Microbiology
Notes…
1
Immunology Lecture.2 The Specific (Adaptive) Immune Response
Non-specific (innate )immunity IS SOMETIMES NOT ENOUGH!!!
Another more powerful type of immunity called specific (adaptive) immunity is required
—That ACQUIRED ability to recognize and destroy an individual pathogen and its
products
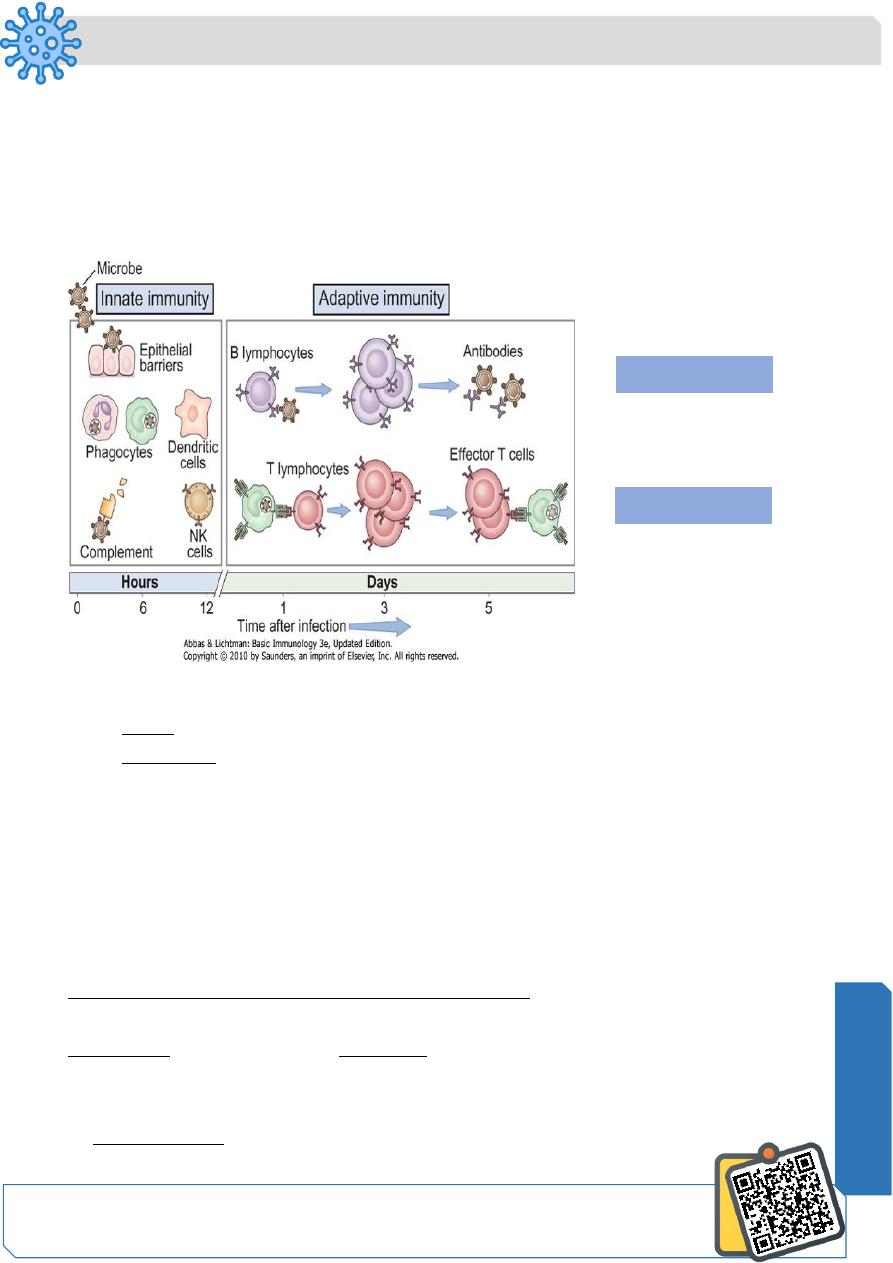
Types of immunity
Origin and Development of B
-
and T – Lymphocytes
• Origin : Stem cells in the bone marrow
• Maturation : Bone marrow( B cell maturation)
Thymus
( T cell maturation)
-
From 1ry lymphoid organs distributed through
lymph and blood to 2ry lymphoid organs :
Lymph nodes
Tonsils
Spleen
Mucosal tissues in lung and gut
Overview of the specific (adaptive) immune response
1. Cell Mediated Immunity ( T cell mediated immunty)
Key players : T - lymphocytes. Two types:
Cytotoxic T cells (CTL) or (CD8+)
T helpers ( TH) cells (CD4+)
- Cytotoxic T cells directly attack and destroy antigen-bearing cells especialy
virally infected cells and tumours
Humoral immunity
Cellular immunity
1
ry
lymphoid
organs
N
eed S
om
e H
el
p
?
