1
Fifth stage
Orthopedic surgery
Lec-
د.يقضان
26/10/2015
Injuries of the upper limbs
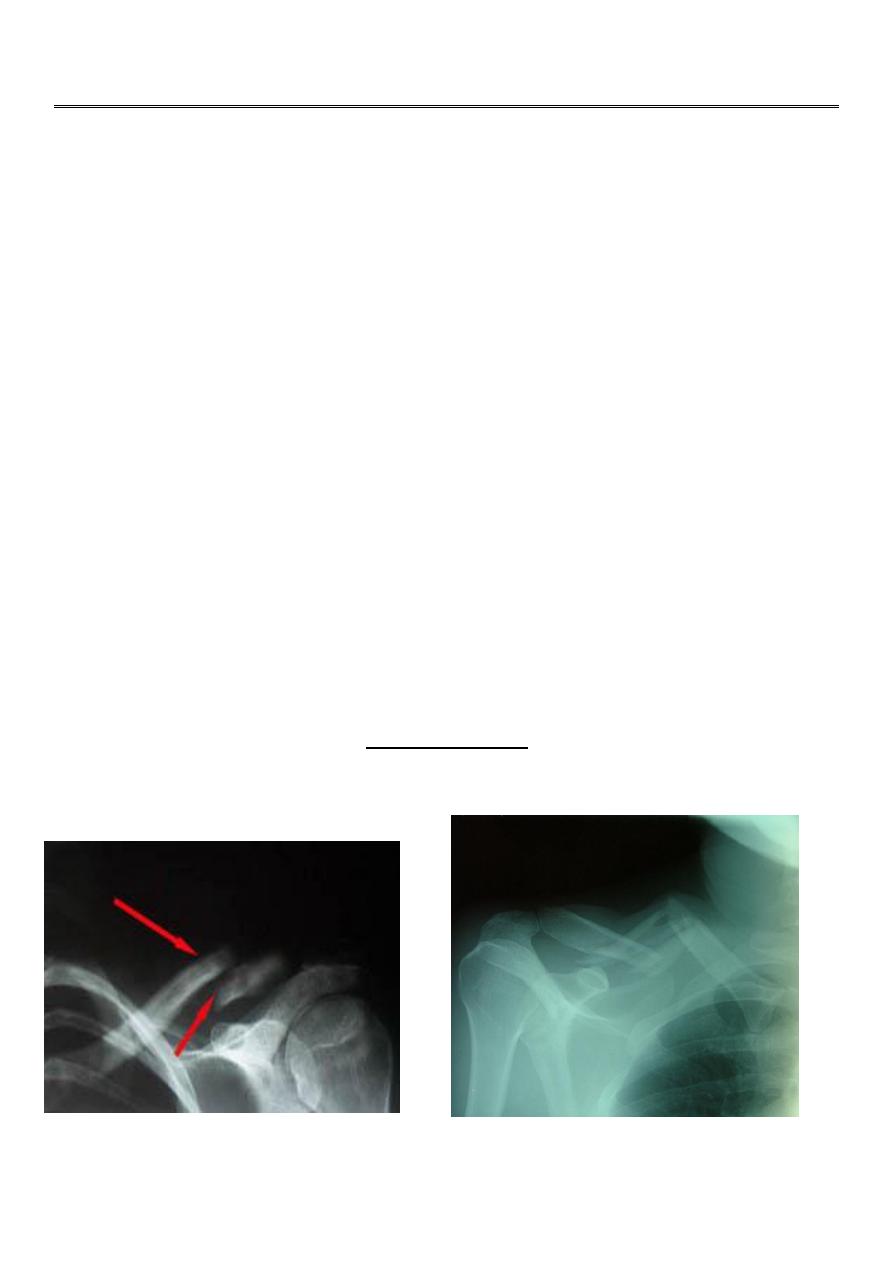
Fracture clavicle
it is occur due to fall on out stretched hands.
The common sites of the fracture in the clavicle is mid shaft .the outer segment displaced
down ward and the medial one displaced upward due to the effect of the stern mastoid
muscle .
