
•
Dr.Khudur Shukur


Three principles :
1-limited space
2-irreversable damage
2-irreversable damage
3-limited time
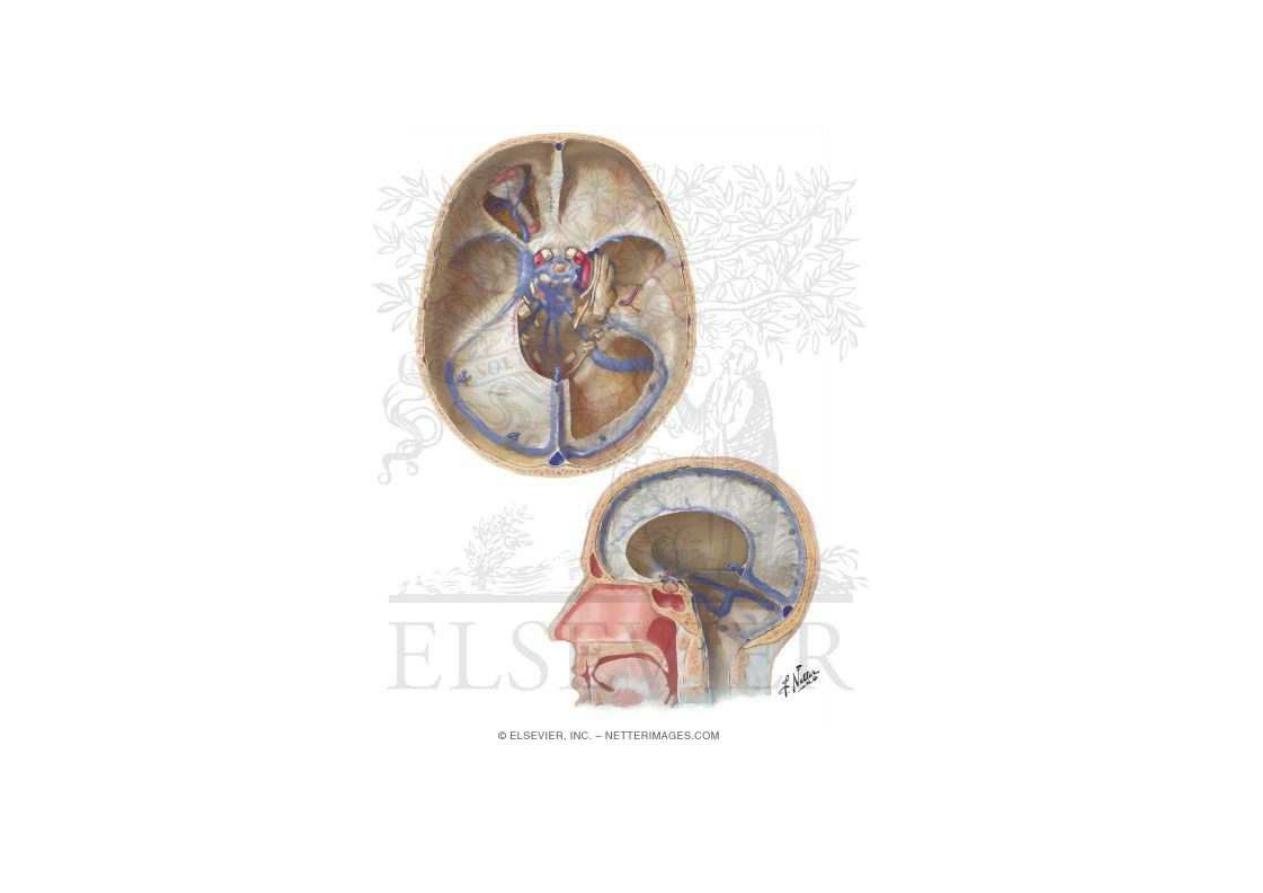
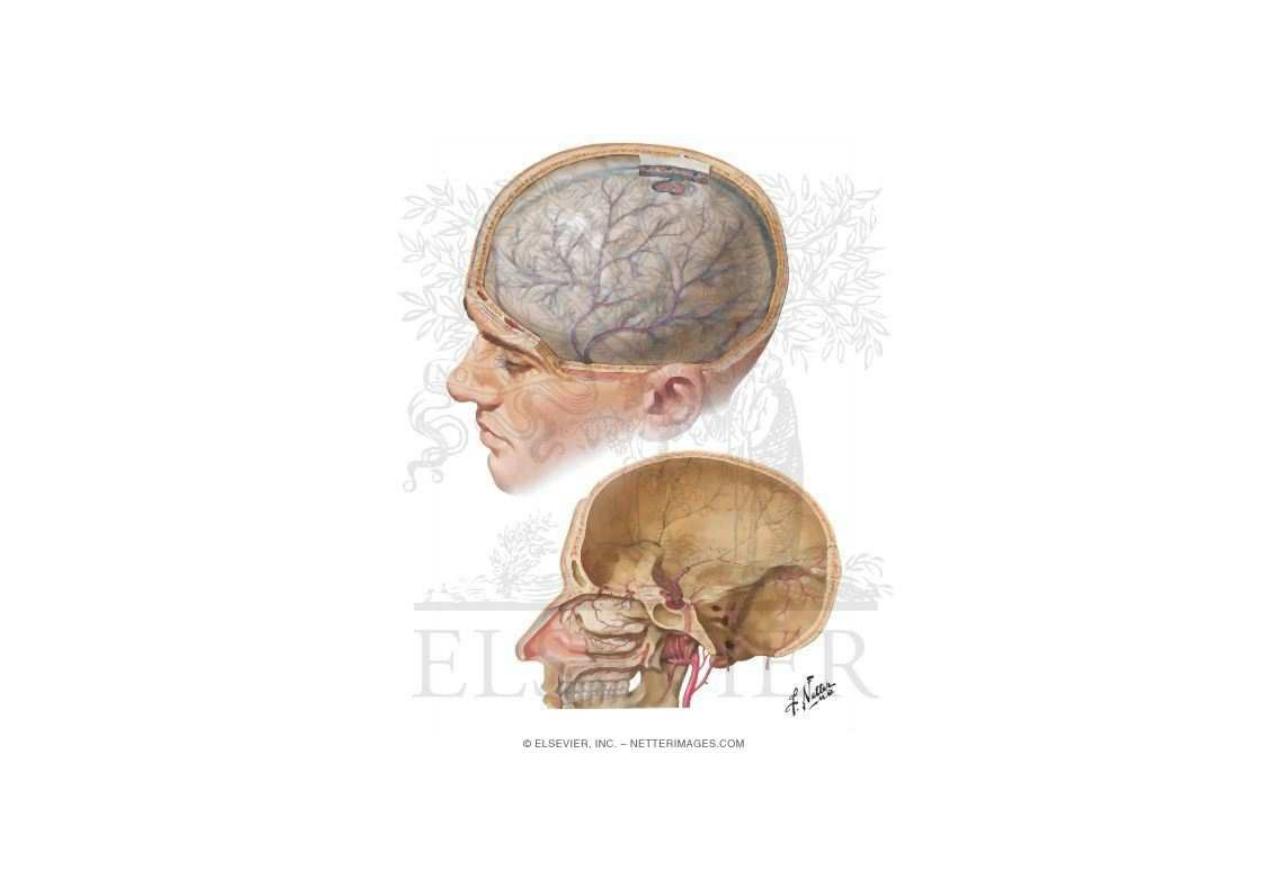

Arteries of the brain

Arteries of the brain
Anterior circulation – internal carotid
artery, from common carotid in the
neck. Bifurcates to MCA and ACA
