1
Fifth stage
Pediatric surgery
Lec-3
د.عبد الرحمن
21/10/2015
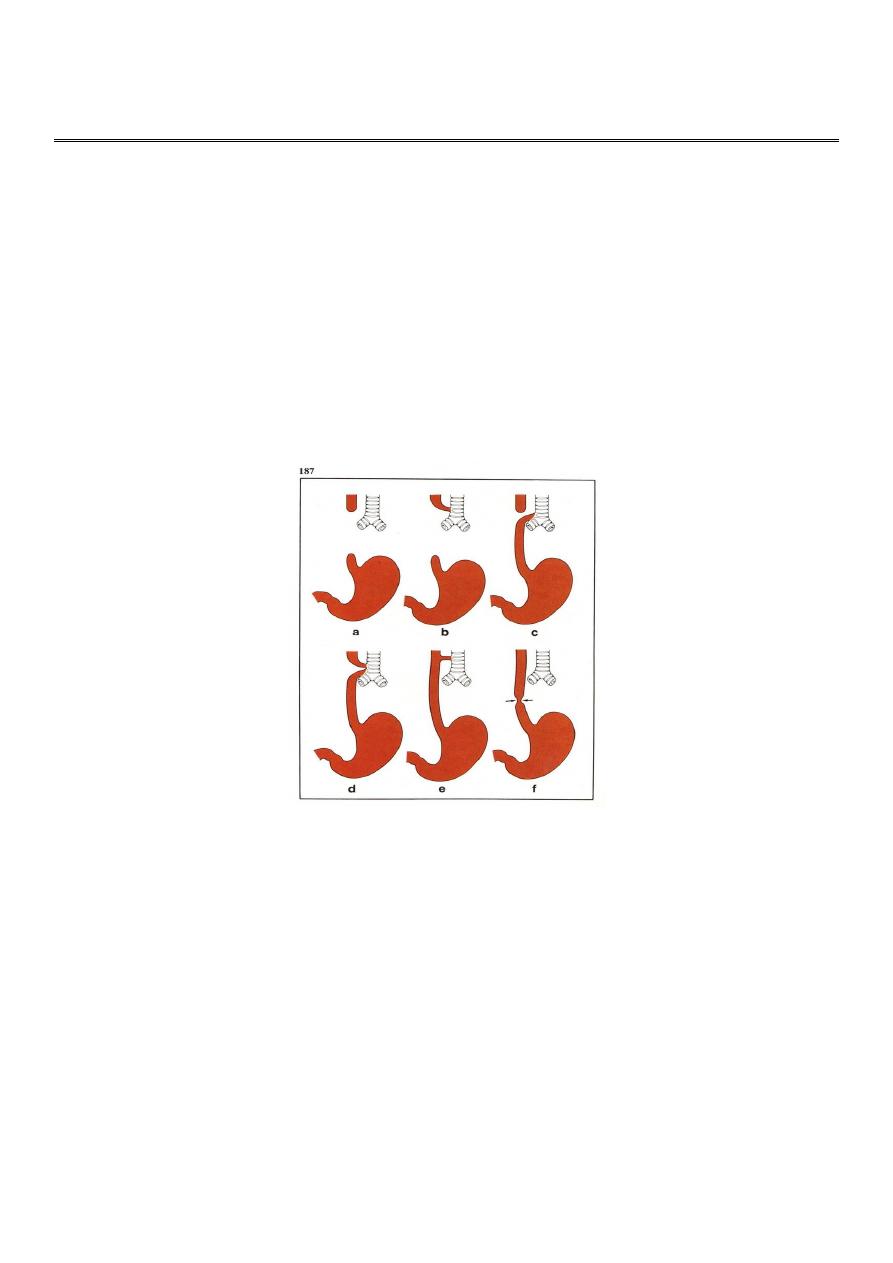
Oesphegeal Atresia
incidence : 1 in 4000 live birth
classification :
1- proximal atresia with distal tracheo-esophegeal fistula 85-90%
2- pure atresia with out fistula 5-7%
3- pure fistula without atresia 2%
4- Oesophegeal atresia with proximal fistula 1%
5- Oesphegeal atresia with proximal & distal fistula 1%
Associated anomalies (55% of the cases)
• cardiac .
• pulmonary.
• Ano-intestional.
• Genitourinary.
• Musculoskeletal.
• Mediastinal .
• Head & neck.
