
Drugs Used to Treat
Asthma
Drugs Used to Treat
Asthma

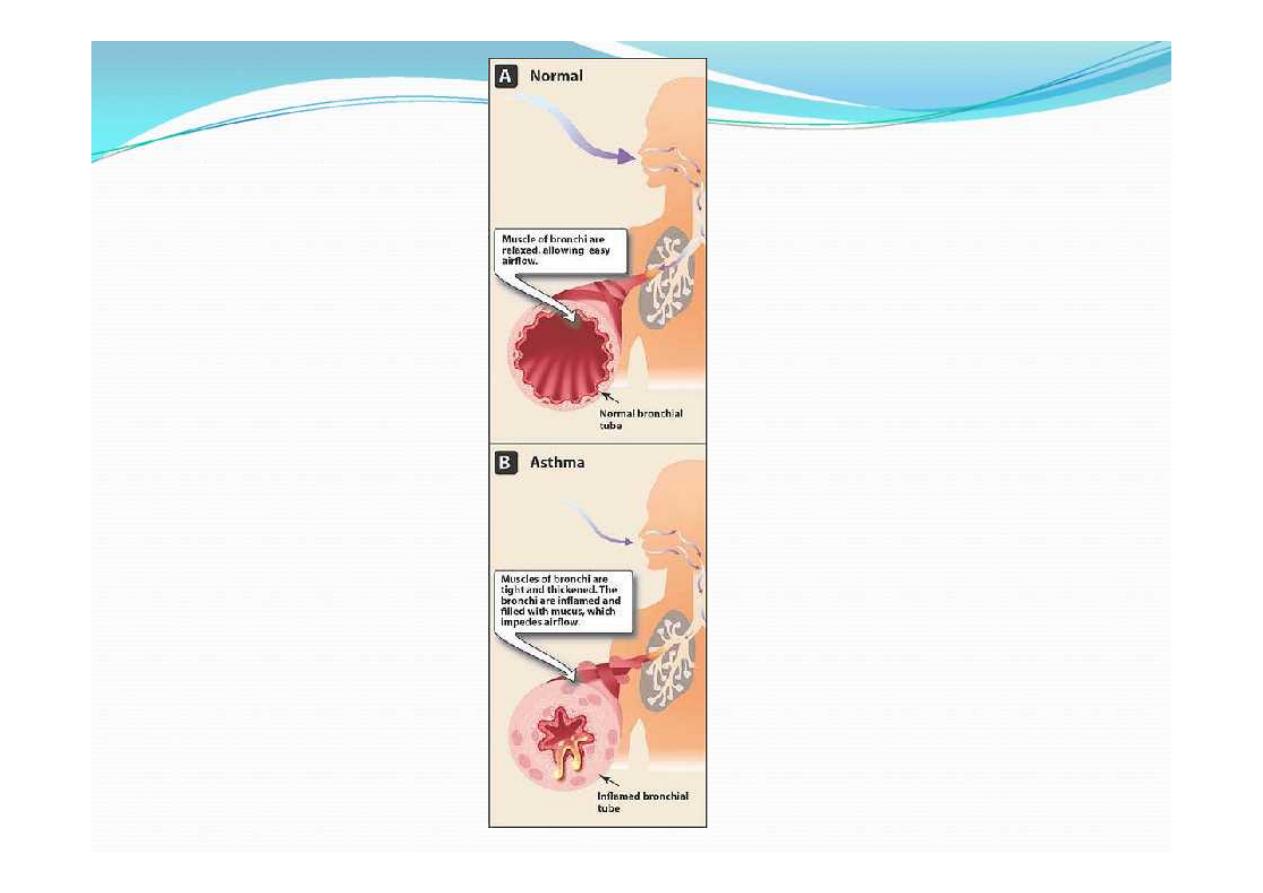
Asthma is an inflammatory disease of the
airways characterized by episodes of acute
bronchoconstriction causing shortness of
breath, cough, chest tightness, wheezing,
and rapid respiration.
Asthma is an inflammatory disease of the
airways characterized by episodes of acute
bronchoconstriction causing shortness of
breath, cough, chest tightness, wheezing,
and rapid respiration.

