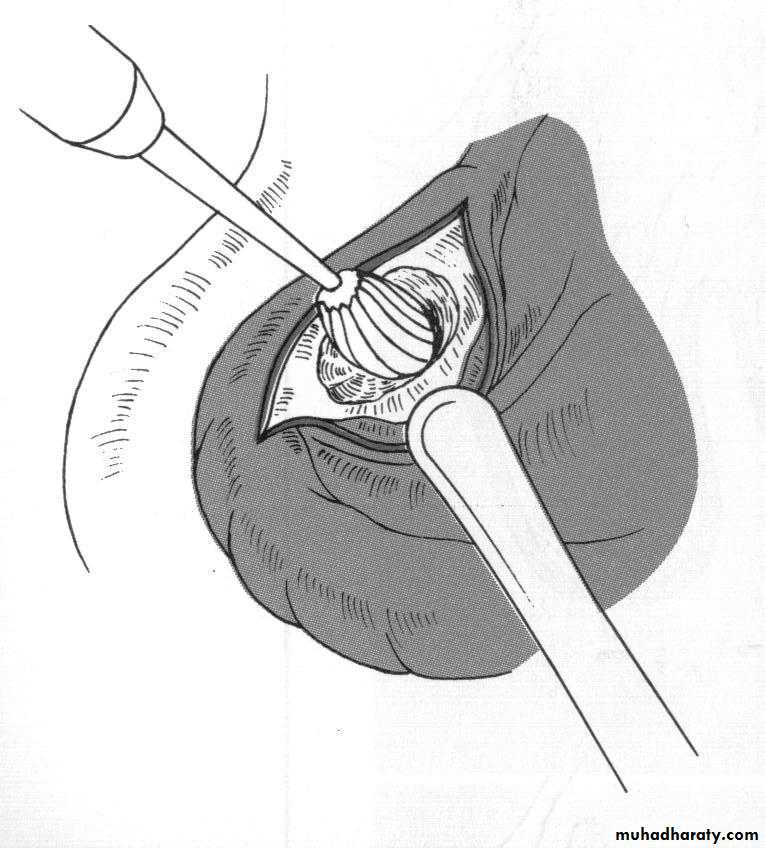
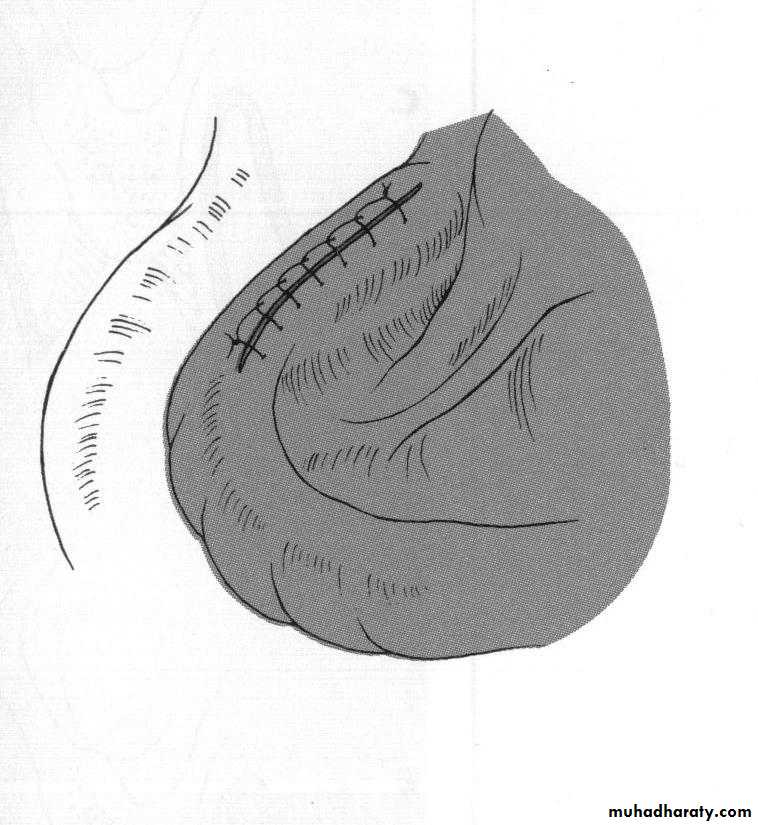
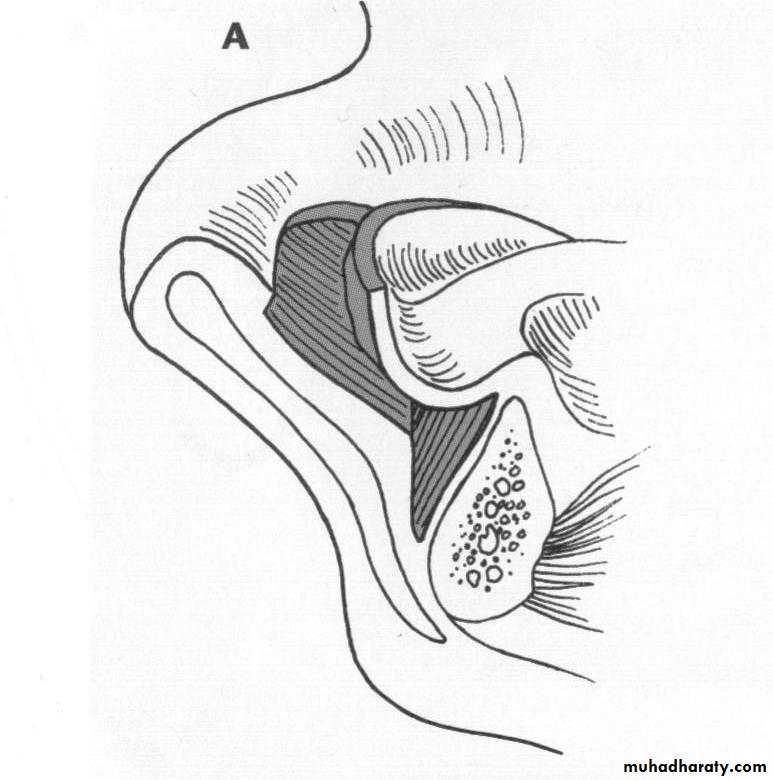
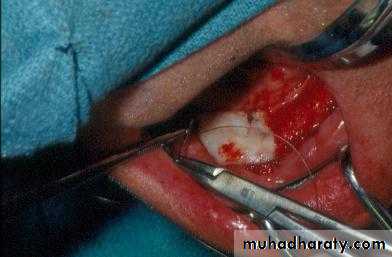
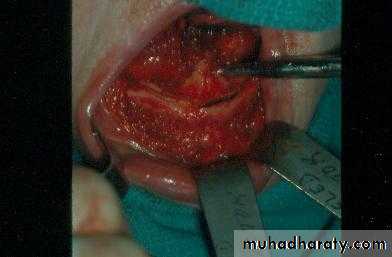
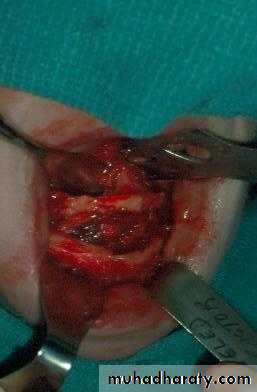