• Chromosoal (Down)
2
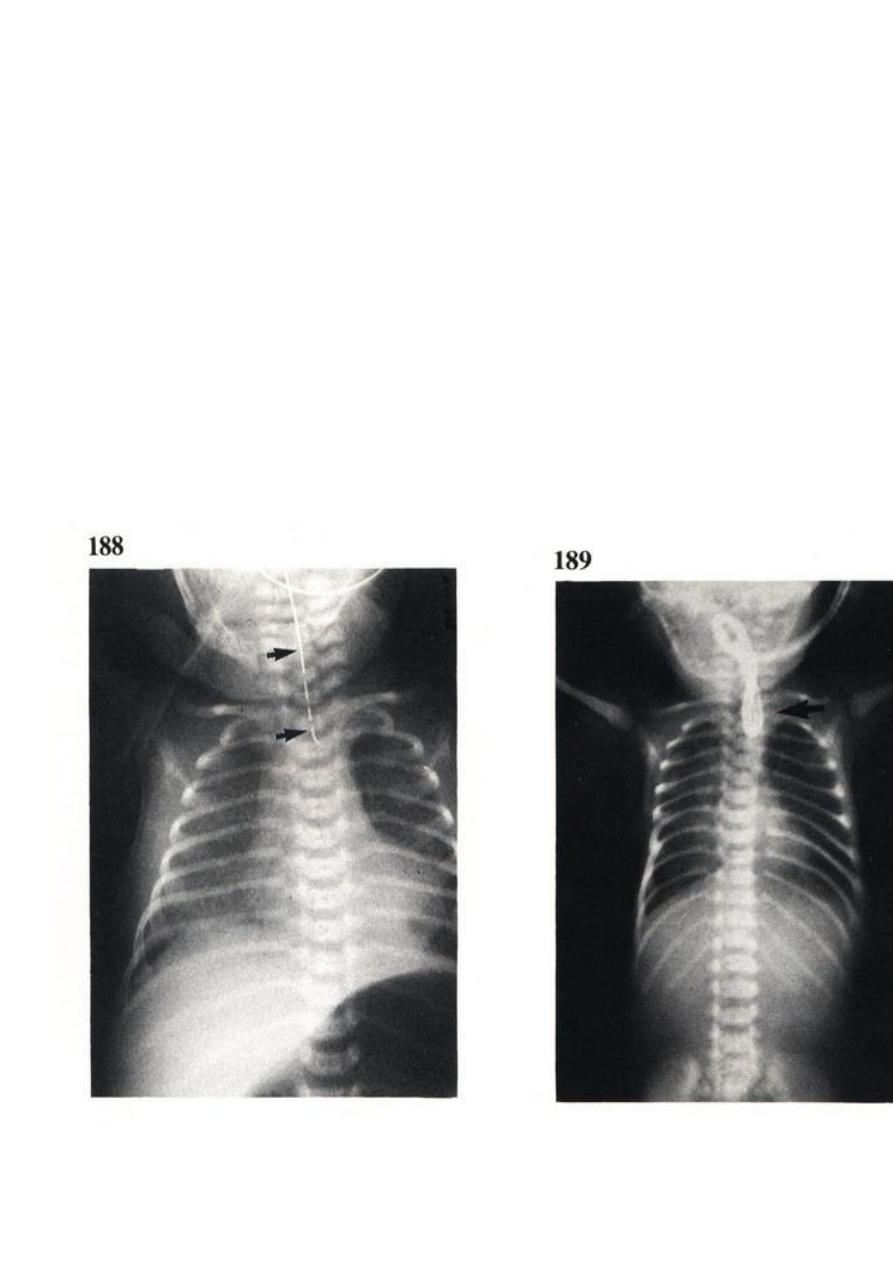
Clinical findings
1- Maternal Polyhydramnios 60-90%
Blind – ending proximal esopegeal pouch on u/s, can be confirmed by MRI
2- After birth :
unable to swallow
Drooling of saliva
spills into the airway (cough or choke)
cyanosis
mucous Babble on mouth & nose
Nasogastric Tube don’t pass more than 12 cm
3- late presentation :
- inhilation of milk (Aspiration).
-reflux of gastric juice (through the distal segmemt(
there will be severe chest infection tachypnea ,cyanosis & hypoxia
3
Diagnosis and management
• Chest x-ray.
• Preoperative resuscitation.
