Amoebas
Amoebas:The genus Entamoeba include many amoebas that infect humans, but not all of them are associated with disease, like E. histolytica which is a pathogenic amoeba causing intestinal and extraintestinal Infections.
None pathogenic amoeba :
These parasites are commensal none pathogenic but they are important because they may be confused with E.
histolytica in diagnostic investigations. These amoebas include many free-living and parasitic amoebas.
The most amoebas affecting human being are:
1- E.coli.
2- E.gingivalis .
3- Dientamoeba fraglis.
4- Endolimax nana .
5- Iodoamoeba butschlii .
6- Other amoebas infecting human are morphologically very simillar to E.histolytica, e.g, E.hartmanni and E.dispar.
7- Free living amoebas are Negleria & Acanthamoeba are accidental parasites of human being .The majority of these amoeba are non-pathogenic commensal parasites or only cause mild infection.
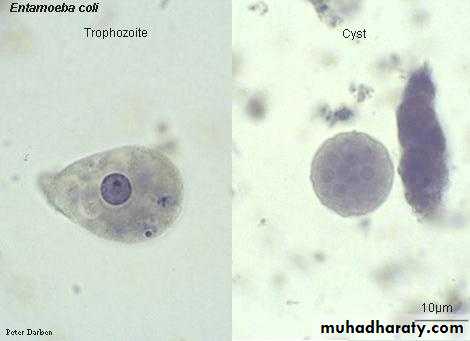
Entamoeba coli :
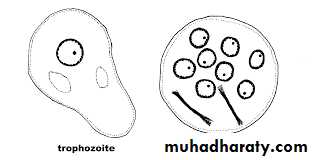
It is a parasite of the large intestine .Its life cycle is similar to that of E.histolytica. It is of medical importance only because it may be mistaken for E.histolytica .It has two stages (trophozoite& cyst). The important morphological features are :Trophozoite:
1- Its size (10-35 µm), it has granular endoplasm containing ingested bacteria and debris (no RBCs) .
2. The ectoplasm is not clear and it has small pseudopodia.
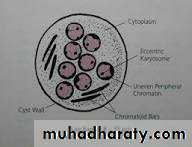
3. It has one nucleous contain large eccentric karyosome, and large chromatin granules arranged irregularly beneath nuclear membrane.
The cyst : is large oval in shape , 10 – 30 µm and it has 1 - 8 nucli, the characters just like that of trophozoite.