
Drug Interactions
Drug Interactions
(Drug
(Drug--Drug Interactions)
Drug Interactions)

Drug
Drug –– Drug interaction:
Drug interaction:
It is the modification of the effect of one
drug (
the object drug
)
By
By
The prior or concomitant administration
of another (
precipitant drug
).
Drug
Drug –– Drug interaction:
Drug interaction:
It is the modification of the effect of one
drug (
the object drug
)
By
By
The prior or concomitant administration
of another (
precipitant drug
).

Outcomes of drug interactions
Outcomes of drug interactions
Desired (Beneficial
Effects)
undesired (Harmful
Effects)

Risk Factors for Drug Interactions
Risk Factors for Drug Interactions
High Risk Patients
Elderly, young, very sick, multiple disease
Multiple drug therapy, Renal, liver
impairment
High Risk Drugs
Narrow therapeutic index drugs e.g.(digoxin ,
warfarin , theophylline
Recognized enzyme inhibitors or inducers
Risk Factors for Drug Interactions
Risk Factors for Drug Interactions
High Risk Patients
Elderly, young, very sick, multiple disease
Multiple drug therapy, Renal, liver
impairment
High Risk Drugs
Narrow therapeutic index drugs e.g.(digoxin ,
warfarin , theophylline
Recognized enzyme inhibitors or inducers

Site of interaction:
Site of interaction:
Outside the body.
Inside the body
Site of interaction:
Site of interaction:
Outside the body.
Inside the body

Outside the body:
Outside the body:
Reaction of IV drugs resulting in solutions
after mixing that are not longer safe for the
patient alter stability(change the PH) or
structure leading to:
Loss of drug activity
Formation of precipitates.
Development of toxic product
Outside the body:
Outside the body:
Reaction of IV drugs resulting in solutions
after mixing that are not longer safe for the
patient alter stability(change the PH) or
structure leading to:
Loss of drug activity
Formation of precipitates.
Development of toxic product

Penicillin and aminoglycoside should
never be placed in the same infusion
fluid because of formation of inactive
complex.
Protamine zinc insulin + soluble insulin
lead to reduces the immediate effect of
the dose.
With calcium – ceftriaxone precipitates
in the lung and kidneys premature
neonates.
Penicillin and aminoglycoside should
never be placed in the same infusion
fluid because of formation of inactive
complex.
Protamine zinc insulin + soluble insulin
lead to reduces the immediate effect of
the dose.
With calcium – ceftriaxone precipitates
in the lung and kidneys premature
neonates.

Drug Interactions Inside the body
Drug Interactions Inside the body
Pharmacokinetics
drug
interactions
Pharmacodynamics
drug
interactions
Drug Interactions Inside the body
Drug Interactions Inside the body
Pharmacokinetics
drug
interactions
Pharmacodynamics
drug
interactions

Pharmacokinetics drug interactions
Pharmacokinetics drug interactions
Involve the effect of a drug on another
from the point of view that includes :
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
Pharmacokinetics drug interactions
Pharmacokinetics drug interactions
Involve the effect of a drug on another
from the point of view that includes :
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion

Interaction at the site of absorption
Interaction at the site of absorption
1. Formation of drug Chelates or
complexes.
2. Altered gut Flora
3. Altered GIT Motility.
4. Altered PH
5. Drug induced Mucosal damage
6. Malabsorption caused by other drugs
7. Interaction other than in the Gut
Interaction at the site of absorption
Interaction at the site of absorption
1. Formation of drug Chelates or
complexes.
2. Altered gut Flora
3. Altered GIT Motility.
4. Altered PH
5. Drug induced Mucosal damage
6. Malabsorption caused by other drugs
7. Interaction other than in the Gut

11. Direct chemical interaction in the gut and
. Direct chemical interaction in the gut and
formation of drug
formation of drug
Chelates
Chelates
or complex
or complex
Calcium (milk), iron, anti acid (Al or Mg
hydroxide) +
Tetracyclin
insoluble
complex
levothyroxine ,digoxine and some acidic
drugs e.g warfarine +
Colestyramine
decrease their absorption
11. Direct chemical interaction in the gut and
. Direct chemical interaction in the gut and
formation of drug
formation of drug
Chelates
Chelates
or complex
or complex
Calcium (milk), iron, anti acid (Al or Mg
hydroxide) +
Tetracyclin
insoluble
complex
levothyroxine ,digoxine and some acidic
drugs e.g warfarine +
Colestyramine
decrease their absorption

