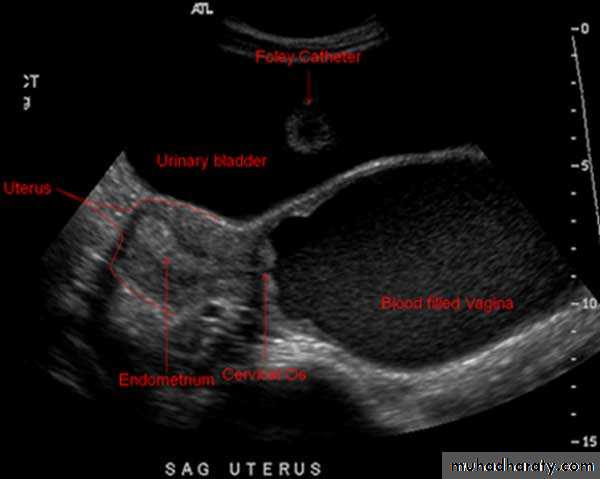
Ultrasonography in Gynaecology
Dr Sameer Abdul Lateef.Introduction
Ultrasound was first introduced by Ian Donald (Glasgow 1950) in the field of medicineSonography is widely used in Gynaecology either with the transabdominal (TAS) or with the transvaginal (TVS) probe
Because of the safety, high patient acceptance and relatively low cost, ultrasonography has become a common diagnostic modality in gynaecology these days.
Use of Ultrasound in Gynaecology
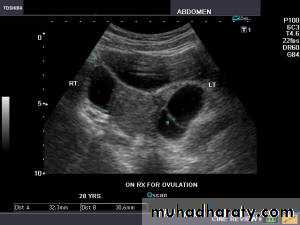
Use of infertility workupSerial measurement of ovarian follicular diameter (folliculometry) and endometrial thickness are done using TVS.
Ultrasound can provide presumptive evidence of ovulation. Following ovulation, internal echoes appear and free fluid is observed in pouch of Douglas.
To detect correcting time of ovulation by folliculometry in conjuction with plasma oestradiol.
Sonographic guided oocyte retrieval in IVF and GIFT programmes.
Use of ultrasound in Gynaecology
Ectopic pregnancy can be detected on TVS as a “tubal ring” separate from the ovary in a patient with empty uterine cavity.Pelvic mass can be evaluated as regard to its location and consistency. Uterine fibroid, ovarian mass, endometrioma, tubo-ovarian mass, etc. can be delineated when there is confusion in clinical diagnosis.
Oncology: TV-CDS can assess the vascularity of the mass. Low flow impedance with a high flow velocity raises the suspicion of a malignant tumor.
Use of Ultrasound in Gynaecology
Endometrial disease: Women with unexplained uterine bleeding, or postmenopausal bleeding .
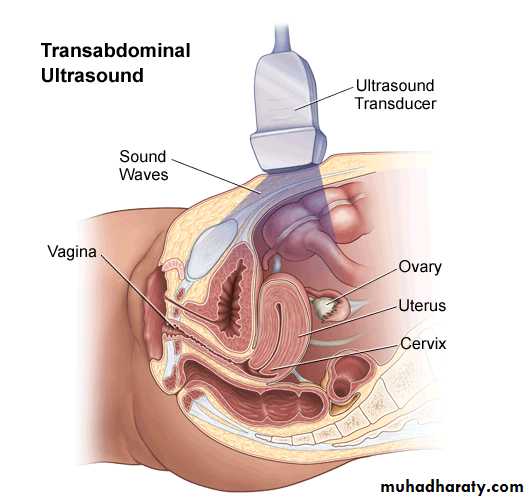
Transabdominal sonography
Transabdominal sonography
Is done with a linear or curvilinear array transducer operating at 2.5-3.5 MHz.TAS requires full bladder to displace the bowel out of pelvis.
Other wise gas in the bowel acts as a complete barrier to ultrasound waves.
Transabdominal sonography
TAS is best used for large masses like fibroid or ovarian tumorHigher is the frequency of ultrasound wave, better is the image resolution but lesser is the depth of tissue penetration
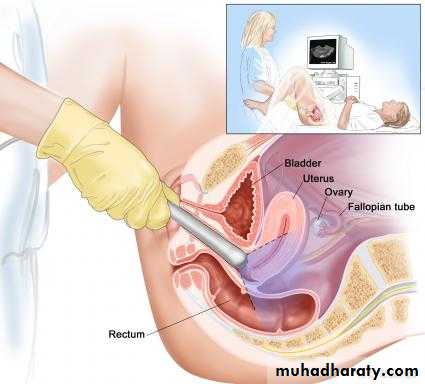
Transvaginal Sonography (TVS)
It is done with a probe which is placed close to the targt organ.Preparing patient
There is no need of a full bladder
It also avoids the difficulties due to obesity, faced in TAS
Transvaginal Sonography
Transvaginal ultrasound may be done for the following problems:Abnormal findings on a physical exam, such as cysts, fibroid tumors, or other growths
Abnormal vaginal bleeding and menstrual problems
Certain types of infertility
Ectopic pregnancy
Pelvic pain
Transvaginal sonography
TVS operates at a high frequency (5-8 MHz).Therefore, detailed evaluation of the pelvic organs (within 10 cm of the field) is possible with TVS.
But the drawbacks of TVS are mainly due to narrow vagina as in virgins, postmenopausal women or post radiation vaginal stenosis.