Posterior circulation – vertebral arteries
that join to form the basilar artery
that will then bifurcate to 2 PCA

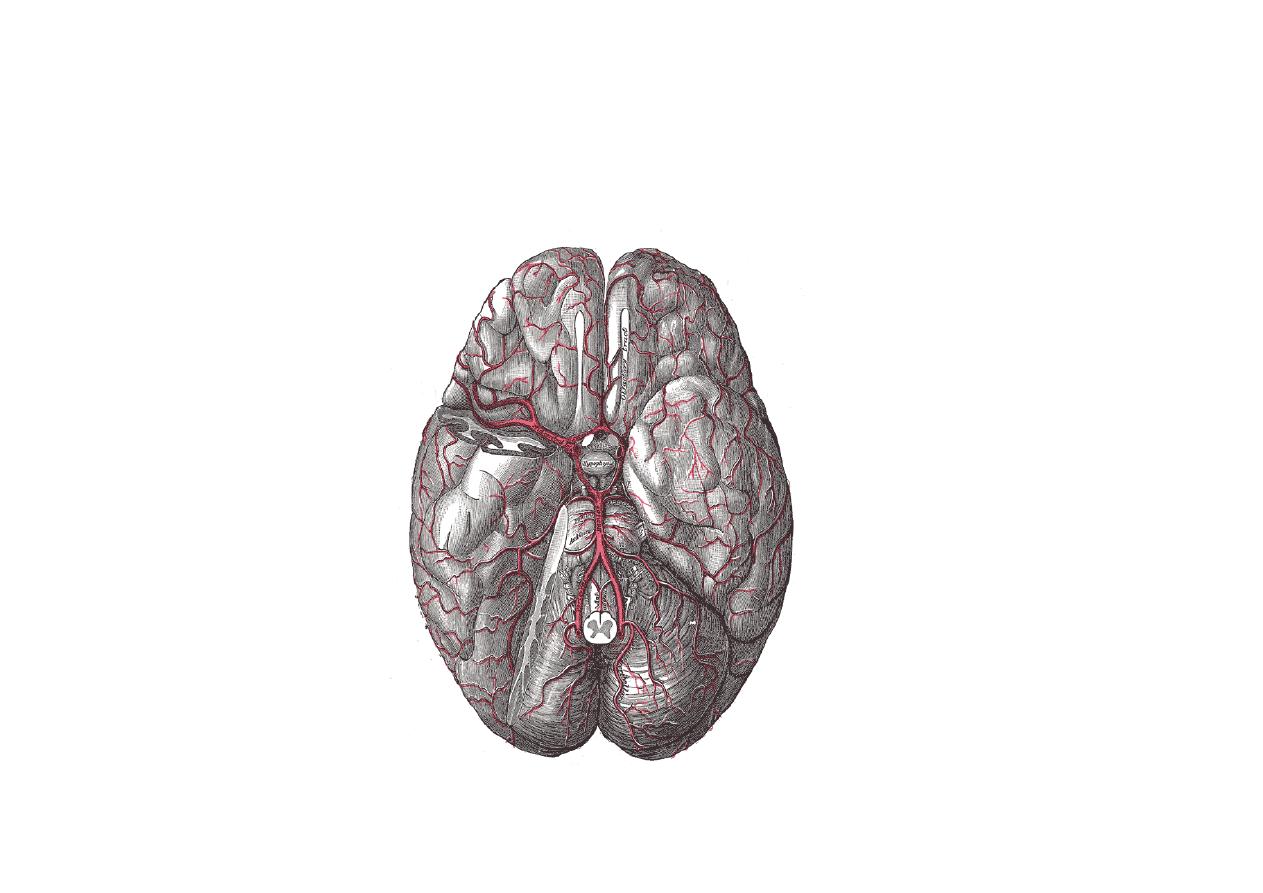
Circle of Willis
- Communication between 2 sides
anterior communicating (a-com)
- Communication between anterior and
posterior circulation – posterior ---
posterior circulation – posterior ---
communicating (p-com)
