
Lecture 2
النسائية
د
. سجى
Progestogen only contraception / IUD
Page 1 of 8
Progestogen Only Contraception
o All other types of hormonal contraception in current use in
the world are progestogen -only and share many similar features in terms
of mode of action and side effects.
o Because they do not contain oestrogen, they are extremely safe & can be
used if woman has cardiovascular risk factors.
o The dose of progestogen within them varies from very low to high
The current methods of progestogen-only contraception are
1. progestogen-only pill, or 'mini-pill'
2. subdermal implant Implanon®
3. injectables
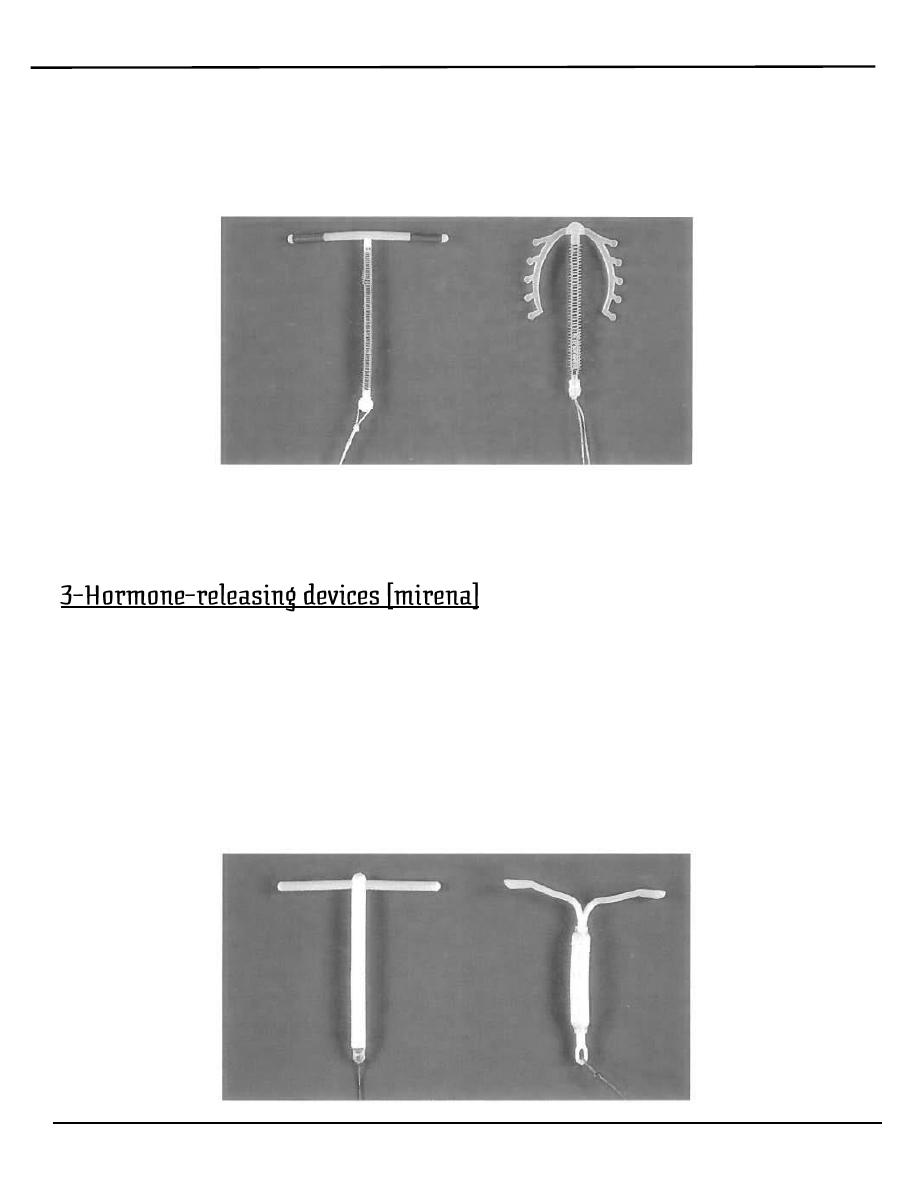
4. hormone-releasing intrauterine system
Mechanism of action
1-periphyral effects
a) Local effect on cervical mucus making it hostile to ascending sperm.
b) Local effect on the endometrium making it thin&atrophic thereby
preventing implantation
c) Progestin use also causes decreased tubal and endometrial motility.
2-central effects
Higher dose progestogen-only methods can act centrally&inhibit ovulation .
Side effects
o Menstrual disturbances either irregular vaginal bleeding or amenorrhea.
o Functional ovarian cyst
o Increase risk of ectopic pregnancy: this has not been confirmed, although it
is probably that POP protect much more effectively against intrauterine
than ectopic pregnancy.
:العدد
4
17/3/2014

