
1
Fifth stage
Gynecology
Lec-1-2
د.سراب
18/11/2015
Menopause
Menopause:
means final menstrual period (menos: month, pausos: ending) or 12 months
of amenorrhea.
Menopause different from female to female, some of them have regular cycle and stop
suddenly, some female have cycle that decrease gradually in frequency, some have cycle
that decrease in amount, some have cycle that decrease in both amount and frequency.
Usually the age of menopause is between 50 – 55 years and the average age is 52 years.
Premature menopause occur before 40 years (0.1% of female).
Women will spend 1/3 of her life in menopause.
Climacteroid:
represent the transitional period from reproductive to non-reproductive
state in a woman (2-3 years before stoppage of menstruation, 2-3 years after stoppage of
menstruation) in which there are endocrinal changes, psychological changes, metabolic
changes.
Why menopause occurs? "pathophysiology"
Ovaries consists of cortex (in which the developing follicles of various developmental
changes present) & central medulla (highly vascularized area).
Each ovary contains several million germ cells (primordial follicles & oocytes), During
embryological life: when ovaries will form, oogonia suffer a mitotic division, mitotic
division stopped, the maximum number will be at 20wks of female embryological life,
then all of them will enter the meiotic division, it is stopped at prophase at 1
st
meiotic
division.
At birth, 22 millions of follicles are present, steady decline in these follicles over
