
Anxiolytic
Anxiolytic ,,
Sedative
Sedative
and
and
Hypnotic
Hypnotic
Drugs
Drugs--2
2
Anxiolytic
Anxiolytic ,,
Sedative
Sedative
and
and
Hypnotic
Hypnotic
Drugs
Drugs--2
2

Benzodiazepines are the most widely
Benzodiazepines are the most widely
used
used anxiolytic
anxiolytic drugs.
drugs. They have largely
They have largely
replaced barbiturates because:
replaced barbiturates because:
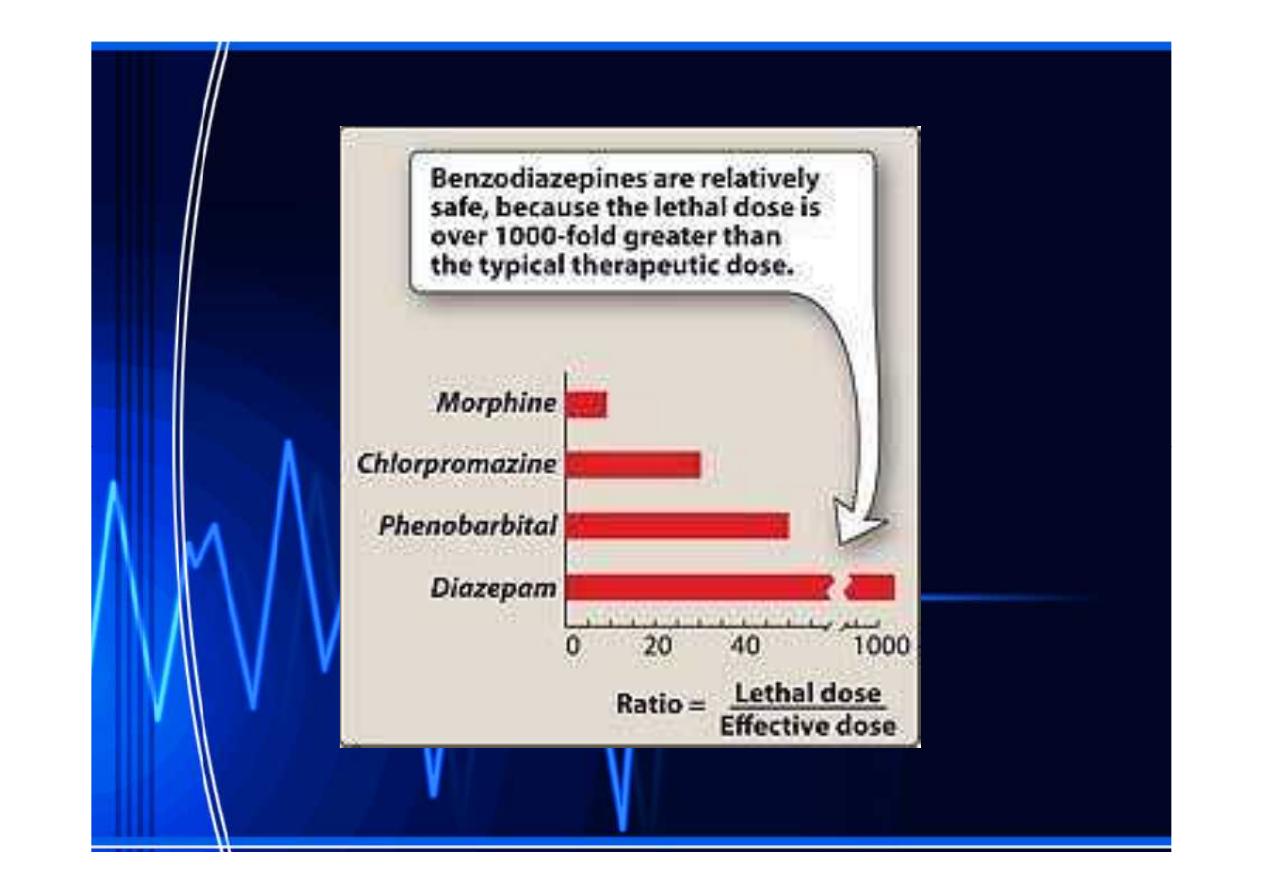
The
The benzodiazepines are safer(have a
benzodiazepines are safer(have a
wide
wide therapeutic index)
therapeutic index) and more
and more
effective
effective
Not
Not cause drug
cause drug –
– drug
drug interaction(not
interaction(not
induce hepatic
induce hepatic microsomal
microsomal enzyme)
enzyme)
Produce
Produce tolerance and psychological
tolerance and psychological
dependence but physical dependence
dependence but physical dependence
and withdrawal symptom are less
and withdrawal symptom are less marked
marked
Benzodiazepines are the most widely
Benzodiazepines are the most widely
used
used anxiolytic
anxiolytic drugs.
drugs. They have largely
They have largely
replaced barbiturates because:
replaced barbiturates because:
The
The benzodiazepines are safer(have a
benzodiazepines are safer(have a
wide
wide therapeutic index)
therapeutic index) and more
and more
effective
effective
Not
Not cause drug
cause drug –
– drug
drug interaction(not
interaction(not
induce hepatic
induce hepatic microsomal
microsomal enzyme)
enzyme)
Produce
Produce tolerance and psychological
tolerance and psychological
dependence but physical dependence
dependence but physical dependence
and withdrawal symptom are less
and withdrawal symptom are less marked
marked

Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are classified according to
are classified according to
their duration of action into:
their duration of action into:
Short
Short –
– acting
acting :: Oxazepam
Oxazepam,, Triazolam
Triazolam ((3
3--8
8))
hours
hours
Intermediate
Intermediate –
– acting
acting :: Alprazolam
Alprazolam,,
Lorazepam
Lorazepam,, Temazepam
Temazepam ((10
10--20
20)) hours
hours
Long
Long--acting
acting :: Chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide, Diazepam,
, Diazepam,
Flurazepam
Flurazepam,,
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are classified according to
are classified according to
their duration of action into:
their duration of action into:
Short
Short –
– acting
acting :: Oxazepam
Oxazepam,, Triazolam
Triazolam ((3
3--8
8))
hours
hours
Intermediate
Intermediate –
– acting
acting :: Alprazolam
Alprazolam,,
Lorazepam
Lorazepam,, Temazepam
Temazepam ((10
10--20
20)) hours
hours
Long
Long--acting
acting :: Chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide, Diazepam,
, Diazepam,
Flurazepam
Flurazepam,,

Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines
ANXIOLYTIC
ANXIOLYTIC:: Alprazolam
Alprazolam,,
chlordiazepoxide
chlordiazepoxide,, diazepam,
diazepam,
lorazepam
lorazepam
HYPNOTIC:
HYPNOTIC: Triazolam
Triazolam,, temazepam
temazepam,,
flurazepam
flurazepam..
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines
ANXIOLYTIC
ANXIOLYTIC:: Alprazolam
Alprazolam,,
chlordiazepoxide
chlordiazepoxide,, diazepam,
diazepam,
lorazepam
lorazepam
HYPNOTIC:
HYPNOTIC: Triazolam
Triazolam,, temazepam
temazepam,,
flurazepam
flurazepam..
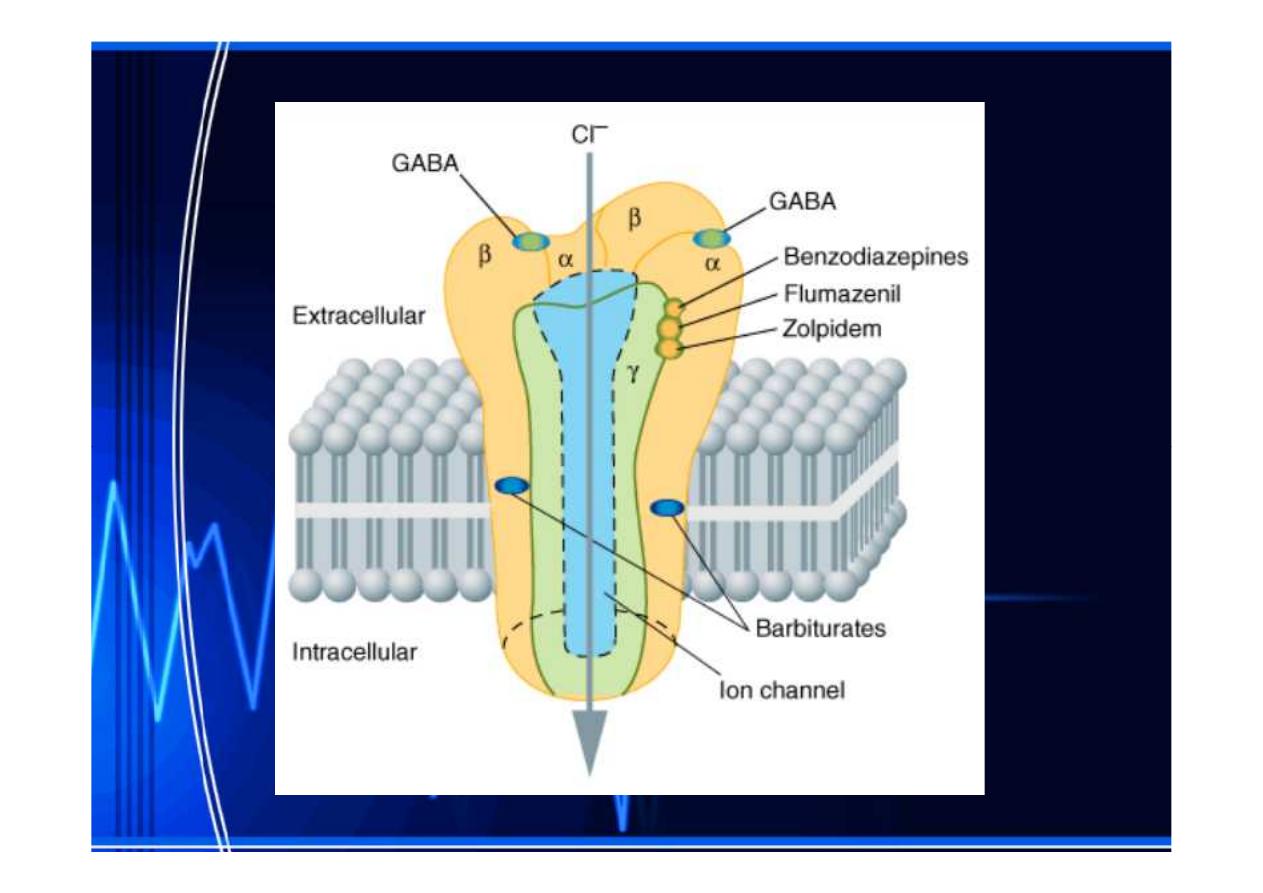
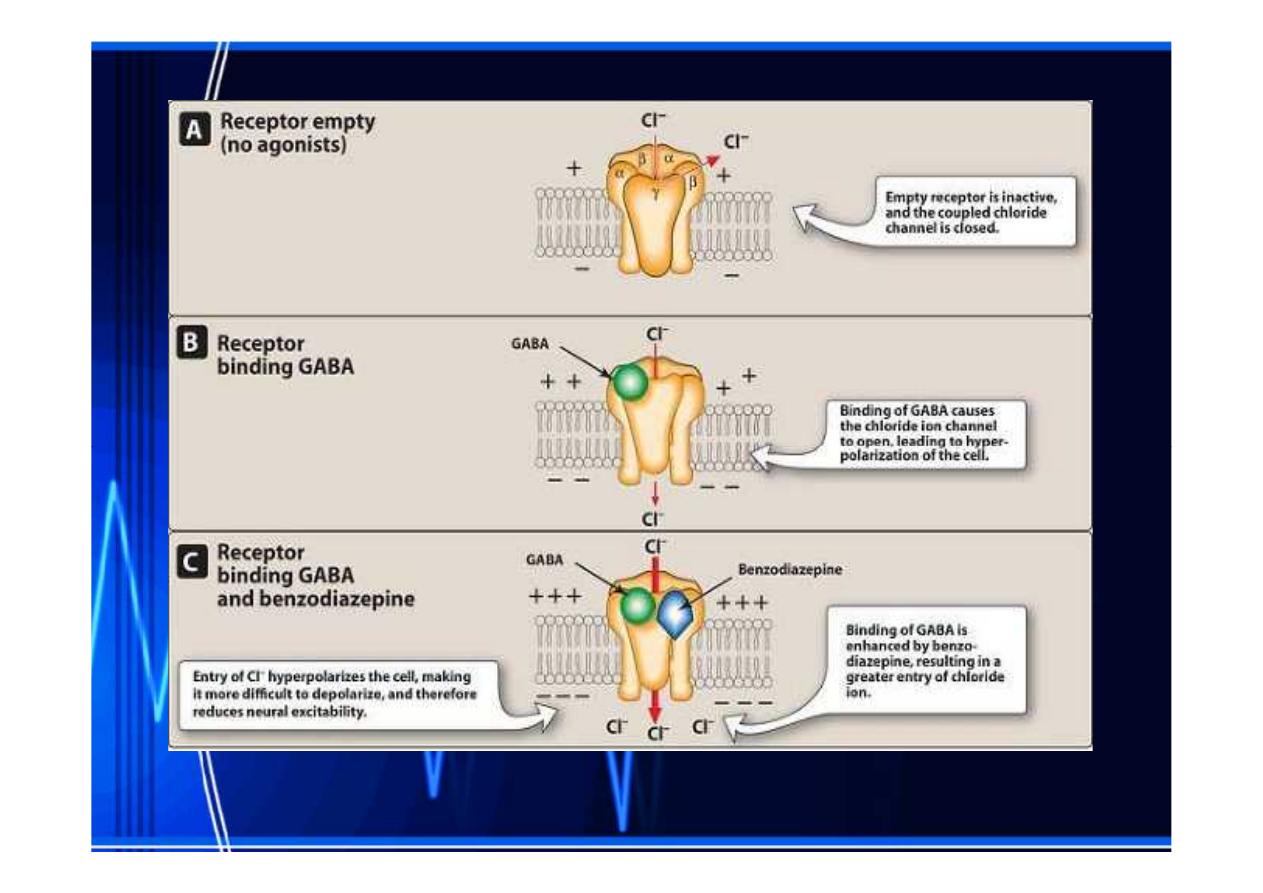
Mechanism of action:
Mechanism of action:
Binding of GABA (the major inhibitory
Binding of GABA (the major inhibitory
neurotransmitter in the central nervous
neurotransmitter in the central nervous
system
system)) to its receptor
to its receptor triggers
triggers an opening of
an opening of
a chloride channel
a chloride channel,, which leads to an
which leads to an
increase in chloride conductance
increase in chloride conductance
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines increase the frequency
increase the frequency of
of
channel openings produced by GABA. The
channel openings produced by GABA. The
influx of chloride ions causes
influx of chloride ions causes
hyperpolarization
hyperpolarization of the cell making it more
of the cell making it more
difficult to depolarize and there for reduces
difficult to depolarize and there for reduces
neural excitability
neural excitability
Mechanism of action:
Mechanism of action:
Binding of GABA (the major inhibitory
Binding of GABA (the major inhibitory
neurotransmitter in the central nervous
neurotransmitter in the central nervous
system
system)) to its receptor
to its receptor triggers
triggers an opening of
an opening of
a chloride channel
a chloride channel,, which leads to an
which leads to an
increase in chloride conductance
increase in chloride conductance
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines increase the frequency
increase the frequency of
of
channel openings produced by GABA. The
channel openings produced by GABA. The
influx of chloride ions causes
influx of chloride ions causes
hyperpolarization
hyperpolarization of the cell making it more
of the cell making it more
difficult to depolarize and there for reduces
difficult to depolarize and there for reduces
neural excitability
neural excitability