Microbiology
Notes…
2
- Helper T cells act indirectly by secreting proteins called cytokines that
activate other cells such as macrophages to destroy the antigen-bearing cells
CAN you name another immunological cell type that also functions as CYTOTOXIC cells
?????.What are the main differences between them?
CD 8
+
cells
Mechanism of cytotoxicity by CTL (CD8)
+
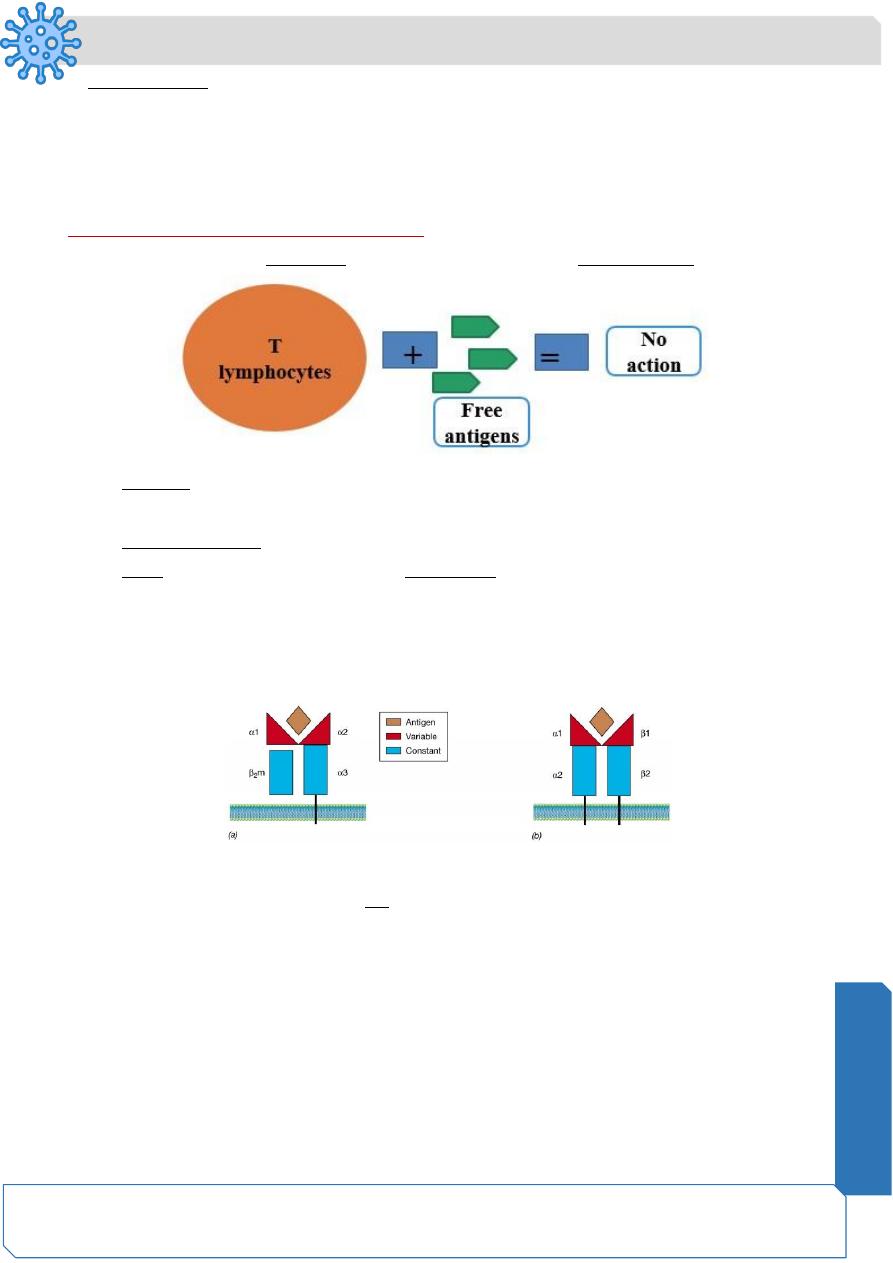
• T - lymphocytes CAN NOT recognize and respond to free antigens
• 1st step : virally infected or tumour transformed cells will be engulfed by the
phagocytes (macrophages) at the site of infection or transformation
(internalization)
• Next , internalized antigen is processed inside the macrophages where the
antigen is degraded and fragment of it binds to MHC class I molecule
( Major
Histocompatibility Class I molecule)
Major Histocompatibility complex proteins are found on the surface of cells:: T cells
cannot recognize foreign antigens unless they are associated with these MHC proteins
ALL MHC proteins are imbedded in the cytoplasmic membrane of cells and project
outward from the cell surface
•
THEN
, the processed antigens bind to Class I (Ag-MHC class I complex ) are