Complication:
Early: injuries to subclavian artery, brachial
Plexus, pneumothorax all are rare.
Late : mansion, nonunion.
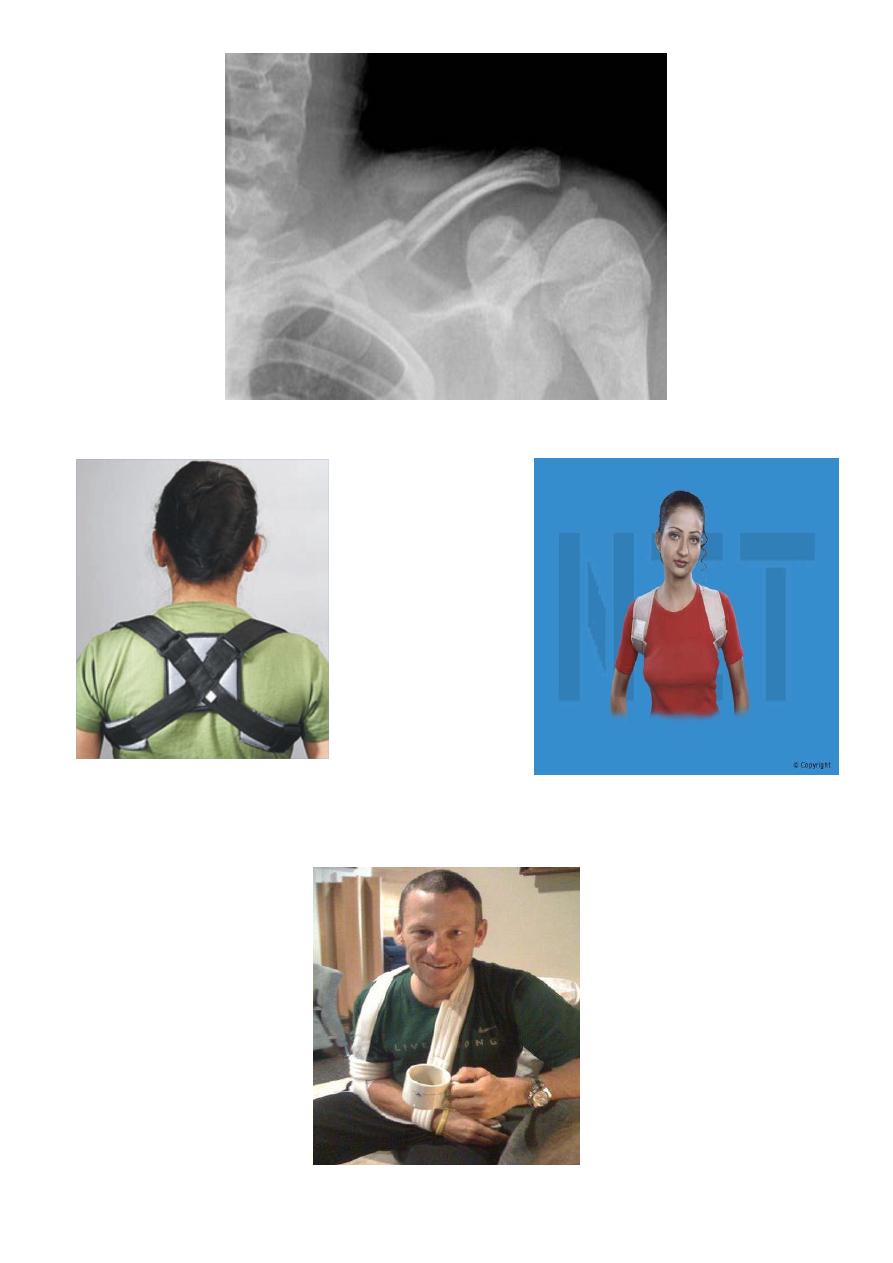
Treatment: by
splinting the arm by sling or by use
Figure of 8 for one month.
Accurate reduction is neither possible nor essential... If there is complication
then open reduction and fixation (rarely required)
Fracture clavicle
2
Figure of 8 in treatment of fracture clavicle
3
Shoulder dislocation
Shoulder joint is the commonest large joint which suffer from dislocation; due to many
factors like shallow globoid and its wide range of movements.