Actions
Actions::
The benzodiazepines have
The benzodiazepines have neither
neither
antipsychotic activity nor analgesic
antipsychotic activity nor analgesic action
action
Reduction of anxiety:
Reduction of anxiety: At low doses, the
At low doses, the
benzodiazepines are
benzodiazepines are anxiolytic
anxiolytic
..

Sedative and hypnotic actions:
Sedative and hypnotic actions: All of
All of
the benzodiazepines used to treat
the benzodiazepines used to treat
anxiety have some sedative properties,
anxiety have some sedative properties,
and some can produce hypnosis
and some can produce hypnosis
(artificially produced sleep) at higher
(artificially produced sleep) at higher
doses.
doses.
Anticonvulsant:
Anticonvulsant: some are used to treat
some are used to treat
epilepsy (status
epilepsy (status epilepticus
epilepticus)) and other
and other
seizure disorders.
seizure disorders.
Muscle relaxant:
Muscle relaxant: At high doses, the
At high doses, the
benzodiazepines relax the spasticity of
benzodiazepines relax the spasticity of
skeletal muscle
skeletal muscle
Sedative and hypnotic actions:
Sedative and hypnotic actions: All of
All of
the benzodiazepines used to treat
the benzodiazepines used to treat
anxiety have some sedative properties,
anxiety have some sedative properties,
and some can produce hypnosis
and some can produce hypnosis
(artificially produced sleep) at higher
(artificially produced sleep) at higher
doses.
doses.
Anticonvulsant:
Anticonvulsant: some are used to treat
some are used to treat
epilepsy (status
epilepsy (status epilepticus
epilepticus)) and other
and other
seizure disorders.
seizure disorders.
Muscle relaxant:
Muscle relaxant: At high doses, the
At high doses, the
benzodiazepines relax the spasticity of
benzodiazepines relax the spasticity of
skeletal muscle
skeletal muscle

Therapeutic
Therapeutic uses
uses::
Anxiety
Anxiety disorders: Benzodiazepines are
disorders: Benzodiazepines are
effective for the treatment of the
effective for the treatment of the anxiety.
anxiety.
generalized
generalized anxiety disorder,
anxiety disorder, specific phobias,
specific phobias,
such as fear of flying.
such as fear of flying.
Muscular disorders:
Muscular disorders: Diazepam is useful in the
Diazepam is useful in the
treatment of skeletal muscle spasms,
treatment of skeletal muscle spasms, multiple
multiple
sclerosis and cerebral palsy
sclerosis and cerebral palsy
..
Therapeutic
Therapeutic uses
uses::
Anxiety
Anxiety disorders: Benzodiazepines are
disorders: Benzodiazepines are
effective for the treatment of the
effective for the treatment of the anxiety.
anxiety.
generalized
generalized anxiety disorder,
anxiety disorder, specific phobias,
specific phobias,
such as fear of flying.
such as fear of flying.
Muscular disorders:
Muscular disorders: Diazepam is useful in the
Diazepam is useful in the
treatment of skeletal muscle spasms,
treatment of skeletal muscle spasms, multiple
multiple
sclerosis and cerebral palsy
sclerosis and cerebral palsy
..

