Introduction To Parasitology
ParasitologyIs a science, study the relationship between two organisms one called parasite & the other is called the host .
CLASSIFICATION OF PARASITES:
Parasitic kingdom include three phyla1- Protozoa.
2- Helminths.
3- Arthropods.
I- Protozoa:
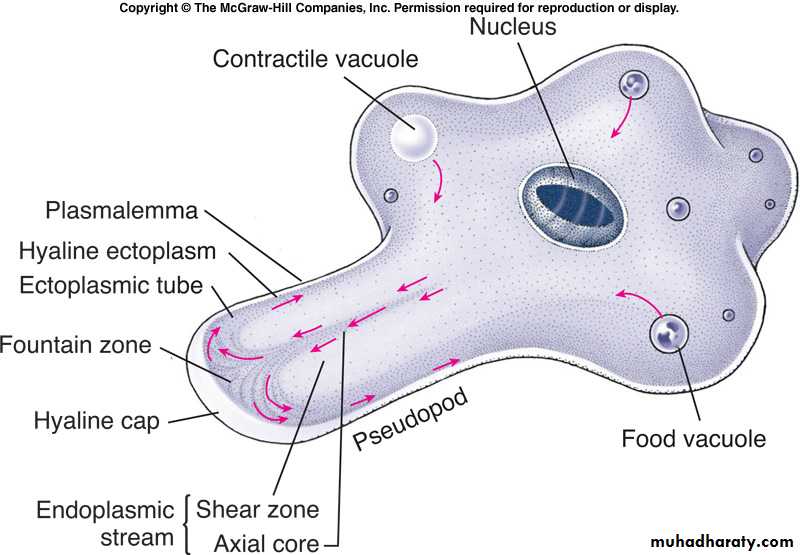
Is a phylum of the animal kingdom consisting of unicellular parasites, divided into 4 classes according to the organ of locomotion:1- Class sarcodina: Parasites that move by means of pseudopodia example Entamoeba histolytica.
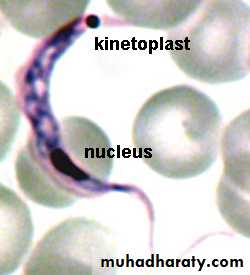
2-Class mastigophora : Parasites that move by means of flagella example Giardia lamblia
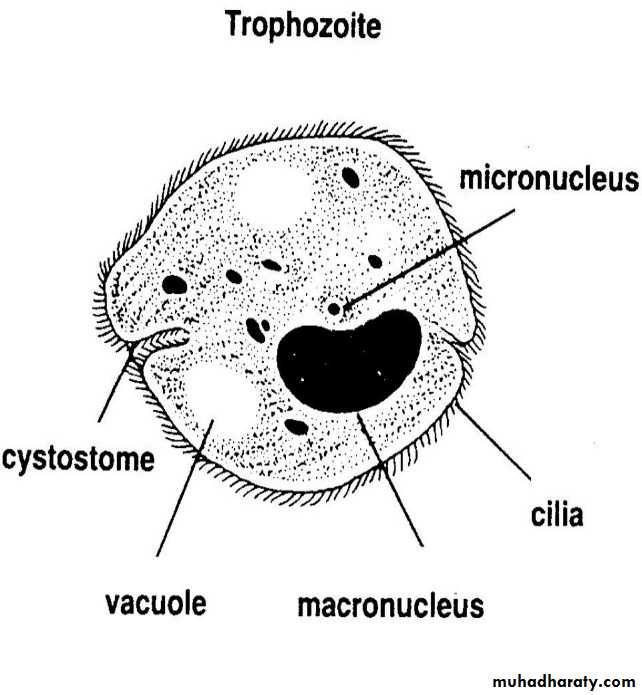
3- Class ciliates : parasites that move by means of cilia example Balantidium coli .
4- Class Sporozoa : parasites have both sexual and asexual reproductive organs, all these parasites are intracellular and they have no organ of locomotion example Plasmodium parasites causing malaria.
II- Helminths:
They are metazoa (Multicellular parasite) wormlike parasite, divided into 3 classes:1.Class Nematoda ( Roundworms ) :
a- Intestinal nematodes, e.g, Ascaris lumbricoides .
b- Tissue nematodes, e.g, Wuchereria bancrofti .
2- Class Cestoda ( Tapeworms) :
They are flattened and segmented worms e.g: Taenia saginata .
3- Class Trematoda (Flukes):
They are flattened leaf- shaped worms e.g: Schistosoma heamatobium.
III- Arthropods :
These parasites having exoskeleton and jointed legs, divided into 2 classes:
1- Class Insecta :e.g. Mosquitoes, lice and fleas .
2- Class Arachnida :e.g. Ticks and mites .
GENERAL TERMINOLOGY:
*pathogenic parasite (parasitism): A parasite infect the host and cause tissue changes or a disease (harmful parasite).*Commensal parasite (Commensalism): The association of two different species of organisms in which one of them is benefited and the other neither benefited nor injured .
*Ectoparasite: A parasite present on or in the exterior surface of a host.
*Endoparasite: A parasite present within the body of its host .
Facultative parasite: A parasite capable of living an independent or a parasitic existence.
Obligatory parasite: A parasite is capable of living as parasitic on a host, but it cannot exist as independent living.
Types of hosts
*Definitive host:The animal or human in which a parasite passes its adult stage and / or the sexual reproductive phase can take place.
*Reservoir host:
An animal e.g. (dogs, cats or rodents) which carry a species of parasite from which man become infected. The host do not get the disease or its carried as a subclinical infection.
*Carrier. A host carring a parasite but not showing any clinical sings or symptoms.
*Accidental (or incidental ) host : Infection of a host other than the normal host species.
Vector:
Any arthropod or other living carrier which transport a pathogenic micro-organism from an infected to a non infected host. A vector may transmit disease:
(1) passively called (mechanical vector) e.g. housefly
(2) The vector is essential in the life cycle of the pathogenic parasites called (biologic vector) e.g. mosqutoes.
Ectoplasm: The gelatinous material beneath the cell membrane.
Endoplasm: The fluid & inner material of a protozoal parasite.
Flagellum (flagella):
An extension of ectoplasm which provides locomotion similar to a tail.Pseudopod:A protoplasmic extension on the trophozoites of amoeba allowing them to move and engulf food .
Cilia: Hairlike processes attached to a free surface of a cell; function for motility of fluids at the surface of the cell, e.g. Balantidium coli .