Transvaginal sonography
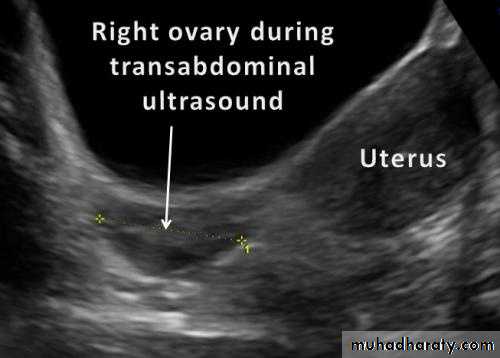
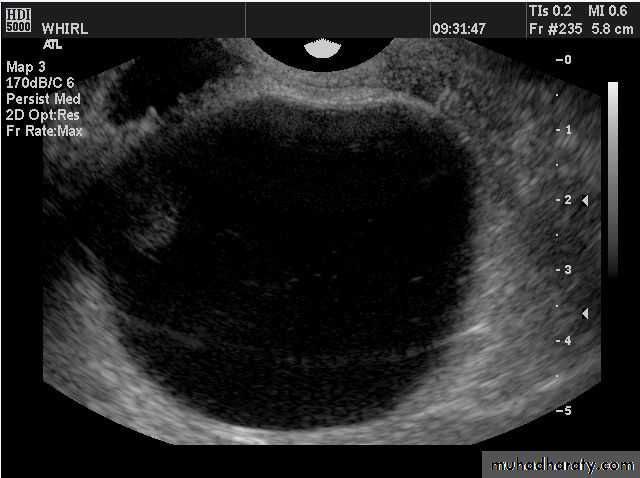
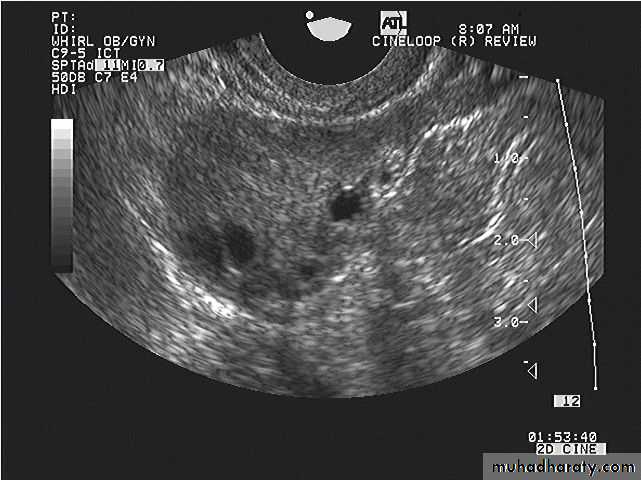
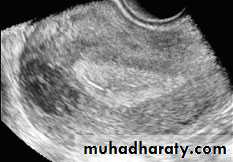
Ultrasound of Normal ovary
Normal Ovary
Normal ovary during a natural menstrual cycle demonstrating normal follicle population and distribution on day 12 postmenstruation. A dominant follicle is visualized in the central portion of the image and several subordinate follicles from the wave (2–5 mm) are observed in the left lateral aspect of the ovary.
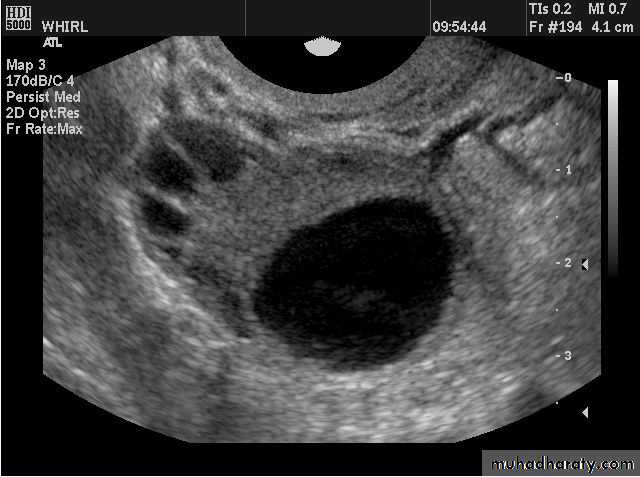
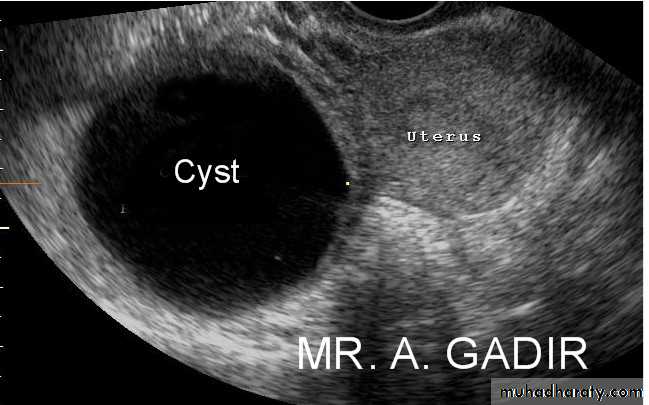
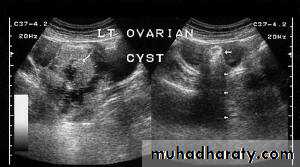
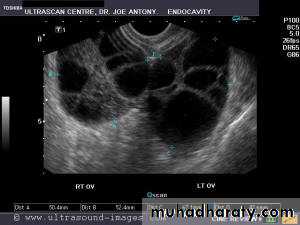
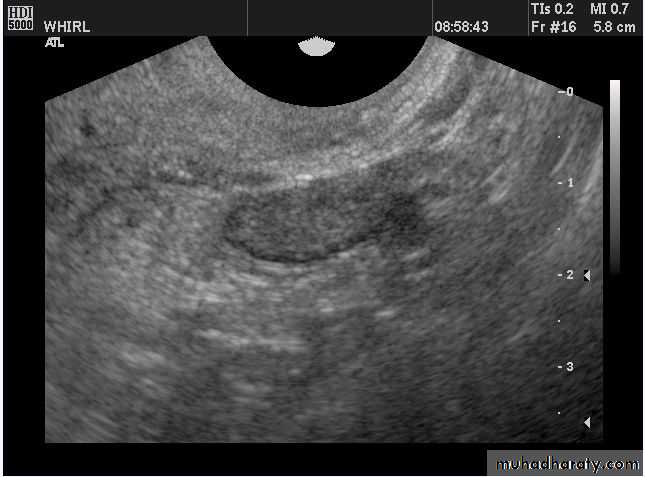
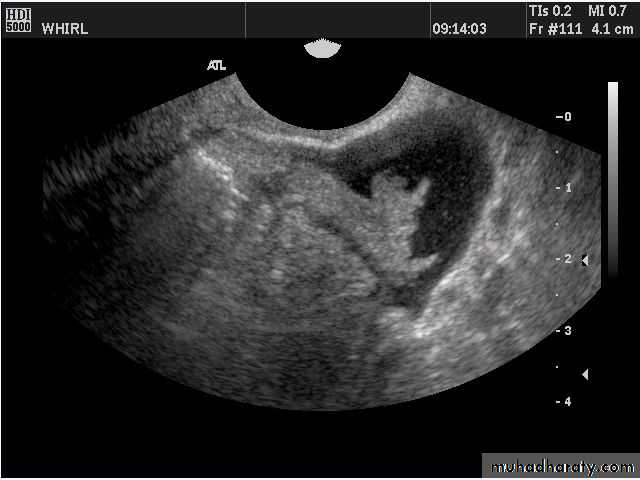
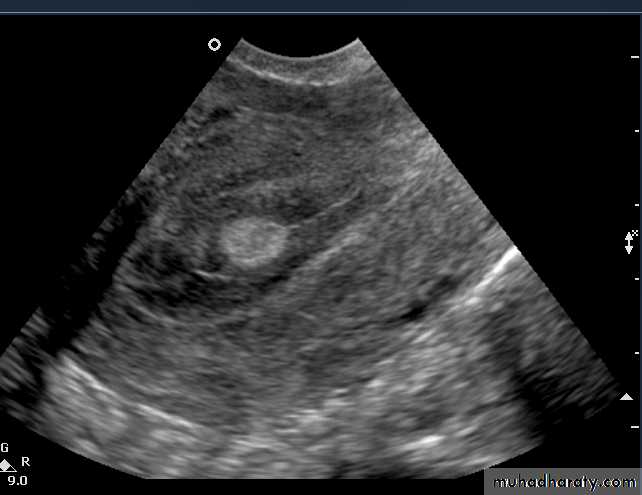
Functional cysts of the ovary - Follicular cysts:
This young female patient underwent sonography for non-specific pain in the lower abdomen. Ultrasound images of the pelvis show bilateral ovarian cysts which show absence of internal nodules, septae or debris. These findings are typical of follicular cysts of the ovaries. Follicular cysts are functional cysts and are enlarged ovarian follicles that have not ruptured (ovulated). They are usually unilateral.
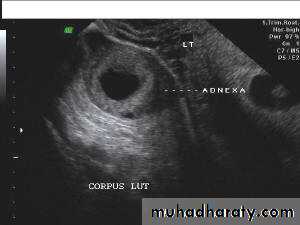