Airflow obstruction in asthma is due to
bronchoconstriction that results from:
contraction of bronchial smooth
muscle
inflammation of the bronchial wall
increased mucous secretion
Airflow obstruction in asthma is due to
bronchoconstriction that results from:
contraction of bronchial smooth
muscle
inflammation of the bronchial wall
increased mucous secretion

TYPES OF ASTHMA
Asthma associated with specific allergic
Reactions
Asthma not associated with known allergy
Exercise-induced asthma
Asthma associated with chronic pulmonary
disease
TYPES OF ASTHMA
Asthma associated with specific allergic
Reactions
Asthma not associated with known allergy
Exercise-induced asthma
Asthma associated with chronic pulmonary
disease

APPROACHES TO TREATMENT
Prevention of exposure to allergen(s)
Reduction of the bronchial
inflammation and hyperreactivity.
Dilatation of narrowed bronchi
APPROACHES TO TREATMENT
Prevention of exposure to allergen(s)
Reduction of the bronchial
inflammation and hyperreactivity.
Dilatation of narrowed bronchi

Reduction of the bronchial inflammation
and hyperreactivity.
1.Glucocorticoids
2.Mast Cell Stabilizers: Sodium cromoglicate
(cromolyn, Intal)
Nedocromil sodium
3.Other drugs. Ketotifen
Reduction of the bronchial inflammation
and hyperreactivity.
1.Glucocorticoids
2.Mast Cell Stabilizers: Sodium cromoglicate
(cromolyn, Intal)
Nedocromil sodium
3.Other drugs. Ketotifen

1
.( Glucocorticoids)
prednisolone (orally)
beclomethasone, fluticasone and
budesonide (by inhalation)
1
.( Glucocorticoids)
prednisolone (orally)
beclomethasone, fluticasone and
budesonide (by inhalation)

( Glucocorticoids)
MOA:
Inhibition of the influx of inflammatory cells into the lung after
allergen exposure
inhibition of the release of mediators from macrophages and
eosinophils, and T lymphocytes)
reversing mucosal edema
decreasing the permeability of capillaries
inhibiting the release of leukotrienes.
After several months of regular use reduce the hyperresponsiveness of
the airway smooth muscle to stimuli, such as allergens, irritants, cold
air, and exercise.
Increase the number of B2 recepters so promote bronchodilatation
mediated by B2 receptors
( Glucocorticoids)
MOA:
Inhibition of the influx of inflammatory cells into the lung after
allergen exposure
inhibition of the release of mediators from macrophages and
eosinophils, and T lymphocytes)
reversing mucosal edema
decreasing the permeability of capillaries
inhibiting the release of leukotrienes.
After several months of regular use reduce the hyperresponsiveness of
the airway smooth muscle to stimuli, such as allergens, irritants, cold
air, and exercise.
Increase the number of B2 recepters so promote bronchodilatation
mediated by B2 receptors

Oral/systemic: Patients with severe exacerbation of
asthma (status asthmaticus) may require intravenous
administration of methylprednisolone or oral
prednisone.
Oral/systemic: Patients with severe exacerbation of
asthma (status asthmaticus) may require intravenous
administration of methylprednisolone or oral
prednisone.