22. Altered
. Altered intestinal bacterial flora
intestinal bacterial flora
Antibiotics
kill a large number of the normal
flora of the intestine
Antimicrobials
may potentiates
Oral
Anticoagulant
by reducing bacterial synthesis
of vitamin K
In 10% 0f patients receiving
Digoxin
…..40% or
more
of the administered dose is metabolized by
the intestinal flora
Increase digoxin conc.
and increase its toxicity
22. Altered
. Altered intestinal bacterial flora
intestinal bacterial flora
Antibiotics
kill a large number of the normal
flora of the intestine
Antimicrobials
may potentiates
Oral
Anticoagulant
by reducing bacterial synthesis
of vitamin K
In 10% 0f patients receiving
Digoxin
…..40% or
more
of the administered dose is metabolized by
the intestinal flora
Increase digoxin conc.
and increase its toxicity

Antibiotics and Oral Contraceptives
Antibiotics and Oral Contraceptives
Antibiotics kill bacteria in gut
Oestrogen conjugates not hydrolysed
Conjugates not re-absorbed
Less oestrogen - loss of contraceptive effect
(No effect on progestogen component.)
Antibiotics and Oral Contraceptives
Antibiotics and Oral Contraceptives
Antibiotics kill bacteria in gut
Oestrogen conjugates not hydrolysed
Conjugates not re-absorbed
Less oestrogen - loss of contraceptive effect
(No effect on progestogen component.)

33. Altered gut motility
. Altered gut motility
Slowing
of gastric emptying such as
antimuscarinic drugs and opiate analgesics
anticholinergics
anticholinergics + acetaminophen
+ acetaminophen
Impact: delay in absorption of
Impact: delay in absorption of
acetaminophen
acetaminophen
OR
OR
Accelerated
by drugs e.g metclopromide
which hasten gastric emptying
33. Altered gut motility
. Altered gut motility
Slowing
of gastric emptying such as
antimuscarinic drugs and opiate analgesics
anticholinergics
anticholinergics + acetaminophen
+ acetaminophen
Impact: delay in absorption of
Impact: delay in absorption of
acetaminophen
acetaminophen
OR
OR
Accelerated
by drugs e.g metclopromide
which hasten gastric emptying

44. Altered PH.
. Altered PH.
The
non-ionized
form of a drug is more
lipid soluble and more readily absorbed
from GIT than the
ionized
form does.

HH--22 blockers , anti acid +
blockers , anti acid + ketoconazole
ketoconazole
Decrease gastric acid
Decrease gastric acid
,, dissolution of
dissolution of
ketoconazole
ketoconazole is decreased, resulting in
is decreased, resulting in
reduced absorption
reduced absorption
Therefore
, These drugs must be separated
by at least 2h
in the time of administration.
HH--22 blockers , anti acid +
blockers , anti acid + ketoconazole
ketoconazole
Decrease gastric acid
Decrease gastric acid
,, dissolution of
dissolution of
ketoconazole
ketoconazole is decreased, resulting in
is decreased, resulting in
reduced absorption
reduced absorption
Therefore
, These drugs must be separated
by at least 2h
in the time of administration.

55. Drug
. Drug--induced
induced mucosal
mucosal damage:
damage:
Colchicine (which cause local Mucosal
damage)
Can
decrease absorption
of poorly absorbed
drugs e.g. (digoxin, phenytoin)
55. Drug
. Drug--induced
induced mucosal
mucosal damage:
damage:
Colchicine (which cause local Mucosal
damage)
Can
decrease absorption
of poorly absorbed
drugs e.g. (digoxin, phenytoin)

6
-Malabsorption
caused by other
drugs
Orlistat
(Xenical)
Inhibits pancreatic
lipases ,preventing hydrolysis of ingested fat)
Orlistat
(Xenical) +
fat soluble
vitamins (A,D,E,K)
6
-Malabsorption
caused by other
drugs
Orlistat
(Xenical)
Inhibits pancreatic
lipases ,preventing hydrolysis of ingested fat)
Orlistat
(Xenical) +
fat soluble
vitamins (A,D,E,K)
malabsorption of Fat-soluble vitamins

77. Interaction
. Interaction
other than the gut
other than the gut
Addition of vasoconstrictors e.g
adrenalin to local anesthetics delay
absorption and prolong local anesthesia