Types of shoulder dislocation
:
1- Anterior dislocation (the commonest).
2-posterior dislocation (rare).
3- Inferior dislocation (rare)
.
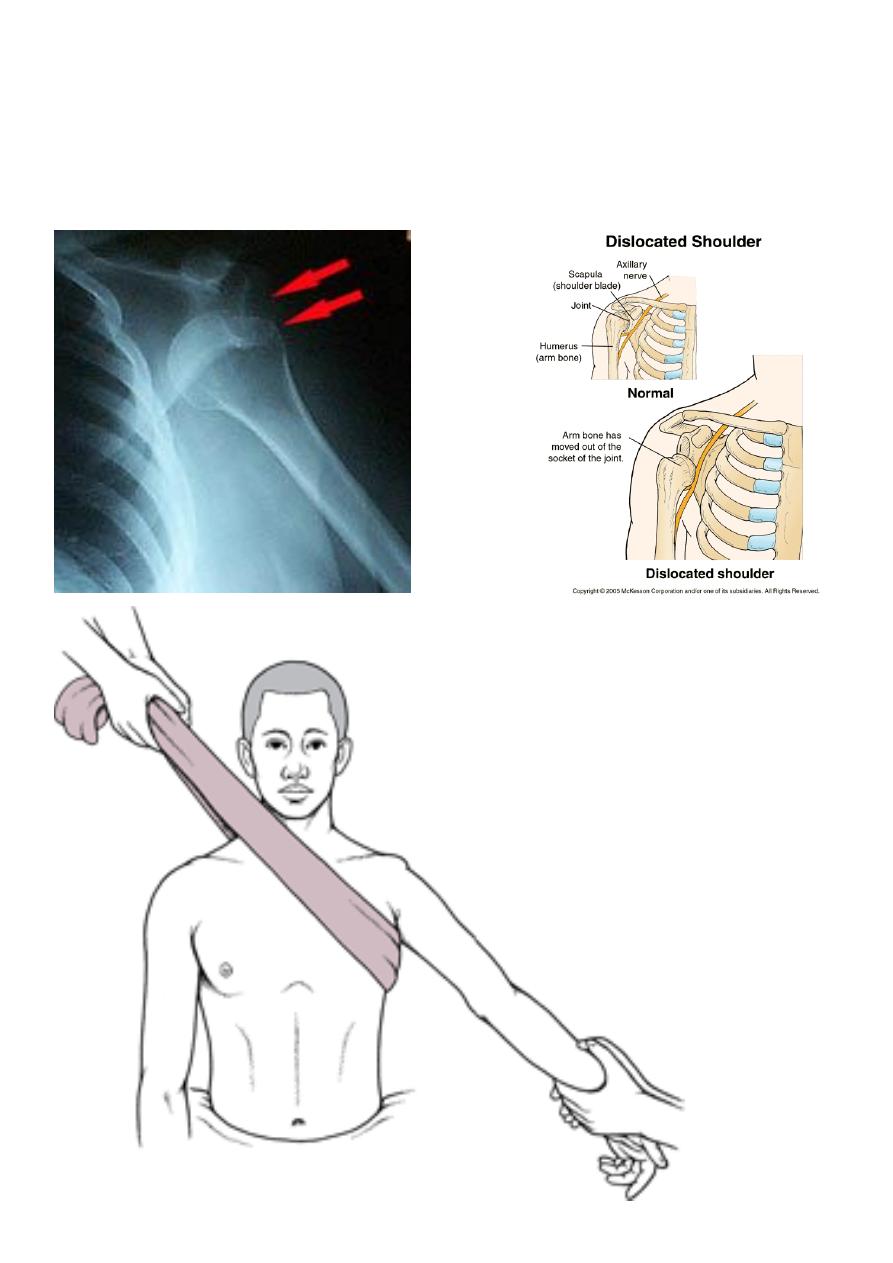
Anterior dislocation of the shoulder
It caused by fall on out stretched hand, the head of the homers driven foreword tearing the
capsule or avulsing the globoid labrum, and settled under the clavicle in the infraclavicular
fossa.
