X-Radiation
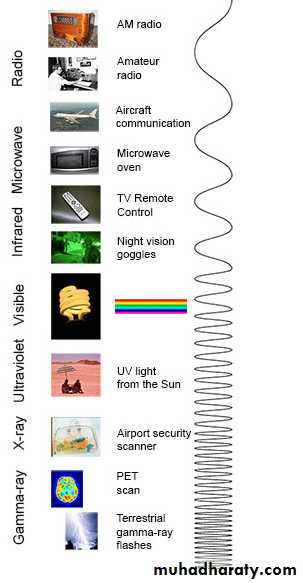
IntroductionX-rays were discovered by Roentgen in 1895. They are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation and are part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which also includes low energy radio waves, television and visible light.
*Radiography — the techniques involved inproducing the various radiographic images *Radiology — the interpretation of theseradiographic images.*X-rays are described as consisting of wavepackets of energy. Each packet is called a photon and is equivalent to one quantum of energy. The X-ray beam is made up of millions of individual photons.
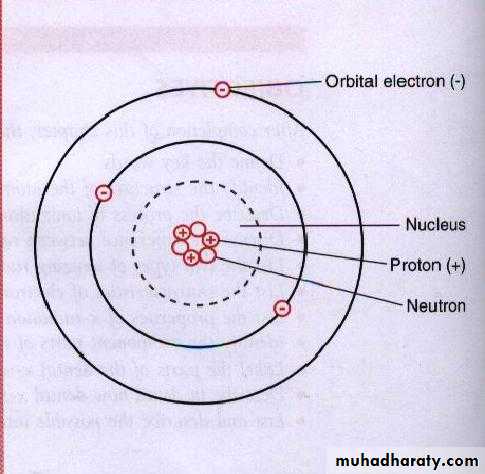
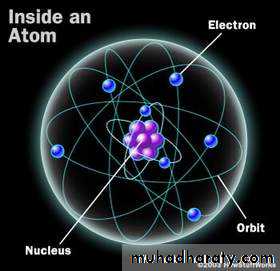
Is the fundamental unit of matter
Atom
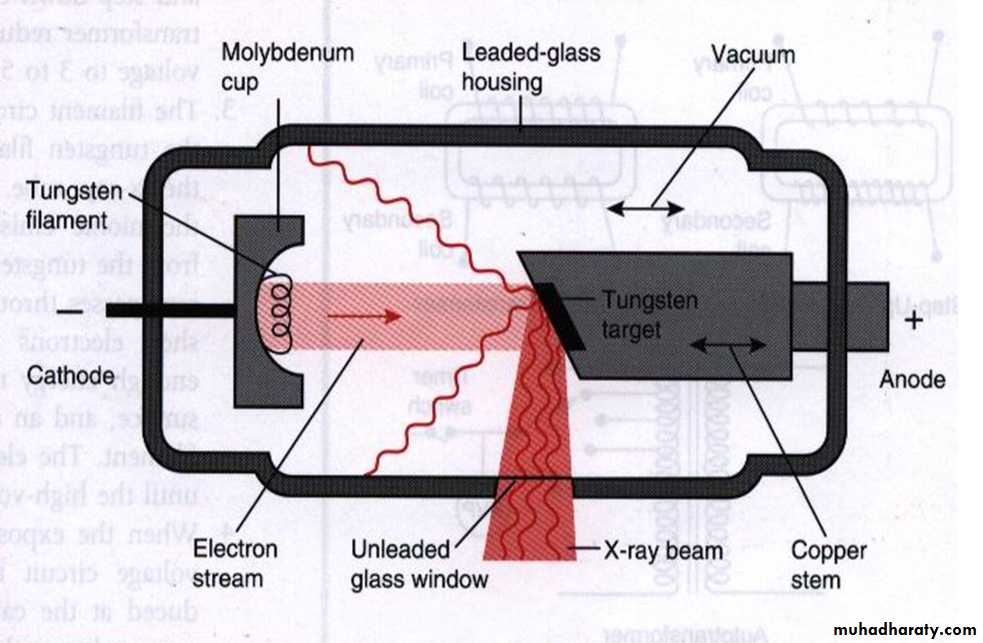
X-ray production:X-rays are produced when energetic (high-speed) electrons bombard a target material and arebrought suddenly to rest. This happens inside a small evacuated glass envelope called the X-raytube.