Effect of drug distribution
Effect of drug distribution
Displacement from plasma protein binding
It depends on the affinity of the drug to
plasma protein.
The most likely bound drugs is capable to
displace others.
The free drug is increased.
Sodium valproates displaces phyentoin from
its binding site on plassma albumin in
addition to inhibit its metabolism
Effect of drug distribution
Effect of drug distribution
Displacement from plasma protein binding
It depends on the affinity of the drug to
plasma protein.
The most likely bound drugs is capable to
displace others.
The free drug is increased.
Sodium valproates displaces phyentoin from
its binding site on plassma albumin in
addition to inhibit its metabolism

Displacement from tissue bindings
Displacement from tissue bindings
Binding Quinidine with digoxin and
cause increase concentration of free
digoxin in addition to impair renal
excretion
Displacement from tissue bindings
Displacement from tissue bindings
Binding Quinidine with digoxin and
cause increase concentration of free
digoxin in addition to impair renal
excretion
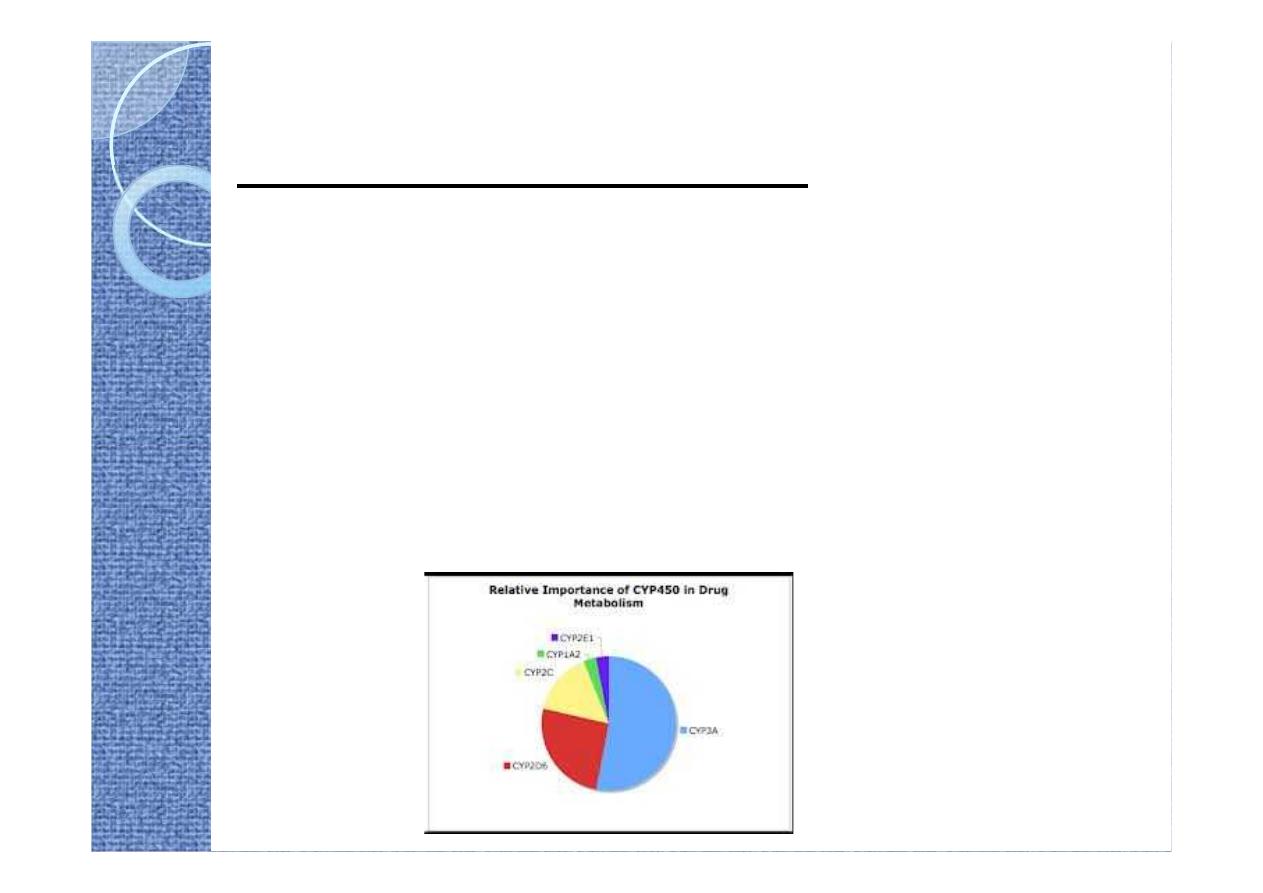
Altered drug
Altered drug metabolism
metabolism
The effect of one drug on the metabolism
of the other is well documented.
The liver is the major site of drug
metabolism
CYP450 family
is the major metabolizing
enzyme in phase I (oxidation process).
Altered drug
Altered drug metabolism
metabolism
The effect of one drug on the metabolism
of the other is well documented.
The liver is the major site of drug
metabolism
CYP450 family
is the major metabolizing
enzyme in phase I (oxidation process).