Lecture 2
النسائية
د
. سجى
Progestogen only contraception / IUD
Page 2 of 8
Progestogen-only pills
They contain;
o the second-generation progestogen norethisterone or norgestrel (or their
derivatives)
o or the third-generation progestogen desogestrel.
The POP is taken every day without a break
Particular indications for the POP include:
1. breastfeeding
2. older age
3. cardiovascular risk factors
4. Diabetes.
Injectable progestogens
o Two injectable progestogens are marketed.
Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate 150 mg
(Depo-Provera or DMPA) which lasts around 12-13 weeks .
Norethisterone enanthate 200 mg (Noristerat) which only lasts for 8
weeks and is not nearly so widely used.
o Depo-Provera is a highly effective method of contraception and it is given
by deep intramuscular injection Most women who use it develop very light
or absent menstruation. Depo-Provera will improve PMS and can be used
to treat menstrual problems such as painful or heavy periods.
o It is particularly useful for women who have difficulty remembering to
take a pill
Particular side effects of Depo-Provera
1. weight gain of around 3 kg in the first year,
2. delay in return of fertility - it may take around 6 months longer to
conceive compared to a woman who stops COC,

Lecture 2
النسائية
د
. سجى
Progestogen only contraception / IUD
Page 3 of 8
3. persistent menstrual irregularity ,irregular vaginal bleeding may occur or
amenorrhea in prolonged use of this injection
4. very long-term use may slightly increase the risk of osteoporosis
(because of low oestrogen levels)
This injection can be given within five days after the onset of menses, or
within 6 weeks after delivery if breast-feeding infant.
Also it can be used after having an abortion
Particular indications for depo provera
1. contraindication to estrogen
2. Following rubella vaccination in peurperium.
3. Husband waiting for effect of vasectomy.
4. Mental retarded women. .
5. Breast-feeding.
6. Population control in developing countries.
Subdermal implants
o Implanon consists of a single silastic rod that is inserted subdermally
under local anaesthetic into the upper arm. It releases the progestogen
etonogestrel 25-70 Mg daily (the dose released decreases with time), which
is metabolized to the third-generation progestogen desogestrel. Implanon
was introduced into the UK in the late 1990s
o Other type of implant is the six-rod implant Norplant, which is withdrawn
from the market.
o It lasts for 3 years and thereafter can be easily removed or a further implant
inserted.
o Implanon is particularly useful for women who have difficulty
remembering to take a pill and who want highly effective long-term
contraception. There is a rapid return of fertility when it is removed.

Lecture 2
النسائية
د
. سجى
Progestogen only contraception / IUD
Page 4 of 8
Emergency contraception
Post-coital contraception is any drug or device used prevent pregnancy after
unprotected intercourse, there are two types of emergency contraception
[EC]:
A-hormonal emergency contraception
o Combination of 100 microgram ethinyl estradiol &0.5 mg levonorgestrel
is taken twice the two doses being 12 hours apart & started within 72
hours of unprotected intercourse
o Nausea & vomiting are common side effects.
o The precise mechanism of action is not known but probably involves
disruption of ovulation or corpus luteal function depending on the time
in the cycle when hormonal EC is taken so it inhibit ovulation or
interfere with implantation.
o Levonorgestrel 0.75 mg taken twice with two doses separated by 12
hours ,it may be more effective & better tolerated
o It has to be taken within 72 hours of an episode of unprotected
intercourse and is more effective the earlier it is taken
B -intrauterine device
o A copper-bearing IUD is highly effective post-coital contraceptive with
failure rate less than 1%,used up to five days after the estimated day of
ovulation.It prevent implantation &the copper exerts an embryotoxic effect
o The hormone-releasing IUS has not been shown to be effective for EC and
should not be used in this situation

Lecture 2
النسائية
د
. سجى
Progestogen only contraception / IUD
Page 5 of 8
Intrauterine Contraception Device
o An IUD is ideal for women who want a long-term method of contraception
and where regular compliance is not required.
o IUDs protect against both intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy, but if
pregnancy occurs, there is a higher chance than normal that it will be
ectopic
Types
o (Lippes Loop or Saf-T coil), which often caused significantly heavier
and more painful menstrual periods, These are no longer available,
although some women may still have them in situ.
o Once fitted, they could be left until the menopause.
o Which are available in various shapes and sizes they cause much less
menstrual disruption than the older plastic devices.
Lecture 2
النسائية
د
. سجى
Progestogen only contraception / IUD
Page 6 of 8
o Most copper-bearing IUDs are licensed for between 3 and 5 years of use,
but many will last longer, possibly up to 10 years. The more copper wire
a device has, the more effective it is
Copper-bearing intrauterine devices: Multiload,Copper T 380.
o have also been developed
o The levonorgestrel-releasing in trauterinesystem (IUS) has the
advantages (and disadvantages) of both hormonal and intrauterine
contraception (Table 6.5).
o It is associated with a dramatic reduction in menstrual blood loss and is
licensed for contraception and the treatment of menorrhagia