• Dental X-Ray Machine
• The cathode (negative) :a heated filament of tungsten that provides the source of electrons.
The anode (positive) :a target (a tungsten filament) set into the angled face of a large copper block to allow efficient removal of heat
A focusing device(Molybdnum cup): aims the stream of electrons at the focal spot on the target.
A high-voltage (kilovoltage, kV) connected between the cathode and anode accelerates the electrons from the negative filament to the positive target.
A current (milliamperage, mA) flows from the cathode to the anode. This is a measure of the quantity of electrons being accelerated.
A surrounding lead casing absorbs unwanted X-rays as a radiation protection measure since X-rays are emitted in all directions.
Surrounding oil facilitates the removal of heat.
X-Ray tube
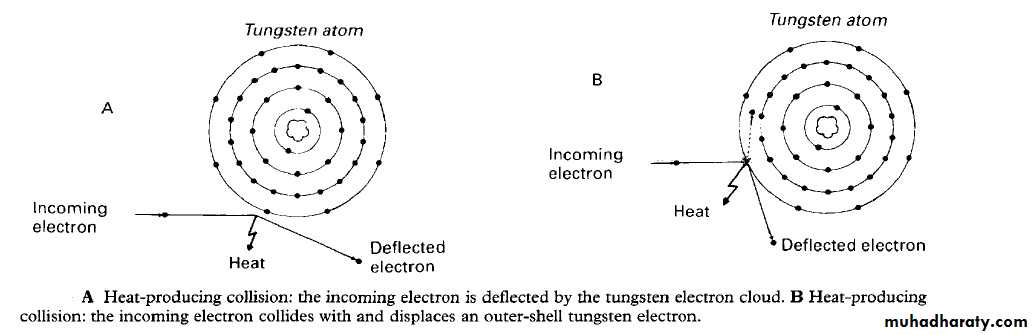
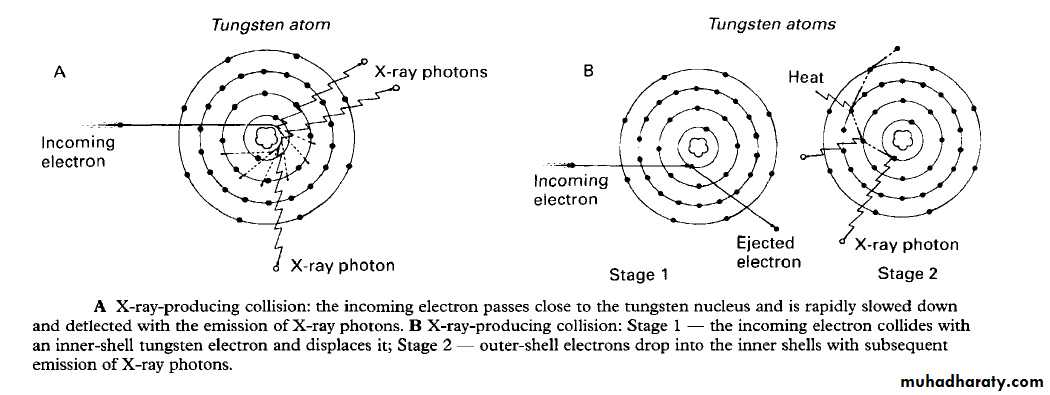
The sequence of events of X-rays production :1. The filament is electrically heated and a cloud of electrons is produced around the filament.2. The high-voltage (potential difference) across the tube accelerates the electrons at very high speed towards the anode. 3. The focusing device aims the electron stream at the focal spot on the target.4. The electrons bombard the target and are brought suddenly to rest.5. The energy lost by the electrons is transferred into either heat (about 99%) or X-rays (about 1%).6. The heat produced is removed and dissipated by the copper block and the surrounding oil.7. The X-rays are emitted in all directions from the target. Those emitted through the small window in the lead casing constitute the beam used for diagnostic purposes..Heat-producing collisions
X-ray-producing collisions
Definition of terms used in X-ray interactions
Scattering: change in direction of a photon with or without a loss of energy.Absorption : deposition of energy, i.e. removal of energy from the beam.