Effect on drug metabolism
Effect on drug metabolism
Enzyme induction
:the drug called(
inducer
)
A drug may induce the enzyme that is responsible for the
metabolism of another drug or even itself e.g:
Carbamazepine
(antiepileptic drug ) increases its
own
Metabolism
Phenytoin
increases hepatic metabolism of
Oral
Contraceptives
Leading to decreased level
Reduced
action and Unplanned Pregnancy
Phenobarbital
Phenobarbital
+ warfarin
metabolism of warfarin
(danger of thrombosis)
Effect on drug metabolism
Effect on drug metabolism
Enzyme induction
:the drug called(
inducer
)
A drug may induce the enzyme that is responsible for the
metabolism of another drug or even itself e.g:
Carbamazepine
(antiepileptic drug ) increases its
own
Metabolism
Phenytoin
increases hepatic metabolism of
Oral
Contraceptives
Leading to decreased level
Reduced
action and Unplanned Pregnancy
Phenobarbital
Phenobarbital
+ warfarin
metabolism of warfarin
(danger of thrombosis)

Enzyme
Enzyme inhibition
inhibition::
It is the decrease of the rate of metabolism of a
drug by another one.
This will lead to the
Increase
of the
concentration of the target drug and leading to
the increase of its
toxicity
.
Cimetidine
Cimetidine ++ Theophylline
Theophylline
cimetidine
cimetidine reduces the clearance of
reduces the clearance of theophylline
theophylline
causing an increase in adverse effects
causing an increase in adverse effects
Enzyme
Enzyme inhibition
inhibition::
It is the decrease of the rate of metabolism of a
drug by another one.
This will lead to the
Increase
of the
concentration of the target drug and leading to
the increase of its
toxicity
.
Cimetidine
Cimetidine ++ Theophylline
Theophylline
cimetidine
cimetidine reduces the clearance of
reduces the clearance of theophylline
theophylline
causing an increase in adverse effects
causing an increase in adverse effects

Inducer
(carbamazepine)
+
Inhibitor
(verapamil)
The effect of the Inhibitor will be
predominant
Inducer
(carbamazepine)
+
Inhibitor
(verapamil)
The effect of the Inhibitor will be
predominant

Most important
Most important
enzyme Inhibitors
enzyme Inhibitors
1. Cimetidine.
2. Erythromycine.
3. Quinolones.
4. Sodium valproate.
5. Allopurinol.
Most important
Most important
enzyme Inhibitors
enzyme Inhibitors
1. Cimetidine.
2. Erythromycine.
3. Quinolones.
4. Sodium valproate.
5. Allopurinol.

Alterations in renal clearance
Alterations in renal clearance
•• Increase in Renal Blood Flow
Increase in Renal Blood Flow
•• Inhibition of Active Tubular Secretion
Inhibition of Active Tubular Secretion
•• Alterations in Tubular
Alterations in Tubular Reabsorption
Reabsorption
Alterations in renal clearance
Alterations in renal clearance
•• Increase in Renal Blood Flow
Increase in Renal Blood Flow
•• Inhibition of Active Tubular Secretion
Inhibition of Active Tubular Secretion
•• Alterations in Tubular
Alterations in Tubular Reabsorption
Reabsorption

Increase in Renal Blood Flow
Increase in Renal Blood Flow
hydralazine
hydralazine ++ digoxin
digoxin
hydralazine
hydralazine increases the renal
increases the renal
clearance of
clearance of digoxin
digoxin
Increase in Renal Blood Flow
Increase in Renal Blood Flow
hydralazine
hydralazine ++ digoxin
digoxin
hydralazine
hydralazine increases the renal
increases the renal
clearance of
clearance of digoxin
digoxin

•• Active
Active tubular secretion:
tubular secretion:
It occurs in the proximal tubules.
The drug combines with a specific protein to pass through
the proximal tubules.
When a drug has a
competitive reactivity
to the protein
that is responsible for active transport of another drug
This will reduce such a drug excretion increasing its conce.
probenecid
probenecid + penicillin
+ penicillin
Decreases tubular secretion of
Pecicillin
•• Active
Active tubular secretion:
tubular secretion:
It occurs in the proximal tubules.
The drug combines with a specific protein to pass through
the proximal tubules.
When a drug has a
competitive reactivity
to the protein
that is responsible for active transport of another drug
This will reduce such a drug excretion increasing its conce.
probenecid
probenecid + penicillin
+ penicillin
Decreases tubular secretion of
Pecicillin