- Many anomalies may exist
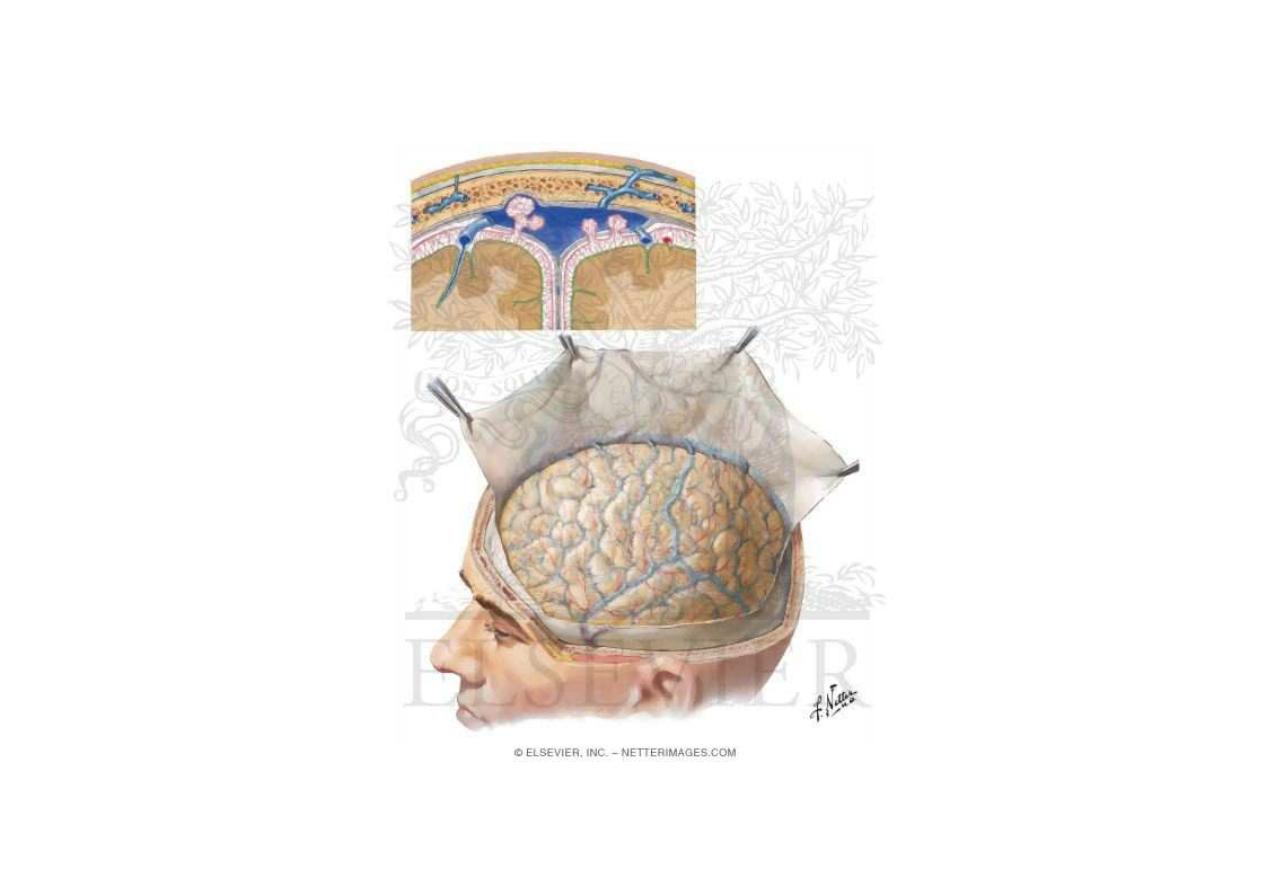
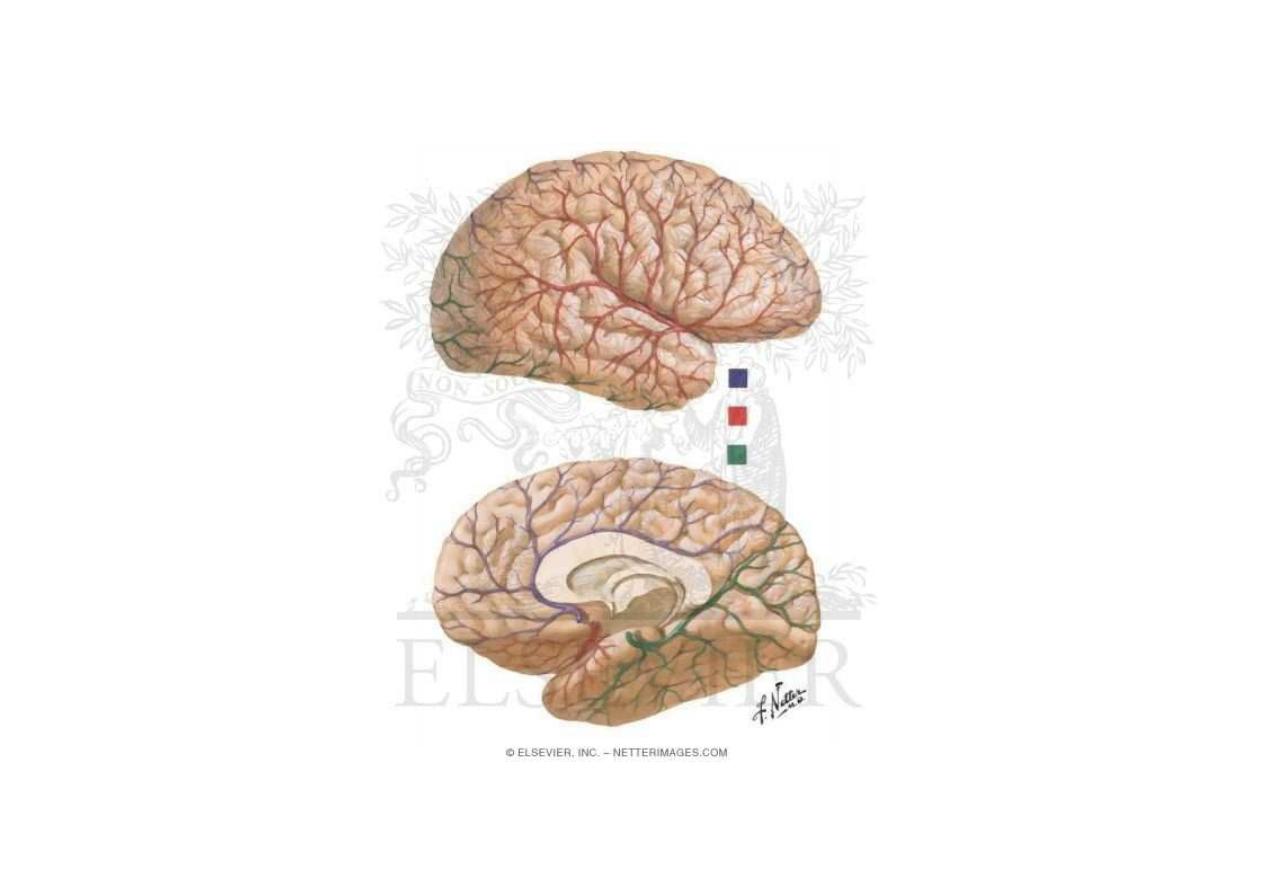
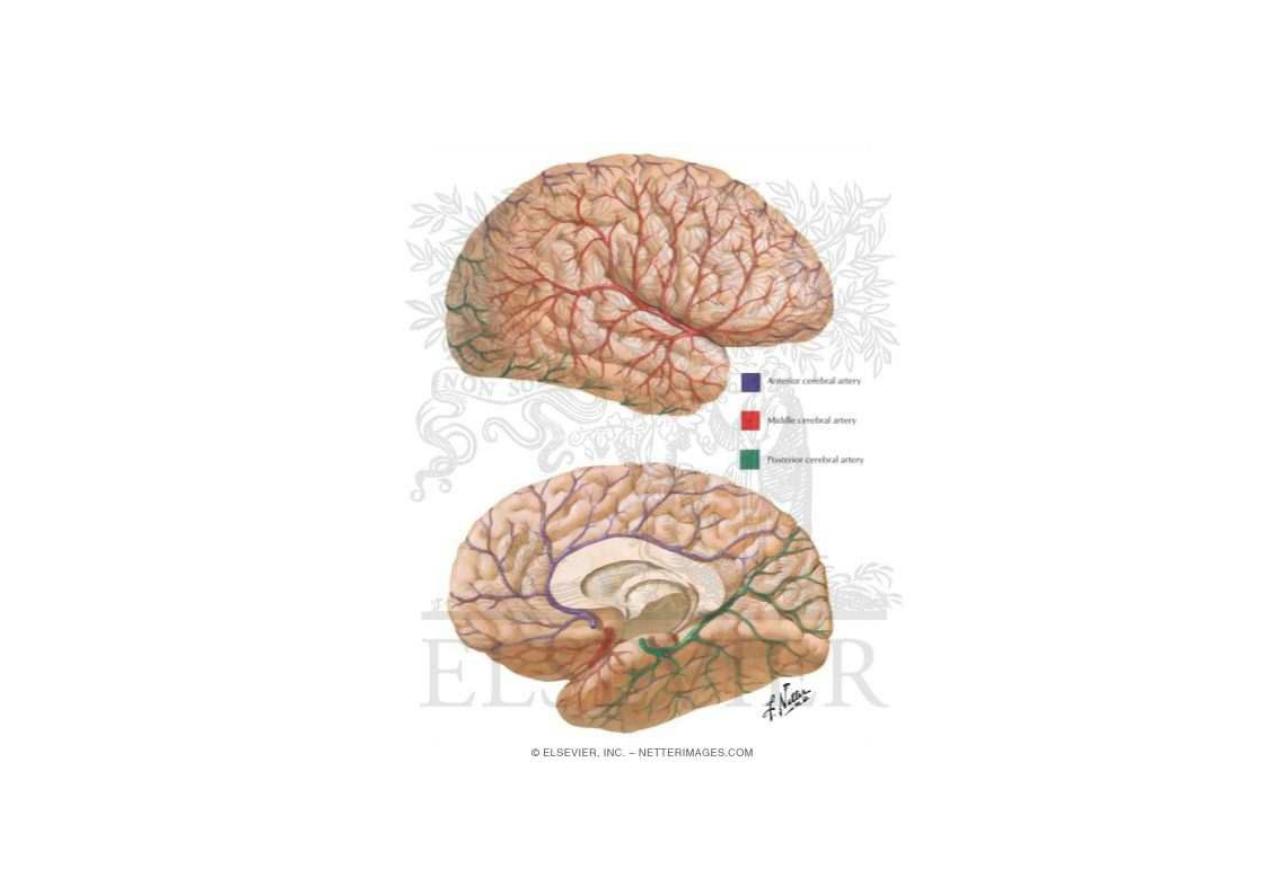
Arteries in the subarachnoid space
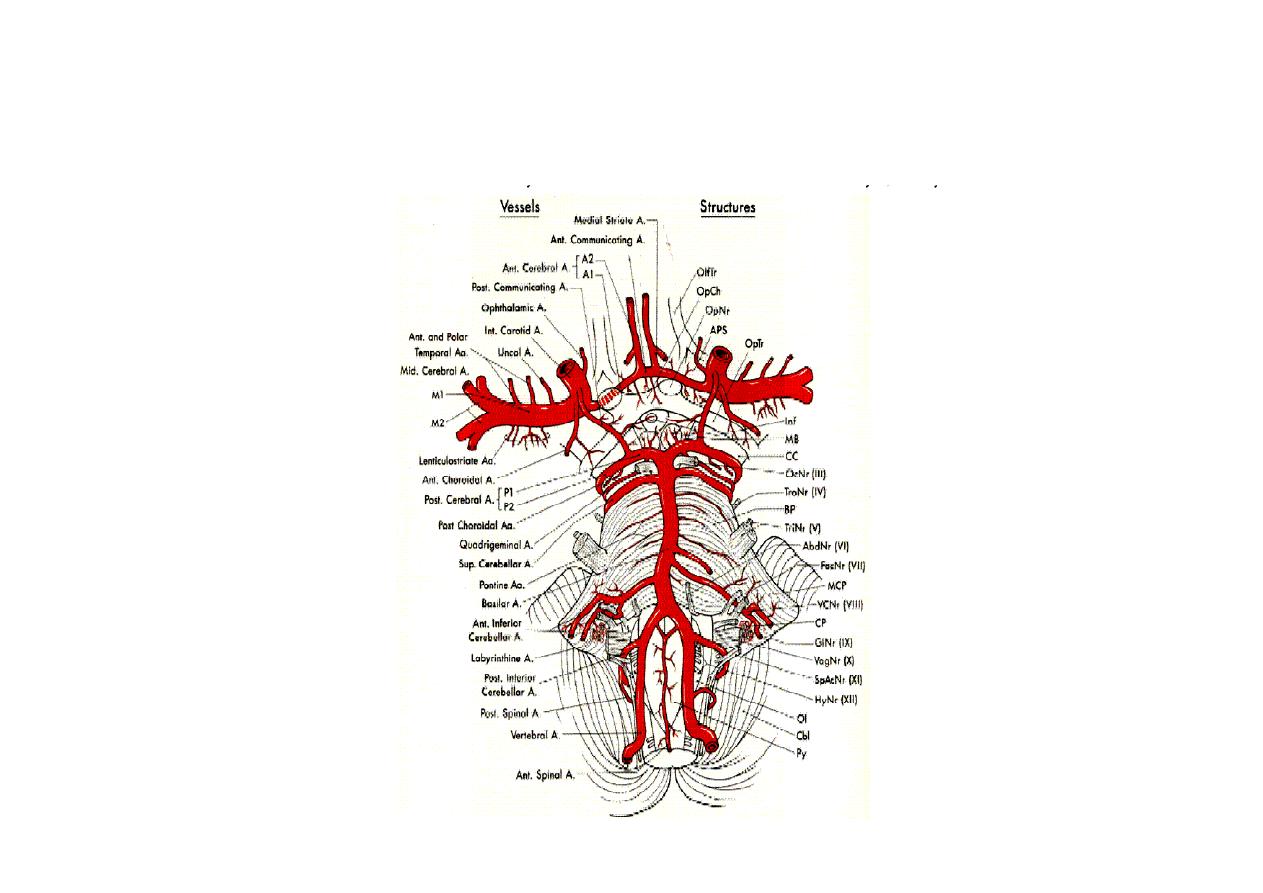
Arteries of the brain
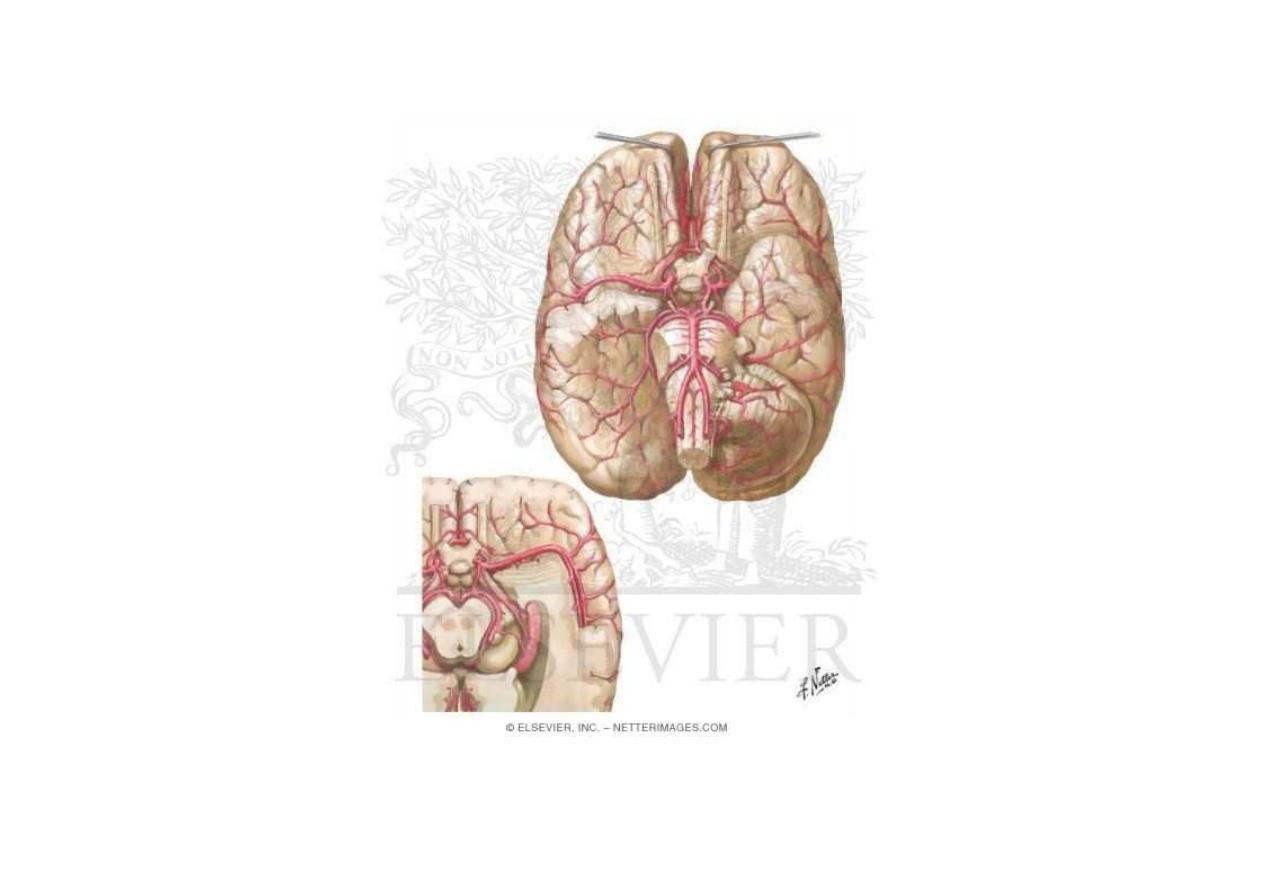
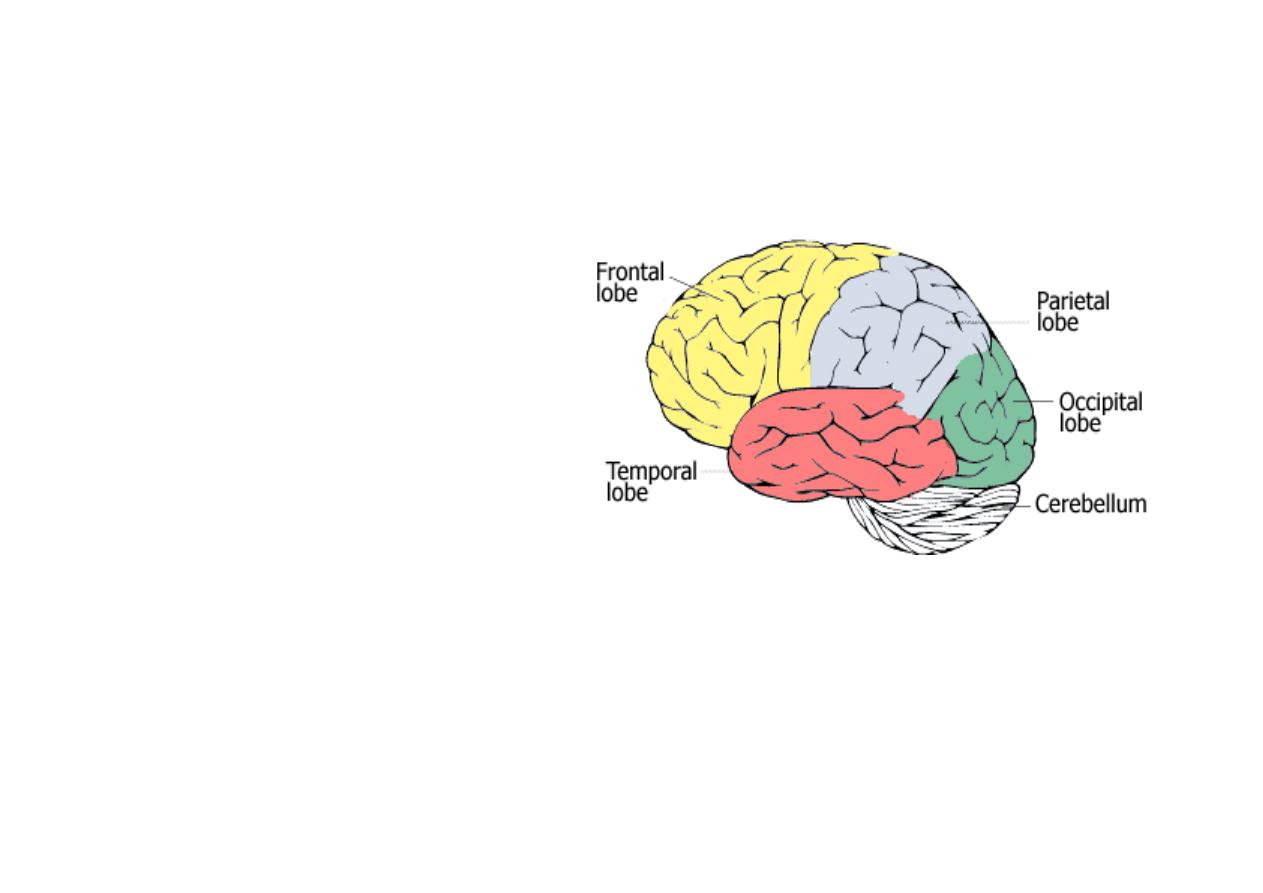
Each hemisphere has lobes:
•
Frontal lobe
•
Parietal lobe
•
Temporal lobe
•
Occipital lobe •
Occipital lobe
•
Insular lobe
•
Limbic lobe
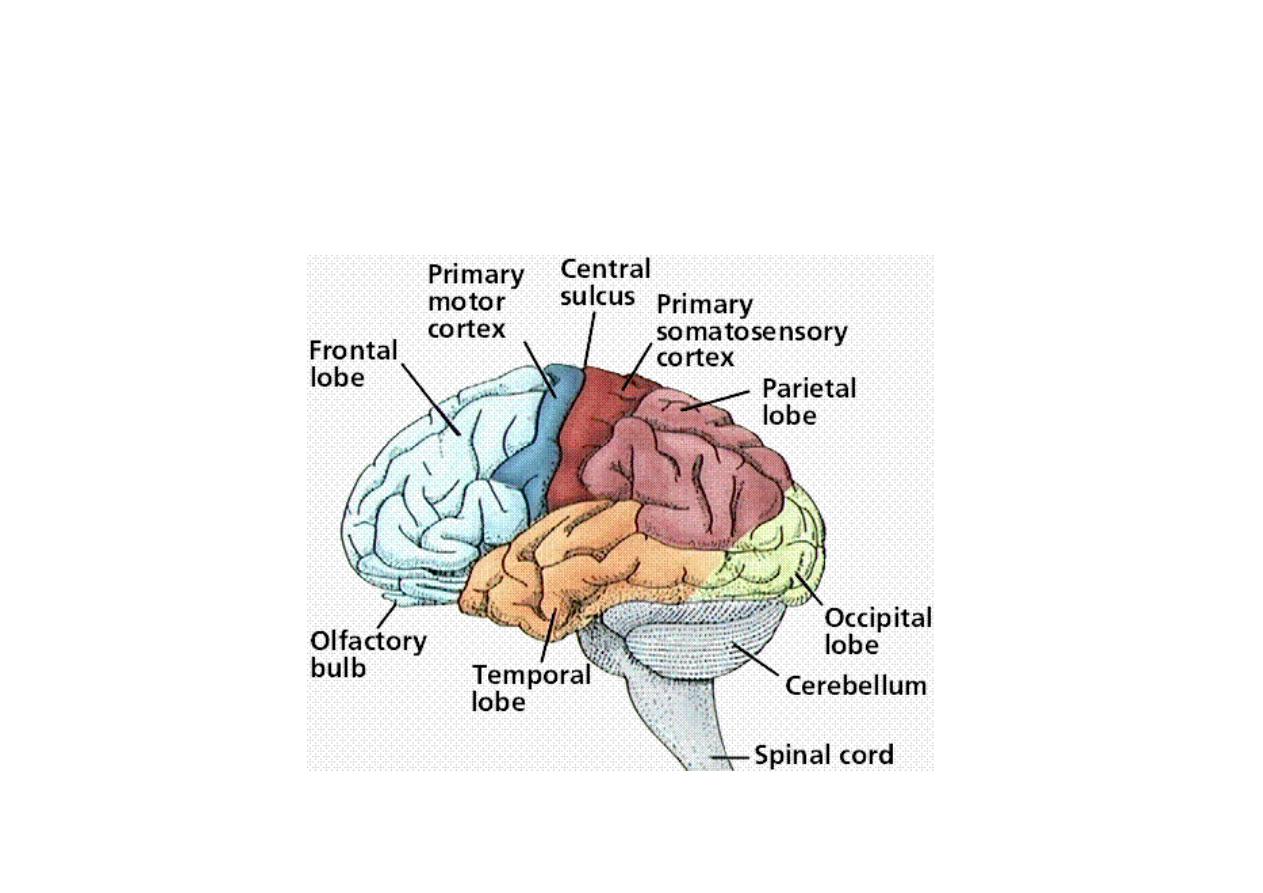
Functional areas
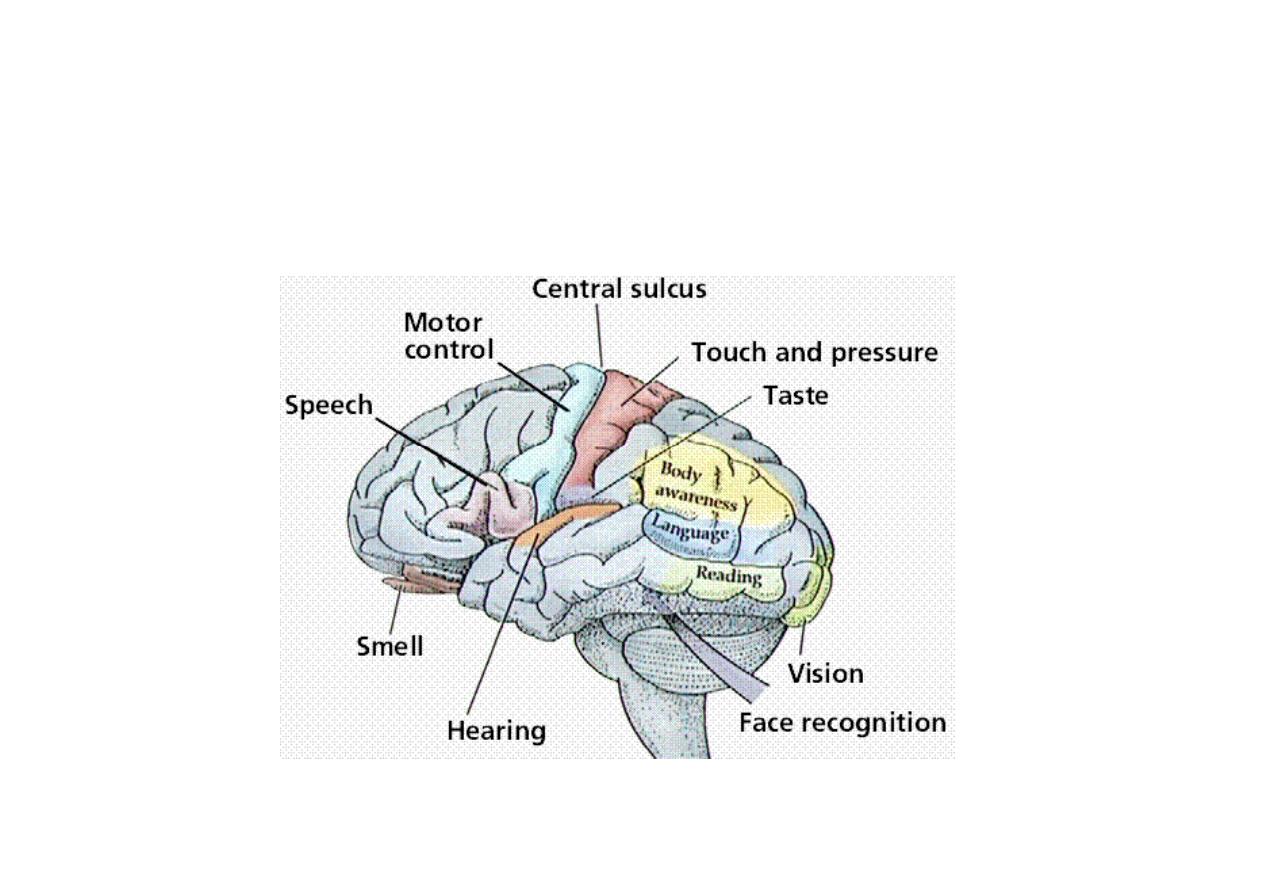
Function 2
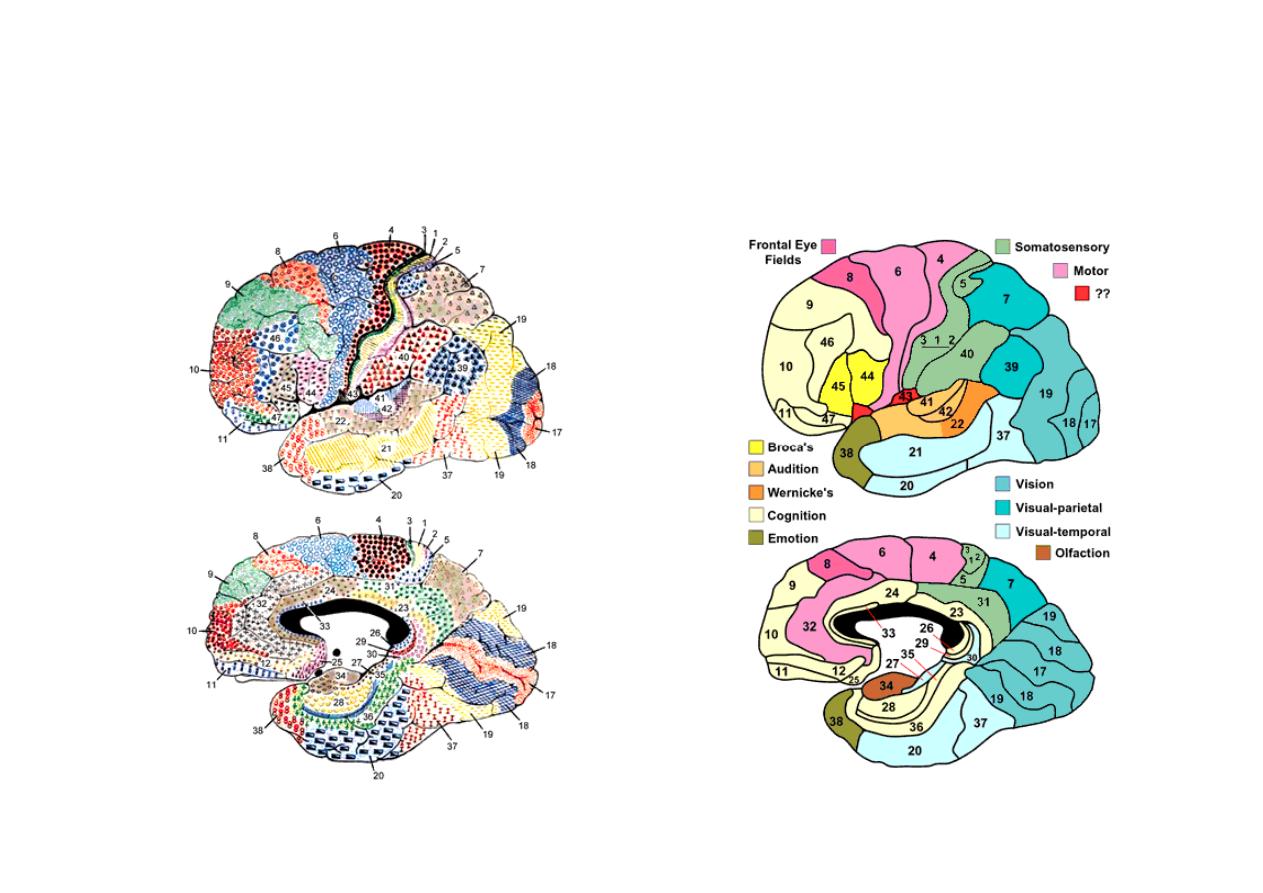
Map
Brodmann
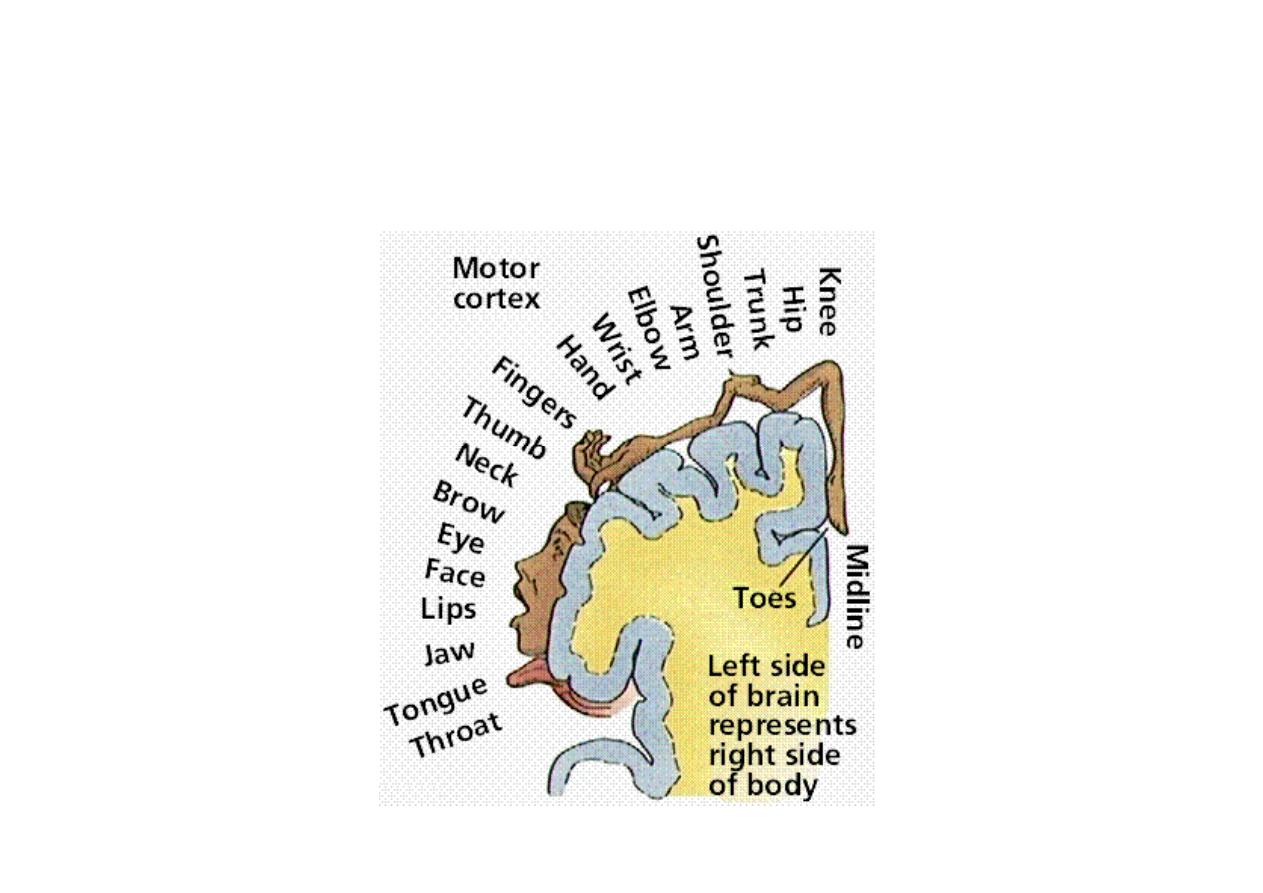
The Motor Strip