The
The shorter
shorter--acting agents are
acting agents are used as
used as
premedication for anxiety
premedication for anxiety--provoking and
provoking and
unpleasant procedures, such as endoscopic,
unpleasant procedures, such as endoscopic,
bronchoscopic
bronchoscopic,, dental procedures.
dental procedures. They
They
cause
cause a form of conscious sedation, allowing
a form of conscious sedation, allowing
the person to
the person to be receptive to instructions
be receptive to instructions
during these procedures
during these procedures..
Midazolam
Midazolam is an
is an injectable
injectable--only
only
benzodiazepine also used for the induction
benzodiazepine also used for the induction
of anesthesia
of anesthesia
The
The shorter
shorter--acting agents are
acting agents are used as
used as
premedication for anxiety
premedication for anxiety--provoking and
provoking and
unpleasant procedures, such as endoscopic,
unpleasant procedures, such as endoscopic,
bronchoscopic
bronchoscopic,, dental procedures.
dental procedures. They
They
cause
cause a form of conscious sedation, allowing
a form of conscious sedation, allowing
the person to
the person to be receptive to instructions
be receptive to instructions
during these procedures
during these procedures..
Midazolam
Midazolam is an
is an injectable
injectable--only
only
benzodiazepine also used for the induction
benzodiazepine also used for the induction
of anesthesia
of anesthesia

Seizures:
Seizures:
Clonazepam
Clonazepam is occasionally used in the treatment
is occasionally used in the treatment
of certain types of
of certain types of epilepsy
epilepsy
Diazepam
Diazepam and
and lorazepam
lorazepam are the drugs of choice
are the drugs of choice
in terminating grand mal epileptic seizures and
in terminating grand mal epileptic seizures and
status
status epilepticus
epilepticus..
chlordiazepoxide
chlordiazepoxide,,
,, diazepam, and
diazepam, and oxazepam
oxazepam are
are
useful in the acute treatment of alcohol
useful in the acute treatment of alcohol
withdrawal
withdrawal
Seizures:
Seizures:
Clonazepam
Clonazepam is occasionally used in the treatment
is occasionally used in the treatment
of certain types of
of certain types of epilepsy
epilepsy
Diazepam
Diazepam and
and lorazepam
lorazepam are the drugs of choice
are the drugs of choice
in terminating grand mal epileptic seizures and
in terminating grand mal epileptic seizures and
status
status epilepticus
epilepticus..
chlordiazepoxide
chlordiazepoxide,,
,, diazepam, and
diazepam, and oxazepam
oxazepam are
are
useful in the acute treatment of alcohol
useful in the acute treatment of alcohol
withdrawal
withdrawal

Sleep
Sleep disorded
disorded ::Flurazepam
Flurazepam has a long
has a long--acting
acting
effect and causes
effect and causes no
no rebound insomnia.
rebound insomnia.
Temazepam
Temazepam:: This drug is useful in patients who
This drug is useful in patients who
experience frequent wakening.
experience frequent wakening. the
the peak sedative
peak sedative
effect occurs
effect occurs 1
1 to
to 3
3 hours after an oral dose;
hours after an oral dose; and
and
should
should be given
be given 1
1 to
to 2
2 hours before
hours before bedtime
bedtime..
Triazolam
Triazolam:: short duration of action and, therefore,
short duration of action and, therefore,
is used to induce sleep in patients with recurring
is used to induce sleep in patients with recurring
insomnia. Whereas
insomnia. Whereas temazepam
temazepam is useful for
is useful for
insomnia caused by the inability to stay asleep,
insomnia caused by the inability to stay asleep,
triazolam
triazolam is effective in treating individuals who
is effective in treating individuals who
have difficulty in going to
have difficulty in going to
sleep
sleep
Sleep
Sleep disorded
disorded ::Flurazepam
Flurazepam has a long
has a long--acting
acting
effect and causes
effect and causes no
no rebound insomnia.
rebound insomnia.
Temazepam
Temazepam:: This drug is useful in patients who
This drug is useful in patients who
experience frequent wakening.
experience frequent wakening. the
the peak sedative
peak sedative
effect occurs
effect occurs 1
1 to
to 3
3 hours after an oral dose;
hours after an oral dose; and
and
should
should be given
be given 1
1 to
to 2
2 hours before
hours before bedtime
bedtime..
Triazolam
Triazolam:: short duration of action and, therefore,
short duration of action and, therefore,
is used to induce sleep in patients with recurring
is used to induce sleep in patients with recurring
insomnia. Whereas
insomnia. Whereas temazepam
temazepam is useful for
is useful for
insomnia caused by the inability to stay asleep,
insomnia caused by the inability to stay asleep,
triazolam
triazolam is effective in treating individuals who
is effective in treating individuals who
have difficulty in going to
have difficulty in going to
sleep
sleep

Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics
•• lipophilic
lipophilic,,
•• rapidly and completely absorbed after oral
rapidly and completely absorbed after oral
administration
administration
•• distribute throughout the body .
distribute throughout the body .
The
The half
half--lives of the benzodiazepines are very
lives of the benzodiazepines are very
important clinically, because the duration of
important clinically, because the duration of
action may determine the therapeutic
action may determine the therapeutic
usefulness,
usefulness, The longer
The longer--acting agents form
acting agents form
active metabolites with long half
active metabolites with long half--lives.
lives.
However, with some benzodiazepines, the
However, with some benzodiazepines, the
clinical durations of action do not always
clinical durations of action do not always
correlate with actual
correlate with actual half
half--lives.
lives.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics
•• lipophilic
lipophilic,,
•• rapidly and completely absorbed after oral
rapidly and completely absorbed after oral
administration
administration
•• distribute throughout the body .
distribute throughout the body .
The
The half
half--lives of the benzodiazepines are very
lives of the benzodiazepines are very
important clinically, because the duration of
important clinically, because the duration of
action may determine the therapeutic
action may determine the therapeutic
usefulness,
usefulness, The longer
The longer--acting agents form
acting agents form
active metabolites with long half
active metabolites with long half--lives.
lives.
However, with some benzodiazepines, the
However, with some benzodiazepines, the
clinical durations of action do not always
clinical durations of action do not always
correlate with actual
correlate with actual half
half--lives.
lives.

