
Principles of fractures
Fracture
: it is break in the structural continuity of the bone .
It is of two main types :
1- simple fracture ( closed ) .
2- compound fracture (open ) .i.e. associated with wound connecting it to the external
environment .
How fracture happen :
1- single traumatic incident .
2- repetitive stress .
3- abnormal weakening of the bone ( pathological fracture ) .
In single traumatic incident the bone sustained sudden and excessive force which may
be direct or indirect :
In direct force the bone break at the point of impact ; while in indirect force the bone is
break at distant from the site of force where it applied .
The force which break the bone is of different types :
A- twisting force . B- bending force .
C-compression force . D- tension force .
Each of them influence the shape of the fracture which is either spiral ,oblique ,
transverse , or fracture with butter – fly segment .
all this is applied to the long bones .
So the fractures either complete or incomplete :
Complete could be t
U
ransverse
U
,
U
oblique , spiral
U
, or
U
comminuted
U
.
And incomplete could be
U
green stick
U
or
U
compression
U
fracture

.
Types of fracture displacement
Fracture healing
: immobilization of the fracture is not
mandatory for fracture healing ; the
splinting of the fracture to ensure :
1- pain relief . 2- union take place in good position .
3- early movement and return to function .
Steps of fracture healing :
1- tissue destruction and haematoma formation .
2- acute inflammatory reaction and cellular proliferation .
3- callus formation (step of union) .
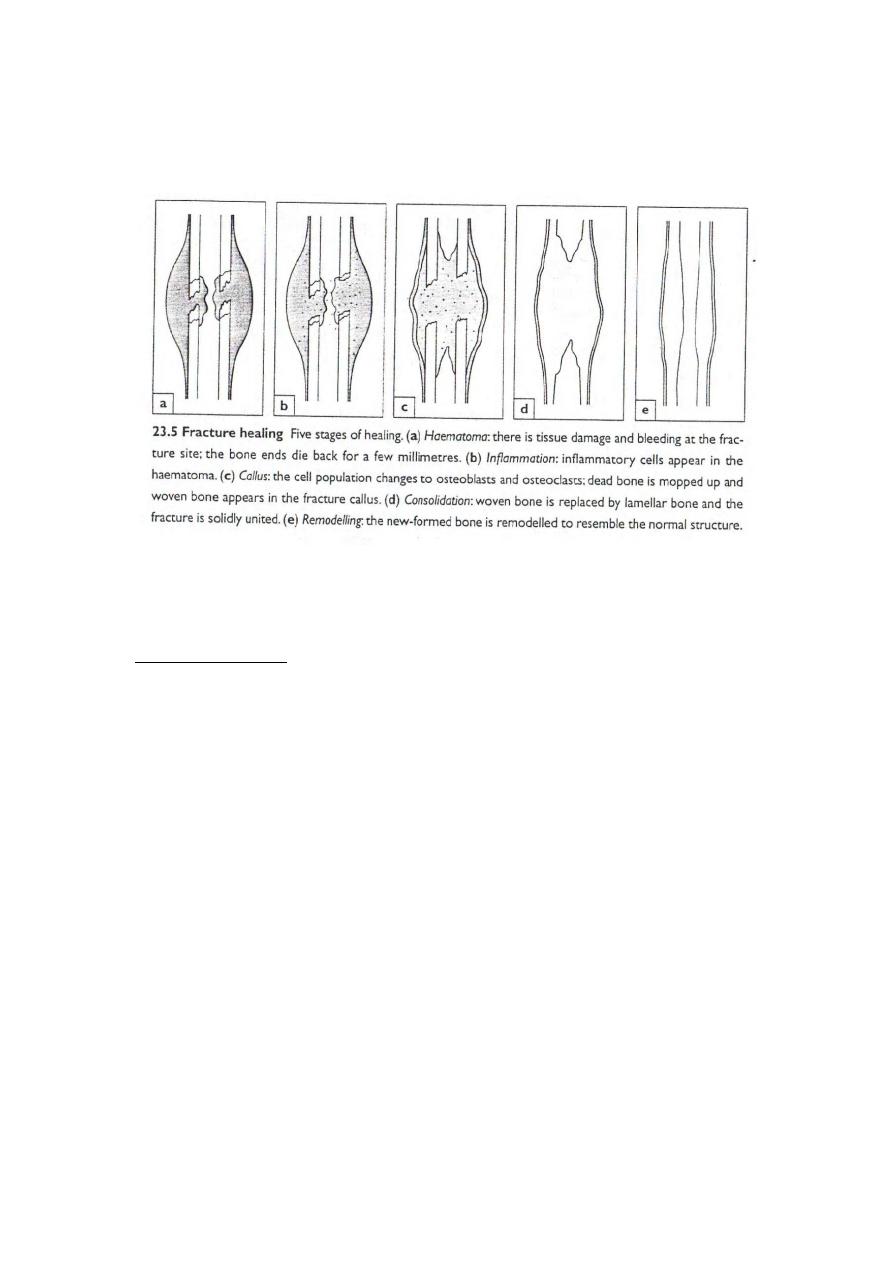
4- consolidation .
