
Drugs used in Peptic ulcer

Regulation of gastric acid secretion
Regulation of gastric acid secretion
Gastric acid secretion is under the control of
Gastric acid secretion is under the control of 33
principal agonists: histamine, acetylcholine and
principal agonists: histamine, acetylcholine and
gastrine
gastrine.. The final common pathway is through
The final common pathway is through
the proton pump, H
the proton pump, H
++
/ K
/ K
++
ATPase
ATPase..
Inhibitiors
Inhibitiors of the activities of the first
of the activities of the first 22
secretagogues
secretagogues and of the proton pump have
and of the proton pump have
been developed
been developed
Regulation of gastric acid secretion
Regulation of gastric acid secretion
Gastric acid secretion is under the control of
Gastric acid secretion is under the control of 33
principal agonists: histamine, acetylcholine and
principal agonists: histamine, acetylcholine and
gastrine
gastrine.. The final common pathway is through
The final common pathway is through
the proton pump, H
the proton pump, H
++
/ K
/ K
++
ATPase
ATPase..
Inhibitiors
Inhibitiors of the activities of the first
of the activities of the first 22
secretagogues
secretagogues and of the proton pump have
and of the proton pump have
been developed
been developed
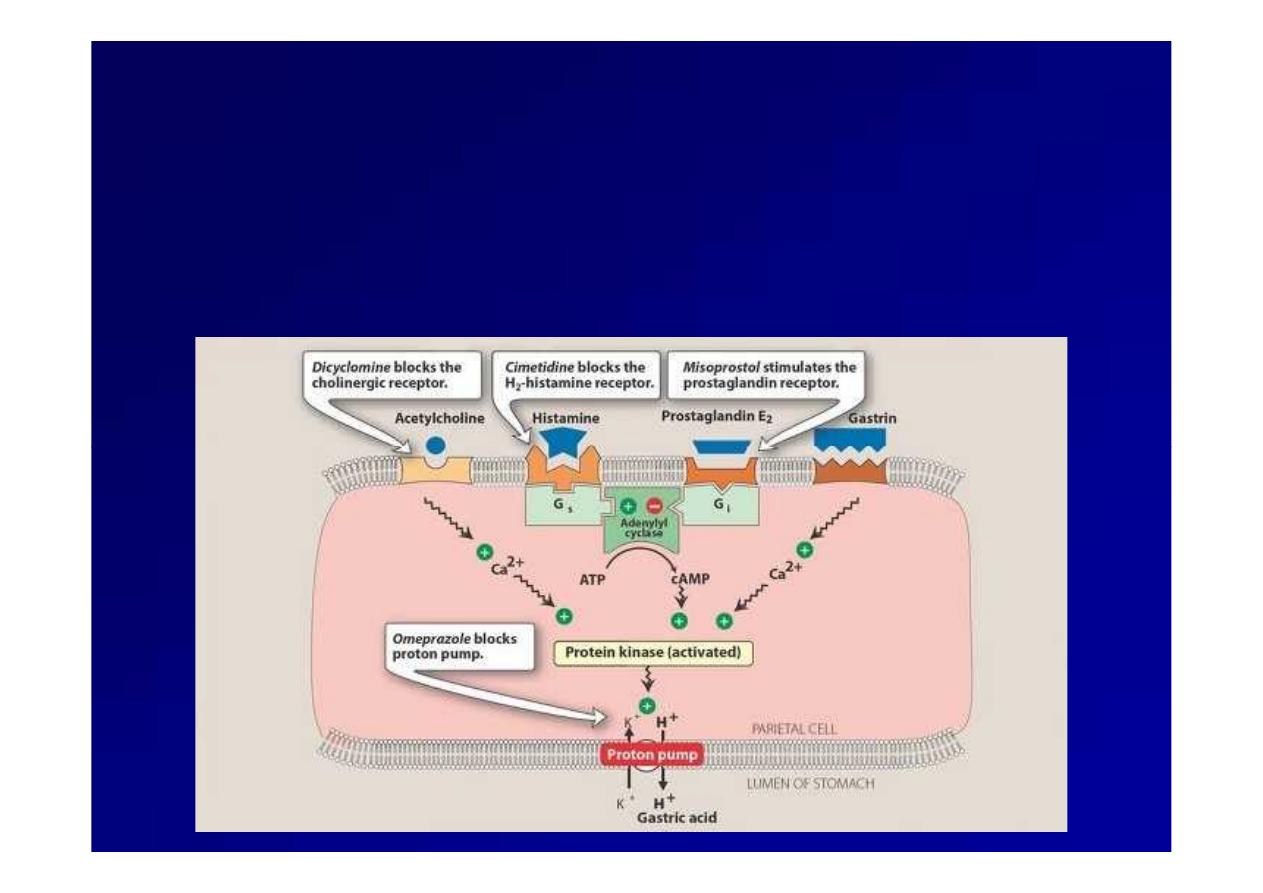
Effects of acetylcholine, histamine, prostaglandin E
Effects of acetylcholine, histamine, prostaglandin E22,,
and gastrin on gastric acid secretion by the parietal cells
and gastrin on gastric acid secretion by the parietal cells
of stomach.
of stomach. Gs
Gs and
and Gi
Gi are membrane proteins that
are membrane proteins that
mediate the stimulatory or inhibitory effect of receptor
mediate the stimulatory or inhibitory effect of receptor
coupling to adenylyl
coupling to adenylyl cyclase
cyclase
Histamine
Histamine
HH--22 Blocker
Blocker
ATP
ATP
cAMP
cAMP
Vagus
Vagus
Nerve
Nerve
From Circulation
From Circulation
Ca
Ca++
++
Ca
Ca++
++
Energy
Energy
H+/K+
H+/K+
ATPase
ATPase
Pump
Pump
H+
H+
K+
K+

