Introduction to Microbiology
Dr. Waleed KhalidLec. : 1
Medical microbiology is the study of the causative agents of infectious diseases of humans and the reaction to such infections. In other words it deals with etiology, pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, specific treatment and control of infection (immunization).
Medical microbiology includes:
Bacteriology – The science that study bacteria, the causative agents of a number of infectious diseases.Virology – The science that study viruses, non-cellular living systems, capable of causing infectious diseases in human being.
Immunology – The science which concerned with mechanisms of body protection against pathogenic microorganisms and foreign cells and substances.
Mycology – The science that deals with the study of fungi .
Protozoology – It deals with pathogenic unicellular animal organisms.
Classification of Microorganisms:-
Classification by structure
Subcellular – DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat – viruses
Prokaryotic – simple cell structure with no nucleus or organelles – bacteriaEukaryotic – complex cell structure with nucleus and specialized organelles – protozoans, fungi, parasites
Naming of Microorganisms:-
Standardized namingGenus
Category of biologic classification
Example – Staphylococcus
Species of organism
Represents a distinct type of microorganisms
Examples – Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis
The genus name is written with a capital letter, and the species name – with a small letter.
How Microorganisms Cause Disease
Microorganisms cause disease in a variety of ways1- By using nutrients needed by cells and tissues
2- By damaging cells directly
3- By producing toxins
These microorganisms may remain localized or become systemic
Transmission
Direct contactIndirect contact
Localized symptoms
SwellingPain
Warmth
Redness
Generalized symptoms
Fever
Tiredness
Aches
Weakness
Normal flora
Provides a barrierCan cause an infection when the immunity decrease .
1- Viruses
They are the smallest known infectious agents
They are subcellular microorganisms that :
Have only nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat
Must live and grow in living cells of other organisms
Hepatitis virus
Illnesses caused by virusesColds
InfluenzaHepatitis
Warts
AIDS
Vaccines are available for many viruses
Mumps
Rubella
Measles
Herpes
2-Bacteria
Single-celled prokaryotic organisms that reproduce rapidly .Classification
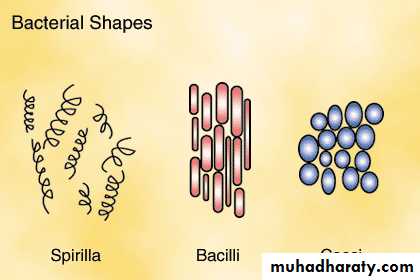
Bacteria can be classified according to:-1- Shape
2- Ability to retain dyes
3- Ability to grow with / without air
4- Biochemical reactions
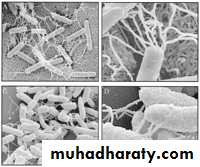
Bacillus bacterial classification
Classification and Identification1- Shape
Coccus – spherical, rounded, or ovoid
Bacillus – rod-shaped
Spirillum – spiral-shaped
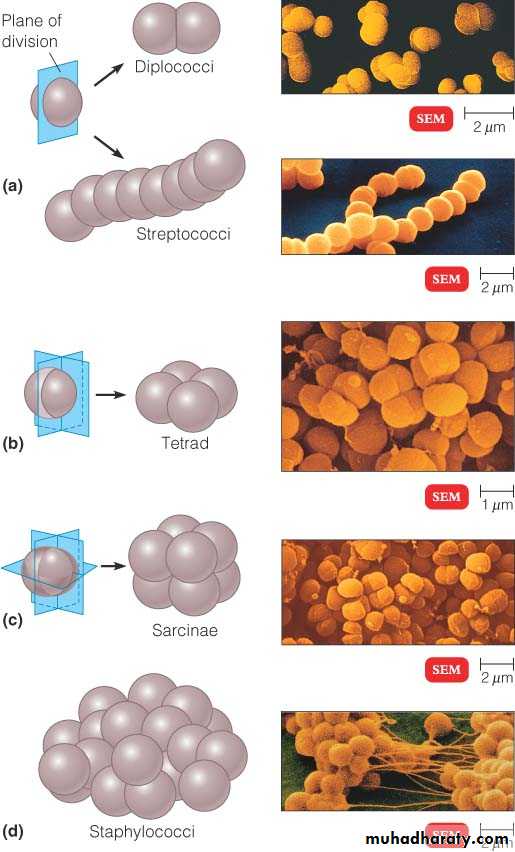
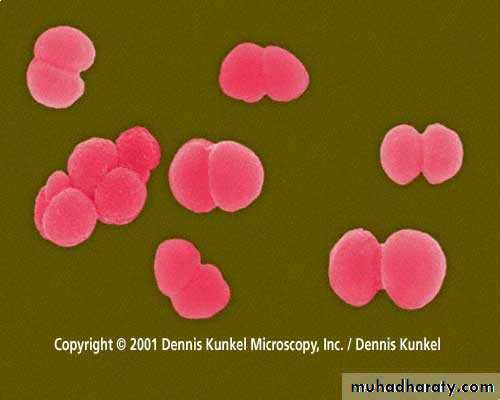
Virbrio – comma-shapedSpherical (cocci) bacteria
• Micrococci
• Diplococci• Streptococci
• Staphylococci
• Tetracocci
• Sarcine
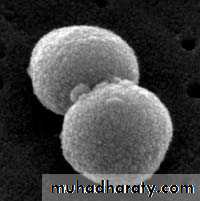
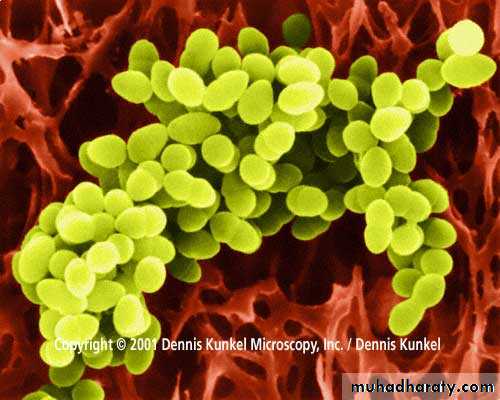
Representatives of pathogenic cocci
1.Scanning Electron Micrograph of Streptococcus pneumoniae
2.Scanning electron micrograph of a Staphylococcus aureus1
2
Electron Micrograph of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Classification and Identification (cont.)
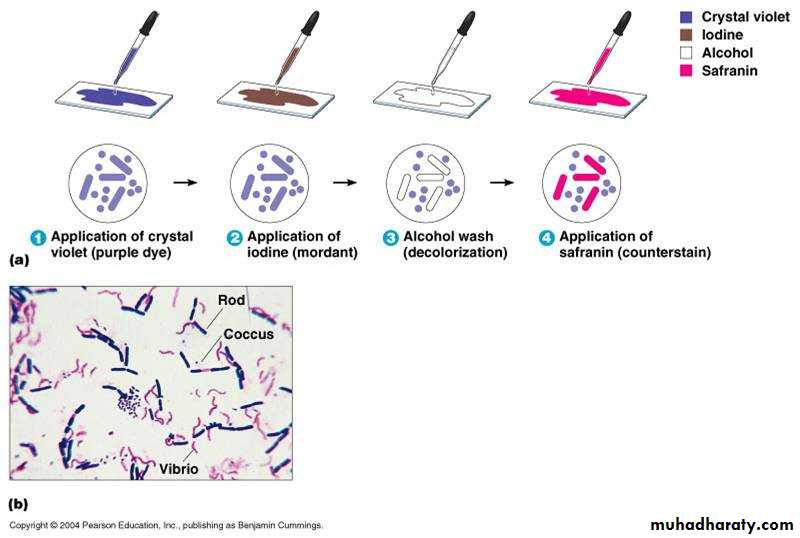
2-Ability to retain certain dyesGram’s stain
Acid-fast stain
3- Ability to grow in presence or absence of air
Aerobes – grow best in the presence of oxygenAnaerobes – grow best in the absence of oxygen
4- Biochemical reactions
Special groups
Mycobacteria – bacilli with a cell wall that differs from most bacteria
Rickettsiae
Very smallLive and grow within other living organisms such as mites and ticks
Chlamydiae
Cell wall structure differs from other bacteria
Live and grow within other living cells
Mycoplasmas – completely lack the rigid cell wall
The size of bacteriaThe size of bacteria is measured in micrometer (m) or micron () (1 micron or micrometer is one thousandth of a millimeter) and varies from 0.1 to 16-18 . Most pathogenic bacteria measure from 0.1 to 10 .
The other units of measurement of microorganisms is nanometer (nm) (one millionth of a millimeter) .