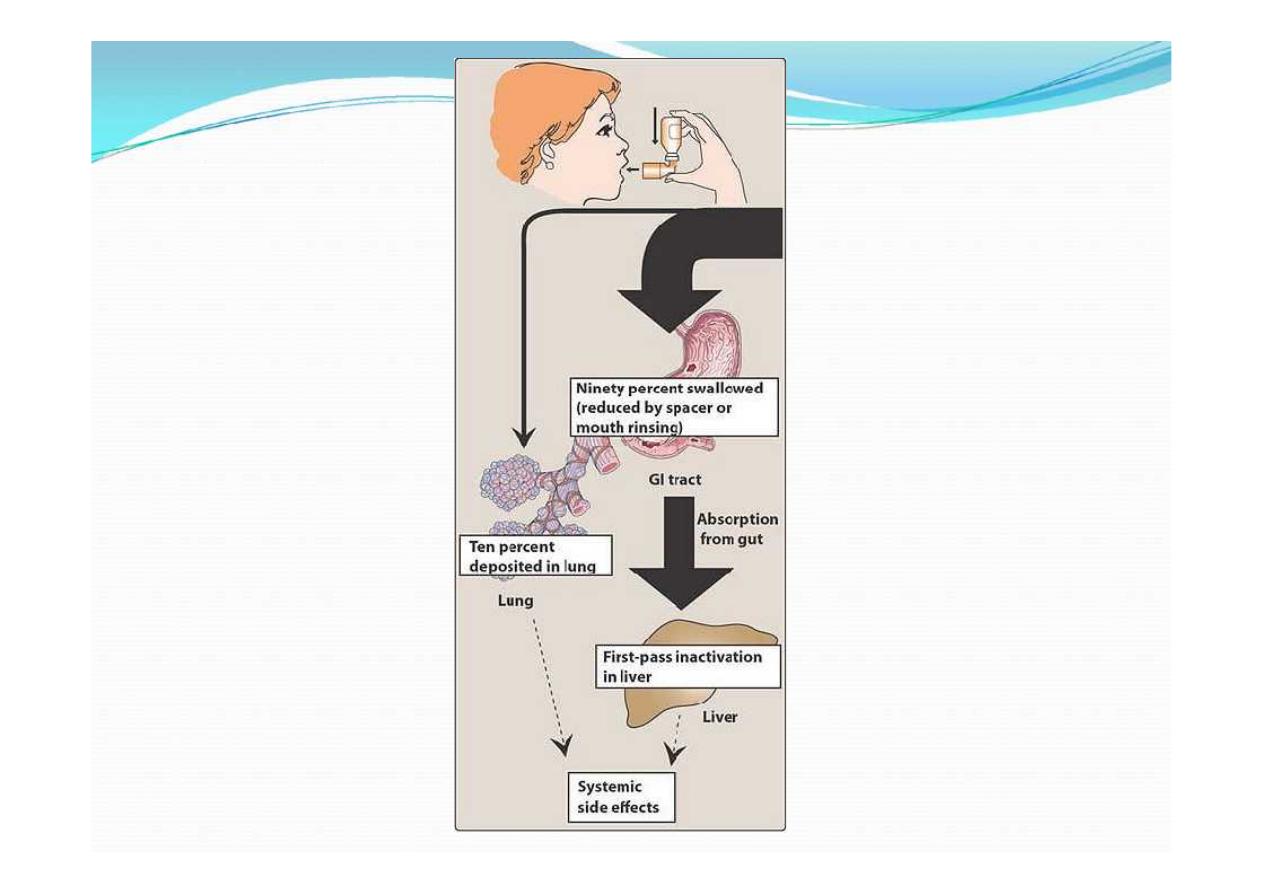
Inhaled Corticosteroids Side Effects:
Pharyngeal irritation
Coughing
Dry mouth
Oral fungal infections (so gargle and rinse the mouth
with water afterward to prevent the development of
oral fungal infection)
Dysphonia (horseness)
Inhaled Corticosteroids Side Effects:
Pharyngeal irritation
Coughing
Dry mouth
Oral fungal infections (so gargle and rinse the mouth
with water afterward to prevent the development of
oral fungal infection)
Dysphonia (horseness)

Oral or parenteral glucocorticoids have a variety of
Adverse effects and potentially serious side effects

2.Sodium cromoglicate (cromolyn, Intal)
MOA:
Stabilize the cell membranes of inflammatory cells
(mast cells, monocytes, macrophages
preventing release of harmful cellular
contents(Indirect-acting agents that prevent
bronchospasm)
2.Sodium cromoglicate (cromolyn, Intal)
MOA:
Stabilize the cell membranes of inflammatory cells
(mast cells, monocytes, macrophages
preventing release of harmful cellular
contents(Indirect-acting agents that prevent
bronchospasm)

pk:
o
poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
well absorbed from the lung given by inhalation (as powder,
aerosol or nebulizer)
o
eliminated unchanged in the urine and bile.