Pathogenesis of peptic ulcer disease
Pathogenesis of peptic ulcer disease
Nonsteroidal
Nonsteroidal anti
anti--inflammatory drug
inflammatory drug
(NSAID) use.
(NSAID) use.
Infection with gram
Infection with gram--negative Helicobacter
negative Helicobacter
pylori
pylori
Increased hydrochloric acid secretion
Increased hydrochloric acid secretion
Inadequate mucosal defense against
Inadequate mucosal defense against
gastric acid.
gastric acid.
Pathogenesis of peptic ulcer disease
Pathogenesis of peptic ulcer disease
Nonsteroidal
Nonsteroidal anti
anti--inflammatory drug
inflammatory drug
(NSAID) use.
(NSAID) use.
Infection with gram
Infection with gram--negative Helicobacter
negative Helicobacter
pylori
pylori
Increased hydrochloric acid secretion
Increased hydrochloric acid secretion
Inadequate mucosal defense against
Inadequate mucosal defense against
gastric acid.
gastric acid.

Treatment approaches
Treatment approaches
1.
1. Eradicating the H. pylori infection
Eradicating the H. pylori infection
2.
2. Reducing secretion of gastric acid with the use
Reducing secretion of gastric acid with the use
of H
of H
22
--receptor antagonists or PPIs, and/or
receptor antagonists or PPIs, and/or
3.
3. protect the gastric mucosa from damage, such
protect the gastric mucosa from damage, such
as
as misoprostol
misoprostol and
and sucralfate
sucralfate..
4.
4. Neutralizing gastric acid with
Neutralizing gastric acid with nonabsorbable
nonabsorbable
antacids
antacids
5.
5. Surgical treatment in( acute complications )
Surgical treatment in( acute complications )
Treatment approaches
Treatment approaches
1.
1. Eradicating the H. pylori infection
Eradicating the H. pylori infection
2.
2. Reducing secretion of gastric acid with the use
Reducing secretion of gastric acid with the use
of H
of H
22
--receptor antagonists or PPIs, and/or
receptor antagonists or PPIs, and/or
3.
3. protect the gastric mucosa from damage, such
protect the gastric mucosa from damage, such
as
as misoprostol
misoprostol and
and sucralfate
sucralfate..
4.
4. Neutralizing gastric acid with
Neutralizing gastric acid with nonabsorbable
nonabsorbable
antacids
antacids
5.
5. Surgical treatment in( acute complications )
Surgical treatment in( acute complications )

Antimicrobial agents
Antimicrobial agents
Combinations of antimicrobial
Combinations of antimicrobial drugs.Give
drugs.Give 90
90 % or
% or
greater eradication rate.
greater eradication rate.
Triple therapy
Triple therapy consisting of a PPI with either
consisting of a PPI with either
metronidazole or amoxicillin plus
metronidazole or amoxicillin plus clarithromycin
clarithromycin
Or
Or
Quadruple therapy
Quadruple therapy of bismuth subsalicylate and
of bismuth subsalicylate and
metronidazole plus tetracycline plus a PPI
metronidazole plus tetracycline plus a PPI
Are administered for a
Are administered for a 22--week course.
week course.
Note:
Note:
Bismuth salts inhibit pepsin and increase the
Bismuth salts inhibit pepsin and increase the
secretion of mucus& form a barrier against the
secretion of mucus& form a barrier against the
diffusion of acid in the ulcer.
diffusion of acid in the ulcer.
Antimicrobial agents
Antimicrobial agents
Combinations of antimicrobial
Combinations of antimicrobial drugs.Give
drugs.Give 90
90 % or
% or
greater eradication rate.
greater eradication rate.
Triple therapy
Triple therapy consisting of a PPI with either
consisting of a PPI with either
metronidazole or amoxicillin plus
metronidazole or amoxicillin plus clarithromycin
clarithromycin
Or
Or
Quadruple therapy
Quadruple therapy of bismuth subsalicylate and
of bismuth subsalicylate and
metronidazole plus tetracycline plus a PPI
metronidazole plus tetracycline plus a PPI
Are administered for a
Are administered for a 22--week course.
week course.
Note:
Note:
Bismuth salts inhibit pepsin and increase the
Bismuth salts inhibit pepsin and increase the
secretion of mucus& form a barrier against the
secretion of mucus& form a barrier against the
diffusion of acid in the ulcer.
diffusion of acid in the ulcer.