prepebertal & reproductive years.
For every follicle which matures to ovulation, up to 1000 follicles fail & become atretic
& only 400 of 400 000 follicles present at puberty ever mature to ovulation.
The majority of circulating plasma estradiol, progesterone & inhibin produced by
developing follicle.
As the ovary ages, remaining follicles less likely to matureovulation deline, because
of gradual fall in ovarian function.

2
The first endocrinal changes: Fall in inhibin production by the ovaries (inhibin controls
anterior pituitary production of FSH) rise in levels of FSH (state similar to ovarian
failure) so estradiol production falls & the effects of decline in estradiol on estrogen
sensitive tissues appears as menopause ensues.
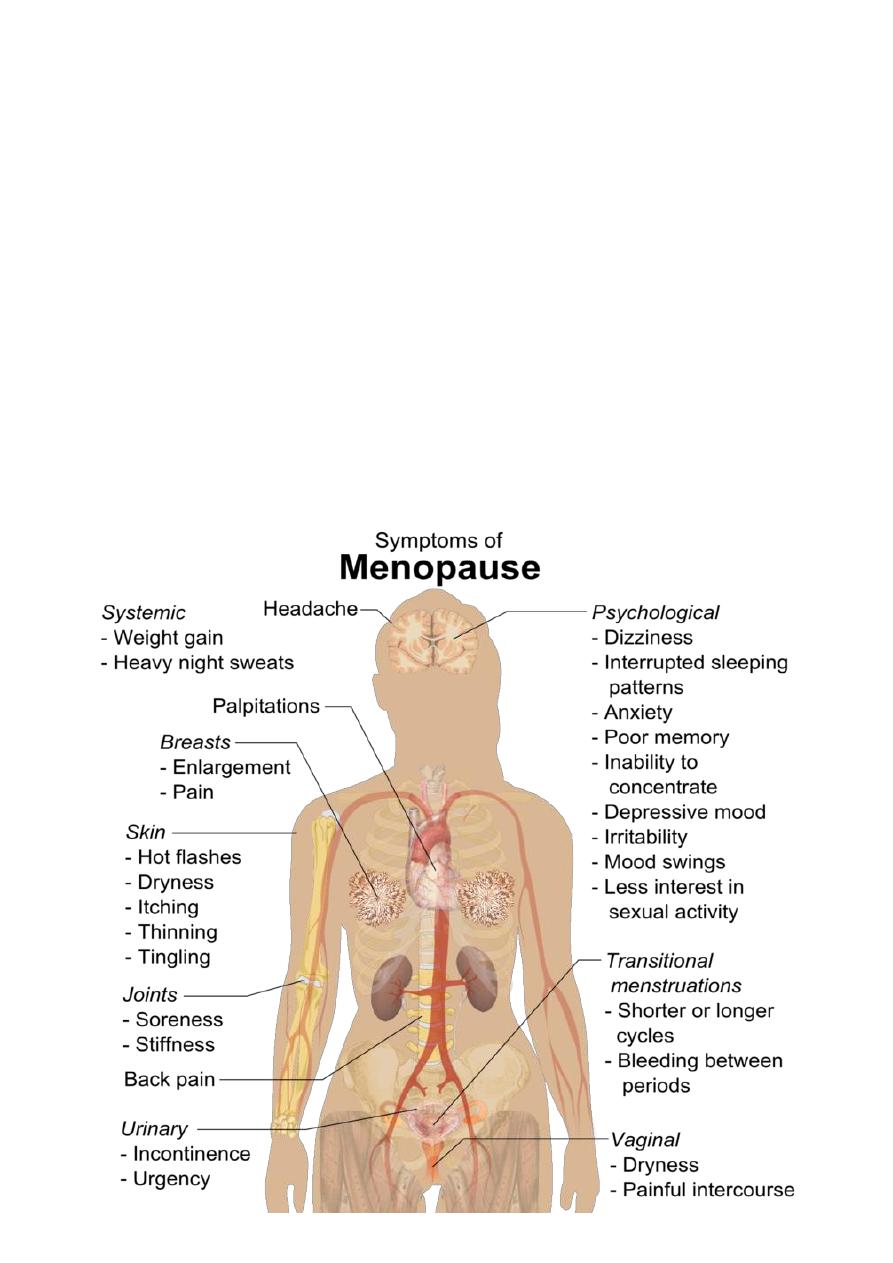
Signs & symptoms:
The cause is estrogen deficiency, increase in FSH or serotonin disturbances.
First 5 years:
1. Hot flushes
2. Night sweats
3. Hair changes
4. Changes in skin
5. Itching
6. Poor concentration
7. Poor sleep
8. Depression
9. Irritability
Second 5 years:
#Changes in genital system:
1. Dry vagina
2. Vulvar soreness
3. Atrophic changes in genital system
4. Dyspareunia
#Changes in the urinary system:
1. Urgency
2. Frequency
3. Repeated urinary tract infection
4. Urinary disturbance
#Changes in the supportive tissue:
1. Urterovaginal prolapse
2. Exaggeration of already presented prolapse.
3
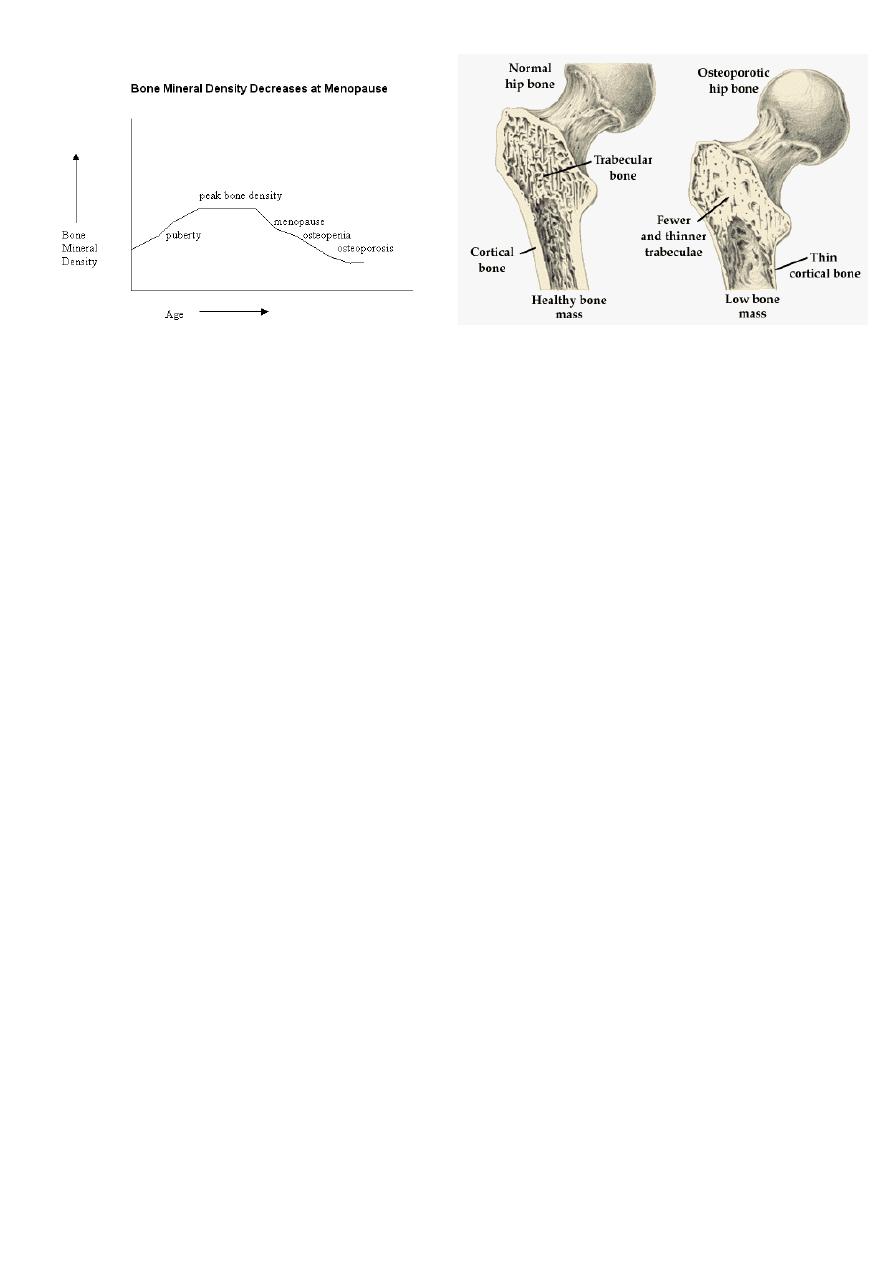
After 10 years:
#Bone change in the trabecular bones (radius, vertebrae, neck of femur):
1. Reduce length of female.
2. Fracture of neck of femur.
3. Fracture of vertebrae.
4. Vertebrae and neck of femur are the most affected bones because they are weight
bearing bones.
#Changes in the CVS:
They are exposed to IHD, CVA as estrogen increases HDL level while reducing LDL, VLDL (it is
protective against IHD)
#Changes in memory:
Dementia & Alzheimer (due to the effects of estrogen on serotonin).
4
Differential diagnosis of symptoms of menopause:
Patient takes buscopan (laxative drug).
Carcinoid.
How to diagnose menopause?
1- Stoppage of menstruation for 1 year.
2- Symptoms of menopause like hot flushes, poor sleep, frequency, and others.
3- Sign of vulva vulvar atrophy.
4- Investigations:
FSH rise:
o Do it for premature menopause.
o FSH above 30 with stop on menstruation in young female it means premature
menopause or ovarian failure.
o This hormone fluctuate during menstruation.
LH rise: increased not associated with ovulation is diagnostic.
Estrogen level: not necessary.
Progesterone level: not necessary.
Progesterone withdrawal test:
o Give progesterone for 5 days then stop it, if there is withdrawal bleeding it means
normal estrogen.
o If bleeding not occur no estrogen because axis not work or endometrium
not work.

5
o Give estrogen + progesterone and stop them if there is bleeding it means
normal endometrium and abnormal axis.
o If there is no bleeding it means abnormal endometrium.
Estrogen withdrawal:
o +ve (in PCOS) –ve (menopause).
o If estrogen withdrawal +ve do FSH level, if FSH level high it means …… and if FSH
level low it means ……. and we give hormonal replacement therapy if she want to
become pregnant.
Tran-vaginal US.
Anti-mullerian hormone:
o Not fluctuate during menstrual cycle.
o Produced by small antral follicles.
Consultation:
History
o History of breast cancer or endometrial cancer.
o Family history of colonic cancer.
o Search for other risk factors of IHD, osteoporosis, DVT and cancers.
o History of PCOS.
Blood pressure measurement very important as IHD risk is high.
Weight measurement.
Breast examination (Mammography screening) do it every 3 years.
Cervical smear (PAP smear) do it every 5 years in menopause female because they
are not sexually active (due to effect of decrease libido and dyspareunia)
Screening for bone density.
Screening for risks of IHD high cholesterol.
Screening for cancer if she has post-menopausal bleeding.
Management:
Reassurance.
Life style changes vitamins replacement, stop smoking, stop alcohol, balanced
diet, decrease fat, exercise, increase ca intake, decrease caffeine intake.
Treat the symptoms.
Non-medical treatment (for hot flushes) reflexology, acupuncture, magnetic,
herbal (red cohash, ginger).
Hormonal replacement therapy:

6
o Types: estrogen (better), progesterone, SSRI, nonselective noradrenaline blockers.
o Route:
Progesterone: Minera (ICUD)
Estrogen:
1- Local cream, gel, suppositories.
2- Systemic inplants, pills, transdermal // it used in treatment of bone and
symptoms // when stop the treatment the symptoms will reoccur // give
estrogen with progesterone to avoid endometrial cancer.
o Risk factors of hormone replacement therapy estrogen (breast cancer,
endometrial cancer, DVT), progesterone (gallbladder stone).
o Benefits of hormone replacement therapy decrease bone osteoporosis,
decrease stoke, decrease colonic cancer, benefits to genital system.
Treatment of osteoporosis Alendronate, raloxifene (estrogen receptor modulator
which protect against breast cancer and osteoporosis).
Causes of premature menopause:
Chromosomal disorder Turners syndrome (mosaic), fragile x syndrome.
Autosomal disorders Addison's disease, type1 DM, thyroiditis.
……… galactosemia.
Drugs chemotherapy (kill the oocytes), radiotherapy, surgery.
Note: Premature menopsause
need investigations for bone density, need hormone
replacement therapy, have problems with infertility.
Post-menopausal bleeding:
1- Any bleeding occur after 1 year of menopause.
2- Risk of endometrial CA.
3- Most commonly not due to CA f endometrium.
Diagnosis:
Vulva atrophic changes, itching, scratching, carbuncles.
Vagina atrophic changes, trauma, risk of infection.
Cervix atrophic changes, polyp, trauma, tumor, infection.
Uterus dysfunctional bleeding (due to peripheral conversion of estrogen), polyp,
tumor.
Ovary granulosa cell tumor (produce hormones).

7
Symptoms: postmenopausal bleeding.
Investigations:
Trans-vaginal US see endometrial thickness less than 4 no problem, above 4
make endometrial sampling then hysteroscopy and take direct biopsy.
Also by Trans-vaginal US see the ovary for ovarian mass (primary granulosa cell
tumor) (secondary metastasis of endometrial cancer).
Treatment: according to the cause.
Notes:
Risk of prolapse occurs mostly in women with chronic cough & women suffered from
difficult labor.
Uterogenital prolapse: protrusion of uterus beyond its normal position (either within
the vagina or to introitus or outside the introitus) as the tissue supporting structures
suffer from laxity.
Types of dementia (ischemic & non-ischemic) ischemic dementia is caused by
atherosclerotic process, while neurogenic (non-ischemic) dementia is caused by
serotonin effects.