Uses:
chronic asthma
Children asthma
Pregnant wemon
Exercise induced asthma
Allergic rhinitis
3.Other drugs. Ketotifen is a histamine H1-receptor
blocker which may also have some antiasthma
Effects .In common with other antihistamines
it causes drowsiness.
Uses:
chronic asthma
Children asthma
Pregnant wemon
Exercise induced asthma
Allergic rhinitis
3.Other drugs. Ketotifen is a histamine H1-receptor
blocker which may also have some antiasthma
Effects .In common with other antihistamines
it causes drowsiness.

bronchodilators
1.
Adrenergic agonists
2.
Xanthine Derivatives
3.
Antimuscarinic bronchodilator
bronchodilators
1.
Adrenergic agonists
2.
Xanthine Derivatives
3.
Antimuscarinic bronchodilator

1.Adrenergic agonists
Nonselective adrenergics
Stimulate alpha
1
, beta
1
(cardiac), and beta
2
(respiratory)
receptors.
Example: epinephrine are less safe, being
more likely to cause cardiac arrhythmias
Nonselective beta-adrenergics
Stimulate both beta
1
and beta
2
receptors.
Example: isoproterenol
Selective beta
2
drugs
Stimulate only beta
2
receptors.
Example: albuterol
1.Adrenergic agonists
Nonselective adrenergics
Stimulate alpha
1
, beta
1
(cardiac), and beta
2
(respiratory)
receptors.
Example: epinephrine are less safe, being
more likely to cause cardiac arrhythmias
Nonselective beta-adrenergics
Stimulate both beta
1
and beta
2
receptors.
Example: isoproterenol
Selective beta
2
drugs
Stimulate only beta
2
receptors.
Example: albuterol

BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS
MOA
Activation of beta
2
receptors activate cAMP, which
relaxes smooth muscles of the airway and results
in bronchial dilation and increased airflow.
B2- adrenoceptor activation also stabilises mast cells
BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS
MOA
Activation of beta
2
receptors activate cAMP, which
relaxes smooth muscles of the airway and results
in bronchial dilation and increased airflow.
B2- adrenoceptor activation also stabilises mast cells

BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS
Albuterol, terbutaline, salbutamol
Short-acting
Rapid onset of action 15-30min and provide
relief for 4-6 hours
Drug of choice for acute asthma
BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS
Albuterol, terbutaline, salbutamol
Short-acting
Rapid onset of action 15-30min and provide
relief for 4-6 hours
Drug of choice for acute asthma
BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS
Albuterol, terbutaline, salbutamol
Short-acting
Rapid onset of action 15-30min and provide
relief for 4-6 hours
Drug of choice for acute asthma
BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS
Albuterol, terbutaline, salbutamol
Short-acting
Rapid onset of action 15-30min and provide
relief for 4-6 hours
Drug of choice for acute asthma

BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS
Salmeterol and formoterol
Slow onset of action
Long-acting
12 h or more
Used for prophylaxis
BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS
Salmeterol and formoterol
Slow onset of action
Long-acting
12 h or more
Used for prophylaxis
BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS
Salmeterol and formoterol
Slow onset of action
Long-acting
12 h or more
Used for prophylaxis
BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS
Salmeterol and formoterol
Slow onset of action
Long-acting
12 h or more
Used for prophylaxis

Side effect:
Cardiac arrythmia(dose depended)
Oral and parenteral B2 agonist cause vasodilatation in
the skeletal muscle vessels and this may lead to
hypotension and tremor.
Side effect:
Cardiac arrythmia(dose depended)
Oral and parenteral B2 agonist cause vasodilatation in
the skeletal muscle vessels and this may lead to
hypotension and tremor.

