
1
Fifth stage
Practical pediatric
كتابة الطالب
22/11/2015
Jaundice clinical assessment
Background:
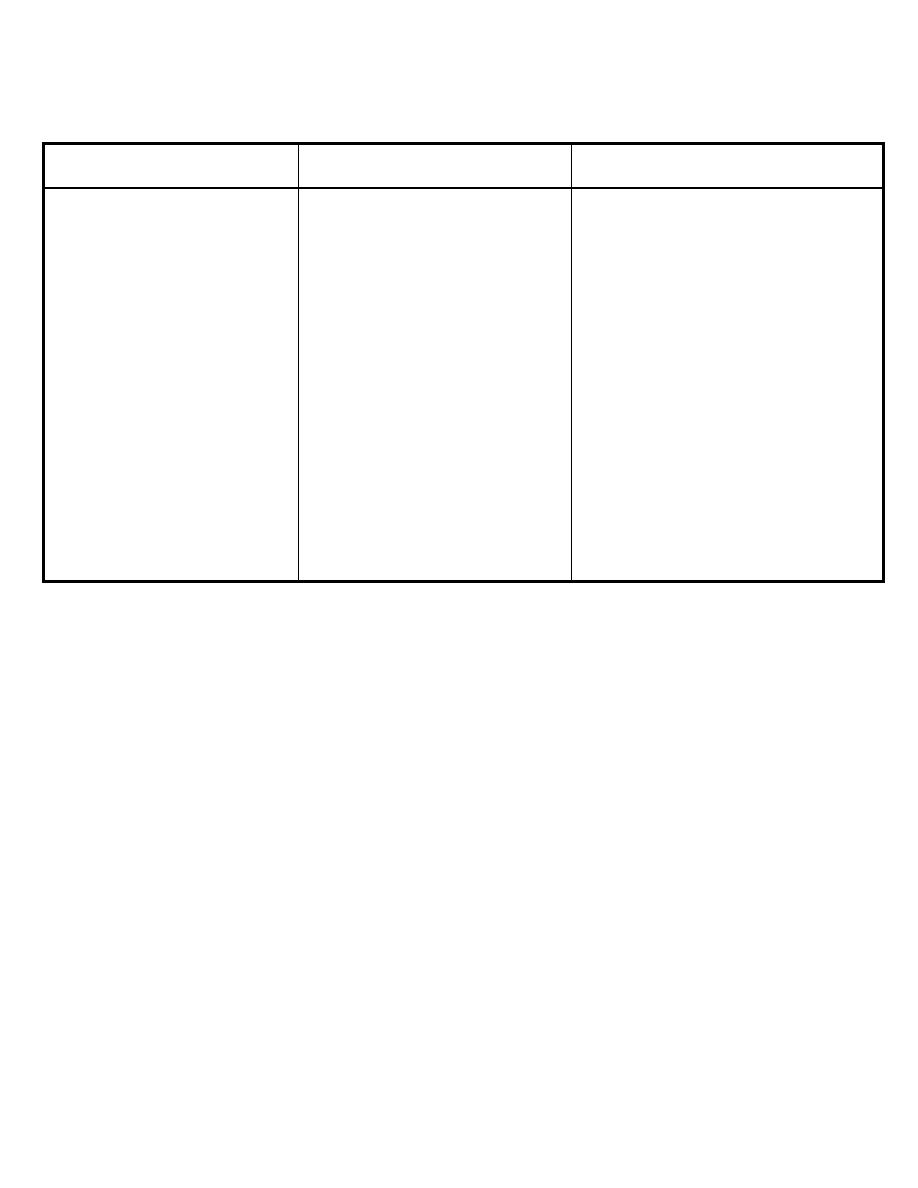
Jaundice (or hyperbilirubinaemia) occurs in approximately 60% of full term babies (80%
of pre-term babies) within the first week of life
Visual assessment of bilirubin level is unreliable
Kernicterus is a rare complication of unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia"Indirect
hyperbilirubinemia"that can lead to major long-term neurological sequelae.
As non-conjucated indirect bilirubin is lipid soluble,so it can cross BBB.