••
Passive tubular
Passive tubular Reabsorption
Reabsorption
Acidification
of urine increases reabsorption and
decreases excretion of weak acids, and, in contrast,
decreases reabsorption of weak bases.
Alkalinization
of urine has the opposite effect.
In some cases of overdose, these principles are used
to enhance the excretion of weak bases or acids
••
Passive tubular
Passive tubular Reabsorption
Reabsorption
Acidification
of urine increases reabsorption and
decreases excretion of weak acids, and, in contrast,
decreases reabsorption of weak bases.
Alkalinization
of urine has the opposite effect.
In some cases of overdose, these principles are used
to enhance the excretion of weak bases or acids
e.g. sodium bicarbonate
+
salicylates(weak acid)
decrease
reabsorption and Increase excretion of salicylates

Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics
Interaction
Interaction
Pharmacodynamics
are related to the
pharmacological activity of the interacting
drugs .
Both drugs act on the target site of clinical
effect.
Synergism
Summation or Additive
Potentiation
Antagonism
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics
Interaction
Interaction
Pharmacodynamics
are related to the
pharmacological activity of the interacting
drugs .
Both drugs act on the target site of clinical
effect.
Synergism
Summation or Additive
Potentiation
Antagonism
Results of drug interactions:
Results of drug interactions:
Synergism:
occures when the effects of 2 drugs
having the same action or increase the action of
another drugs
1-Summation(Additive):
Ex. β-adrenoceptor blocker + thiazide
additive
anti hypertension effect
1 + 1 = 2
2-Potentiation:
When one drug
Increase
the action of another
1 + 1 = more than 2
Ex. Trimethprim + sulfamethaxazole
Results of drug interactions:
Results of drug interactions:
Synergism:
occures when the effects of 2 drugs
having the same action or increase the action of
another drugs
1-Summation(Additive):
Ex. β-adrenoceptor blocker + thiazide
additive
anti hypertension effect
1 + 1 = 2
2-Potentiation:
When one drug
Increase
the action of another
1 + 1 = more than 2
Ex. Trimethprim + sulfamethaxazole

Antagonism
Antagonism
When the action of one drug
opposes
the
action of another.
1 + 1 = 0 (or 0.5)
Ex.
Histamine
and
Adrenaline
on
Bronchi(physiological
antagonism)
Flumazenil
and
diazepam
they compete
reversibly for the same drug
receptor(
competitive antagonism
)
Antagonism
Antagonism
When the action of one drug
opposes
the
action of another.
1 + 1 = 0 (or 0.5)
Ex.
Histamine
and
Adrenaline
on
Bronchi(physiological
antagonism)
Flumazenil
and
diazepam
they compete
reversibly for the same drug
receptor(
competitive antagonism
)

Interactions directly on Receptor or
Interactions directly on Receptor or
body system
body system
Actions on receptors
Beneficial interaction
Naloxone for morphin over dose(opiod
receptor)
Unwanted interaction
Atenolol +cold remedies containing
ephedrine or Phenylephrine loss of
antihypertensive effect
Interactions directly on Receptor or
Interactions directly on Receptor or
body system
body system
Actions on receptors
Beneficial interaction
Naloxone for morphin over dose(opiod
receptor)
Unwanted interaction
Atenolol +cold remedies containing
ephedrine or Phenylephrine loss of
antihypertensive effect

Action on body system
Action on body system
NSAIDs especially
indomethacin
+ α
adrenoicepter blocker lead to loss some
antihypertensive efficacy
By inhibition of production of vasodilator
prostpglandins by the kidney leading to
sodium retention
Action on body system
Action on body system
NSAIDs especially
indomethacin
+ α
adrenoicepter blocker lead to loss some
antihypertensive efficacy
By inhibition of production of vasodilator
prostpglandins by the kidney leading to
sodium retention

Onset of drug
Onset of drug interaction
interaction
•
It may be seconds up to weeks
•
For example in case of enzyme induction,
it needs weeks for protein synthesis
•
while enzyme inhibition occurs rapidly.
Onset of drug
Onset of drug interaction
interaction
•
It may be seconds up to weeks
•
For example in case of enzyme induction,
it needs weeks for protein synthesis
•
while enzyme inhibition occurs rapidly.