Xanthine Derivatives
Theophylline, a methylxanthine
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase (PDE),since this enzyme
hydrolyzes cyclic nucleotides and this lead to increase cAMP
cause bronchodilation by relaxing smooth muscles of the
airways.
relief of bronchospasm and greater airflow into and out of the
lungs.
causes CNS stimulation.
causes cardiovascular stimulation: increased force of
contraction and increased HR, resulting in increased cardiac
output
increased blood flow to the kidneys (diuretic effect).
Xanthine Derivatives
Theophylline, a methylxanthine
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase (PDE),since this enzyme
hydrolyzes cyclic nucleotides and this lead to increase cAMP
cause bronchodilation by relaxing smooth muscles of the
airways.
relief of bronchospasm and greater airflow into and out of the
lungs.
causes CNS stimulation.
causes cardiovascular stimulation: increased force of
contraction and increased HR, resulting in increased cardiac
output
increased blood flow to the kidneys (diuretic effect).

Pk:
rapid and complete Absorption from GIT
90% is metabolised by the liver
The tl/2 is 8 h
tobacco smoking enhances theophylline clearance by
inducing hepatic P450 enzymes.
low therapeutic index,
use of theophylline in status asthmaticus.
Pk:
rapid and complete Absorption from GIT
90% is metabolised by the liver
The tl/2 is 8 h
tobacco smoking enhances theophylline clearance by
inducing hepatic P450 enzymes.
low therapeutic index,
use of theophylline in status asthmaticus.

Side effect of theophyllin
nausea and diarrhoea, Vomiting ,Gastroesophageal reflux during
sleep
the chief dangers are cardiac arrhythmia, hypotension,
hypokalaemia and seizures.
DRUG INTERACTION of theophyllin
Enzyme inhibition by erythromycin, allopurinol or oral
contraceptives increases the plasma concentration of
theophylline;
enzyme inducers such as carbamazepine, phenytoin and
rifampicin reduce the concentration.
Side effect of theophyllin
nausea and diarrhoea, Vomiting ,Gastroesophageal reflux during
sleep
the chief dangers are cardiac arrhythmia, hypotension,
hypokalaemia and seizures.
DRUG INTERACTION of theophyllin
Enzyme inhibition by erythromycin, allopurinol or oral
contraceptives increases the plasma concentration of
theophylline;
enzyme inducers such as carbamazepine, phenytoin and
rifampicin reduce the concentration.

3.Antimuscarinic bronchodilators
Blockade of muscarinic (M3) receptors and causes
bronchodilation,
the preferred antimuscarinics
ipratropium
oxitropium.
These synthetic compounds permanently charged
molecules ,prevents absorption after inhalation And
minimises antimuscarinic effects outside of the lung.
Uses:
acute severe asthma when combined with (B2-
adrenoceptor agonists.
3.Antimuscarinic bronchodilators
Blockade of muscarinic (M3) receptors and causes
bronchodilation,
the preferred antimuscarinics
ipratropium
oxitropium.
These synthetic compounds permanently charged
molecules ,prevents absorption after inhalation And
minimises antimuscarinic effects outside of the lung.
Uses:
acute severe asthma when combined with (B2-
adrenoceptor agonists.