Important
Important HH22--Antagonists
Antagonists
Cimetidine
Cimetidine
Ranitidine
Ranitidine
Famotidine
Famotidine
Nizatidine
Nizatidine
Roxitidine
Roxitidine
HH22 Antagonists bind to H
Antagonists bind to H22 receptor, preventing
receptor, preventing
histamine from binding to these receptors.
histamine from binding to these receptors.
Block
Block the action of histamine on stomach cell
the action of histamine on stomach cell
thus reducing stomach acid
thus reducing stomach acid
Important
Important HH22--Antagonists
Antagonists
Cimetidine
Cimetidine
Ranitidine
Ranitidine
Famotidine
Famotidine
Nizatidine
Nizatidine
Roxitidine
Roxitidine
HH22 Antagonists bind to H
Antagonists bind to H22 receptor, preventing
receptor, preventing
histamine from binding to these receptors.
histamine from binding to these receptors.
Block
Block the action of histamine on stomach cell
the action of histamine on stomach cell
thus reducing stomach acid
thus reducing stomach acid

Indication of use of H
Indication of use of H22--Antagonists :
Antagonists :
1.
1. Peptic
Peptic ulcer
ulcer..
2.
2. Gastro esophageal reflux disease(GERD)
Gastro esophageal reflux disease(GERD)
3.
3. Erosive
Erosive esophagitis.
esophagitis.
4.
4. Zollinger
Zollinger--Ellison
Ellison syndrome.
syndrome.
5.
5. Before
Before anesthesia
anesthesia
..

Cimetidine
Cimetidine: cause
: cause gynecomastia
gynecomastia,, galactorrhea
galactorrhea,,
and reduced sperm count& inhibits metabolism
and reduced sperm count& inhibits metabolism
of
of warfarin
warfarin,, phenytoin
phenytoin..
Ranitidine:
Ranitidine: Compared to
Compared to cimetidine
cimetidine, ranitidine is
, ranitidine is
longer acting, and is
longer acting, and is 55--10
10 fold more potent.
fold more potent.
Famotidine
Famotidine isis 33--20
20 times more potent than
times more potent than
ranitidine.
ranitidine.
Are metabolized by liver but
Are metabolized by liver but nizatidine
nizatidine isis
eliminated principally by kidney
eliminated principally by kidney
..
Cimetidine
Cimetidine: cause
: cause gynecomastia
gynecomastia,, galactorrhea
galactorrhea,,
and reduced sperm count& inhibits metabolism
and reduced sperm count& inhibits metabolism
of
of warfarin
warfarin,, phenytoin
phenytoin..
Ranitidine:
Ranitidine: Compared to
Compared to cimetidine
cimetidine, ranitidine is
, ranitidine is
longer acting, and is
longer acting, and is 55--10
10 fold more potent.
fold more potent.
Famotidine
Famotidine isis 33--20
20 times more potent than
times more potent than
ranitidine.
ranitidine.
Are metabolized by liver but
Are metabolized by liver but nizatidine
nizatidine isis
eliminated principally by kidney
eliminated principally by kidney
..

Pharmacokinetic of H
Pharmacokinetic of H22--Antagonists :
Antagonists :
Well absorbed from the gut.
Well absorbed from the gut.
Undergo varying degrees of hepatic inactivation
Undergo varying degrees of hepatic inactivation
before being excreted in the urine.
before being excreted in the urine.
Half
Half--life is
life is 22--33 hours.
hours.
Duration of action is longer.
Duration of action is longer.
Administered once or twice daily
Administered once or twice daily
..
Pharmacokinetic of H
Pharmacokinetic of H22--Antagonists :
Antagonists :
Well absorbed from the gut.
Well absorbed from the gut.
Undergo varying degrees of hepatic inactivation
Undergo varying degrees of hepatic inactivation
before being excreted in the urine.
before being excreted in the urine.
Half
Half--life is
life is 22--33 hours.
hours.
Duration of action is longer.
Duration of action is longer.
Administered once or twice daily
Administered once or twice daily
..