• Operative management.
• Post operative follow up.
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
The diaphragm forms between the 4
th
and 8
th
weaks gestation and divides the coelomic
cavity into pleural & peritoneal cavities.
The diaphragm forms from central tendon derives from the transverse septum and
peripheral muscular portion of the diaphragm arise from the posterolateral
pleuroperitoneal membrane , which eventually fuse with transverse septum
Failure of fusion is the cause of posterolateral diaphragmatic Hernia (Bochdalek Hernia).
Because the left side of the diaphragm closes after the right side.
most diaphragm hernia occur on the left side (90%)
- Anterior local defect results in Anteror diaphragmatic defect (Morgagni hernia).
- Diffuse muscular defect result in weak atnuated diaphragm (eventration of diaphragm).
4
Other types of diaphramatic hernia
Hiatal hernia through the esophegeal hiatus.
Traumatic diaphramatic hernia result from severe blunt truma to the abdomin (teared
diaphram).
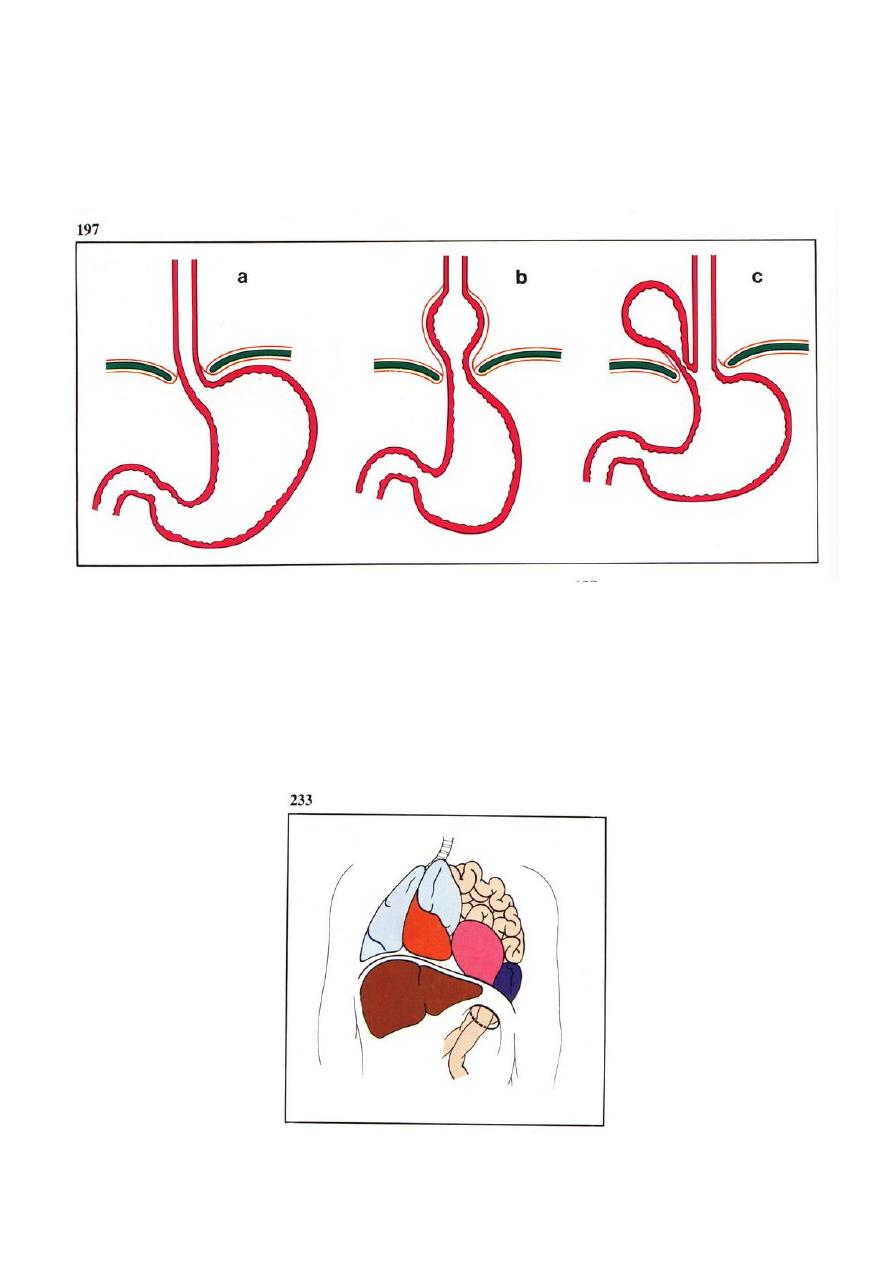
Bochdalek Hernia
This is the commonest and the most serios type. It is more common on the left side 90% it
present itself in two ways.