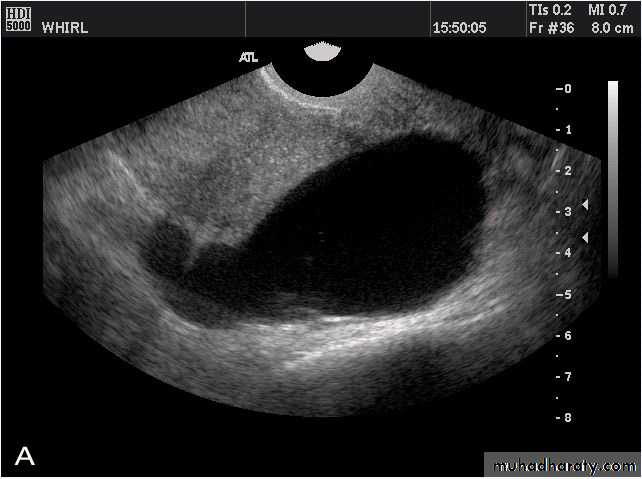
• Functional cysts of the ovary – Corpus Luteum cysts
Lt. adnexal cystic mass- Luteal cyst(Lt. ovary):• Functional cysts of the ovary – Corpus Luteum cysts
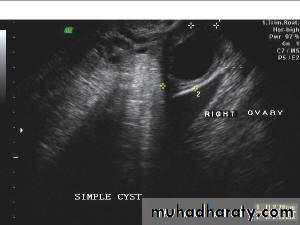
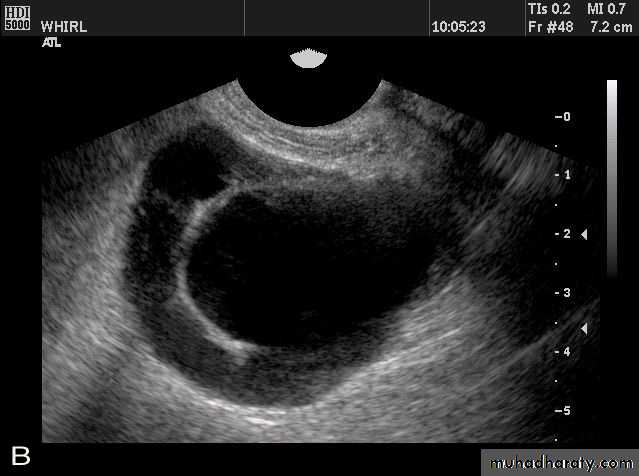
Rt. ovarian simple cyst:
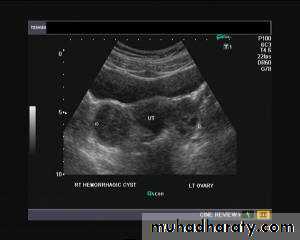
Hemorrhagic ovarian cysts:
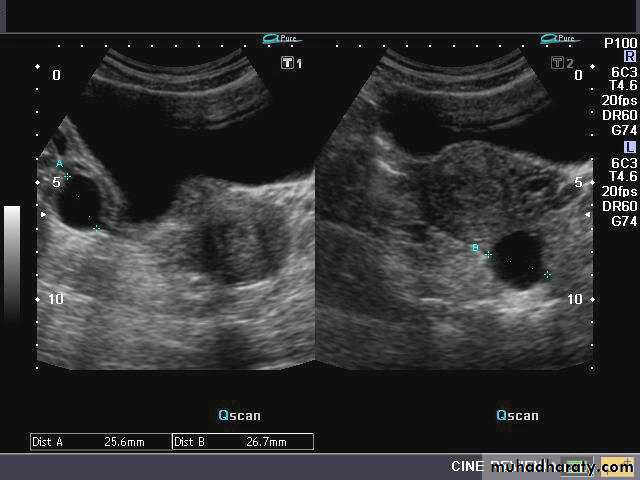
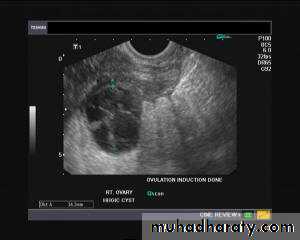
Hemorrhagic cyst of ovary resulting from Ovulation inductionThis young nulliparous female patient undwerwent ultrasonography following ovulation induction. The right ovary shows a typical hemorrhagic cyst formed from the corpus luteum. The first image (top row- left) is a transabdominal ultrasound image showing fine fibrinous strands within the cystic mass in the right ovary. Transvaginal ultrasound and color Doppler images confirm these findings. The uterus shows typical secretory changes in the endometrium suggesting post ovulatory phase.
Hemorrhagic ovarian cysts:
Hemorrhagic cyst of ovary resulting from Ovulation inductionThis young nulliparous female patient undwerwent ultrasonography following ovulation induction. The right ovary shows a typical hemorrhagic cyst formed from the corpus luteum. The first image (top row- left) is a transabdominal ultrasound image showing fine