L.2
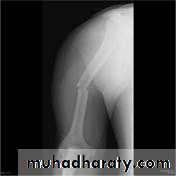
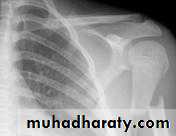
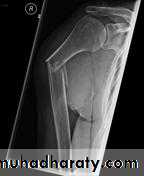
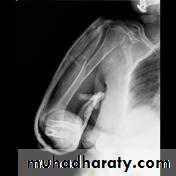
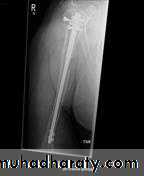
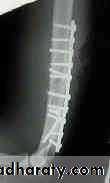
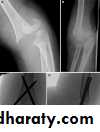
د.محمد الموسوي 12-10-2015Fracture shaft of humerus:
Traumatic & pathological3-5% of all fractures
Bimodal age distribution
young patients with high-energy trauma
Elderly, osteopenic patients with low-energy injuries or due to 2ndary metastasis.
Fracture location: proximal, middle or distal third.
Fracture pattern: spiral, transverse, comminuted or oblique.
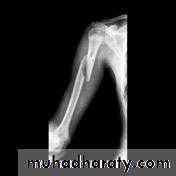
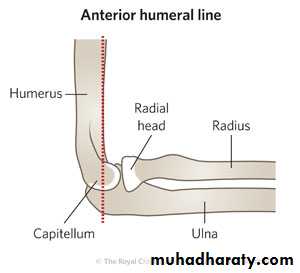
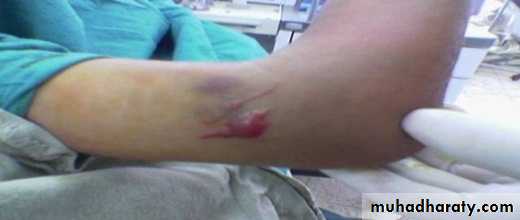
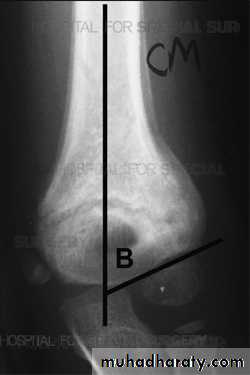
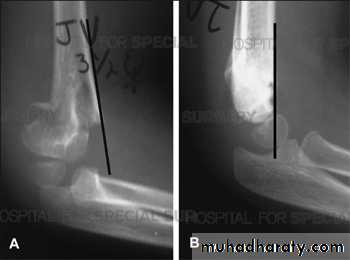
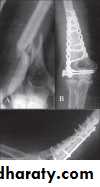
Supracondylar fracture of humerus:
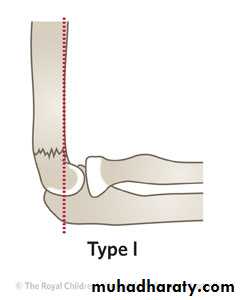
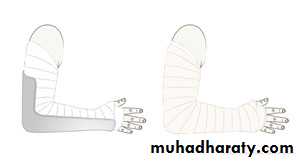
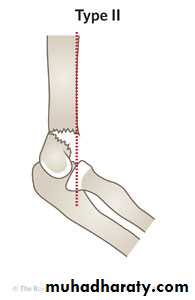
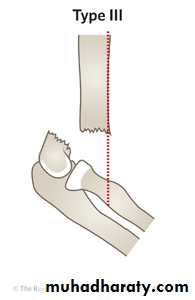
Supracondylar humeral fracture in children is one of the most common fractures seen in the pediatric orthopedic clinic setting worldwide. It's a fracture that occurs at the supracondylar area or the metaphysis of the distal humerus & accounts for 65.4% of upper extremity fractures in children .There are two types of supracondylar fractures in children according to direction of displacement of distal fragment i.e. extension type (97%) and flexion (3%).Immobilisation in an above-elbow backslab in 90 degrees elbow flexion with sling for 3 weeks. The backslab and sling should be worn under clothing (e.g. loose fitting shirt) and not through the sleeve
A gentle reduction can be achieved by an anterior push on the distal fragment as the elbow is flexed to 90 degrees
Requires urgent reduction and percutaneous pin fixation
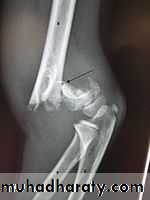
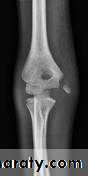
Intercondylar fracture of humerus:
Lateral condyle fracture of humerus:
Medial condyle fracture of humerus:
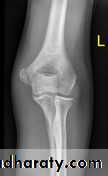
Failure to diagnose these injuries can lead to significant long term disability. Fortunately as these injuries involve an apophysis rather than an epiphysis, no growth arrest of the arm occurs, however elbow instability and even recurrent dislocations can result from suboptimal healing.Fifty percent of medial epicondyle fractures are associated with an elbow dislocation.
It is important to distinguish a medial epicondyle fracture (common) from a medial condyle fracture (very rare). Medial condyle fractures are intraarticular, extending into the elbow joint and require urgent open reduction internal fixation (ORIF).