Most benzodiazepines, including
Most benzodiazepines, including
chlordiazepoxide
chlordiazepoxide and diazepam, are
and diazepam, are
metabolized by the hepatic
metabolized by the hepatic microsomal
microsomal
system to compounds that are also
system to compounds that are also
active.
active.
The
The benzodiazepines are excreted in
benzodiazepines are excreted in
the urine as
the urine as glucuronides
glucuronides or oxidized
or oxidized
metabolites
metabolites..
Most benzodiazepines, including
Most benzodiazepines, including
chlordiazepoxide
chlordiazepoxide and diazepam, are
and diazepam, are
metabolized by the hepatic
metabolized by the hepatic microsomal
microsomal
system to compounds that are also
system to compounds that are also
active.
active.
The
The benzodiazepines are excreted in
benzodiazepines are excreted in
the urine as
the urine as glucuronides
glucuronides or oxidized
or oxidized
metabolites
metabolites..

All the benzodiazepines cross the
All the benzodiazepines cross the
placental barrier and may depress the
placental barrier and may depress the
CNS of the newborn if given before
CNS of the newborn if given before
birth.
birth.
Nursing infants may also become
Nursing infants may also become
exposed to the drugs in breast milk
exposed to the drugs in breast milk

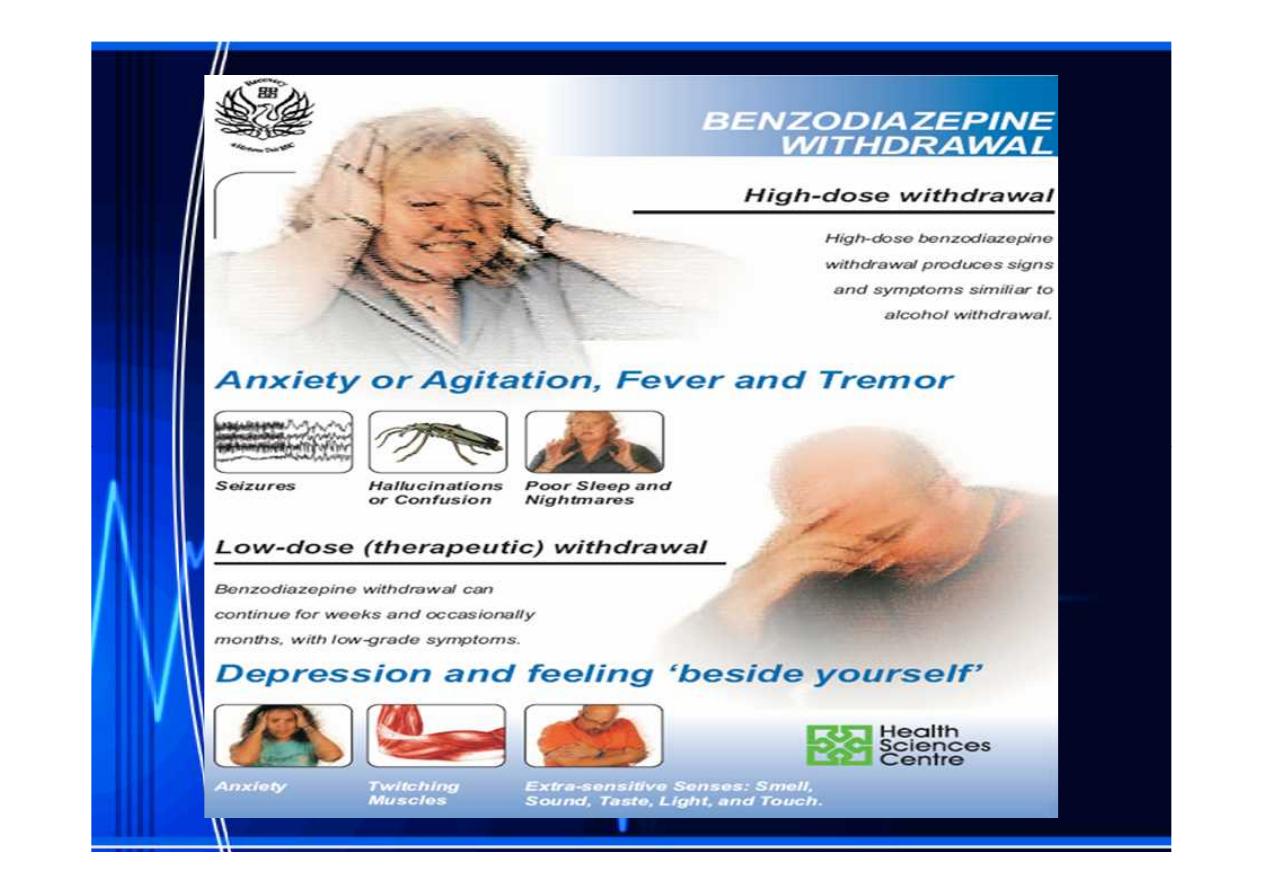
Adverse effects
Adverse effects
Drowsiness
Drowsiness and confusion
and confusion::
Psychological
Psychological and physical dependence on
and physical dependence on
benzodiazepines can develop if high doses of the
benzodiazepines can develop if high doses of the
drugs are given over a prolonged
drugs are given over a prolonged period
period
withdrawal
withdrawal symptoms, including confusion, anxiety
symptoms, including confusion, anxiety,,
insomnia
insomnia,, tension,
tension, and rarely, seizures.
and rarely, seizures.
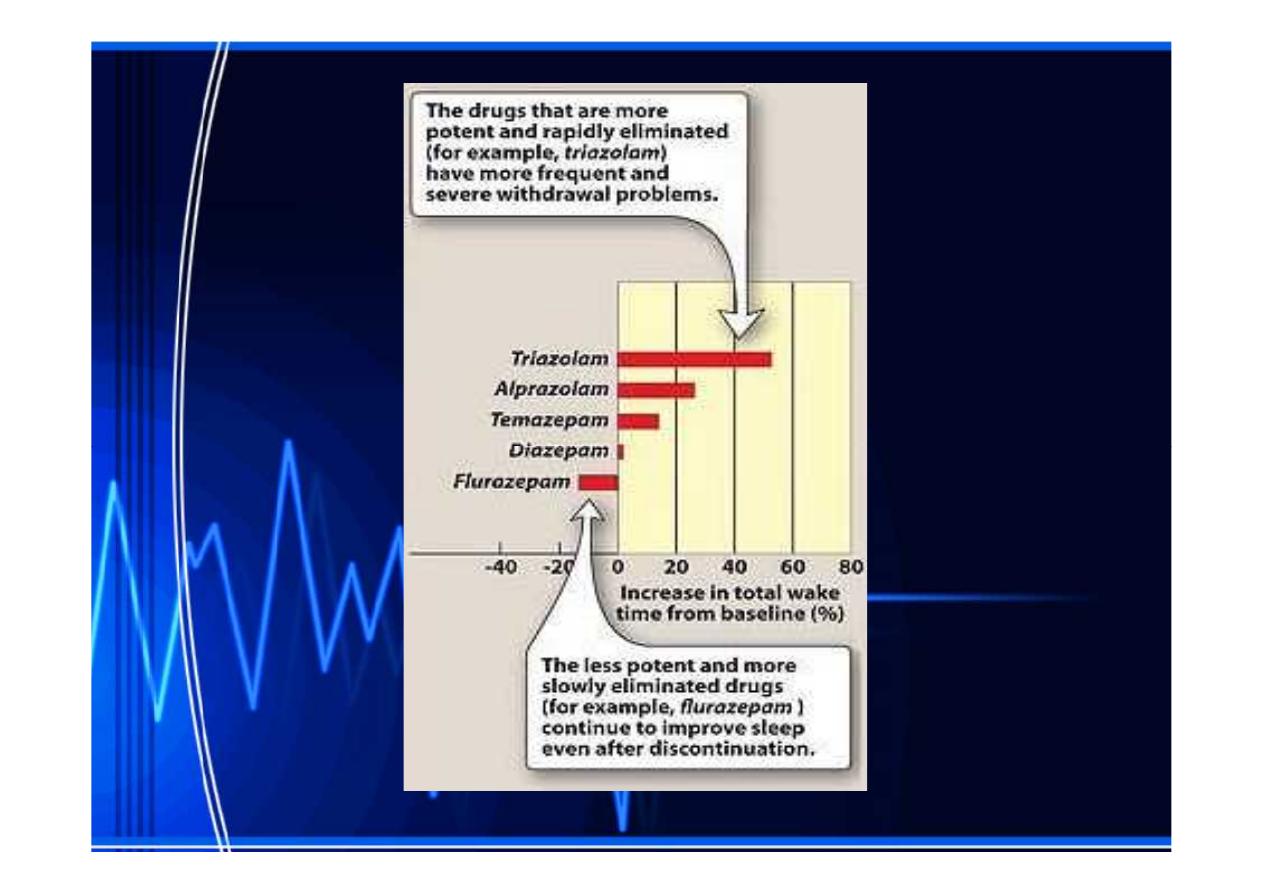
••
a short
a short elimination
elimination half
half--life(rapidly
life(rapidly eleminated
eleminated),
), such
such
as
as triazolam
triazolam,, induce more abrupt
induce more abrupt severe
severe withdrawal
withdrawal
reactions than
reactions than drugs
drugs that are slowly eliminated, such
that are slowly eliminated, such
as
as flurazepam
flurazepam
Adverse effects
Adverse effects
Drowsiness
Drowsiness and confusion
and confusion::
Psychological
Psychological and physical dependence on
and physical dependence on
benzodiazepines can develop if high doses of the
benzodiazepines can develop if high doses of the
drugs are given over a prolonged
drugs are given over a prolonged period
period
withdrawal
withdrawal symptoms, including confusion, anxiety
symptoms, including confusion, anxiety,,
insomnia
insomnia,, tension,
tension, and rarely, seizures.
and rarely, seizures.
••
a short
a short elimination
elimination half
half--life(rapidly
life(rapidly eleminated
eleminated),
), such
such
as
as triazolam
triazolam,, induce more abrupt
induce more abrupt severe
severe withdrawal
withdrawal
reactions than
reactions than drugs
drugs that are slowly eliminated, such
that are slowly eliminated, such
as
as flurazepam
flurazepam