fibrinous strands within the cystic mass in the right ovary. Transvaginal ultrasound and color Doppler images confirm these findings. The uterus shows typical secretory changes in the endometrium suggesting post ovulatory phase.
Hemorrhagic ovarian cysts:
Hemorrhagic cyst of ovary with co-existing chocolate cyst/ endometrioma:This patient has a co-existing chocolate cyst with a hemorrhagic cyst in the same (right) ovary. The cyst on the left half of the ultrasound image is a hemorrhagic cyst. Note the fine fibrinous strands within the cyst suggesting clot formation. The cyst on the right half of the image is homogenous with fine echoes throughout the ovarian cyst. This is a typical appearance of an endometrioma (chocolate cyst)
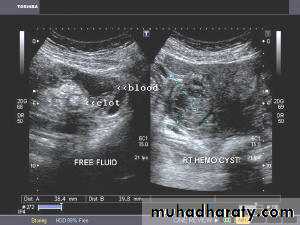
Hemorrhagic ovarian cysts:
Hemorrhagic cyst of ovary with ruptured ectopic pregnancy:This female patient has a left ovarian hemorrhagic cyst (see ultrasound image above-left). In addition, there is a large collection of free fluid with particulate matter in the pelvis. The right fallopian tube is thickened with a ring shaped mass. This suggests that there is significant hemorrhage into the pelvis due to a ruptured ectopic pregnancy (right tubal ectopic gestation). The left ovarian hemorrhagic cyst appears intact, ruling out ruptured hemorrhagic cyst.