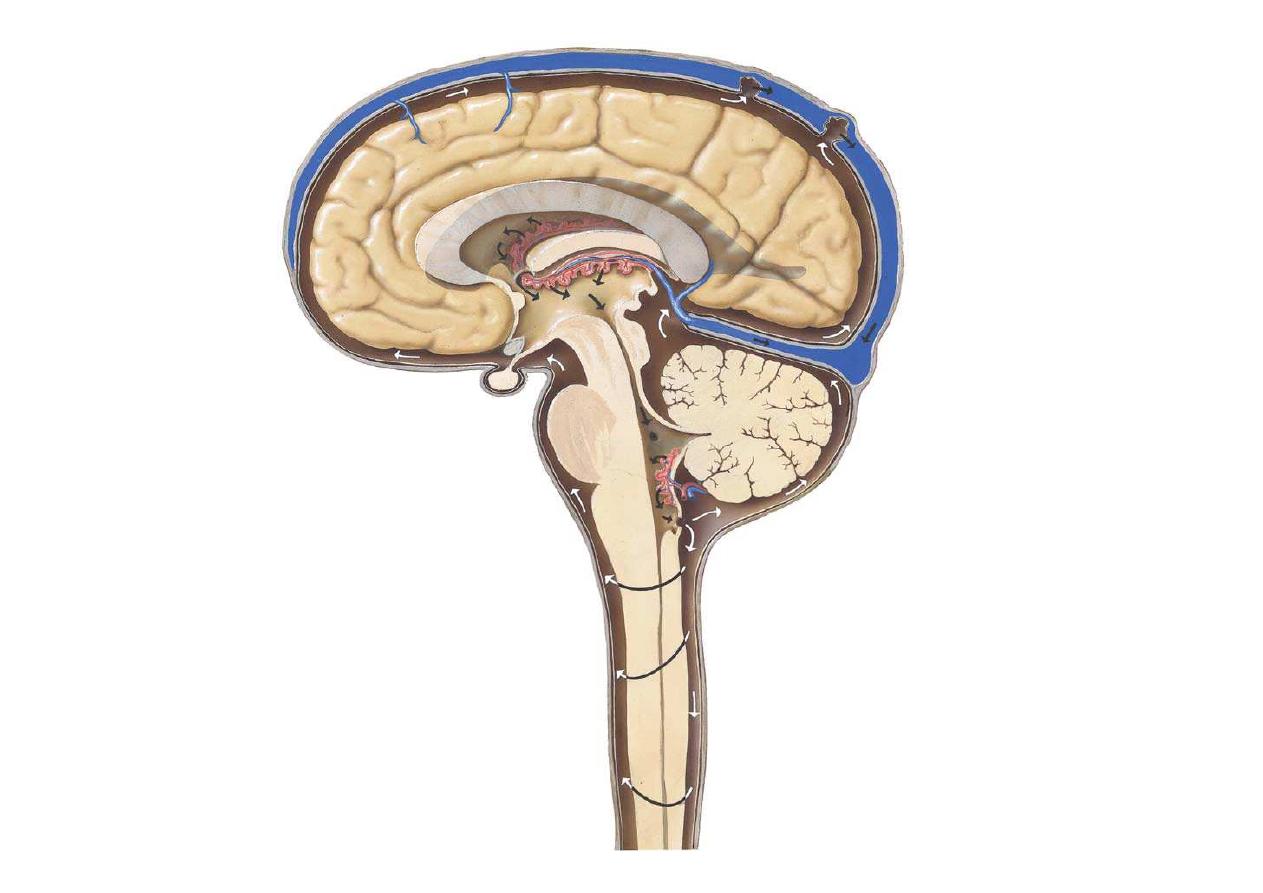
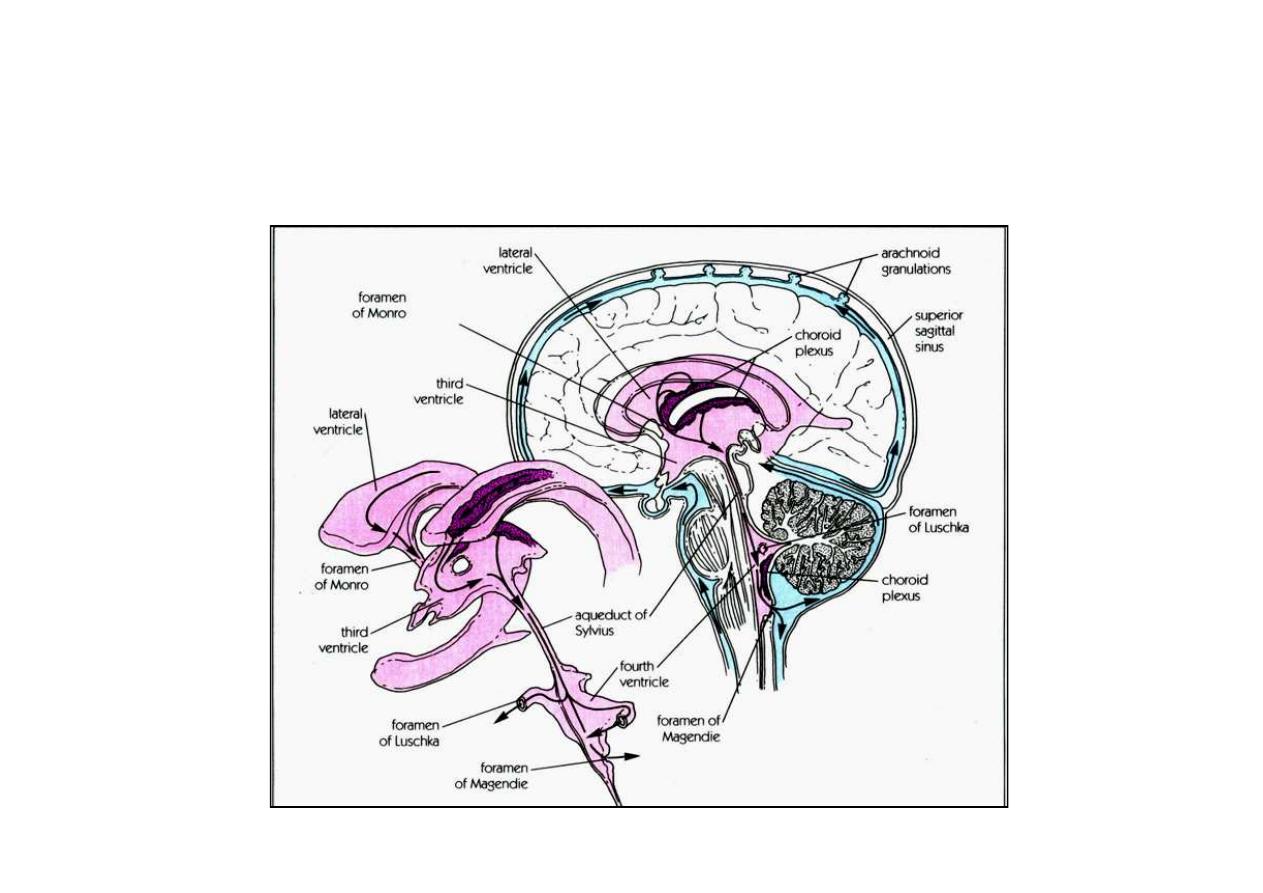
CSF Pathways

Physiology

Blood supply to the brain
The brain gets 15% of the cardiac output and 20% of
the oxygen consumption
The brain tissue gets in average 50ml of blood per
100gr of tissue per minute. The gray matter receives
100gr of tissue per minute. The gray matter receives
about 3 to 4 times more than the white matter
Total blood supply to the brain is about 500-600ml per
minute

Factors Affecting the blood supply
•
Autoregulation
•
Biochemical changes – O
2
and CO
2
•
Biochemical changes – O
2
and CO
2
•
Blood brain barrier - BBB

Autoregulation
Maintains a regular blood supply to the brain
in changing blood pressures
The range is 50-150 mm mercury
Possible mechanisms are the myogenic
Possible mechanisms are the myogenic
control, neurogenic and biochemichal control

CO
2
The most important and powerful mechanism
that controls brain blood flow
A change in 1mm PCO
2
changes the flow in 4-5%
PCO of 70 gives a maximal vasodilatation.
PCO
2
of 70 gives a maximal vasodilatation.