Precautions:
Precautions:
In
In treating patients with liver disease.
treating patients with liver disease.
In
In patients with acute narrow
patients with acute narrow--angle glaucoma.
angle glaucoma.
Alcohol and other CNS depressants enhance
Alcohol and other CNS depressants enhance
the sedative
the sedative--hypnotic effects of the
hypnotic effects of the
benzodiazepines.
benzodiazepines.
Precautions:
Precautions:
In
In treating patients with liver disease.
treating patients with liver disease.
In
In patients with acute narrow
patients with acute narrow--angle glaucoma.
angle glaucoma.
Alcohol and other CNS depressants enhance
Alcohol and other CNS depressants enhance
the sedative
the sedative--hypnotic effects of the
hypnotic effects of the
benzodiazepines.
benzodiazepines.

Benzodiazepine Antagonist
Benzodiazepine Antagonist
Flumazenil
Flumazenil (is a GABA
(is a GABA--receptor antagonist)
receptor antagonist)
that can rapidly reverse the effects of
that can rapidly reverse the effects of
benzodiazepines(competitively occupies a
benzodiazepines(competitively occupies a
GABA
GABA--receptor without
receptor without causing a functional
causing a functional
change in CL channel) .
change in CL channel) .
•• for
for intravenous administration only
intravenous administration only..
•• rapid Onset of action
rapid Onset of action
•• short duration,
short duration, with a half
with a half--life of about
life of about 1
1
hour.
hour.
Frequent
Frequent administration may be necessary to
administration may be necessary to
maintain reversal of a long
maintain reversal of a long--acting
acting
benzodiazepine
benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepine Antagonist
Benzodiazepine Antagonist
Flumazenil
Flumazenil (is a GABA
(is a GABA--receptor antagonist)
receptor antagonist)
that can rapidly reverse the effects of
that can rapidly reverse the effects of
benzodiazepines(competitively occupies a
benzodiazepines(competitively occupies a
GABA
GABA--receptor without
receptor without causing a functional
causing a functional
change in CL channel) .
change in CL channel) .
•• for
for intravenous administration only
intravenous administration only..
•• rapid Onset of action
rapid Onset of action
•• short duration,
short duration, with a half
with a half--life of about
life of about 1
1
hour.
hour.
Frequent
Frequent administration may be necessary to
administration may be necessary to
maintain reversal of a long
maintain reversal of a long--acting
acting
benzodiazepine
benzodiazepine

Side
Side effects:
effects:
1
1.Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and
.Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and agitation
agitation
2
2.withdrawal
.withdrawal in dependent patients
in dependent patients
3
3.. seizures
seizures
•• If
If a benzodiazepine is used to control
a benzodiazepine is used to control
seizure activity
seizure activity
•• If
If the patient ingests
the patient ingests tricyclic
tricyclic antidepressants
antidepressants
Side
Side effects:
effects:
1
1.Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and
.Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and agitation
agitation
2
2.withdrawal
.withdrawal in dependent patients
in dependent patients
3
3.. seizures
seizures
•• If
If a benzodiazepine is used to control
a benzodiazepine is used to control
seizure activity
seizure activity
•• If
If the patient ingests
the patient ingests tricyclic
tricyclic antidepressants
antidepressants