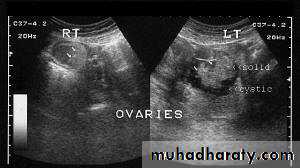
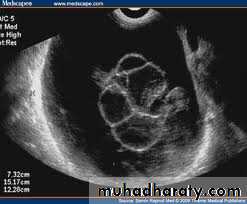
Ovarian dermoid cyst or Cystic teratomas:
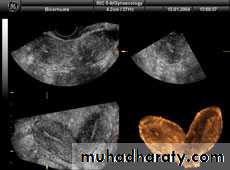
These ultrasound images reveal bilateral ovarian complex masses that contain both solid and cystic components. The right ovary shows a cystic mass with a solid, highly echogenic "dermoid plug". This is a solid nodule containing fat and various tissues including hair. Posterior acoustic shadowing is seen. The left ovary shows a dermoid plug and, in addition, a "dermoid mesh" is also seen, an irregular echogenic solid mass within the cyst. Echogenic debris is seen floating within the fluid
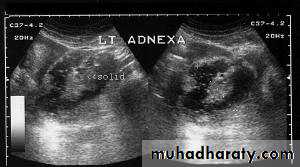
• Ovarian dermoid cyst or Cystic teratomas:
These ultrasound images reveal bilateral ovarian complex masses that contain both solid and cystic components. The right ovary shows a cystic mass with a solid, highly echogenic "dermoid plug". This is a solid nodule containing fat and various tissues including hair. Posterior acoustic shadowing is seen. The left ovary shows a dermoid plug and, in addition, a "dermoid mesh" is also seen, an irregular echogenic solid mass within the cyst. Echogenic debris is seen floating within the fluid• Ovarian dermoid cyst or Cystic teratomas:
These ultrasound images reveal bilateral ovarian complex masses that contain both solid and cystic components. The right ovary shows a cystic mass with a solid, highly echogenic "dermoid plug". This is a solid nodule containing fat and various tissues including hair. Posterior acoustic shadowing is seen. The left ovary shows a dermoid plug and, in addition, a "dermoid mesh" is also seen, an irregular echogenic solid mass within the cyst. Echogenic debris is seen floating within the fluid• Ovarian dermoid cyst or Cystic teratomas:
These ultrasound images reveal bilateral ovarian complex masses that contain both solid and cystic components. The right ovary shows a cystic mass with a solid, highly echogenic "dermoid plug". This is a solid nodule containing fat and various tissues including hair. Posterior acoustic shadowing is seen. The left ovary shows a dermoid plug and, in addition, a "dermoid mesh" is also seen, an irregular echogenic solid mass within the cyst. Echogenic debris is seen floating within the fluidRupture of hemorrhagic ovarian cyst:
Transabdominal scanned image
• Rupture of hemorrhagic ovarian cyst:Transvaginal scanned image
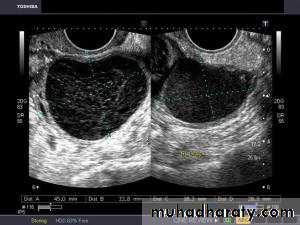
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS):
This young adult female patient was examined to evaluate the uterus and ovaries. She was under treatment for infertility and was using gonadotropins. Ultrasound images of the ovaries show grossly enlarged ovaries with large cysts (measuring 2.6 to 3 cms.) in both ovaries. These ultrasound findings are diagnostic of OHSS or ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
• Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS):
The ultrasound image again show hyperstimulated ovaries. Both ovaries are grossly enlarged and cystic.
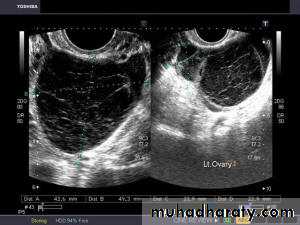
• Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS):
Transvaginal ultrasound images of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome:This young adult female patient showed multiple large theca lutein cysts of both ovaries, arranged in spoke-wheel pattern (ultrasound images above) which were the result of use of gonadotropins in the management of infertility. The cysts vary in size from 2 to 4 cms. with the ovaries massively enlarged (each ovary measures up to 7 cms. in size). This can be classified as grade-2 hyperstimulation of the ovaries (ovarian diameter from 5 to 10 cms.). There is not evidence of ascites. The color Doppler image of the ovaries shows vessels passing along the margins of the cysts. One of the complications of such enlarged ovaries in OHSS is torsion and in certain cases rupture of the ovaries, both of which are medical emergencies. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is known to occur more frequently in patients of pre-existing Polycystic ovaries (PCO).
PERSISTENT ANOVULATORY FOLLICLE
Failure of ovulation and development of “cystic” follicle. The follicle typically grows larger than the mean preovulatory follicle diameter of 23 mm, thin atretic follicle walls are observed and small flecks of particulate matter are frequently seen in the lumen or aggregated at the side of the structure.
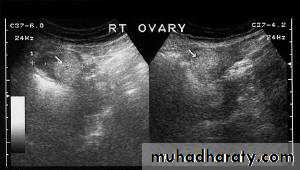
BENIGN OVARIAN NEOPLASIA
Images of a small intraovarian dermoid cyst (A, B). The cyst is completely embedded in the ovary and is surrounded by focal areas of hyperechoicity. Small follicles are observed in the surrounding stroma. Folliculogenesis and ovulation were impaired in this ovary. The contralateral ovary demonstrated compensatory hypertrophy.• BENIGN OVARIAN NEOPLASIA
Images of a small intraovarian dermoid cyst
Premature ovarian failure.
Image from a woman in premature ovarian failure. Only the stroma of the ovary is identified. A very few follicles of less than 1 mm diameter can be observed on the inferior aspect of the ovary.