Adverse effects
Adverse effects
1.
1. Central nervous system.
Central nervous system.
2.
2. Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular reaction.
reaction.
3.
3. Hepatic
Hepatic reaction.
reaction.
4.
4. Hematological
Hematological reaction.
reaction.
5.
5. Endocrine.
Endocrine.
6.
6. Risk to the fetus
Risk to the fetus
Adverse effects
Adverse effects
1.
1. Central nervous system.
Central nervous system.
2.
2. Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular reaction.
reaction.
3.
3. Hepatic
Hepatic reaction.
reaction.
4.
4. Hematological
Hematological reaction.
reaction.
5.
5. Endocrine.
Endocrine.
6.
6. Risk to the fetus
Risk to the fetus
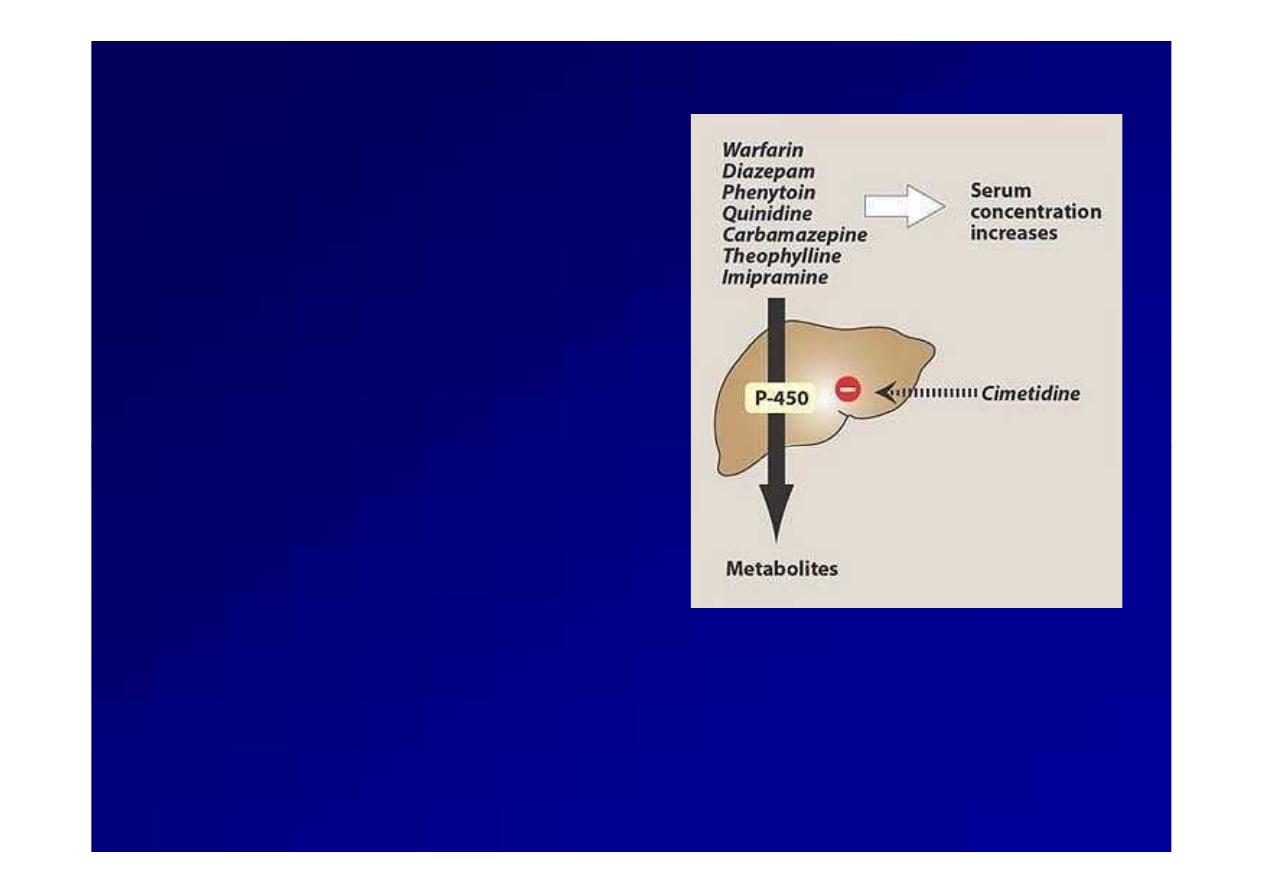
Cimetidine inhibits CYP
Cimetidine inhibits CYP450
450,,
slow metabolism &,
slow metabolism &,
potentiate the action of
potentiate the action of
warfarin, diazepam,
warfarin, diazepam,
phenytoin
phenytoin
Drug interactions with cimetidine
Drug interactions with cimetidine

Inhibitors of the H+/K+
Inhibitors of the H+/K+--ATPase
ATPase proton
proton
pump (PPIs
pump (PPIs
))
Omeprazole
Omeprazole
Lansoprazole
Lansoprazole
Rabeprazole
Rabeprazole
Pantoprazole
Pantoprazole
Esomeprazole
Esomeprazole
The proton pump inhibitors produce quicker
The proton pump inhibitors produce quicker
healing and provide greater symptomatic
healing and provide greater symptomatic
relief than H
relief than H
22
-- antagonists in patients with
antagonists in patients with
peptic ulcer disease and GERD
peptic ulcer disease and GERD
Inhibitors of the H+/K+
Inhibitors of the H+/K+--ATPase
ATPase proton
proton
pump (PPIs
pump (PPIs
))
Omeprazole
Omeprazole
Lansoprazole
Lansoprazole
Rabeprazole
Rabeprazole
Pantoprazole
Pantoprazole
Esomeprazole
Esomeprazole
The proton pump inhibitors produce quicker
The proton pump inhibitors produce quicker
healing and provide greater symptomatic
healing and provide greater symptomatic
relief than H
relief than H
22
-- antagonists in patients with
antagonists in patients with
peptic ulcer disease and GERD
peptic ulcer disease and GERD

