--Hx of CCHD:-
Ask about:-1-Dyspnea on extertion like feeding,crying
2-orthopnea:-on lying down
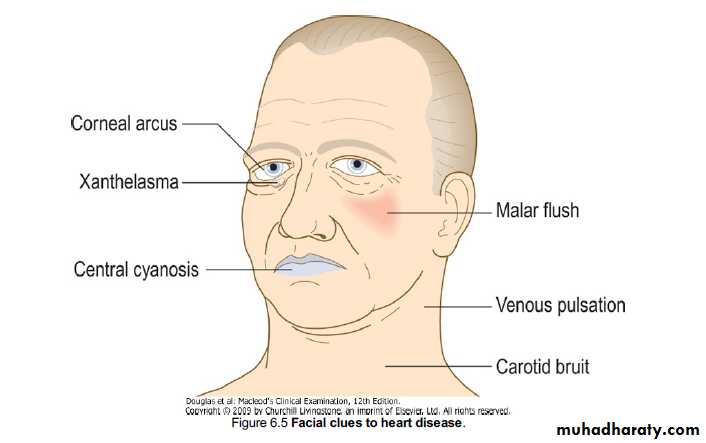
3-cyanosis:-when Hb >50g/l --Hb>5g/dl
Normal physiological cyanosis occurs in :- cold there will be bluish discoloration of skin but NOT mucous membrane
--why do we examine for cyanosis in mucous membrane ?
1)rich of BVs2)transparent
3)one layer
4)no melanin
4-sweating:-by exertion
5-edema :-on examSwelling in Hx
**where we examine it ?
On non –walking child above sacral area"Plz remove the diaper"
In walking child2 fingers above medial melleoullos in the leg.
6-fainting: Syncope is a faint with loss of consciousness
7-in exam :-clubbing
**in TOF no H.F:bec pulmonary stenosis will prevent pulmonary edema**hypercyanotic speels:-relieved by squatting position :knee chest position
**characters in Tof:from lec
*we give them B-blocker to help them relieve the stenosis**fever occurs in Tofblood is hyperviscouspolycythemia-so dehydration will influence them
O2 +rehydration ---imp
**characters of innocent murmers?
1-soft:grades1-3 in intensity & often mid systolic2-localized
3-poorly conducted
4-Not usually conducted posteriorly
5-variable with respirarion & position
Causes of edema :-
Unilateral edemaBilateral edema
1-DVT
2-hemiplegia
3-lymphatic obstruction
1-chronic venous insufficiency
2-H.F
3-inf.vena caval obstruction
4-thiamine deficiency
5-kwashiorker
6-drugs:fludrocortisones
**murmers
Most murmer in pediatric is ejection systolic murmer
1-innocent murmer
2-fever
3-Atrial septal defect
4-severe anemia
5-aortic stenosis
6-pulmonary stenosis
7-aortic regurgitation
**pansystolic murmer
1-VSD2-mitral regurgitation
3-tricuspid regurgitation
**always ask detailed about ht ,wt of pt
Degree of murmers:-in next lec**2nd heart sound varieties:-
Wide split:-inspiration1)VSD
2)pulmonary stenosis
3)pulmonary hypertension
Fixed splitting:-
ASDWide split:-in expiration
Aortic stenosisLt bundle branch block
Varities of 1st heart sound:-
1)quiet2)variable
3)loud
Causes of 3rd heart sound:-
1)m.regurgitation2)pregnany
3)fever
4)athlets
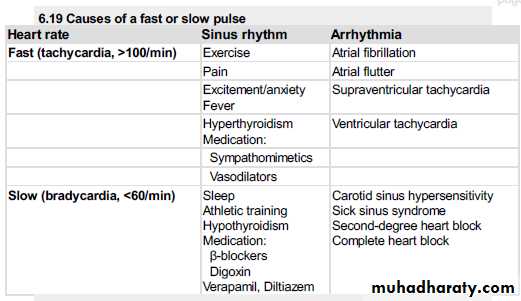
**causes of increased pulse volume?
1-fever
2-thyrotoxicosis
3-anemia
4-aortic regurgitation
5-paget's dis of bone
Causes of reduced pulse volume?
1-shock2-aortic stenosis
3-H.F
---pulsus alternas:-H.F"LT"
--always try to palpate lower edge of liver coz it is enlarged in H.F--how u differentiate murmers "true"from innocent?
1-symptoms2-radiation
3-thrill
Causes of AF:-
1-H.F2-thyrotoxicosis
3-infection
4-mitral valve di
5-hypertension
Pulse volume - decrease in inspiration ?
Due to the raised intrathoracic pressure affects the venous return to the heart .Pulse volumeincrease in expiration
If the variability is exagerratedpulsus paradoxicusOccurs in :- ASTHMA
How to be sure :-measure SBP in inspiration + expiration if more than 15mmhgpathologicalOn exam after the general :-
Assess H.R1)rate
2)rhythm
3)character
4)state of blood vessel
5)radiofemoral delay
6)volume
**in coarctation of aorta:-congenital narrowing of aorta distal to lt subclavian artery
Upper limbs pulses normal ,,lower limb pulses reduced " radiofemoral delay"in children
In adults
1)hypertension
2)H.F
**collapsing pulse:-AR+av malformation
Peak of pulse arrives early & then there is rapid fall or descentManeuvre :-raise the pt's hand above the level of heart
**slow rising pulse :-gradual upstroke with reduced peak
Aortic stenosis(late in systole)**bisferiens pulse:-2 systolic peaks separated by one mid systolic dip
AS+AR**every murmer u hear ,u should analyze the:-
1-timing
2-site
3-intensity
4-radiation
5-pitch
6-duration
For ex:-
I heard 1st & 2nd heart sound with pansystolic murmer concamittant with the first heart sound localized in the apex ,loud ,blowing in character ,maximal intensity at apex & radiated to axilla