Above that the flow is pressure dependent

Hyperventilation
Hyperventilation lowers the PCO
2
It has a strong effect but it is limited in time
Could be dangerous if not regulated- ischemia
Can be regulated with a jugular bulb oximeter
Can be regulated with a jugular bulb oximeter

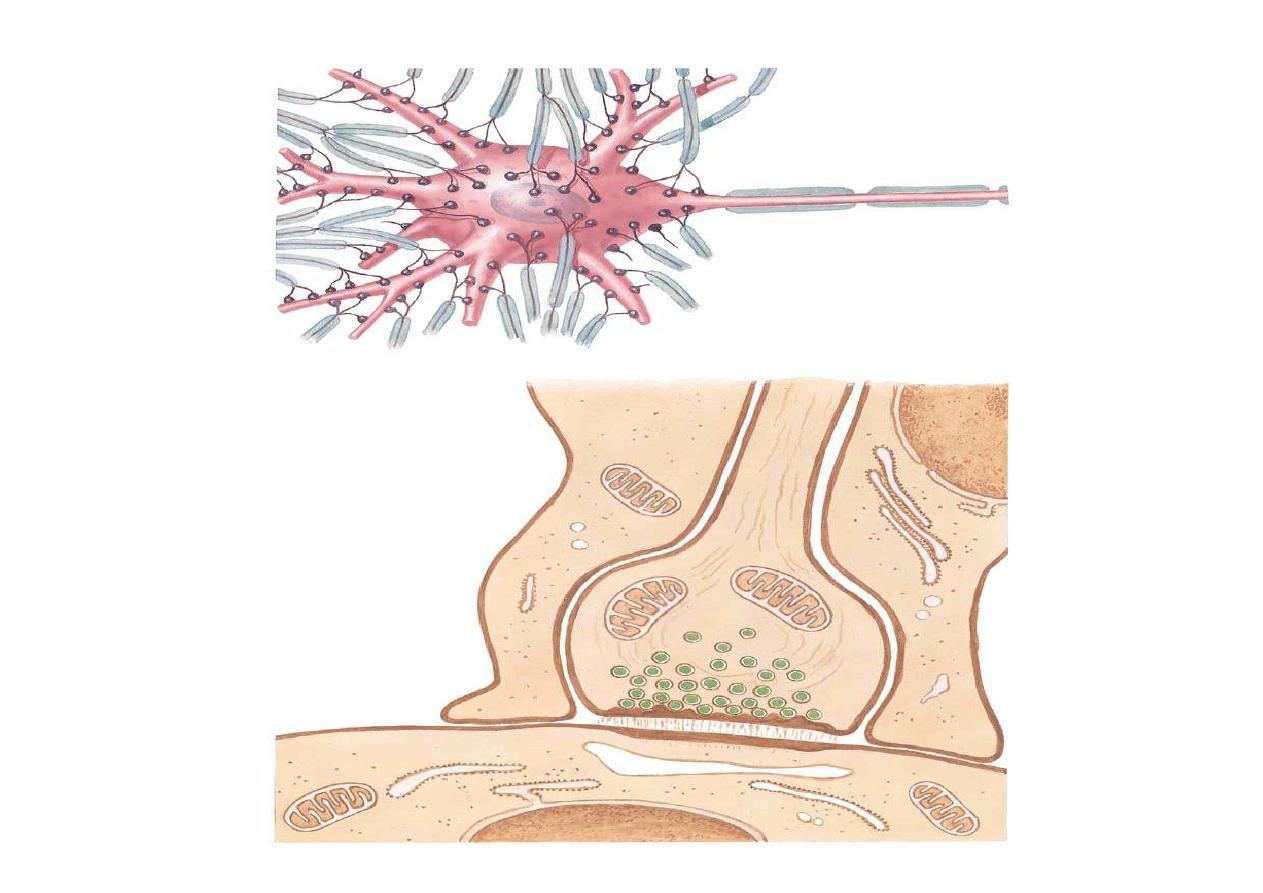
BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER
The BBB is composed of the tight junctions in
the endothelium cells of the blood vessels
Prevents passage of large molecules and even
small ions like Na and Cl
small ions like Na and Cl
Specific substances pass the BBB like glucose
and amino acids

BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER
Because of the BBB, in the brain hydrostatic and
oncotic pressures are not significant. The
important parameter is the osmotic pressure
important parameter is the osmotic pressure
The BBB is damages in trauma, tumor, infarct,
SAH and infection
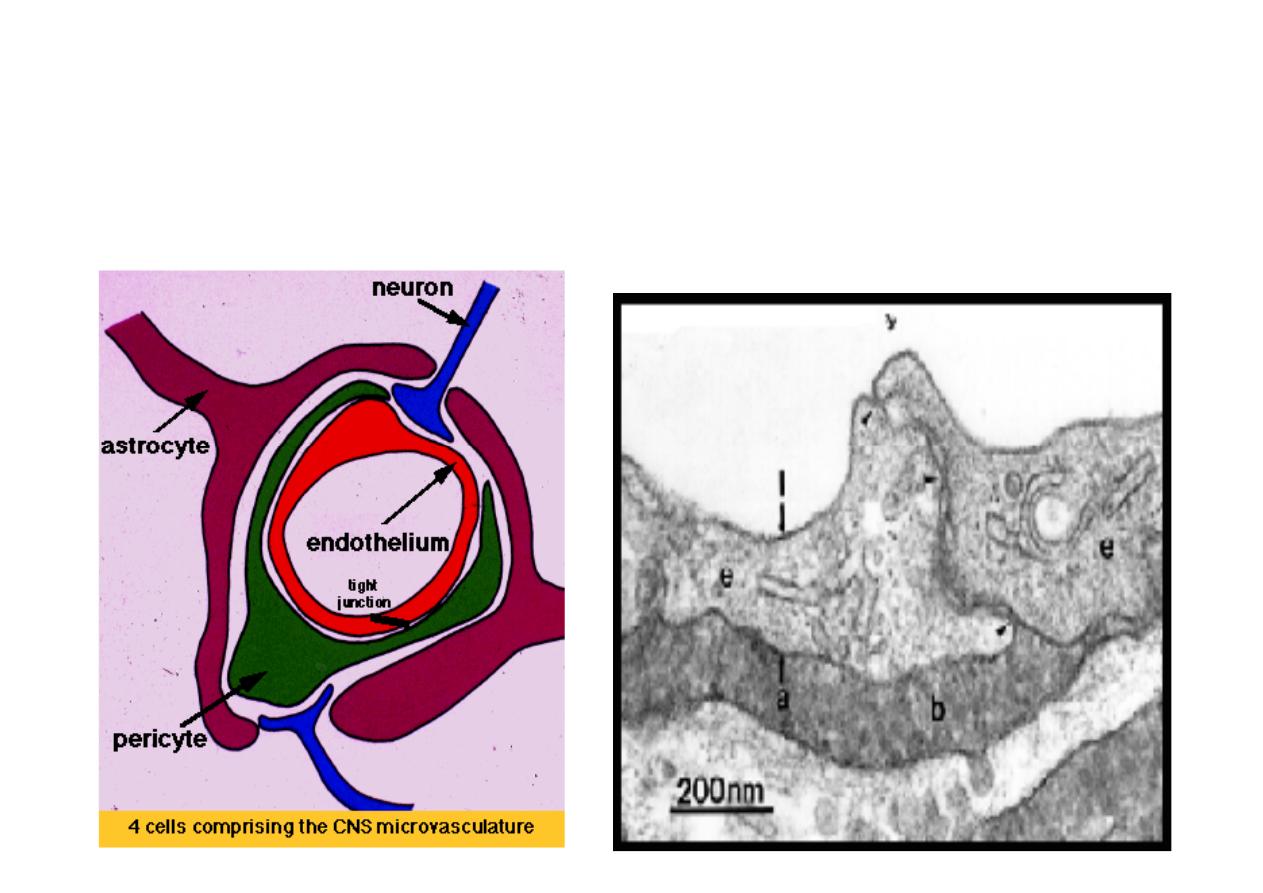
BLOOD BRAIN BARRIER