transported to the cell surface
- The phagocytes ( macrophages) now move toward regional lymph nodes under the
influence of certain chemical substances (chemotaxis)
Class I MHC proteins are
found on the surface of ALL
nucleated cells
Class II MHC proteins are only
found on the surface of
B lymphocytes, macrophages
and other antigen presenting cells
Microbiology
Notes…
3
• In the regional lymph nodes the phagocytes present the antigen in association with
MHC class I molecule to lymphocytes.
• That is why phagocytes ( macrophages) are called antigen presenting cells
( APC)
• CTL interact SPECIFICALLY with the antigen - MHC class I complex through TCR
(T Cell Receptor).
• Each T cell has thousands of copies of the SAME TCR on its surface
• The immune system can generate TCRs that will bind nearly every known peptide
antigen
The TCR can only recognize and bind a peptide antigen if the antigen is bound first to
MHC proteins
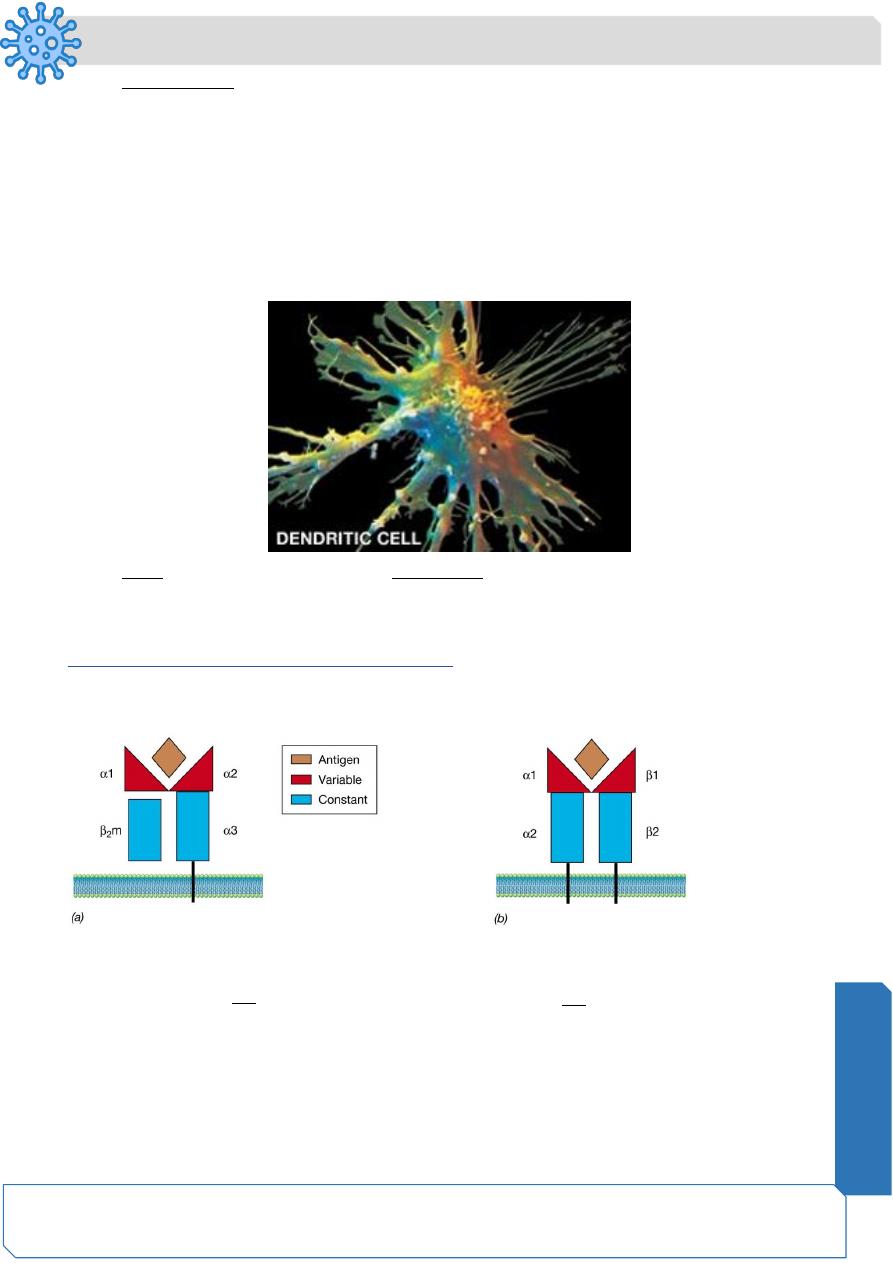
Structure of the T-cell receptor (TCR). The V domains of the alpha chain and beta chain
combine to form the peptide antigen-binding site.