Omeprazole
Omeprazole is the first drug of this class ,it
is the first drug of this class ,it
bind to the H
bind to the H
++
/K
/K
++
--ATPase
ATPase enzyme system
enzyme system
(proton pump) of the parietal cell, thereby
(proton pump) of the parietal cell, thereby
suppressing secretion of hydrogen ions into the
suppressing secretion of hydrogen ions into the
gastric lumen.
gastric lumen.
The proton pump is the final step in the
The proton pump is the final step in the
secretion of gastric acid
secretion of gastric acid
Omeprazole
Omeprazole is the first drug of this class ,it
is the first drug of this class ,it
bind to the H
bind to the H
++
/K
/K
++
--ATPase
ATPase enzyme system
enzyme system
(proton pump) of the parietal cell, thereby
(proton pump) of the parietal cell, thereby
suppressing secretion of hydrogen ions into the
suppressing secretion of hydrogen ions into the
gastric lumen.
gastric lumen.
The proton pump is the final step in the
The proton pump is the final step in the
secretion of gastric acid
secretion of gastric acid

Actions of PPIs
Actions of PPIs
These agents are
These agents are prodrugs
prodrugs with an acid
with an acid--
resistant enteric coating to protect them
resistant enteric coating to protect them
from premature degradation by gastric
from premature degradation by gastric
acid.
acid.
The coating is removed in the alkaline
The coating is removed in the alkaline
duodenum, and the
duodenum, and the prodrug
prodrug, a weak
, a weak
base, is absorbed and transported to the
base, is absorbed and transported to the
parietal cell
parietal cell canaliculus
canaliculus
..
Actions of PPIs
Actions of PPIs
These agents are
These agents are prodrugs
prodrugs with an acid
with an acid--
resistant enteric coating to protect them
resistant enteric coating to protect them
from premature degradation by gastric
from premature degradation by gastric
acid.
acid.
The coating is removed in the alkaline
The coating is removed in the alkaline
duodenum, and the
duodenum, and the prodrug
prodrug, a weak
, a weak
base, is absorbed and transported to the
base, is absorbed and transported to the
parietal cell
parietal cell canaliculus
canaliculus
..

Omeprazole
Omeprazole
Omeprazole
Omeprazole in itself is not the active
in itself is not the active
inhibitor of the H
inhibitor of the H
++
/ K
/ K
++
-- ATPase
ATPase. It needs
. It needs
transformation in acid media to an
transformation in acid media to an
intermediate compound, a
intermediate compound, a sulphenamide
sulphenamide,,
that effectively inhibits the H
that effectively inhibits the H
++
/ K
/ K
++
-- ATPase
ATPase
The
The sulphenamide
sulphenamide interacts covalently with
interacts covalently with
the
the sulphydryl
sulphydryl groups of
groups of cysteine
cysteine residues in
residues in
the extracellular domain of the H
the extracellular domain of the H
++
/ K
/ K
++
--
ATPase
ATPase, thereby inhibiting its activity
, thereby inhibiting its activity
Omeprazole
Omeprazole
Omeprazole
Omeprazole in itself is not the active
in itself is not the active
inhibitor of the H
inhibitor of the H
++
/ K
/ K
++
-- ATPase
ATPase. It needs
. It needs
transformation in acid media to an
transformation in acid media to an
intermediate compound, a
intermediate compound, a sulphenamide
sulphenamide,,
that effectively inhibits the H
that effectively inhibits the H
++
/ K
/ K
++
-- ATPase
ATPase
The
The sulphenamide
sulphenamide interacts covalently with
interacts covalently with
the
the sulphydryl
sulphydryl groups of
groups of cysteine
cysteine residues in
residues in
the extracellular domain of the H
the extracellular domain of the H
++
/ K
/ K
++
--
ATPase
ATPase, thereby inhibiting its activity
, thereby inhibiting its activity

Indications of PPIs
Indications of PPIs
1.
1. Peptic ulcer (Duodenal and Gastric ulcers
Peptic ulcer (Duodenal and Gastric ulcers
2.
2. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in the gut
Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in the gut
that causes ulcers in combination with
that causes ulcers in combination with
antibiotics
antibiotics
3.
3. NSAID
NSAID -- induced gastric ulcers
induced gastric ulcers
4.
4. Gastroesophageal
Gastroesophageal reflux disease ulcers
reflux disease ulcers
5.
5. Zollinger
Zollinger -- Ellison syndrome: proton pump
Ellison syndrome: proton pump
inhibitors are the treatment of choice for
inhibitors are the treatment of choice for
zollinger
zollinger -- Ellison syndrome
Ellison syndrome
Indications of PPIs
Indications of PPIs
1.
1. Peptic ulcer (Duodenal and Gastric ulcers
Peptic ulcer (Duodenal and Gastric ulcers
2.
2. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in the gut
Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in the gut
that causes ulcers in combination with
that causes ulcers in combination with
antibiotics
antibiotics
3.
3. NSAID
NSAID -- induced gastric ulcers
induced gastric ulcers
4.
4. Gastroesophageal
Gastroesophageal reflux disease ulcers
reflux disease ulcers
5.
5. Zollinger
Zollinger -- Ellison syndrome: proton pump
Ellison syndrome: proton pump
inhibitors are the treatment of choice for
inhibitors are the treatment of choice for
zollinger
zollinger -- Ellison syndrome
Ellison syndrome

Pharmacokinetics of PPIs
Pharmacokinetics of PPIs
All these agents are delayed
All these agents are delayed--release
release
formulations and are effective orally.
formulations and are effective orally.
Some are also available for intravenous
Some are also available for intravenous
injection.
injection.
Metabolites of these agents are excreted
Metabolites of these agents are excreted
in urine and feces.
in urine and feces.
Pharmacokinetics of PPIs
Pharmacokinetics of PPIs
All these agents are delayed
All these agents are delayed--release
release
formulations and are effective orally.
formulations and are effective orally.
Some are also available for intravenous
Some are also available for intravenous
injection.
injection.
Metabolites of these agents are excreted
Metabolites of these agents are excreted
in urine and feces.
in urine and feces.