d. Tuberosity reductionPreprosthetic Surgery
d. Tuberosity reduction
Preprosthetic Surgery
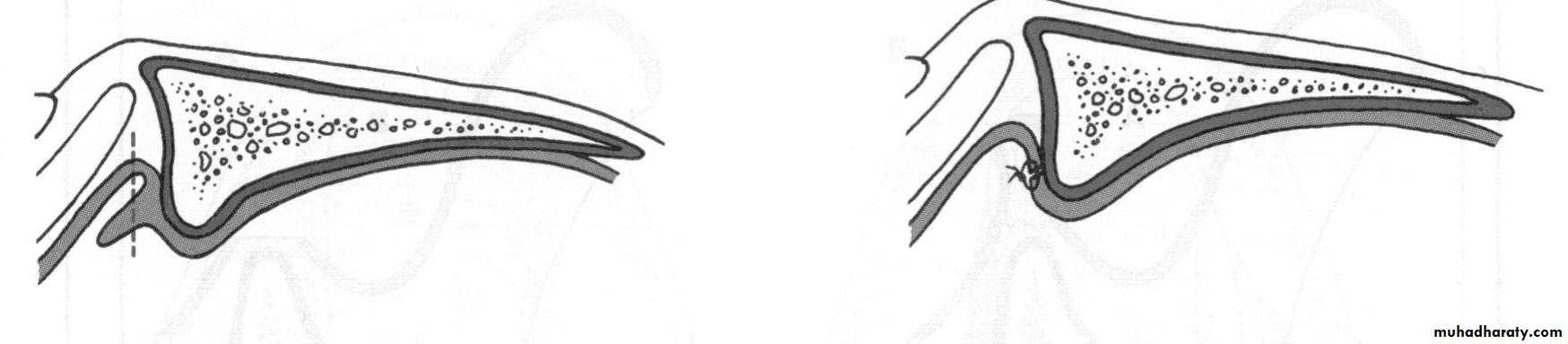
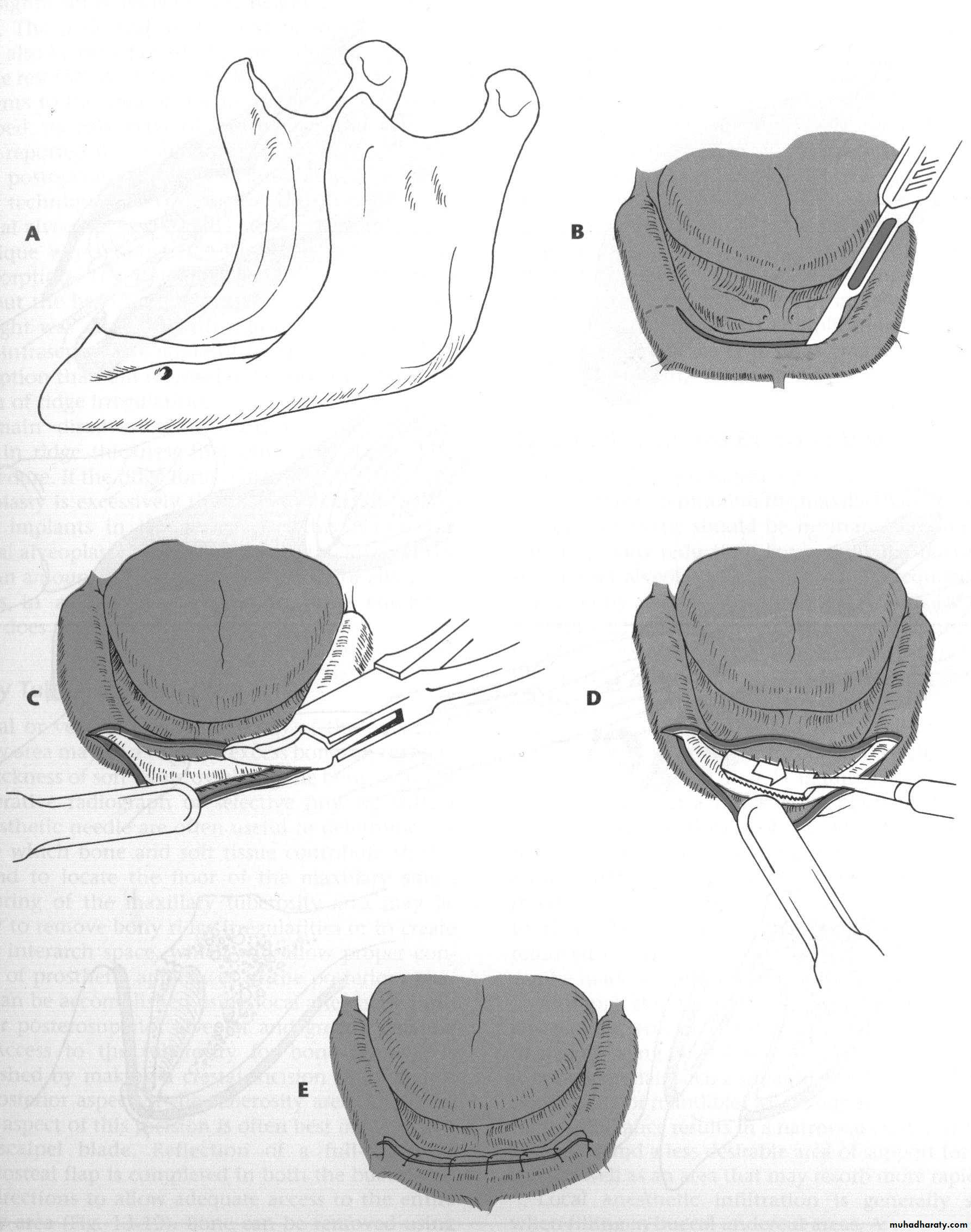
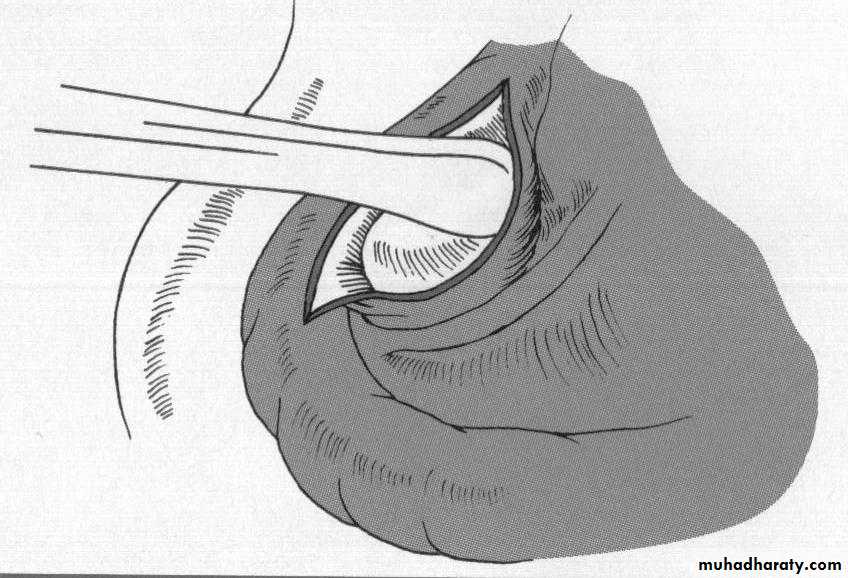
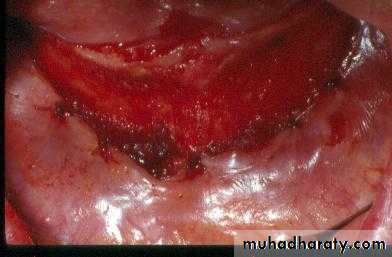