Clinically : history of trauma , sever pain , the patient support his arm with the opposite
hand and resist any kind of examination .
On examination : there is loss of normal contour of the affected shoulder , visible or
palpable boney mass below the clavicle .Neurovascular examination for axillary nerve and
distal pulsation is very important before any attempt of reduction for medicoleagal
purpose.
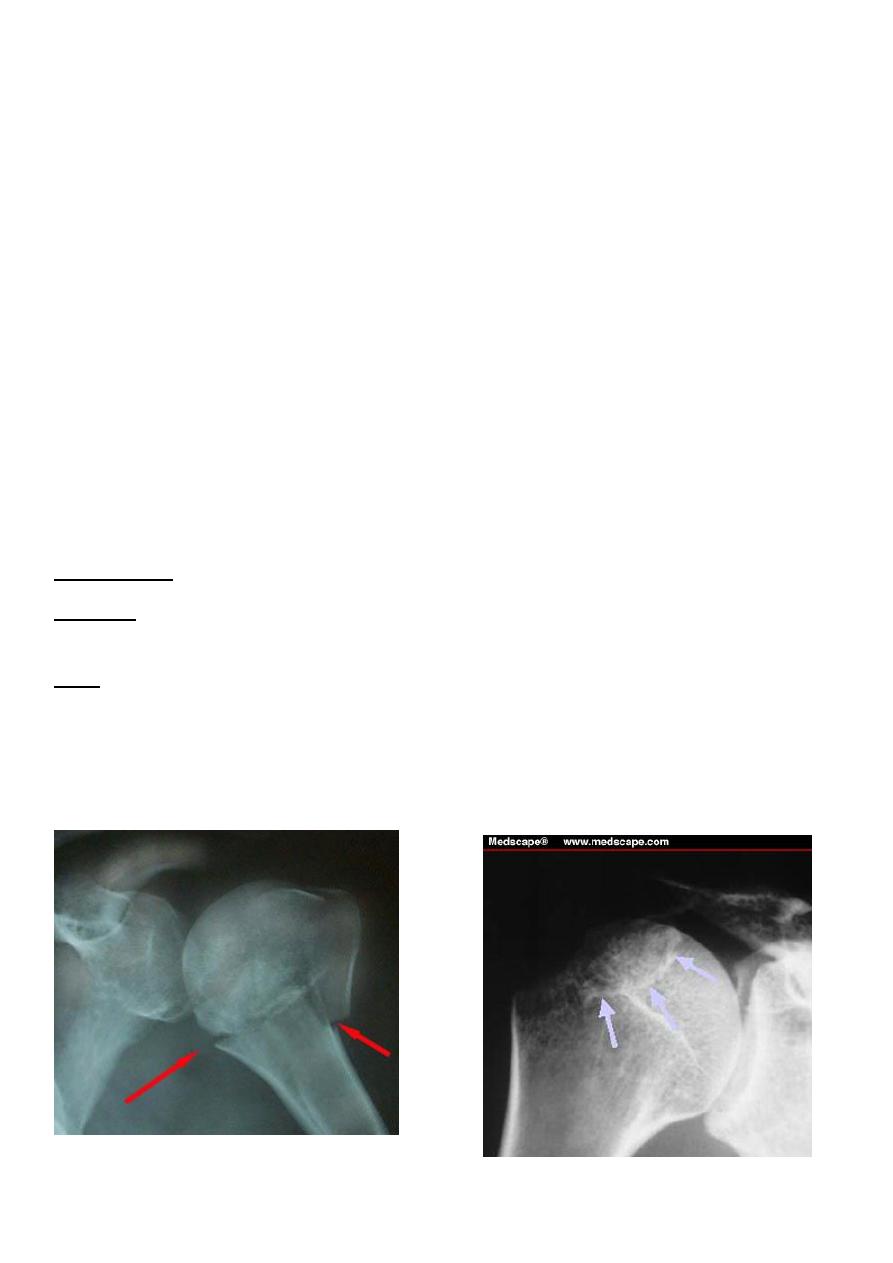
X –ray : 1- antero-posterior view show the head of the humerus out of the glenoid and
located usually below of the clavicle or the coracoid process .