Lecture 2
النسائية
د
. سجى
Progestogen only contraception / IUD
Page 7 of 8
Mode of action
1. All IUDs induce an inflammatory response in the endometrium which
prevents implantation. However,
2. Copper-bearing IUDs work primarily by a toxic effect on sperm which
prevents fertilization.
3. The mirena IUS prevents pregnancy primarily by a local hormonal effect
on the cervical mucus and endometrium
Contraindications
1. Previous PID.
2. Previous ectopic pregnancy.
3. Known malformation of the uterus.
4. Copper allergy (but could use an IUS).
abnormal uterine bleeding
nulliparity
Side effects
1. Menstrual disturbance:menorrhagia & 2ry dysmenorrhea may occur .
2. Expulsion: This is most likely to occur in the first year which may occur
sometime without noticing
3. Perforation: Occur at time of insertion in 1.3 /1000 insertions.
Routine follow–up 6 weeks after insertion allows most perforations to be
detected.
4. Increased risk of pelvic infection in the first few weeks following insertion,
Although IUDs increase the risk of PID in the first few weeks after
insertion, the long-term risk is similar to that of women who are not using
any method of contraception
5. pregnancy :if failure occur there is high incidence that pregnancy is
ectopic.if intrauterine pregnancy occur there is more risk of abortion ,
preterm labor & antepartum hemorrhage
Lecture 2
النسائية
د
. سجى
Progestogen only contraception / IUD
Page 8 of 8
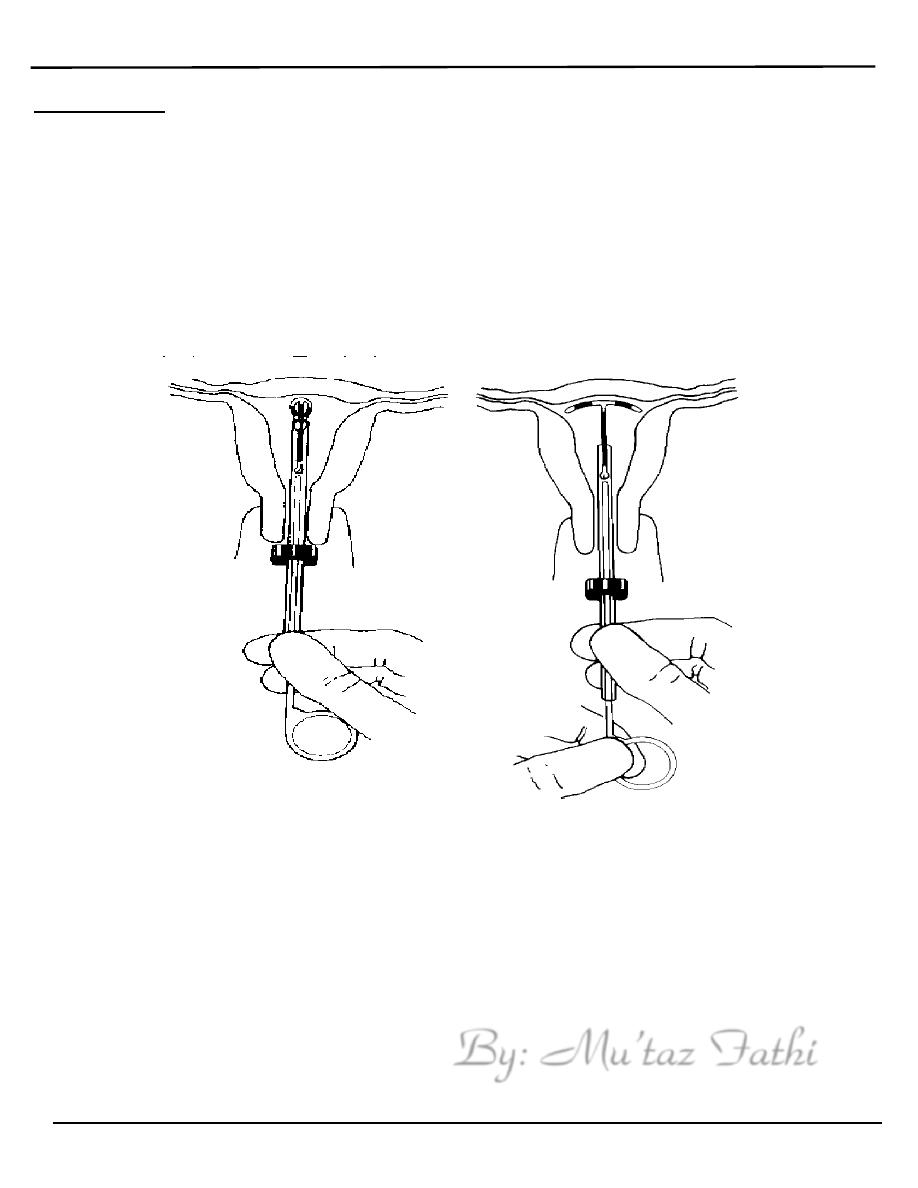
Insertion
o It is better to be inserted in the first even days of menstrual bleeding so
there is no pregnancy & the cervix is soft
o The cervix is exposed with speculum,Uterine sound is used to measure
length of uterine cavity.
o The introducer is inserted and the IUD expelled into the cavity then its
thread is cut short
By: Mu’taz Fathi