5- remodeling .
Time table
:
For fracture healing the time change according to age , blood supply , type of the fracture
……etc.
U
Perkin`s time table
U
is very simple table to asses that time :
Spiral or oblique fracture in the upper limb unite in 3 weeks .
Transverse fracture in the upper limbs unite in 6 weeks .
For consolidation multiply by 2 .
In the lower limbs :
Oblique or spiral fracture need 6 weeks for union .
Transverse fracture need 12 weeks .
For consolidation multiply by 2 .
Clinical features of the fracture :
A – symptoms :
1- history of trauma followed by inability to use the injured
limb ; if the trauma is simple and weak force we suspect
pathological fracture .

2- pain . 3- brusing . 4- swelling . 5- deformity .
B – signs :
1- swelling . 2- Bruising . 3- deformity . 4- tenderness .
5- crepitus . 6- loss of function .
U
X – ray
U
: it is mandatory for diagnosis of fractures .
U
Role of twos
U
:
1 – two views .
2 – two joints .
3 – two limbs .
4 – two injuries . e. g. fracture calcaneum .
.
5 – two occasions e.g. fracture scaphoid
6 - two tissue .
Special imaging
:
1- tomography . 2- C.T. 3- MRI . 4- bone scan .
Treatment of closed fracture
:
A – the general treatment is the first consideration i. e.
the air way patency , breathing and circulation .
B – treatment of the fracture itself : this include :
1- reduction .
2- holding .
3- physiotherapy and rehabilitation .
1- reduction of the fracture :
It should be taken in the first 12 hours from the trauma , because the oedema and
swelling make the reduction difficult after that time .

Two types of reduction :
1- closed reduction ( by manipulation ) .
2-open reduction ( by surgical approach ) .
Open reduction is indicated in :
1- when close reduction fail .
2- when there is large articular fragment need accurate
reduction .
3- for traction fractures in which the fragments are held
apart .
Holding of the fractures
: by :
1- continuous traction .
2- cast splintage ( plster of paris P.O.P) .
3- functional bracing .
4- internal fixation .
5- external fixation .
Traction
: types of traction :
1-
U
traction by gravity
U
: this is used only in upper limb .e.g hanging cast .
2-
U
skin traction
U
: it is available in special kit , it is used
mainly in the lower limb .
3-
U
skeletal traction
U
.
Skin traction
U
Principle of it's use
U
:
1- applied distal to the fracture site .

2- weight used is 10% of the body wt. and not more than 5 kg , if we need more than 5
kg
then we use skeletal traction .
3- removal of the hair before application .
U
Indication of skin traction
U
:
1- used in fractures of the lower limbs vertebras and pelvis .
2- in dislocations of the lower limbs .
3- for resting of the limb e.g. in arthritis , osteomyelitis ,
septic arthritis , irritable hip etc…….
4- in treatment of back ache .