2- axillary view is very helpful also .
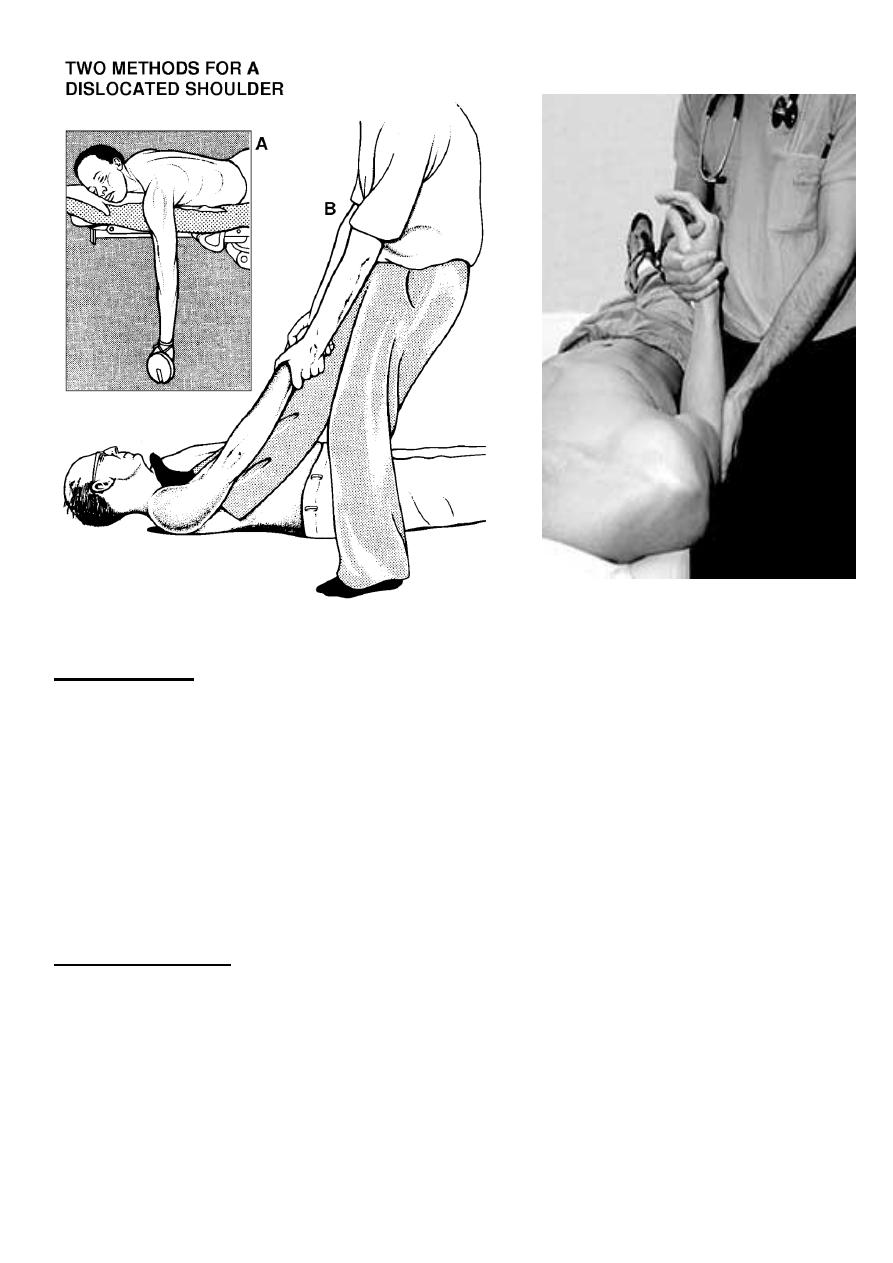
Treatment : 3 methods of reduction :
1- Kocher’s maneuver : most commonly used
under general anesthesia , with the assistant do counter traction, flexion of the elbow 90`
and held close to the body , no traction , slow lateral rotation of the arm then adduction
and medial rotation .