1. Very early presentation (immediately after birth.
2. Late presentation after several months or years.
5
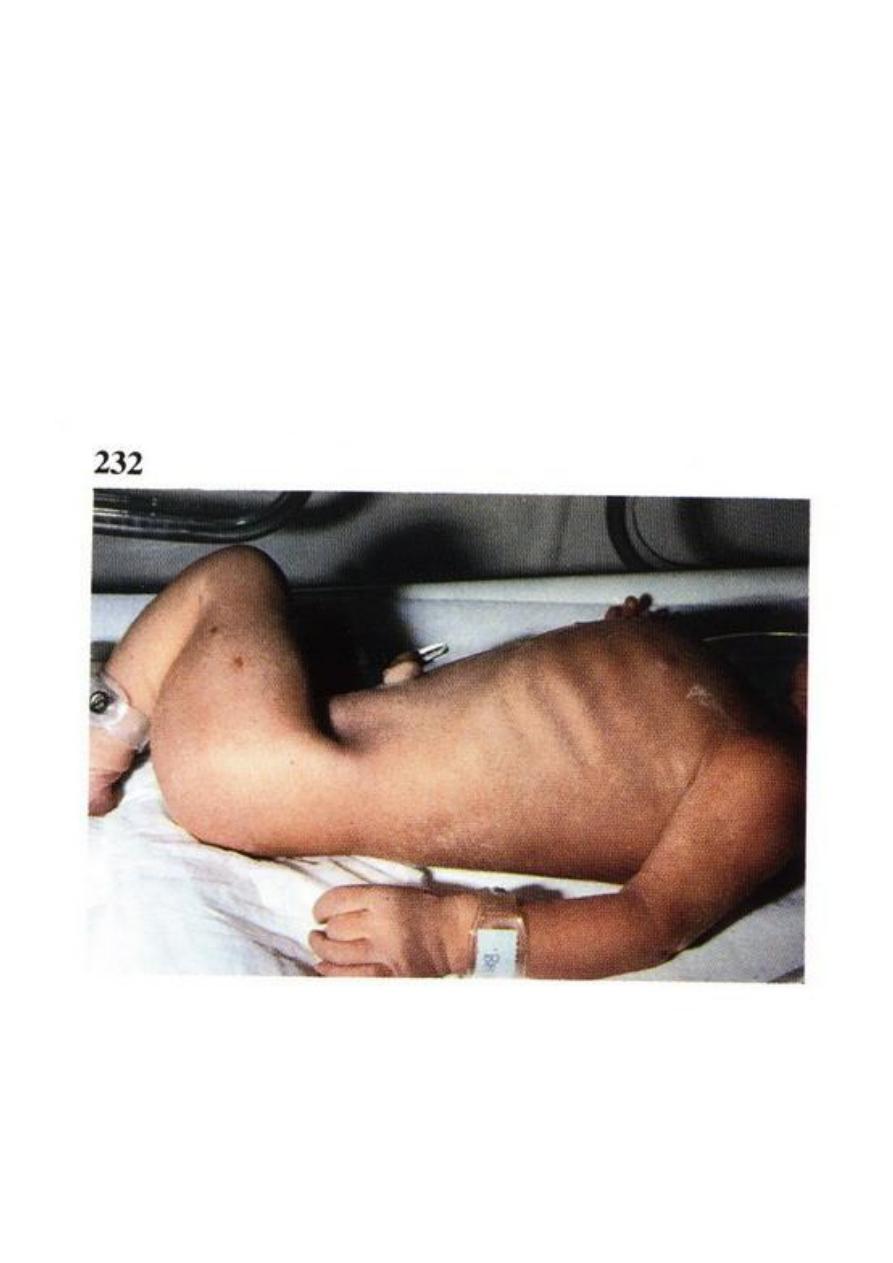
Clinical presentations
• The new born baby presented with severe respirator distress.
• Cyanosis.
• Vomiting.
On examination:
• Scaphoid abdomen.
• Tachypnea and cyanosis.