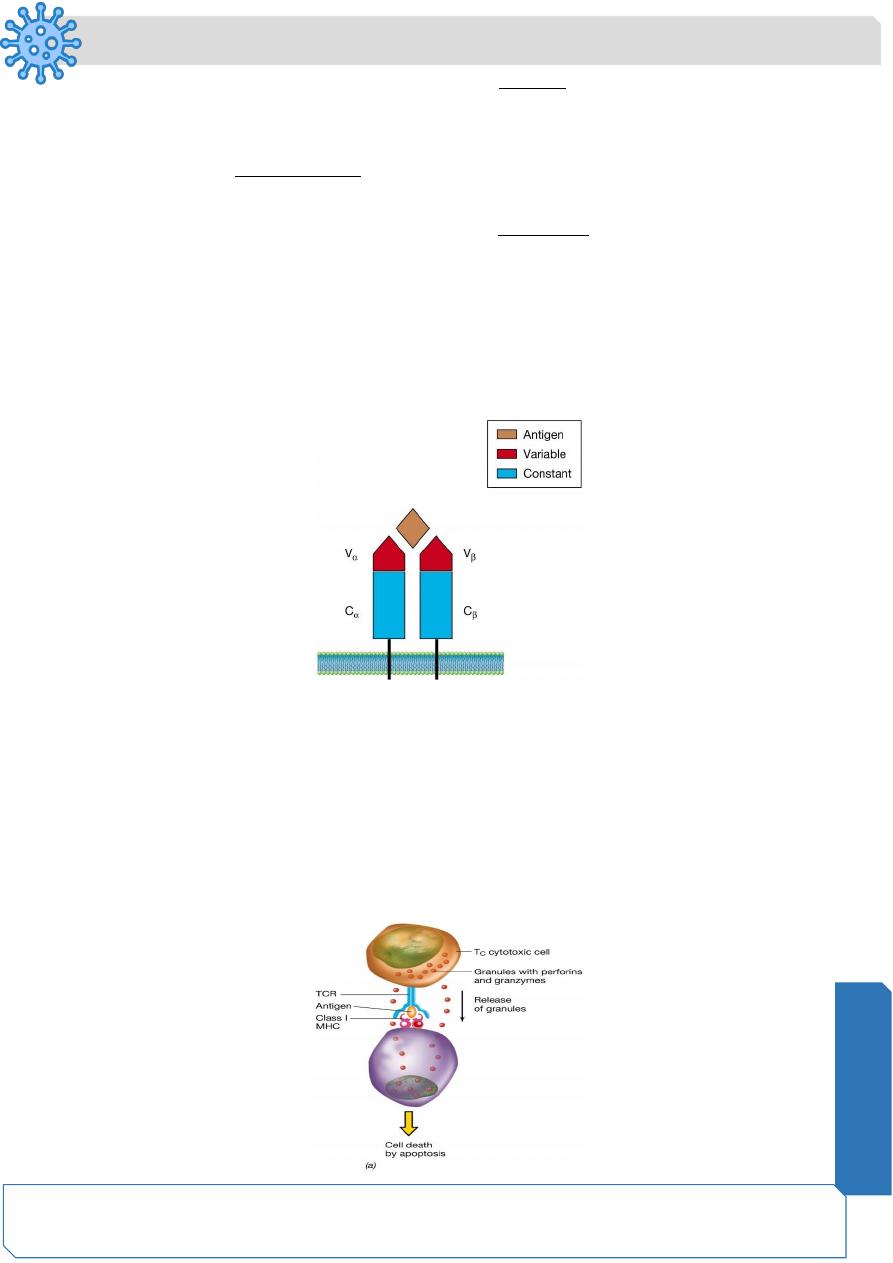
Class I MHC proteins and cytotoxic T cells (Tc)
The cell-cell interaction between the infected cell and the Tc cell is mediated by the MHC
class I - antigen complex and TCR.
The Tc cell produces cytotoxic proteins
perforins
—produce holes or pores in the target
cell and
granzymes
enter the virus infected cell causing apoptosis or programmed cell
death.
The cytotoxic proteins only affect those cells to which the Tc cell has specifically
interacted.
The T cell receptor extends
from the surface of a T cell
Cytoplasmic membrane
of a T cell
Microbiology
Notes…
4
Mechanism of cytotoxicity by CTL (CD8+)- Continue
• The first contact of the CTL with the antigen is called primary immune response .
This will take time to develop
( usually several days) and associated with
development of memory cells.
• When the CTL come in contact with same antigen for second time , this is called
secondary immune response. Usually faster than 1ry immune response and more
stronger that leads to eradication of pathogen before symptoms appear .
CD 4 + cells
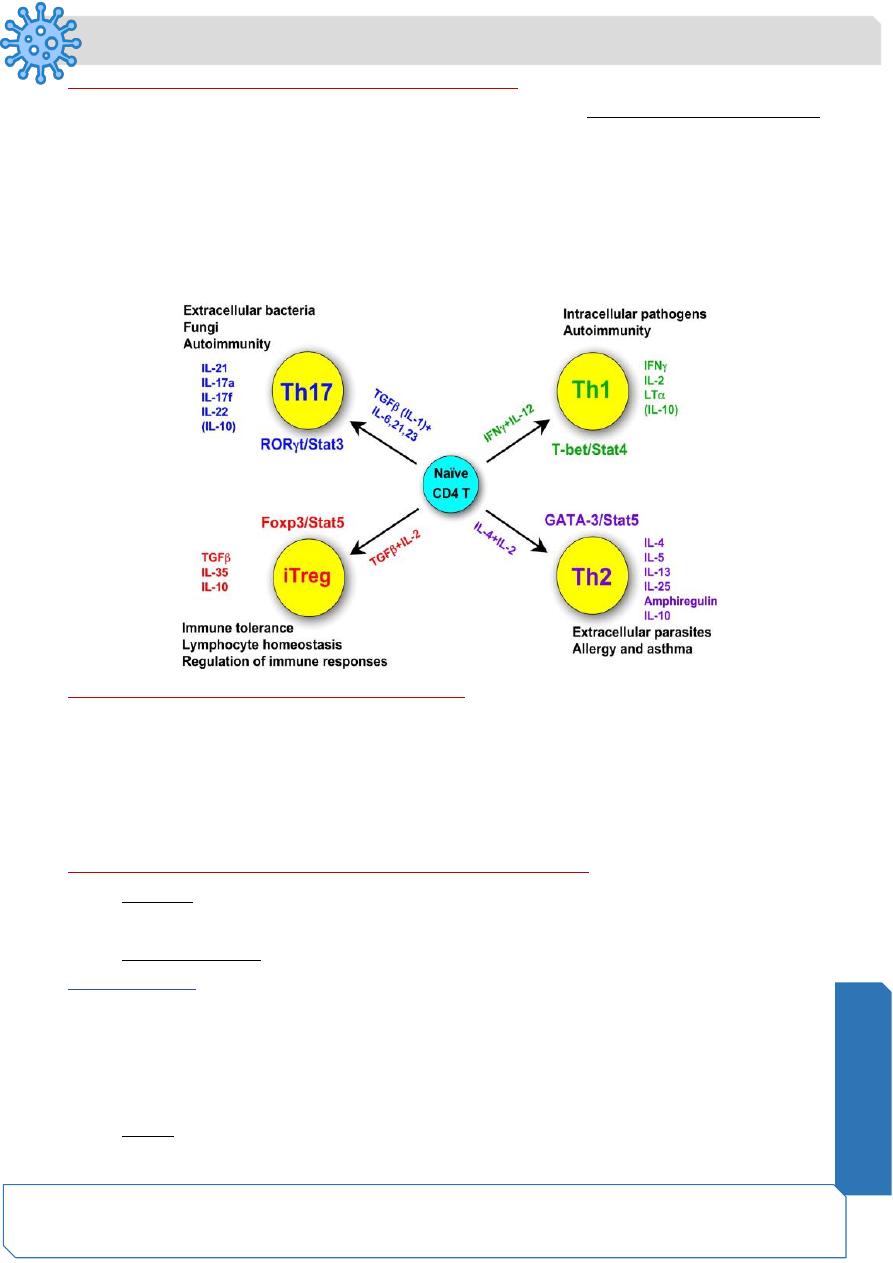
Cellular immune response by TH cells( CD4+)