Adverse effects of PPIs
Adverse effects of PPIs
1.
1. GIT: flatulence, diarrhea (by Clostridium
GIT: flatulence, diarrhea (by Clostridium
difficile
difficile colitis )or constipation, nausea,
colitis )or constipation, nausea,
vomiting or abdominal pain.
vomiting or abdominal pain.
2.
2. CNS:
CNS: paraesthesia
paraesthesia, dizziness, somnolence
, dizziness, somnolence
and headache.
and headache.
3.
3. Skin: rashes, itching
Skin: rashes, itching
4.
4. Muscle: pain (
Muscle: pain (myalgia
myalgia).).
5.
5. Kidney: Interstitial nephritis
Kidney: Interstitial nephritis
..
Adverse effects of PPIs
Adverse effects of PPIs
1.
1. GIT: flatulence, diarrhea (by Clostridium
GIT: flatulence, diarrhea (by Clostridium
difficile
difficile colitis )or constipation, nausea,
colitis )or constipation, nausea,
vomiting or abdominal pain.
vomiting or abdominal pain.
2.
2. CNS:
CNS: paraesthesia
paraesthesia, dizziness, somnolence
, dizziness, somnolence
and headache.
and headache.
3.
3. Skin: rashes, itching
Skin: rashes, itching
4.
4. Muscle: pain (
Muscle: pain (myalgia
myalgia).).
5.
5. Kidney: Interstitial nephritis
Kidney: Interstitial nephritis
..

Prostaglandins
Prostaglandins
Misoprostol
Misoprostol
Prostaglandin E
Prostaglandin E
22
, produced by the gastric mucosa, inhibits
, produced by the gastric mucosa, inhibits
secretion of
secretion of HCl
HCl and stimulates secretion of mucus and
and stimulates secretion of mucus and
bicarbonate (
bicarbonate (cytoprotective
cytoprotective effect).
effect).
Misoprostol
Misoprostol an analog of prostaglandin E
an analog of prostaglandin E
11
, as well as
, as well as
some PPIs, are used for prevention of gastric ulcers
some PPIs, are used for prevention of gastric ulcers
induced by NSAIDs (in the elderly )& also used in patients
induced by NSAIDs (in the elderly )& also used in patients
with ulcer complications
with ulcer complications
It is less effective than H
It is less effective than H
22
antagonists and the PPIs
antagonists and the PPIs
Side effects of
Side effects of Misoprostol
Misoprostol
1.
1. Produces uterine contractions
Produces uterine contractions
2.
2. Diarrhea and nausea
Diarrhea and nausea
Prostaglandins
Prostaglandins
Misoprostol
Misoprostol
Prostaglandin E
Prostaglandin E
22
, produced by the gastric mucosa, inhibits
, produced by the gastric mucosa, inhibits
secretion of
secretion of HCl
HCl and stimulates secretion of mucus and
and stimulates secretion of mucus and
bicarbonate (
bicarbonate (cytoprotective
cytoprotective effect).
effect).
Misoprostol
Misoprostol an analog of prostaglandin E
an analog of prostaglandin E
11
, as well as
, as well as
some PPIs, are used for prevention of gastric ulcers
some PPIs, are used for prevention of gastric ulcers
induced by NSAIDs (in the elderly )& also used in patients
induced by NSAIDs (in the elderly )& also used in patients
with ulcer complications
with ulcer complications
It is less effective than H
It is less effective than H
22
antagonists and the PPIs
antagonists and the PPIs
Side effects of
Side effects of Misoprostol
Misoprostol
1.
1. Produces uterine contractions
Produces uterine contractions
2.
2. Diarrhea and nausea
Diarrhea and nausea