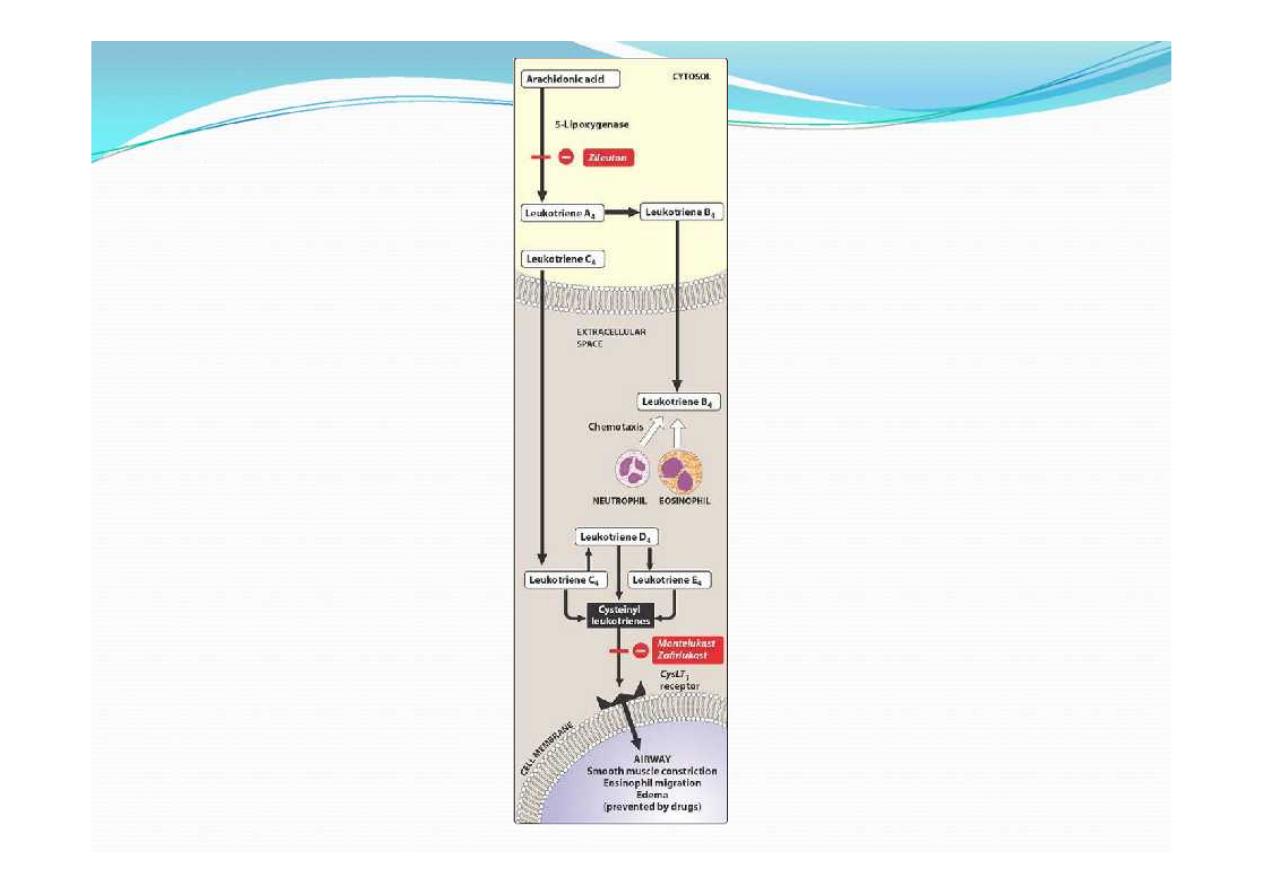
Leukotriene receptor antagonists
montelukast
zafirlukast
zileuton
MOA:
montelukast Zafirlukast are competitively prevent the
bronchoconstrictor effects of leukotrienes
(by blocking their receptor)
prevent leukotrienes from attaching to receptors on cells
in the lungs and in circulation.
Blocking the Inflammation in the lungs
Leukotriene receptor antagonists
montelukast
zafirlukast
zileuton
MOA:
montelukast Zafirlukast are competitively prevent the
bronchoconstrictor effects of leukotrienes
(by blocking their receptor)
prevent leukotrienes from attaching to receptors on cells
in the lungs and in circulation.
Blocking the Inflammation in the lungs

Montelukast (once per day
Zafirlukast( twice per day)
Leukotriene receptor antagonists USES:
Prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma
Montelukast (once per day
Zafirlukast( twice per day)
Leukotriene receptor antagonists USES:
Prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma
