
1
forth stage
Surgery (Urology)
Lec-2
د.ﻣﺣﻣد اﻟﺷﮭواﻧﻲ
20/10/2015
Congenital anomaly of urinary system
Congenital abnormalities of the kidney
•
Its relatively uncommon
•
Usually symtomless
•
if symptomatic its due to
infection
stone
hydronephrosis
•
Often discovered by accident
Anomalies of number
•
Bilateral renal agenesis ( not compatible with life )
•
Unilateral renal agenesis
asymptomatic
Accidentally discovered
association with other anomalies
Anomalies of position
Ectopia :
•
Pelvic
•
lumber
•
Rarely thoracic
40% symptomatic, association with other anomalies
Crossed ectopia :
•
Non fused
•
Fused
2
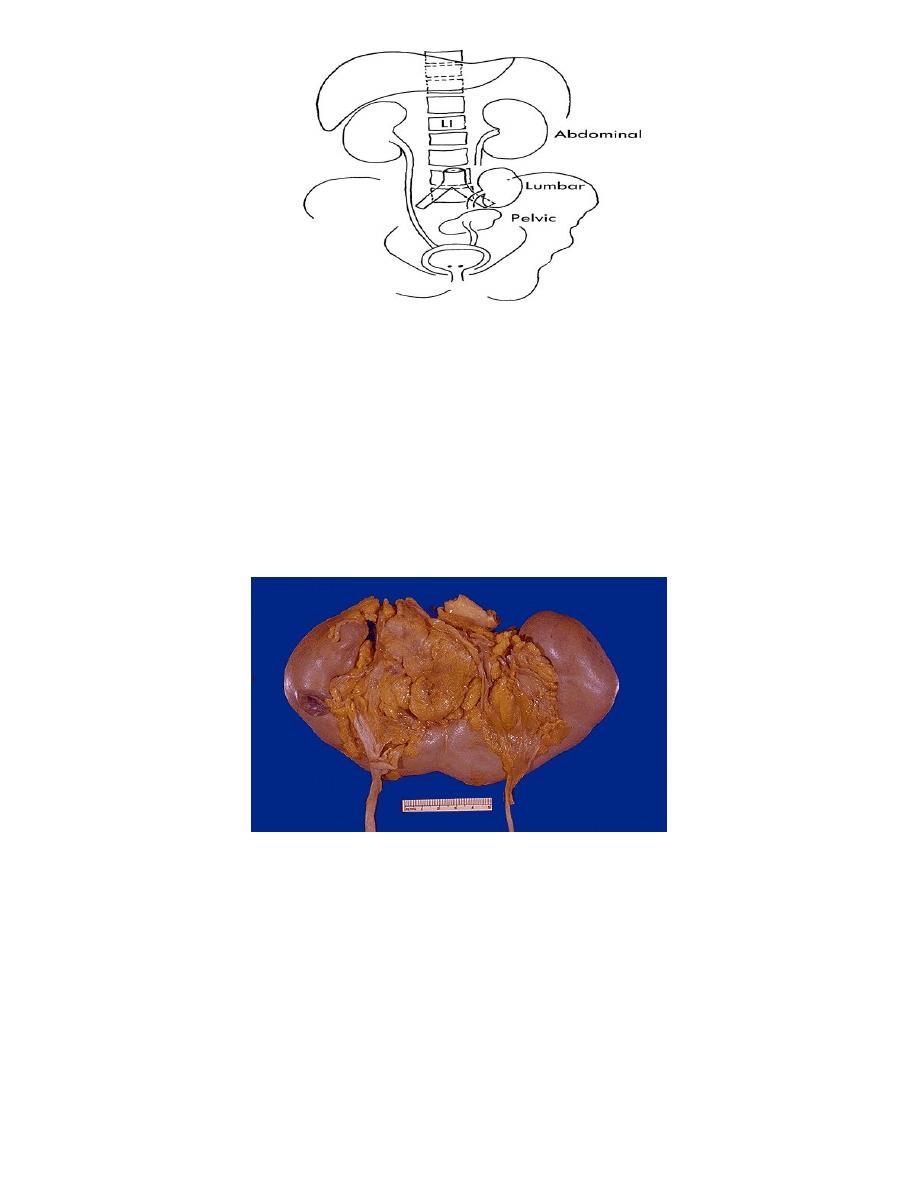
Horse shoe kidney
The commonest fusion anomalies
1/3rd of cases are symptomatic
Symptoms related to: -Infection -Stones -Hydronephrosis
Diagnosis: May be palpable, US, IVU. MRI
treatment:
1. Treat Infection ,stone, hydronephrosis ( If present )
2. Division of the esthmus is only indicated in the course of surgery for
abdominal aortic aneurysm
Parenchymal anomalies
•
Hypoplasia (small kidney)
•
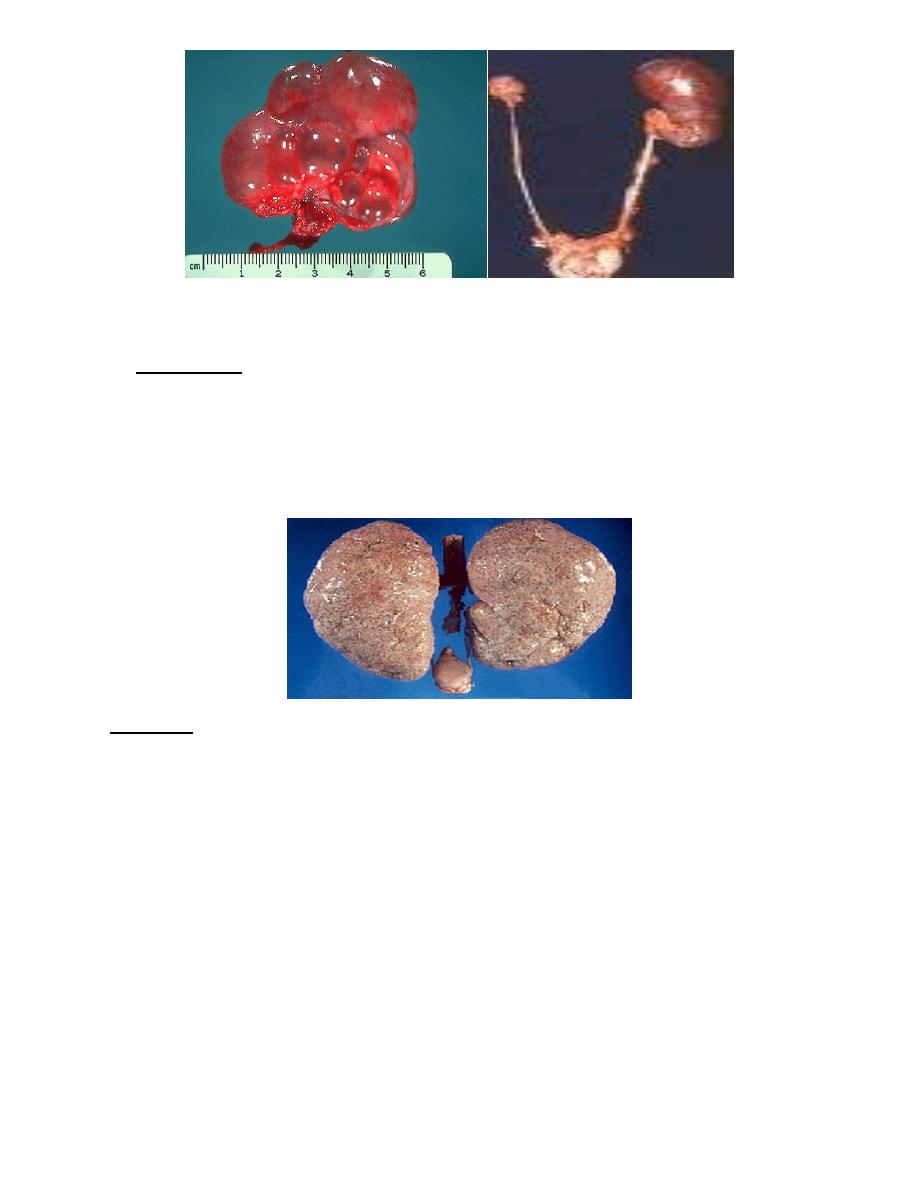