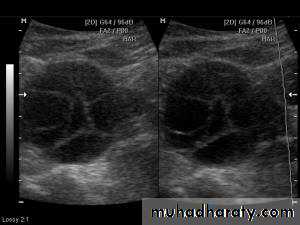
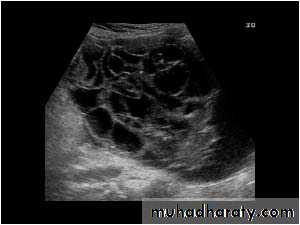
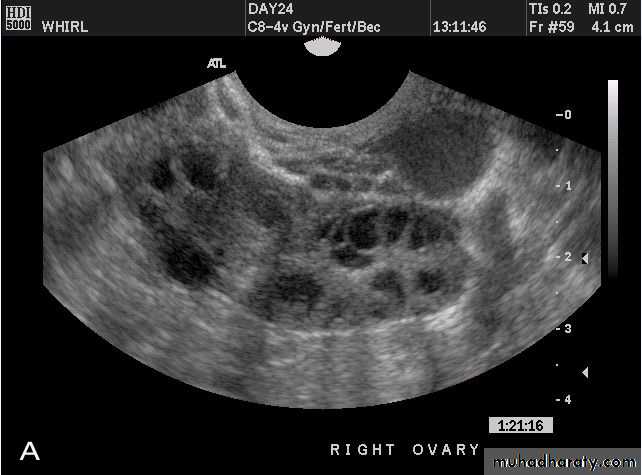
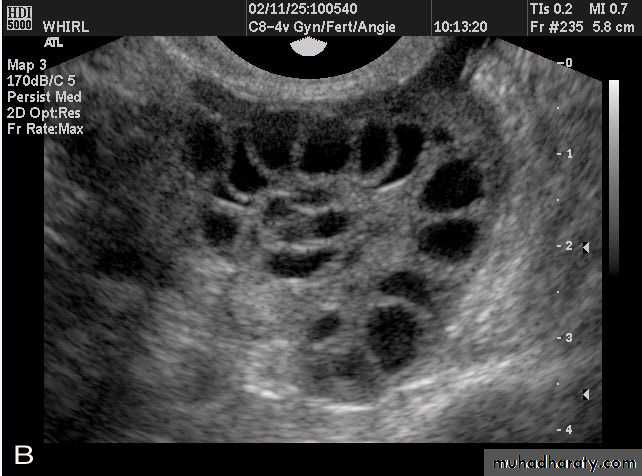
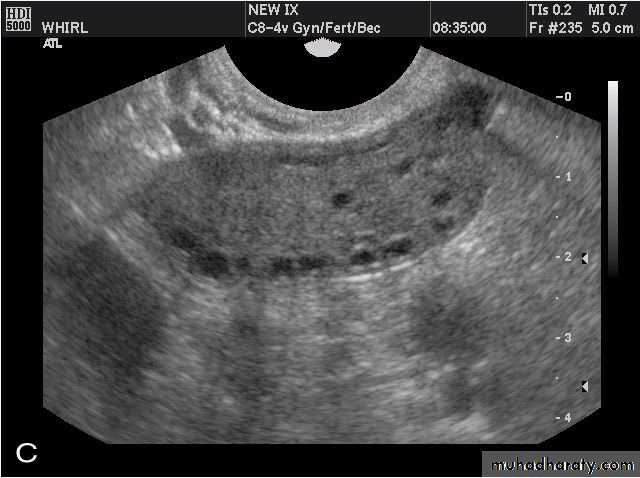
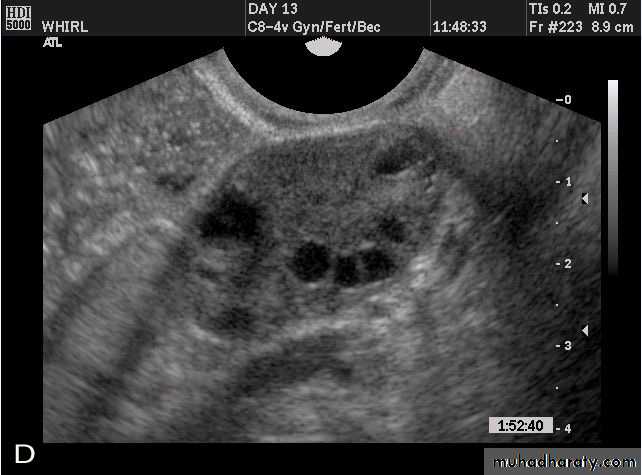
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
Images from women with differing expressions of the four major subtypes of the metabolic syndrome associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (A–D). The images exhibit quite differing ultrasonographic appearances in the size and distribution of follicles within PCOS ovaries. A recent corpus luteum is clearly visible in the ovary in panel (D).
• POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
Images from women with differing expressions of the four major subtypes of the metabolic syndrome associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (A–D). The images exhibit quite differing ultrasonographic appearances in the size and distribution of follicles within PCOS ovaries. A recent corpus luteum is clearly visible in the ovary in panel (D).• POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
Images from women with differing expressions of the four major subtypes of the metabolic syndrome associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (A–D). The images exhibit quite differing ultrasonographic appearances in the size and distribution of follicles within PCOS ovaries. A recent corpus luteum is clearly visible in the ovary in panel (D).• POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
Images from women with differing expressions of the four major subtypes of the metabolic syndrome associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (A–D). The images exhibit quite differing ultrasonographic appearances in the size and distribution of follicles within PCOS ovaries. A recent corpus luteum is clearly visible in the ovary in panel (D).The Oviduct (Fallopian Tube)
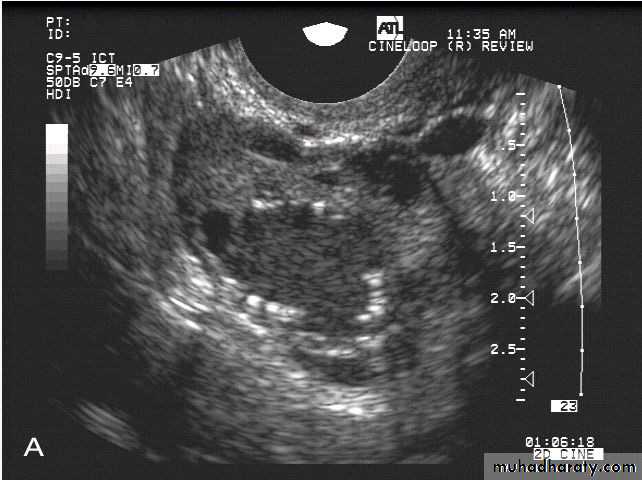
Normal OviductAn image of an oviduct visualized from the uterine cornu to the fimbria. The ampulla, infundibulum and very fine interfaces representing the fimbria may be appreciated on the superior aspects of the ovaries.