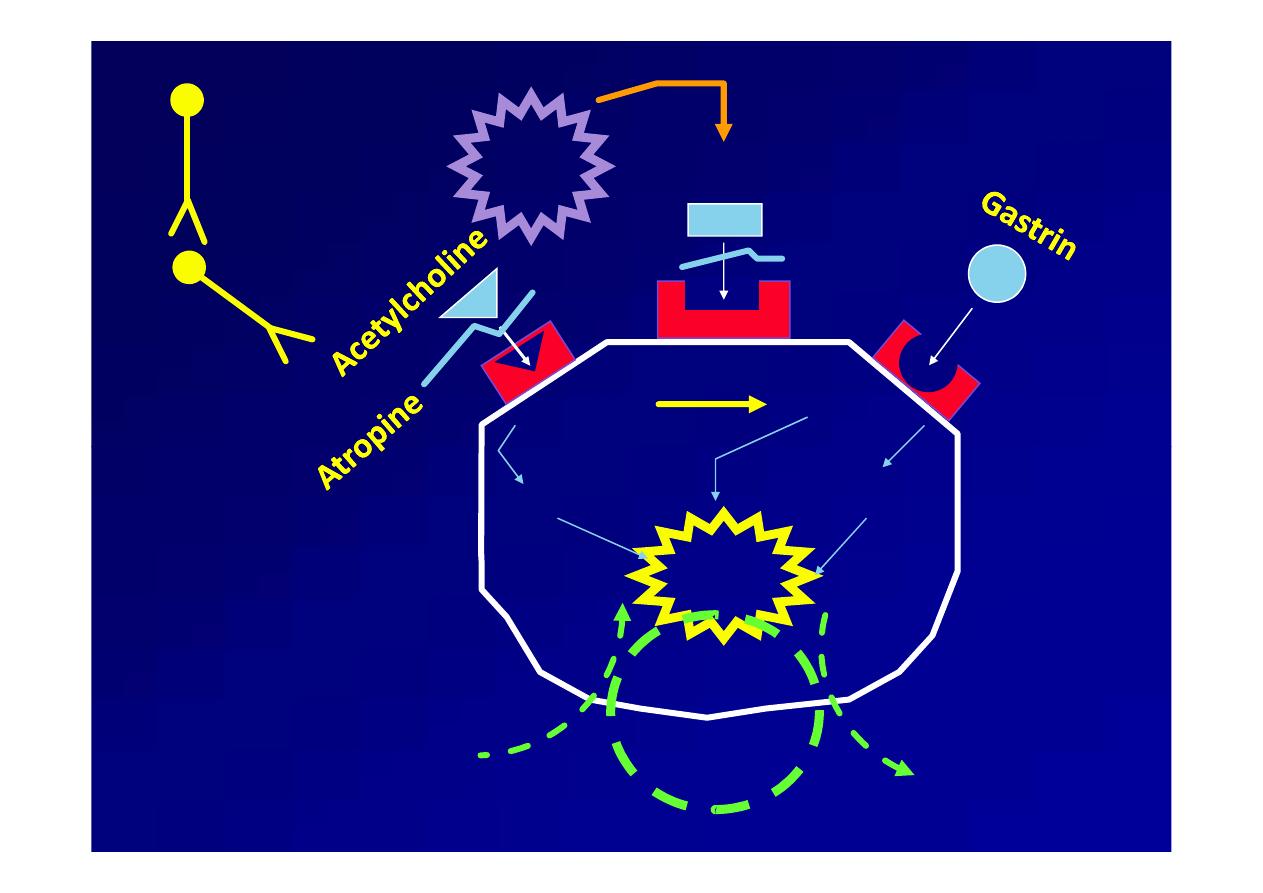
Antimuscarinic
Antimuscarinic agents (
agents (anticholinergic
anticholinergic agents)
agents)
Muscarinic
Muscarinic receptor stimulation increases
receptor stimulation increases
gastrointestinal motility and
gastrointestinal motility and secretory
secretory activity.
activity.
A cholinergic antagonist, such as
A cholinergic antagonist, such as dicyclomine
dicyclomine can
can
be used as an adjunct in the management of
be used as an adjunct in the management of
peptic ulcer disease and
peptic ulcer disease and Zollinger
Zollinger--Ellison
Ellison
syndrome, particularly in patients who are
syndrome, particularly in patients who are
refractory to standard therapies.
refractory to standard therapies.
Its many side effects (for example, cardiac
Its many side effects (for example, cardiac
arrhythmias, dry mouth, constipation, and urinary
arrhythmias, dry mouth, constipation, and urinary
retention) limit its use.
retention) limit its use.
Antimuscarinic
Antimuscarinic agents (
agents (anticholinergic
anticholinergic agents)
agents)
Muscarinic
Muscarinic receptor stimulation increases
receptor stimulation increases
gastrointestinal motility and
gastrointestinal motility and secretory
secretory activity.
activity.
A cholinergic antagonist, such as
A cholinergic antagonist, such as dicyclomine
dicyclomine can
can
be used as an adjunct in the management of
be used as an adjunct in the management of
peptic ulcer disease and
peptic ulcer disease and Zollinger
Zollinger--Ellison
Ellison
syndrome, particularly in patients who are
syndrome, particularly in patients who are
refractory to standard therapies.
refractory to standard therapies.
Its many side effects (for example, cardiac
Its many side effects (for example, cardiac
arrhythmias, dry mouth, constipation, and urinary
arrhythmias, dry mouth, constipation, and urinary
retention) limit its use.
retention) limit its use.