2-Hippocratic’s method . Traction on the line of the limb with counter traction.
3-stimson’s technique (gravity) .patient prone the arm hanged beside the bed for 15 – 20
minutes.
4
Anterior shoulder dislocation
5
Complications :
Early :1- nerves injuries : axillary nerve is the most commonly injured ; the patient is unable
to do contraction of the deltoid muscle and there will be small patch of anesthesia over the
tip of the shoulder . The lesion is usually neuropraxia and recovery will occur after few
weeks
2-vascular injuries : mainly the axillary vessels .
3- rotator cuff tear : there will be difficulty in abduction of the shoulder .
4- associated fractures : fracture proximal humerus , fracture greater tuberosity of hum.
Late complication :
1- stiffness of the shoulder .
2- recurrent dislocation . It occur due to avulsion of the labrum or sever tear of the capsule .
It should be treated by surgery.
3- unreduced dislocation .(missed)
6
Posterior shoulder dislocation
It is rare less than 2% it occur due to marked internal rotation with adduction ; it occur in
Convulsion or with electrical shock .
Clinically : the arm is held in medial rotation and it locked in that position .
Fracture proximal humerus
This type of fracture occur in old and middle age osteoporotic people .
In the majority of the cases displacement is not marked , only 20% of cases has
considerable displacement .
The fracture occur due to fall on out stretched arm Proximal humerus include 4 major
components these are :
1-head of humerus . 2-greater tuberosity .
3-lesser tuberosity . 4-surgical neck of the humerus .
Classification of this fracture called neer classification .
Clinically : history of trauma , pain ,loss of function , swelling , bruises on theskin , sign of
axillary nerve or brachial plexus injury may be detected .
X-ray :a-p , lat.view or axillary view should be taken to exclude associated dislocation .
Proximal humerus fracture

7
Treatment :
Minimally displaced fracture (majority) need only sling of the arm for 3 weeks until the pain
subside and then gentle passive movement is advised ; active movements is encouraged
after 6 weeks .
If there is considerable displacement of one or more of the 4 components , then
manipulation is advised , if fail then open reduction and fixation .
If the fracture is 4 peaces and displaced and the patient is old then do prosthetic
replacement of the proximal humerus .
Complication :
Early : neurovascular injuries (axillary n. , a.)
Late :
1- stiffness of the shoulder ; this can minimized by early mobilization .
2- avascular necrosis of the head of the humerus .
Fracture shaft of humerus
this fracture caused by fall on out stretched Hands or by direct blow on the arm .
Fracture above the deltoid insertion (deltoid tuberosity), the proximal segment is adducted
by pectoralis major muscle , and if the fracture below the deltoid insertion then the
proximal segment is abducted by the effect of the deltoid muscle .
Injury to the radial nerve is common with this fracture mainly at the junction of the upper
two third and the lower one third of the shaft due to close contact of the nerve to the bone
at that site so it is very important to test for the radial nerve function with this fracture
before and after treatment and this is done by assessing active extension of fingers and
wrist .
Treatment :
Conservative treatment : this include hanging cast which is p.o.p cast made from the arm
to the wrist with elbow flexed 90`, the limb is slinged from the wrist so the weight of the
cast will pull the fragments into alignment this can be left for 2-3 weeks and then replaced
by shoulder to elbow cast (u-shape slab) for further 4-6 weeks .
Exercise of the wrist and the fingers should be started from the beginning to avoid stiffness.
Exercise of the shoulder should be started as early as possible to avoid stiffness( mainly in
elderly)

8
Operative treatment :
Types of fixation :
1-compresion plate and screws .
2-inter locking intra medullary nail .
3-external fixators .
Indications of fixation :
1-sever multiple injuries .2-open fracture .
3-segmental fracture . 4- pathological fracture .
5-radial nerve palsy after manipulation .
6- non-union .
Complications :
Early :
1-vascular injury (brachial artery) .
2- nerve injury ; radial nerve palsy will cause
wrist drop .
Late complication :
1- delayed union and non union .
2- joint stiffness (minimized by early activ