e. Alveoplasty: flap…recontour…closePreprosthetic Surgery
e. Alveoplasty: flap…recontour…closePreprosthetic Surgery
e. Torus reduction: flap…recontour…closePreprosthetic Surgery
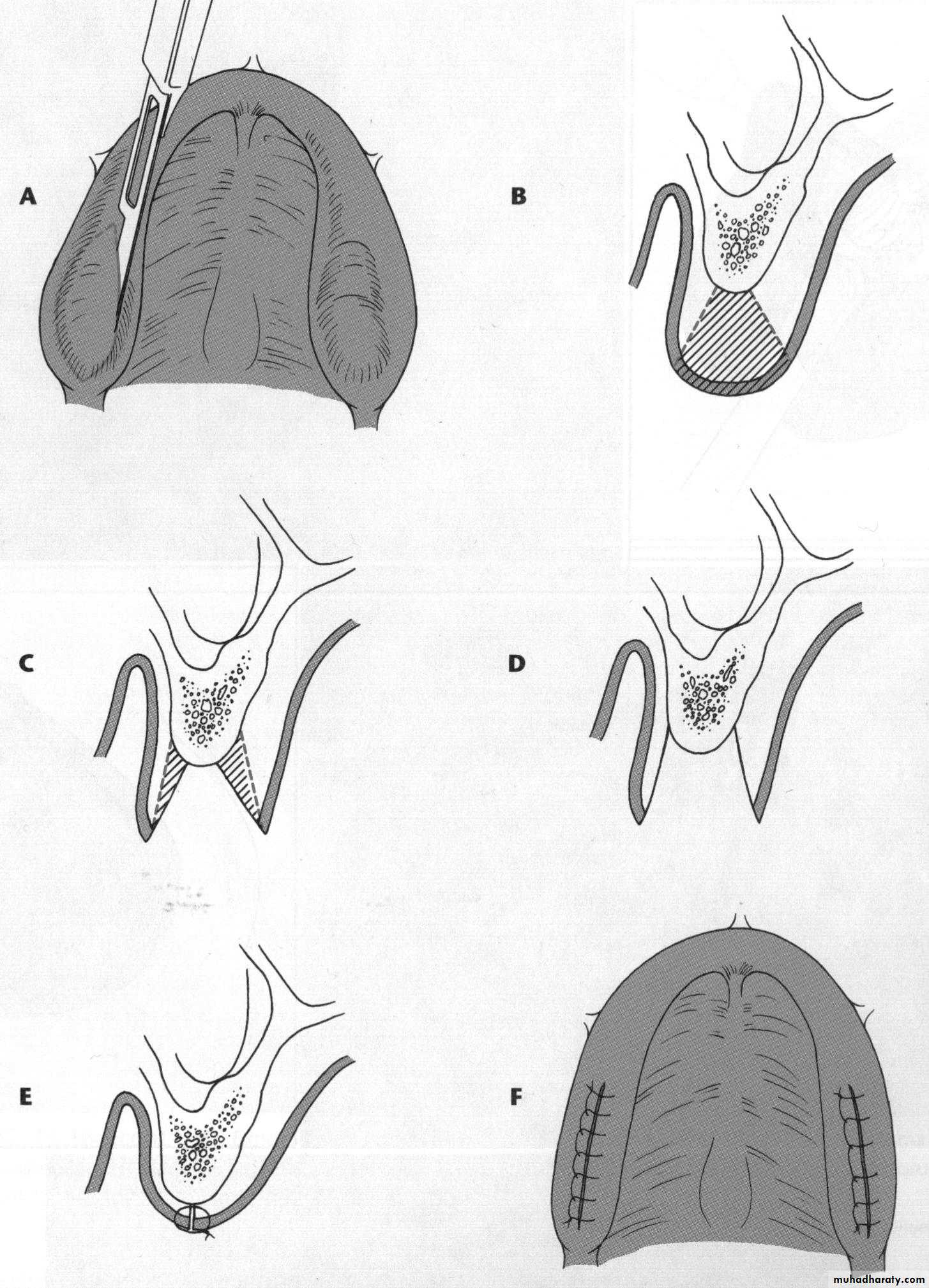
f. Vestibuloplasty: ridge extension … move muscle attachment and retain with soft tissue graftPreprosthetic Surgery
f. Vestibuloplasty: move muscle attachment and retain with soft tissue graft
Preprosthetic Surgery
f. Vestibuloplasty: Maxillary palatal graft vestibuloplastyf. Bone grafting:
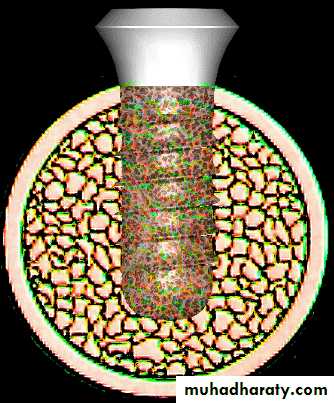
f. Bone grafting: replacement of bone loss alveolar atrophy … benefit ??? … typically ALL of the newly grafted bone is gone within 5 years … unless … supported by implants+
=