Particularly useful in eradicating pathogenic bacteria especially intracellular bacteria
Act indirectly by secreting chemical mediators called cytokines that activate other cells
such as macrophages to destroy the antigen-bearing cells
Activated macrophages can then kill intracellular pathogens that would normally divide
in a non-activated macrophages
Mechanism of cellular immune response by TH cells( CD4+)
• 1st step : foreign antigen will be captured and engulfed by the phagocytes
(macrophages )and another cell type called dendritic cells at the site of infection
(internalization)
Dendritic Cells
• Named so because they resemble dendrites of neurons
THEY ARE NOT NEURONS!!!
Their main function is to capture , concentrate and present antigens to lymphocytes
(APC)
• Origin : stem cells in bone marrow
Microbiology
Notes…
5
• Several Type
Langerhans
( LC )found in skin
Circulating DCs
Myeloid (MDC1 and MDC2)
Plasmacytoid
Interstitial DCs
Heart, lungs, liver, intestines
Interdigitating DCs ,T-cell areas of lymph nodes and Thymic medulla
• Next , internalized antigen is processed inside the macrophages and dendritic
cells where the antigen is degraded and fragment of it binds to MHC class II
molecule
(Major Histocompatibility Class II molecule(
Major Histocompatibility complex proteins are found on the surface of cells:: T cells
cannot recognize foreign antigens unless they are associated with these MHC proteins
ALL MHC proteins are imbedded in the cytoplasmic membrane of cells and project
outward from the cell surface
• THEN , the processed antigens bind to Class II (Ag-MHC class II complex ) are
transported to the cell surface where they expressed.
Class I MHC proteins are
found on the surface of ALL
nucleated cells
Class I MHC proteins are
found on the surface of ALL
nucleated cells
Microbiology
Notes…
6
- The macrophages and dendritic cells now move toward regional lymph nodes under
the influence of certain chemical substances (chemotaxis)
• In the regional lymph nodes the phagocytes and dendritic cells present the antigen
in association with MHC class II molecule to CD4+lymphocytes.
• That is why macrophages and dendritic cells are called antigen presenting cells
(APC)
• The part of the CD4 +that comes in contact with the antigen - MHC class II complex
is called TCR( T Cell Receptor).