History & Examination:
features particularly relevent to jaundice:
Is the infant unwell? (sepsis & GIT obstruction can cause jaundice)
Is there dehydration or poor wt-gain? (both exacerbate jaundice)
Jaundice before 48 hrs of age (suggests haemolysis)
Onset of jaundice after 3 days of age (more likely to be pathological)
Birth trauma such as cephalhaematoma, significant bruising (breakdown of heme)
Maternal history (blood group, viral serology)
Family history of haemolytic disease (ABO/G6PD, spherocytosis)
Dark urine or pale stools (suggest biliary obstruction)
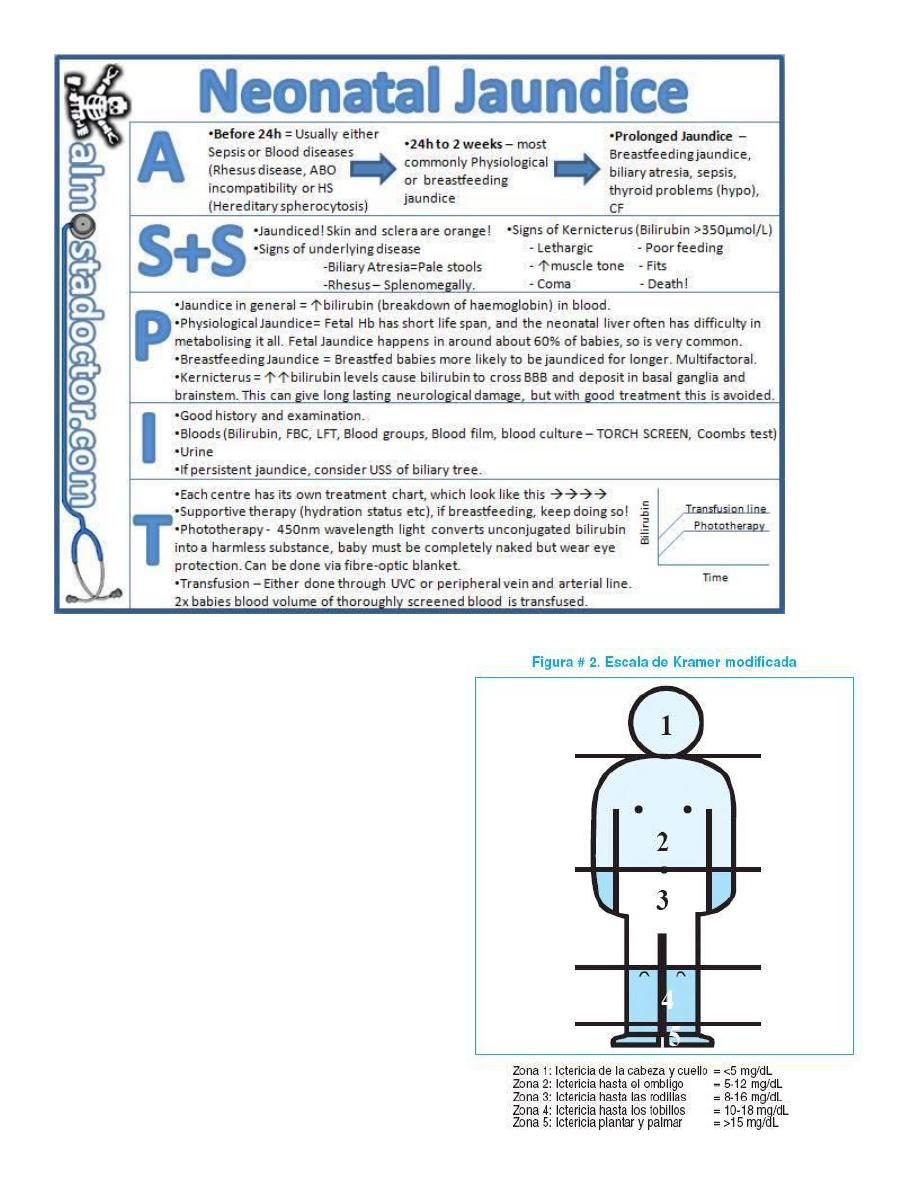
Level of icterus in terms of cephalocaudal progression (but often unreliable)
Plethora (may suggest polycythaemia)
Hepatosplenomegaly (viral hepatitis, metabolic problems)
#Most important findings to look for on examination of neonate with jaundice:
1. Color of the skin (to be checked in naked baby , natural light , non-yellow
background , minimum blanching over bony surface )
2. Severity of jaundice ( krammers staging of jaundice )
3. Anaemia , sign of dehydration
4. Hepatosplenomgaly
5. Complete neurological examination
6. Abdominal mass distention (ascites)
#Causes of neonatal jaundice:
Best classified by age of onset and duration:
1. Early: within 24 hrs of life
2
2. Intermediate: 2 days to 2 weeks
3. Late: persists for >2 weeks
Physiological Jaundice:
Is an exaggerated physiological response
Should resolve within 2 weeks in a term baby (3 weeks in a pre-term baby).
Breast Milk Jaundice:
Common
jaundice may continue for many weeks
Cessation of breast feeding is NOT indicated
Early
Intermediate
Late/prolonged
• Haemolytic causes:
– Rh
isoimmunisation
– ABO
incompatibility
– G6PD deficiency
• Congenital infection
• Physiological jaundice
• Breast milk jaundice
(inadequate intake)
• Sepsis
• Haemolysis
• Crigler-Najjar
syndrome (glucuronyl
transferase
absent/reduced)
• Polycythaemia,
bruising
• Conjugated (dark urine,
pale stools):
– Bile duct obstruction
– Biliary atresia
– Choledochal cyst
– Neonatal hepatitis.
– CF.
– Inborn error of
metabolism
• Unconjugated:
– Physiological
– Breast milk jaundice
– Infection
– Hypothyroidism
3
#krammer's staging of jaundice :
Patient presented with jaundice what
investigations will you send him for?
All patients with symptoms or signs require:-
1-determination of the direct and indirect
bilirubin fractions.
2-hemoglobin level.
3-reticulocyte count.
4-blood type
5-Coombs test.
6-examination of a peripheral blood smear.

4
What is the difference between "breast feeding jaundice"&"breast milk jaundice?
--we suspect breast feeding jaundice when the baby is poorly weight gaining with
insuuficient milk intake ->increase the level of unconjucated hyperbilirubinemia secondary
to exaggerated enterohepatic circulation of bilirubin.
--Breast milk jaundice:-baby is thriving well,with normal growth,no evidence of hemolysis
,infection or metabolic diseases .
This occurs due to some sorts of fatty acids in breast milk that interfere with bilirubin
conjucation .
Notes:
breast feeding is NOT contraindicated in any state even if there is toxic thyroid
nodules, but the real contraindications are:
1-active tuberculosis of the mother.
2-syphilis.
3-varicella.
4-herpetic lesions on the breast of the mother.
5-galactosemia.