Hanging cast/skin traction/thomas splint
Skin traction kit
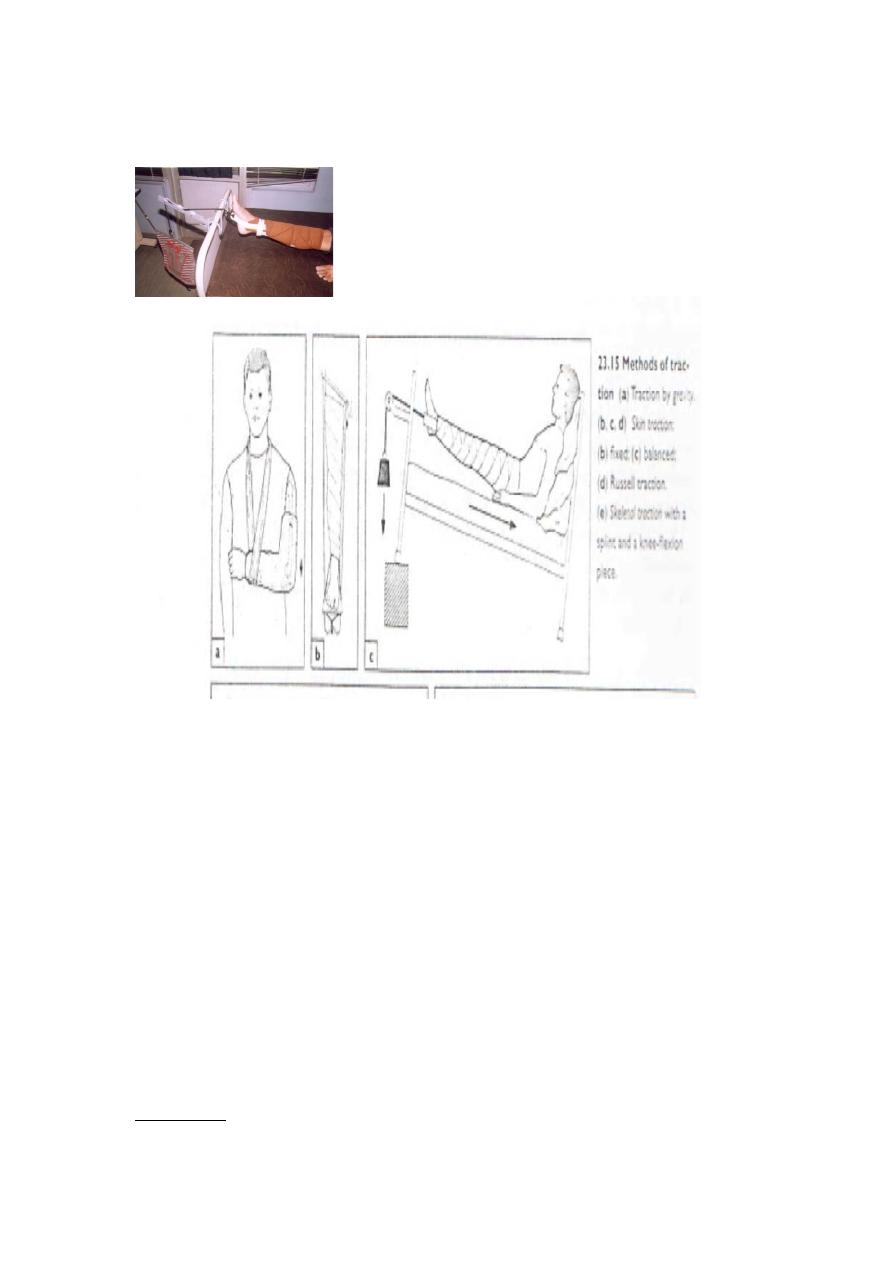
skin traction
Complication of skin traction
:
1- allergy to the adhesive material of the plaster lead to
ulceration of the skin .
2- compression of the vessels lead to compartment
syndrome .
3- compression of the nerves lead to neuropraxia .
4- excessive traction (when use over wt.) lead to non union
5- failure of the kit .