• Cell -
cell interaction mediated by TCR (from CD4+ T lymphocytes) and antigen -
MHC class II complex (from macrophages or dendritic cells) will activate TH CD4
+to produce chemical mediators called cytokines( hormones of the immune
system :
Interferon - gamma (IFN -
gamma(
Tumour necrosis factor - alpha (TNF-alpha)
Granulocyte monocyte- colony stimulating factor
( GM-SF)
• These cytokines further stimulate macrophages to increase phagocytic activity
and to in turn produce cytokines that promote inflammation
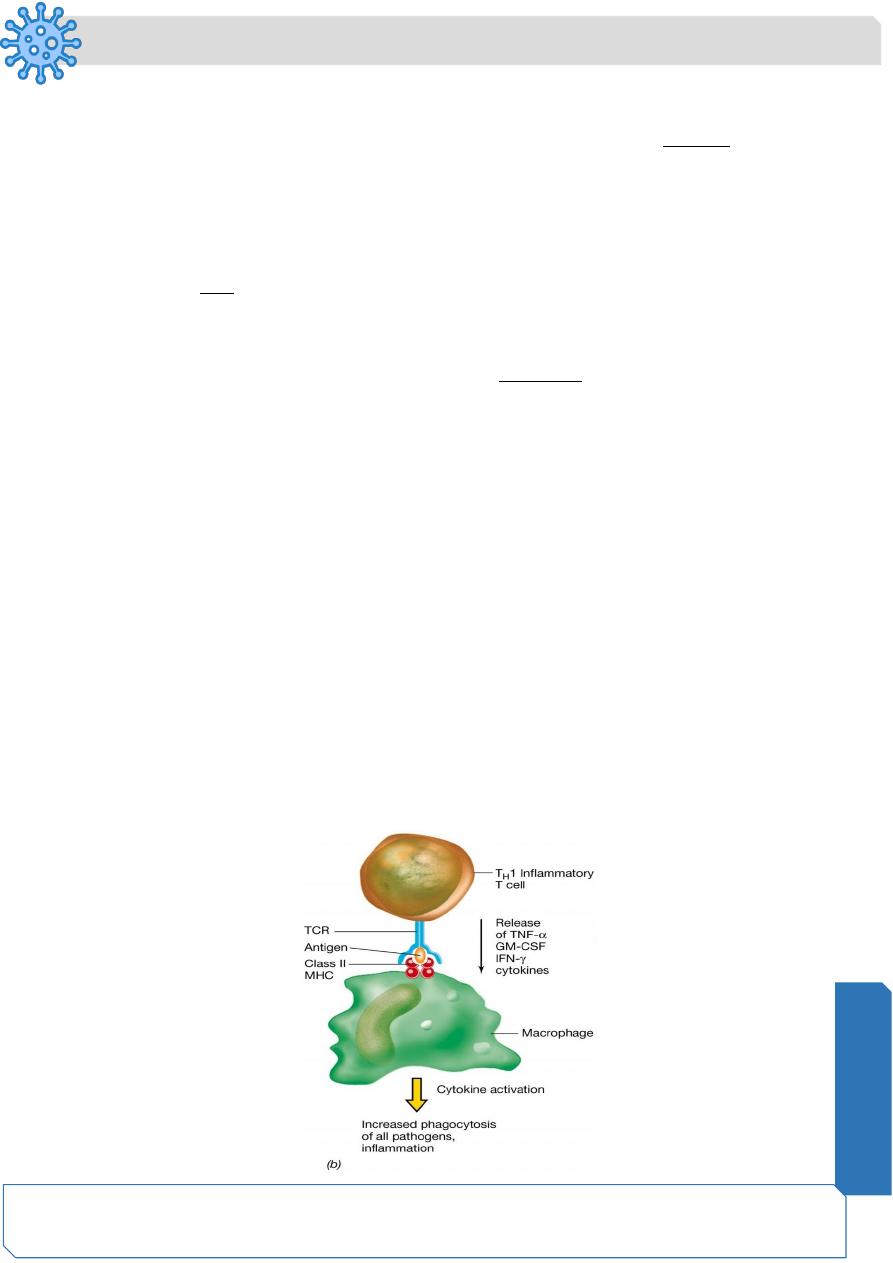
Class II MHC proteins and helper T cells (TH)
Specialized TH cell involved in the inflammatory response Cell-cell interaction mediated
by the TCR and the class II MHC-antigen complex activatesThe TH cell which produces
cytokines
TNF-alpha (tumor necrosis factor)
IFN-gamma (interferon)
GM-CSF (granulocyte-monocyte colony stimulating factor)
These cytokines further stimulate macrophages to increase phagocytic activity and to in
turn produce cytokines that promote inflammation