••
Other
Other anxiolytic
anxiolytic drugs:
drugs: buspirone
buspirone,,
hydroxyzine
hydroxyzine

Buspirone
Buspirone
••
Is useful in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder
Is useful in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder
••
has efficacy comparable to that of the benzodiazepines.
has efficacy comparable to that of the benzodiazepines.
••
Mode of action differs from that of the benzodiazepines
Mode of action differs from that of the benzodiazepines
because:
because:
••
The actions of
The actions of buspirone
buspirone appear to be mediated by
appear to be mediated by
Buspirone
Buspirone
••
Is useful in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder
Is useful in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder
••
has efficacy comparable to that of the benzodiazepines.
has efficacy comparable to that of the benzodiazepines.
••
Mode of action differs from that of the benzodiazepines
Mode of action differs from that of the benzodiazepines
because:
because:
••
The actions of
The actions of buspirone
buspirone appear to be mediated by
appear to be mediated by

•• Serotonin (
Serotonin (5
5--HT
HT
1
1A
A
) receptors,
) receptors, buspirone
buspirone
displays some affinity for DA
displays some affinity for DA
2
2
dopamine
dopamine
receptors and
receptors and 5
5--HT
HT
2
2A
A
serotonin receptors
serotonin receptors
•• undergoes metabolism by CYP
undergoes metabolism by CYP3
3A
A4
4; thus, its
; thus, its
half
half--life is shortened if taken with
life is shortened if taken with rifampin
rifampin(an
(an
inducer of the enzyme)
inducer of the enzyme)
•• lengthened if taken with erythromycin(an
lengthened if taken with erythromycin(an
inhibitor of the enzyme)
inhibitor of the enzyme)
•• Serotonin (
Serotonin (5
5--HT
HT
1
1A
A
) receptors,
) receptors, buspirone
buspirone
displays some affinity for DA
displays some affinity for DA
2
2
dopamine
dopamine
receptors and
receptors and 5
5--HT
HT
2
2A
A
serotonin receptors
serotonin receptors
•• undergoes metabolism by CYP
undergoes metabolism by CYP3
3A
A4
4; thus, its
; thus, its
half
half--life is shortened if taken with
life is shortened if taken with rifampin
rifampin(an
(an
inducer of the enzyme)
inducer of the enzyme)
•• lengthened if taken with erythromycin(an
lengthened if taken with erythromycin(an
inhibitor of the enzyme)
inhibitor of the enzyme)

•• Adverse effects: Headaches, dizziness,
Adverse effects: Headaches, dizziness,
nervousness
nervousness
•• Disadvantage:
Disadvantage: Buspirone
Buspirone has the slow onset
has the slow onset
of action
of action

Hydroxyzine
Hydroxyzine:: is an antihistamine with
is an antihistamine with
antiemetic activity. It has a low tendency for
antiemetic activity. It has a low tendency for
habituation and, thus, is useful for patients with
habituation and, thus, is useful for patients with
anxiety who have a history of drug abuse. It is
anxiety who have a history of drug abuse. It is
also often used for sedation prior to dental
also often used for sedation prior to dental
procedures or surgery. Drowsiness is a possible
procedures or surgery. Drowsiness is a possible
adverse effect
adverse effect
Hydroxyzine
Hydroxyzine:: is an antihistamine with
is an antihistamine with
antiemetic activity. It has a low tendency for
antiemetic activity. It has a low tendency for
habituation and, thus, is useful for patients with
habituation and, thus, is useful for patients with
anxiety who have a history of drug abuse. It is
anxiety who have a history of drug abuse. It is
also often used for sedation prior to dental
also often used for sedation prior to dental
procedures or surgery. Drowsiness is a possible
procedures or surgery. Drowsiness is a possible
adverse effect
adverse effect

Antidepressants:
Antidepressants: many antidepressants have
many antidepressants have
proven efficacy in managing the long
proven efficacy in managing the long--term
term
symptoms of chronic anxiety disorders and
symptoms of chronic anxiety disorders and
should be considered as first
should be considered as first--line agents,
line agents,
especially in patients with concerns for
especially in patients with concerns for
addiction or dependence or a history of
addiction or dependence or a history of
addiction or dependence to other substances.
addiction or dependence to other substances.
The SSRIs, TCAs,
The SSRIs, TCAs, venlafaxine
venlafaxine,, duloxetine
duloxetine and
and
MAOIs all have potential usefulness in treating
MAOIs all have potential usefulness in treating
anxiety
anxiety
y
Antidepressants:
Antidepressants: many antidepressants have
many antidepressants have
proven efficacy in managing the long
proven efficacy in managing the long--term
term
symptoms of chronic anxiety disorders and
symptoms of chronic anxiety disorders and
should be considered as first
should be considered as first--line agents,
line agents,
especially in patients with concerns for
especially in patients with concerns for
addiction or dependence or a history of
addiction or dependence or a history of
addiction or dependence to other substances.
addiction or dependence to other substances.
The SSRIs, TCAs,
The SSRIs, TCAs, venlafaxine
venlafaxine,, duloxetine
duloxetine and
and
MAOIs all have potential usefulness in treating
MAOIs all have potential usefulness in treating
anxiety
anxiety
y

••
Other Hypnotic Agents
Other Hypnotic Agents
Zolpidem
Zolpidem
•• Is not a benzodiazepine in structure,
Is not a benzodiazepine in structure, but it
but it
acts on a subset of the benzodiazepine
acts on a subset of the benzodiazepine
receptor family, BZ
receptor family, BZ
1
1
..
•• Zolpidem
Zolpidem has no anticonvulsant or muscle
has no anticonvulsant or muscle--
relaxing properties
relaxing properties
••
Other Hypnotic Agents
Other Hypnotic Agents
Zolpidem
Zolpidem
•• Is not a benzodiazepine in structure,
Is not a benzodiazepine in structure, but it
but it
acts on a subset of the benzodiazepine
acts on a subset of the benzodiazepine
receptor family, BZ
receptor family, BZ
1
1
..
•• Zolpidem
Zolpidem has no anticonvulsant or muscle
has no anticonvulsant or muscle--
relaxing properties
relaxing properties