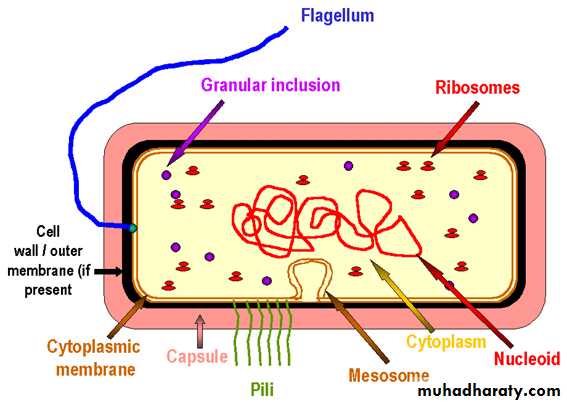
BACTERIAL CELL
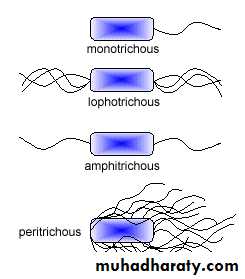
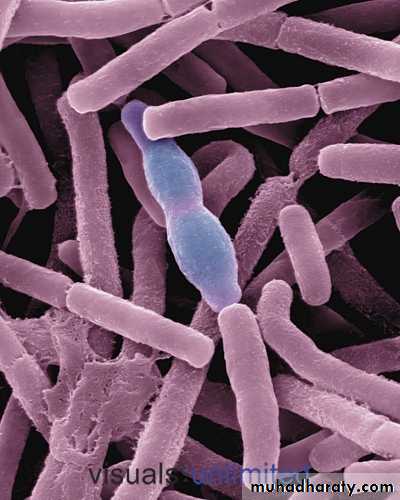
FLAGELLA
Electron Micrograph of Bacteria with Flagella
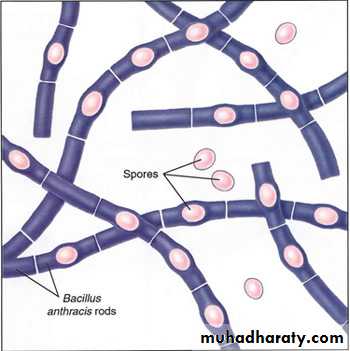
SPORE
Bacillus megateriumBacillus anthracis
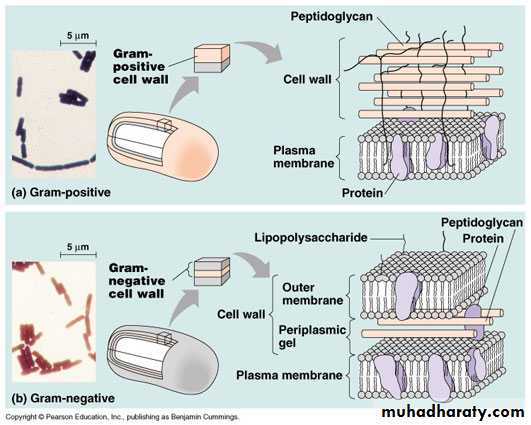
Cell wall
In addition to conferring rigidity upon bacteria, the cell wall protects against osmotic damageChemically, the rigid part of the cell wall is peptidoglycan
Cell wall first described by Gram in 1884. It is used to study morphologic appearance of bacteria. Gram's stain differentiates all bacteria into two distinct groups:
a. Gram-positive organisms
b. Gram-negative organisms
Gram
StainingTechnique
3- Protozoans
Single-celled eukaryotic organisms, larger than bacteria, they are found in soil and water and they are a leading cause of death in developing countriesIllnesses caused by protozoans are
Malaria
Amebic dysentery
Trichomoniasis vaginitis
Protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis
4- Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms with rigid cell wallYeasts
Single-celled
Reproduce by budding
Molds
Large, fuzzy, multicelled organisms
Produce spores
Superficial infections
Athlete’s footRingworm
Thrush
Can cause systemic infections
Yeast: a single-celled fungi
Multicellular ParasitesOrganisms that live on or in another organism and use it for nourishment
Parasitic worms
Usually due to poor sanitation
Roundworms
Flatworms
Tapeworms
Parasitic insects
Bite or burrow under the skinMosquitoes
Ticks
Lice
mites
Apply Your Knowledge
Matching:___ Yeast or mold A. Virus
___ Tapeworm / lice B. Bacteria
___ Classified by shape C. Protozoan
___ Subcellular organism D. Fungus
___ May be aerobic or anaerobic E. Multicellular parasite
___ Smallest known organism
___ Found in soil and water
E
ANSWER:
D
A
B
B
C
A
Very Good!