Attenuation : reduction in the intensity of the main X-ray beam caused by absorption and scattering
Attenuation = Absorption + Scattering
lonization : removal of an electron from a neutral atom producing a negative ion (the electron) and a positive ion (the remaining atom).
Interaction of X-rays with matter
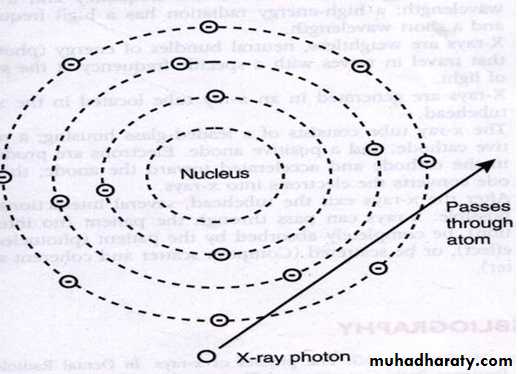
Four main interactions, depending on the energy of the incoming photon:NO Interaction: transmitted unchanged.
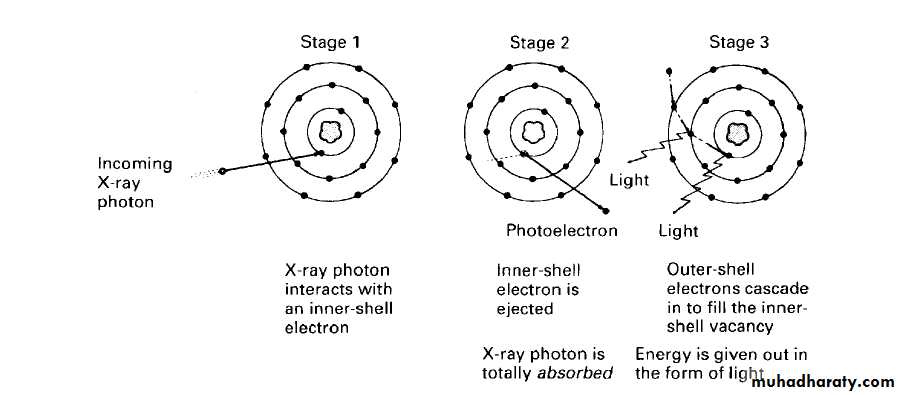
Photoelectric effect: pure absorption
(low-energy photons).
Compton effect — scatter and absorption.
(High-energy photons).
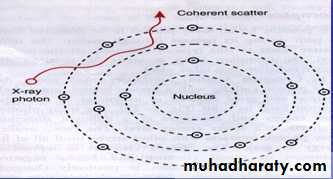
Coherent scattering: pure scattering.
NO Interaction: It is possible for an x-ray photon to pass through matter or the tissues of patient without any interaction.
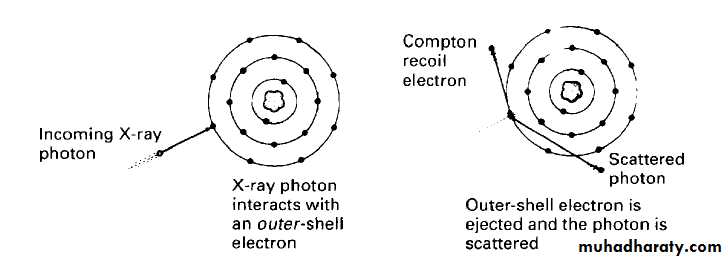
Photoelectric effect
Low energy
Compton effectHigh energy
Coherent scattering unmodified scatter:The photon does not have enough energy to liberate the electron from its bound state (i.e. below the binding energy of the electron) so no energy transfer occurs. The only change is a change of direction (scatter) of the photon, hence 'unmodified' scatter.