• Normal Oviduct
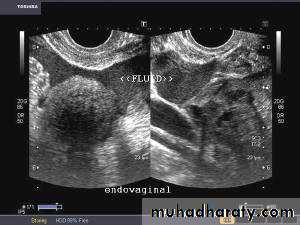
The fimbria of the oviduct are clearly visualized in free fluid surrounding the ovary following ovulation or hysterosalpinography.Hydrosalpinx
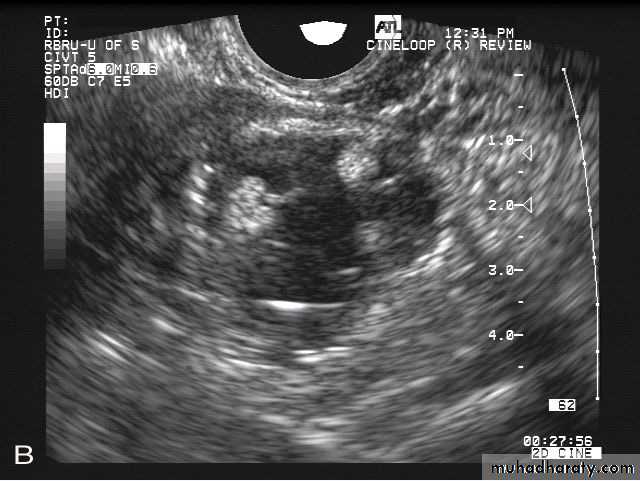
• Hydrosalpinx is usually easily diagnosed as well-constrained fluid accumulation in the adnexae. In some cases, adhesions between the oviduct and ovary may be visualized.
•
• Hydrosalpinx
• Hydrosalpinx is usually easily diagnosed as well-constrained fluid accumulation in the adnexae. In some cases, adhesions between the oviduct and ovary may be visualized.•
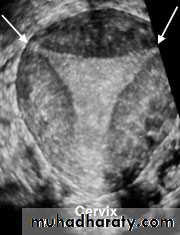
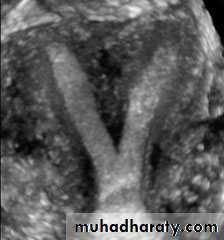
• Uterus
• Reconstructed coronal view of the uterus demonstrating cornuas (arrow) and cervix, with a normal uterine contour• Normal Uterus
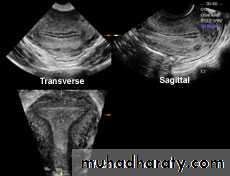
• Planar views of normal uterus using volume contast imagingNormal Uterus
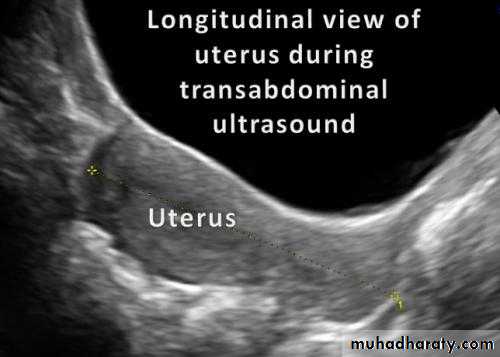
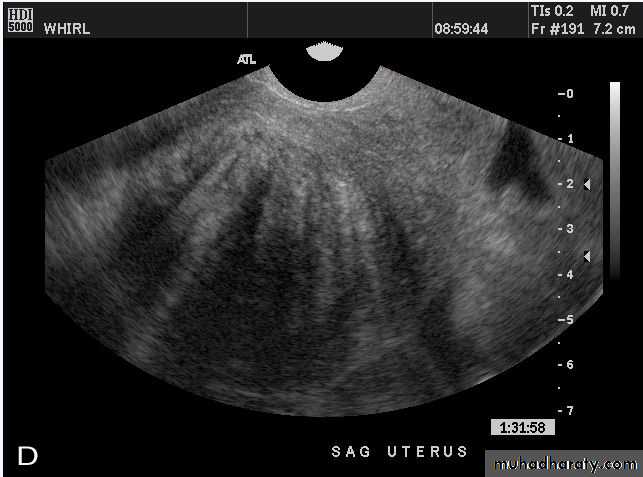
Normal Uterus in longitudinal viewUterine Pathology
Fibroids (leiomyomata)• Intramural leiomyomata are frequently visualized. Examples of fibroids which compromise the contours of the endometrial cavity are shown (A–D). Refraction artifacts resulting from tissue density interfaces and the texture of the fibroids often aid in their identification.