Dysplasia: 1-Cystic dysplasia 2-Polycystic renal disease(Infantile,Adult)
3
"dysplasia" "hypolpasia"
Polycystic kidney
A. infantile type
•
Autosomal recessive
•
US diagnosis
•
Early renal failure
•
incompatable with life
•
causing obstructed labour
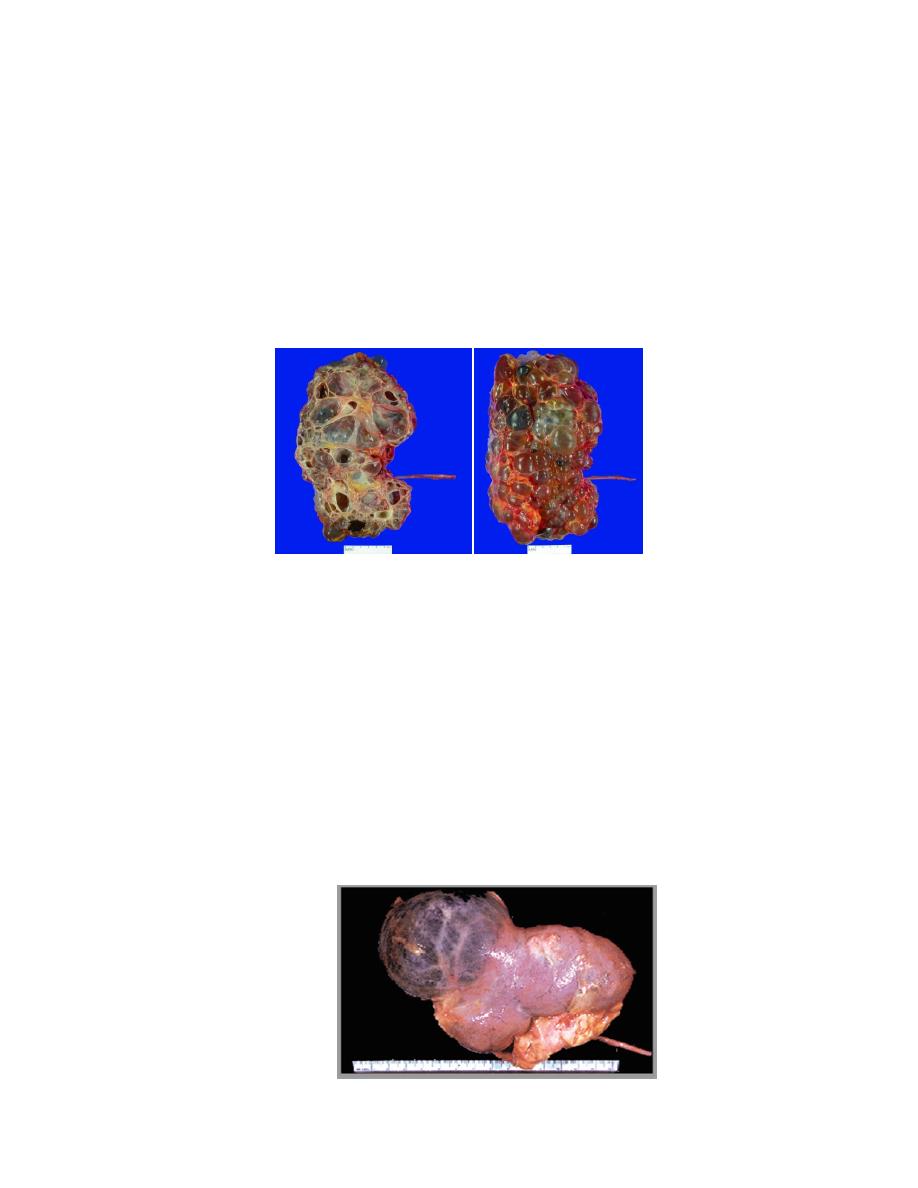
B. Adult type
The most common renal cystic disease Autosomal dominant
Progressive bilateral cystic degeneration
Clinical presentation:
•
Positive family history
•
Loin pain before the development of renal mass
•
Hypertension, hematuria, renal mass
•
Associated liver cystic disease may be seen
•
Renal failure Usually in the early fifty
Imaging
1- Ultra sound is diagnostic 2-IVU 3-MRI 4-CT scan
4
Treatment
•
Medical management of renal failure
•
Surgery :
1. ( cyst puncturing)
2. Renal stone
3. Cyst infection
4. Hemorrhage in the cysts
5. Ureteric obstruction by cyst
•
Definitive treatment is renal transplantation
Simple renal cyst(Solitary renal cyst)(Blue domed cyst)
Unilocular , Avascular,smooth, clear fluid content
Mostly asymptomatic
Large cyst may be felt as a mass
Incidental finding on US or other imaging
renal cell carcinoma should be ruled out
Treatment :