• On auscultation of the chest: bowel sound +.
• Apix beat of the heart displaced to the right side (dextrocardia).
6
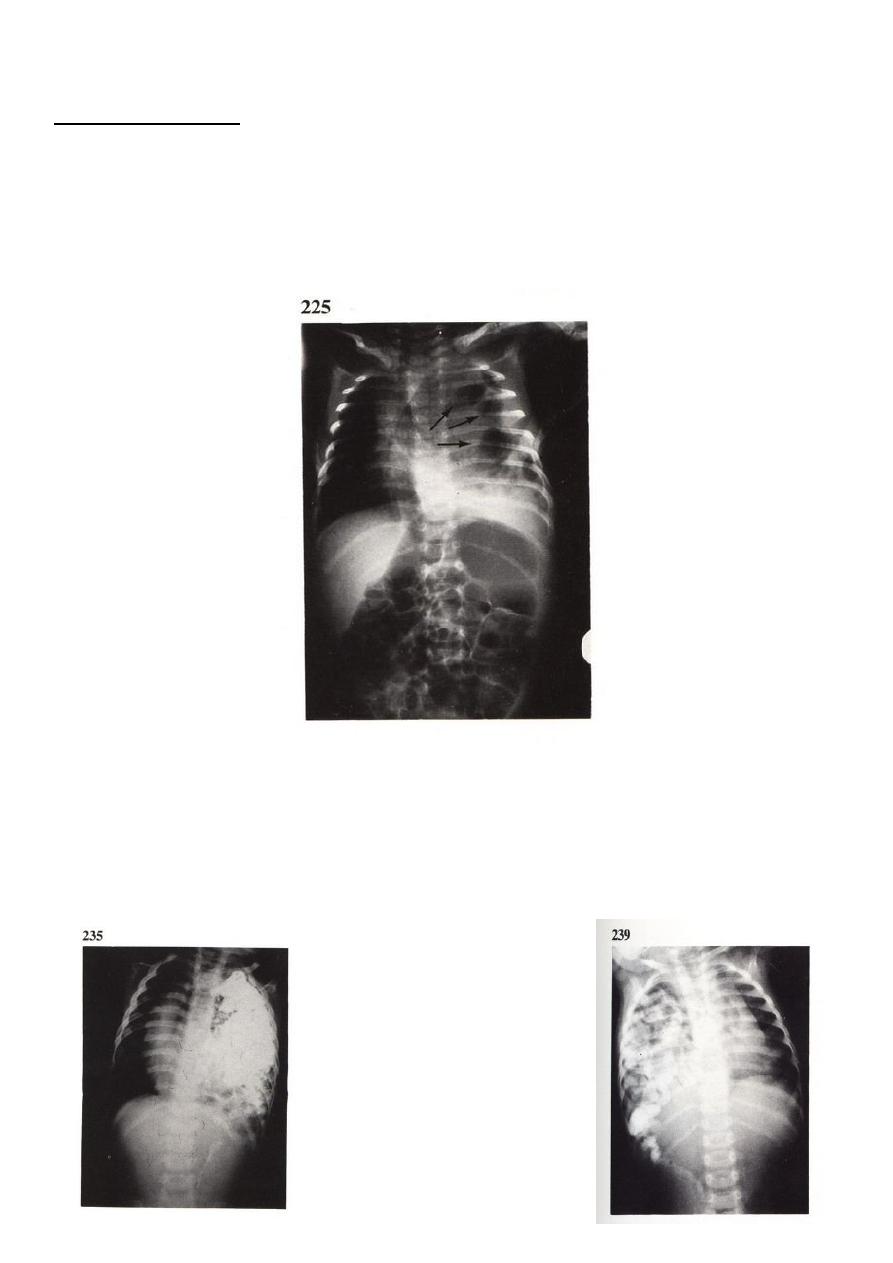
Diagnosis:
Chest x-ray shows :
- Presence of bowel shadow in the chest with compression of the lung of the same side
(hypoplastic lung).
- Displaced mediastinum to the opposite side.
- Compression of the contra lateral lung.
Differentional diagnosis
• Staphylococcal pneumonia.
• Haitul hernia.
• Barium meal may be needed to diagnose this condition

7
Management
Peroperative stabilization:
• Oxygen therapy.
• Antibiotics.
• Iv-line.
Operative repair of the diaphragm.
Post operative care and follow up.