Antacids
Antacids
Aluminum hydroxide
Aluminum hydroxide
Magnesium hydroxide
Magnesium hydroxide
Calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate
Sodium bicarbonate.
Sodium bicarbonate.
Are weak bases that react with gastric acid to
Are weak bases that react with gastric acid to
form water and a salt, thereby diminishing
form water and a salt, thereby diminishing
gastric acidity. Because pepsin is inactive at a pH
gastric acidity. Because pepsin is inactive at a pH
greater than
greater than 44, antacids also reduce pepsin
, antacids also reduce pepsin
activity.
activity.
Used for symptomatic relief of peptic ulcer
Used for symptomatic relief of peptic ulcer
disease and GERD; they may promote healing of
disease and GERD; they may promote healing of
duodenal ulcers
duodenal ulcers
Antacids
Antacids
Aluminum hydroxide
Aluminum hydroxide
Magnesium hydroxide
Magnesium hydroxide
Calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate
Sodium bicarbonate.
Sodium bicarbonate.
Are weak bases that react with gastric acid to
Are weak bases that react with gastric acid to
form water and a salt, thereby diminishing
form water and a salt, thereby diminishing
gastric acidity. Because pepsin is inactive at a pH
gastric acidity. Because pepsin is inactive at a pH
greater than
greater than 44, antacids also reduce pepsin
, antacids also reduce pepsin
activity.
activity.
Used for symptomatic relief of peptic ulcer
Used for symptomatic relief of peptic ulcer
disease and GERD; they may promote healing of
disease and GERD; they may promote healing of
duodenal ulcers
duodenal ulcers

Adverse effects
Adverse effects
1.
1. Constipating (aluminum hydroxide)
Constipating (aluminum hydroxide)
2.
2. Diarrhea (magnesium hydroxide)
Diarrhea (magnesium hydroxide)
3.
3. Preparations that combine these agents aid
Preparations that combine these agents aid
in normalizing bowel function.
in normalizing bowel function.
4.
4. Important consideration in patients with
Important consideration in patients with
hypertension or congestive heart failure
hypertension or congestive heart failure
(sodium content of antacids)
(sodium content of antacids)
Adverse effects
Adverse effects
1.
1. Constipating (aluminum hydroxide)
Constipating (aluminum hydroxide)
2.
2. Diarrhea (magnesium hydroxide)
Diarrhea (magnesium hydroxide)
3.
3. Preparations that combine these agents aid
Preparations that combine these agents aid
in normalizing bowel function.
in normalizing bowel function.
4.
4. Important consideration in patients with
Important consideration in patients with
hypertension or congestive heart failure
hypertension or congestive heart failure
(sodium content of antacids)
(sodium content of antacids)

Mucosal protective agents (
Mucosal protective agents (cytoprotective
cytoprotective
compounds)
compounds)
Sucralfate
Sucralfate
It is complex of aluminum hydroxide and sulfated
It is complex of aluminum hydroxide and sulfated
sucrose
sucrose
It Binds to positively charged groups in proteins of
It Binds to positively charged groups in proteins of
both normal and necrotic mucosa
both normal and necrotic mucosa
Forming complex gels with epithelial cells, &creates
Forming complex gels with epithelial cells, &creates
a physical barrier that impairs diffusion of
a physical barrier that impairs diffusion of HCl
HCl and
and
prevents degradation of mucus by pepsin and acid.
prevents degradation of mucus by pepsin and acid.
It also stimulates prostaglandin release as well as
It also stimulates prostaglandin release as well as
mucus and bicarbonate output, and it inhibits
mucus and bicarbonate output, and it inhibits
peptic digestion
peptic digestion
It is effectively heals duodenal ulcers
It is effectively heals duodenal ulcers
Mucosal protective agents (
Mucosal protective agents (cytoprotective
cytoprotective
compounds)
compounds)
Sucralfate
Sucralfate
It is complex of aluminum hydroxide and sulfated
It is complex of aluminum hydroxide and sulfated
sucrose
sucrose
It Binds to positively charged groups in proteins of
It Binds to positively charged groups in proteins of
both normal and necrotic mucosa
both normal and necrotic mucosa
Forming complex gels with epithelial cells, &creates
Forming complex gels with epithelial cells, &creates
a physical barrier that impairs diffusion of
a physical barrier that impairs diffusion of HCl
HCl and
and
prevents degradation of mucus by pepsin and acid.
prevents degradation of mucus by pepsin and acid.
It also stimulates prostaglandin release as well as
It also stimulates prostaglandin release as well as
mucus and bicarbonate output, and it inhibits
mucus and bicarbonate output, and it inhibits
peptic digestion
peptic digestion
It is effectively heals duodenal ulcers
It is effectively heals duodenal ulcers

Bismuth subsalicylate
Bismuth subsalicylate
This compound effectively heal peptic ulcers.
This compound effectively heal peptic ulcers.
Have antimicrobial actions
Have antimicrobial actions
Inhibit the activity of pepsin
Inhibit the activity of pepsin
Increase secretion of mucus, and interact with
Increase secretion of mucus, and interact with
glycoproteins in necrotic mucosal tissue to
glycoproteins in necrotic mucosal tissue to
coat and protect the ulcer crater.
coat and protect the ulcer crater.
Bismuth subsalicylate
Bismuth subsalicylate
This compound effectively heal peptic ulcers.
This compound effectively heal peptic ulcers.
Have antimicrobial actions
Have antimicrobial actions
Inhibit the activity of pepsin
Inhibit the activity of pepsin
Increase secretion of mucus, and interact with
Increase secretion of mucus, and interact with
glycoproteins in necrotic mucosal tissue to
glycoproteins in necrotic mucosal tissue to
coat and protect the ulcer crater.
coat and protect the ulcer crater.