1. Reassurance and follow up
2. If symptomatic ---> Rovsing operation( Deroofing) by open surgery or
laparoscopic surgery

5
Anomalies of the collecting system
•
bifid pelvis
•
Hydrocalicosis
•
Calycial diverticulum
Ureteral anomalies
•
Duplication ( Partial,Complete)
•
Ectopic ureter
•
Ureterocele(Orthotopic ,Ectopic)
•
Pelviureteric junction obstruction
•
Congenital mega ureter
•
Retrocaval ureter
duplication of ureter :
-partial or complete
-Clinically asymptomatic unless complicated
-Diagnosis: US. IVU . CT scan . MCU
-treatment: Only when symptomatic
"partial" "complete"
Ureterocele
a cystic dilatation of the intravesical sub mucosal part of the ureter
Simple : in normally placed uretric orifice
Ectopic : In lower position placed ureteric orifice , or with ureteric duplication
Diagnosis : ultrasound ,IVU (copra head) ,MCU,Cystourethroscopy
treatment:
1-In simple ureterocele:
a-in functioning kid--->excision & reimplantation
b- If non functioning kidney---> nephrectomy
2-In ectopic ureterocele :if single--->As in simple ureterocele

6
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction
Primary : congenital
Secondary : to refluxing ureter
Mechanism of obstruction:
Intrinsic smooth muscle pathology.
Adynamic segment
Congenital segmental stenosis
Mucosal valve , web , folds
Over riding an aberrant vessel
Clinical presentation
Abdominal mass
Episodic flank pain
Pain & fever when infected
The aggravating factors: Cold, diuresis , fluid over intake
Diagnosis
US
IVU
Diuretic IVU , Diuretic renography
Renal DMSA scan ( functional).
Retrograde pyelography
Treatment
Conservative (Treat the pain ,infection and follow up)
Indication of surgery
1. Recurrent attack of pain,
2. stone,
3. progressive hydronephrosis
*Surgery : Pyeloplasty, by open surgery or laparoscopic pyeloplasty
1. Underson hynes

7
2. Culp
3. Scardino
4. V-Y plasty
Endoscopically :antegrade or retrograde endopyelotomy
Postcaval ureter
treatment : Surgery if causing obstruction and pain By resection of post caval
segment and reanastomose the ureter in front of the IVC
Congenital mega ureter
Functional obstruction of lower end of the ueter leading to a progressive
dilatation
Unilateral or bilateral
Diagnose by IVU
Treatment is by reimplantation