• Fibroids (leiomyomata)
• Intramural leiomyomata are frequently visualized. Examples of fibroids which compromise the contours of the endometrial cavity are shown (A–D). Refraction artifacts resulting from tissue density interfaces and the texture of the fibroids often aid in their identification.• Fibroids (leiomyomata)
• Intramural leiomyomata are frequently visualized. Examples of fibroids which compromise the contours of the endometrial cavity are shown (A–D). Refraction artifacts resulting from tissue density interfaces and the texture of the fibroids often aid in their identification.Congenital anomalies of uterus
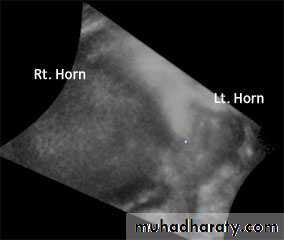
Unicornuate uterusCongenital anomalies of uterus
Bicornuate Bicollis Uterus• Congenital anomalies of uterus
• Didelphic uterus with Left sided hematometra• Congenital anomalies of uterus
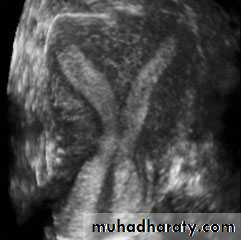
• Subseptate Uterus
• Congenital anomalies of uterus
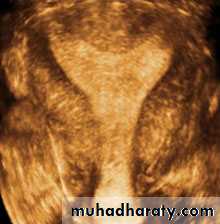
• Complete Septate• Congenital anomalies of uterus
• Arcuate uterusEndometrium
• Endometrium
• Post menstruation• Endometrium
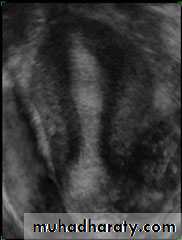
• Trilaminar appearance during proliferation• Endometrium
• Secretory phase• Endometrium
• Premenopausal Endometrium• Endometrium
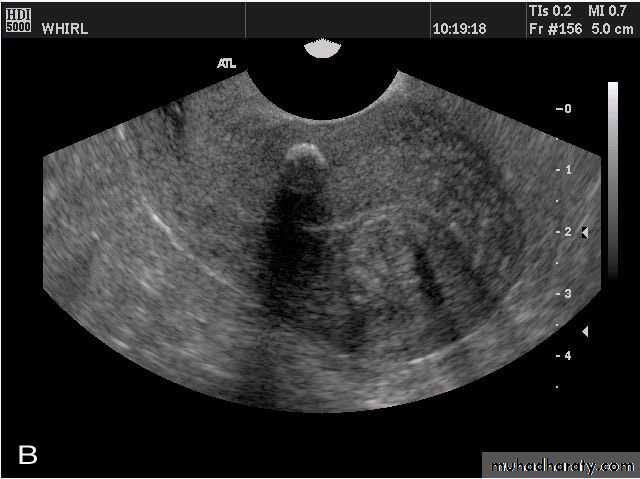
•
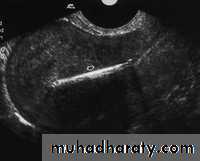
Sagittal US image of the uterus obtained during the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle shows a thickened, echogenic endometrium (cursors).
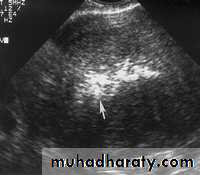
Pathology of Endometrium
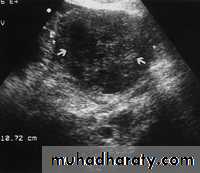
Endometritis. US image demonstrates multiple echogenic foci within the endometrium (arrow) representing gas.
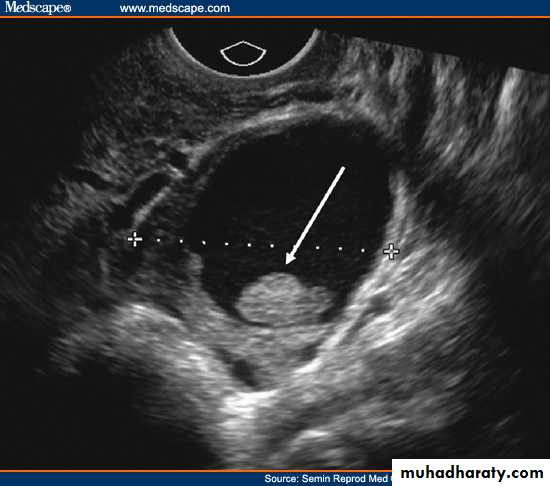
Endomaterial polyp
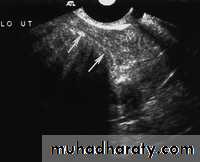
• Pathology of Endometrium
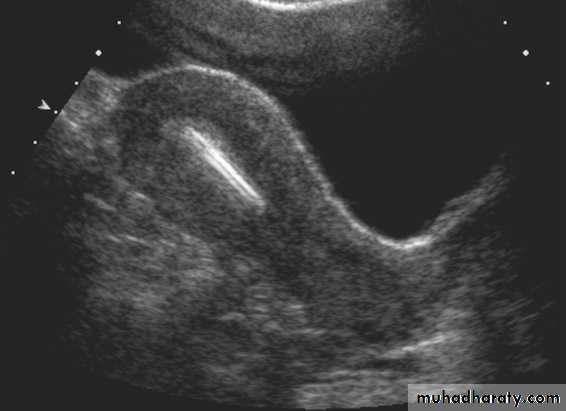
Submucosal fibroid. (a) Transvaginal US image reveals a uterine mass (arrows) with posterior acoustic shadowing.• Pathology of Endometrium
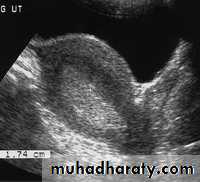
Endometrial hyperplasia. US image shows an endometrium with diffuse thickening (maximum thickness, 1.74 cm) due to hyperplasia (cursors). This finding was confirmed at biopsy.• Pathology of Endometrium
Endometrial adenocarcinoma.
(a) US image reveals a heterogeneous endometrial mass (arrows) that is difficult to distinguish from the myometrium. Cursors indicate the entire transverse width of the uterus.