•• It shows few withdrawal effects, and minimal
It shows few withdrawal effects, and minimal
rebound insomnia, and little or no tolerance
rebound insomnia, and little or no tolerance
occurs with prolonged use.
occurs with prolonged use.
•• Zolpidem
Zolpidem is rapidly absorbed from the
is rapidly absorbed from the
gastrointestinal tract, and it has a rapid onset
gastrointestinal tract, and it has a rapid onset
of action and short elimination half
of action and short elimination half--life (about
life (about
2
2 to
to 3
3 hours).
hours).
•• It shows few withdrawal effects, and minimal
It shows few withdrawal effects, and minimal
rebound insomnia, and little or no tolerance
rebound insomnia, and little or no tolerance
occurs with prolonged use.
occurs with prolonged use.
•• Zolpidem
Zolpidem is rapidly absorbed from the
is rapidly absorbed from the
gastrointestinal tract, and it has a rapid onset
gastrointestinal tract, and it has a rapid onset
of action and short elimination half
of action and short elimination half--life (about
life (about
2
2 to
to 3
3 hours).
hours).

•
.
Zolpidem
Zolpidem undergoes hepatic oxidation by the
undergoes hepatic oxidation by the cytochrome
cytochrome
P
P450
450 system to inactive products.
system to inactive products.
••
Drugs such as
Drugs such as rifampin
rifampin, which induce this enzyme system,
, which induce this enzyme system,
shorten the half
shorten the half--life of
life of zolpidem
zolpidem,,
••
Drugs that inhibit the CYP
Drugs that inhibit the CYP3
3A
A4
4 isoenzyme
isoenzyme may increase the half
may increase the half--
life this drug.
life this drug.

•• Adverse effects of
Adverse effects of zolpidem
zolpidem include
include
nightmares, agitation, headache,
nightmares, agitation, headache,
gastrointestinal upset, dizziness, and daytime
gastrointestinal upset, dizziness, and daytime
drowsiness.
drowsiness.

Ramelteon
Ramelteon::
is a selective agonist at the MT
is a selective agonist at the MT
1
1
and MT
and MT
2
2
subtypes
subtypes
of melatonin receptors
of melatonin receptors
Stimulation of MT
Stimulation of MT
1
1
and MT
and MT
2
2
receptors by melatonin the
receptors by melatonin the
hypothalamus is able to induce and promote sleep
hypothalamus is able to induce and promote sleep
Ramelteon
Ramelteon::
is a selective agonist at the MT
is a selective agonist at the MT
1
1
and MT
and MT
2
2
subtypes
subtypes
of melatonin receptors
of melatonin receptors
Stimulation of MT
Stimulation of MT
1
1
and MT
and MT
2
2
receptors by melatonin the
receptors by melatonin the
hypothalamus is able to induce and promote sleep
hypothalamus is able to induce and promote sleep

Ramelteon
Ramelteon is indicated for the treatment of
is indicated for the treatment of
insomnia in which falling asleep (increased
insomnia in which falling asleep (increased
sleep latency) is the primary complaint.
sleep latency) is the primary complaint.
The potential for abuse of
The potential for abuse of ramelteon
ramelteon is minimal,
is minimal,
and no evidence of dependence or withdrawal
and no evidence of dependence or withdrawal
effects has been observed. Therefore,
effects has been observed. Therefore,
ramelteon
ramelteon can be administered long
can be administered long--term.
term.
.
Ramelteon
Ramelteon is indicated for the treatment of
is indicated for the treatment of
insomnia in which falling asleep (increased
insomnia in which falling asleep (increased
sleep latency) is the primary complaint.
sleep latency) is the primary complaint.
The potential for abuse of
The potential for abuse of ramelteon
ramelteon is minimal,
is minimal,
and no evidence of dependence or withdrawal
and no evidence of dependence or withdrawal
effects has been observed. Therefore,
effects has been observed. Therefore,
ramelteon
ramelteon can be administered long
can be administered long--term.
term.
.

•• Adverse effects of
Adverse effects of ramelteon
ramelteon include
include
dizziness, fatigue .
dizziness, fatigue .
•• Ramelteon
Ramelteon may also increase
may also increase prolactin
prolactin
levels.
levels.
•• Adverse effects of
Adverse effects of ramelteon
ramelteon include
include
dizziness, fatigue .
dizziness, fatigue .
•• Ramelteon
Ramelteon may also increase
may also increase prolactin
prolactin
levels.
levels.

Chloral hydrate
Chloral hydrate
•• The drug is an effective sedative and
The drug is an effective sedative and
hypnotic that
hypnotic that
•• Induces sleep in about
Induces sleep in about 30
30 minutes and the
minutes and the
duration of sleep is about
duration of sleep is about 6
6 hours.
hours.
•• Chloral hydrate is irritating to the
Chloral hydrate is irritating to the
gastrointestinal tract and causes
gastrointestinal tract and causes epigastric
epigastric
distress
distress
•• It also produces an unusual, unpleasant taste
It also produces an unusual, unpleasant taste
sensation.
sensation.
•• It synergizes with ethanol
It synergizes with ethanol
..
Chloral hydrate
Chloral hydrate
•• The drug is an effective sedative and
The drug is an effective sedative and
hypnotic that
hypnotic that
•• Induces sleep in about
Induces sleep in about 30
30 minutes and the
minutes and the
duration of sleep is about
duration of sleep is about 6
6 hours.
hours.
•• Chloral hydrate is irritating to the
Chloral hydrate is irritating to the
gastrointestinal tract and causes
gastrointestinal tract and causes epigastric
epigastric
distress
distress
•• It also produces an unusual, unpleasant taste
It also produces an unusual, unpleasant taste
sensation.
sensation.
•• It synergizes with ethanol
It synergizes with ethanol
..

Antihistamines:
Antihistamines: diphenhydramine
diphenhydramine
•• They are effective in treating mild types of
They are effective in treating mild types of
insomnia.
insomnia.
•• They have numerous undesirable side effects
They have numerous undesirable side effects
(such as
(such as anticholinergic
anticholinergic effects) that make
effects) that make
them less useful than the benzodiazepines.
them less useful than the benzodiazepines.
Antihistamines:
Antihistamines: diphenhydramine
diphenhydramine
•• They are effective in treating mild types of
They are effective in treating mild types of
insomnia.
insomnia.
•• They have numerous undesirable side effects
They have numerous undesirable side effects
(such as
(such as anticholinergic
anticholinergic effects) that make
effects) that make
them less useful than the benzodiazepines.
them less useful than the benzodiazepines.