3- skeletal traction :
Pin is inserted distal to the fracture site usually behind the tibial tuberosity or lower
femoral condyles , the wt. used is one six (1/6) of the body wt. .
U
Complication
U
: 1- broken of the pin . 2- pin tract infection . 3- over (excessive )
traction .
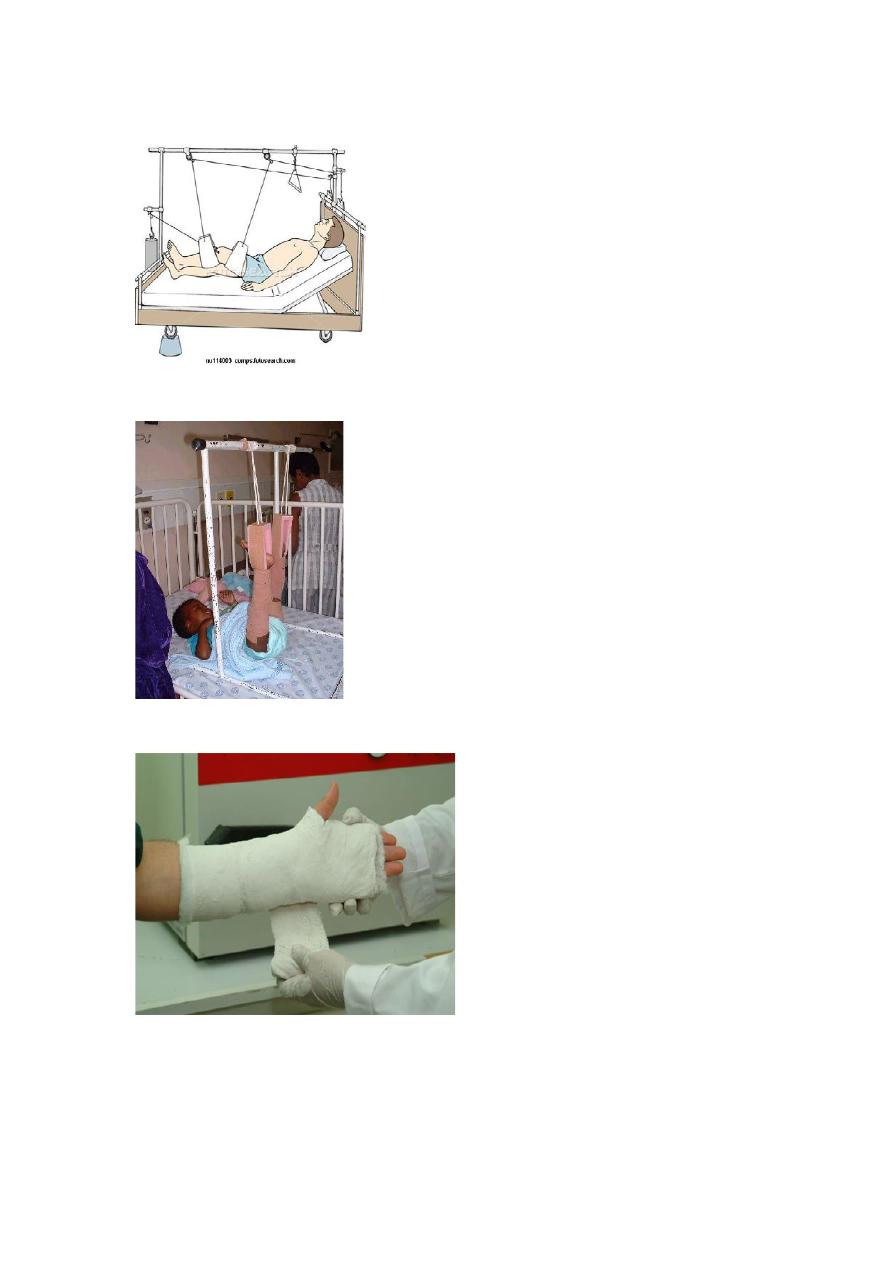
Balanced traction//counter traction
Counter traction//gallos traction
Plaster of paris
