Microbiology
Notes…
1
Bacteriology Lecture.3
Microbial Growth
Microbial growth = increase in number of cells, not cell size
The Requirements for Growth: Physical Requirements
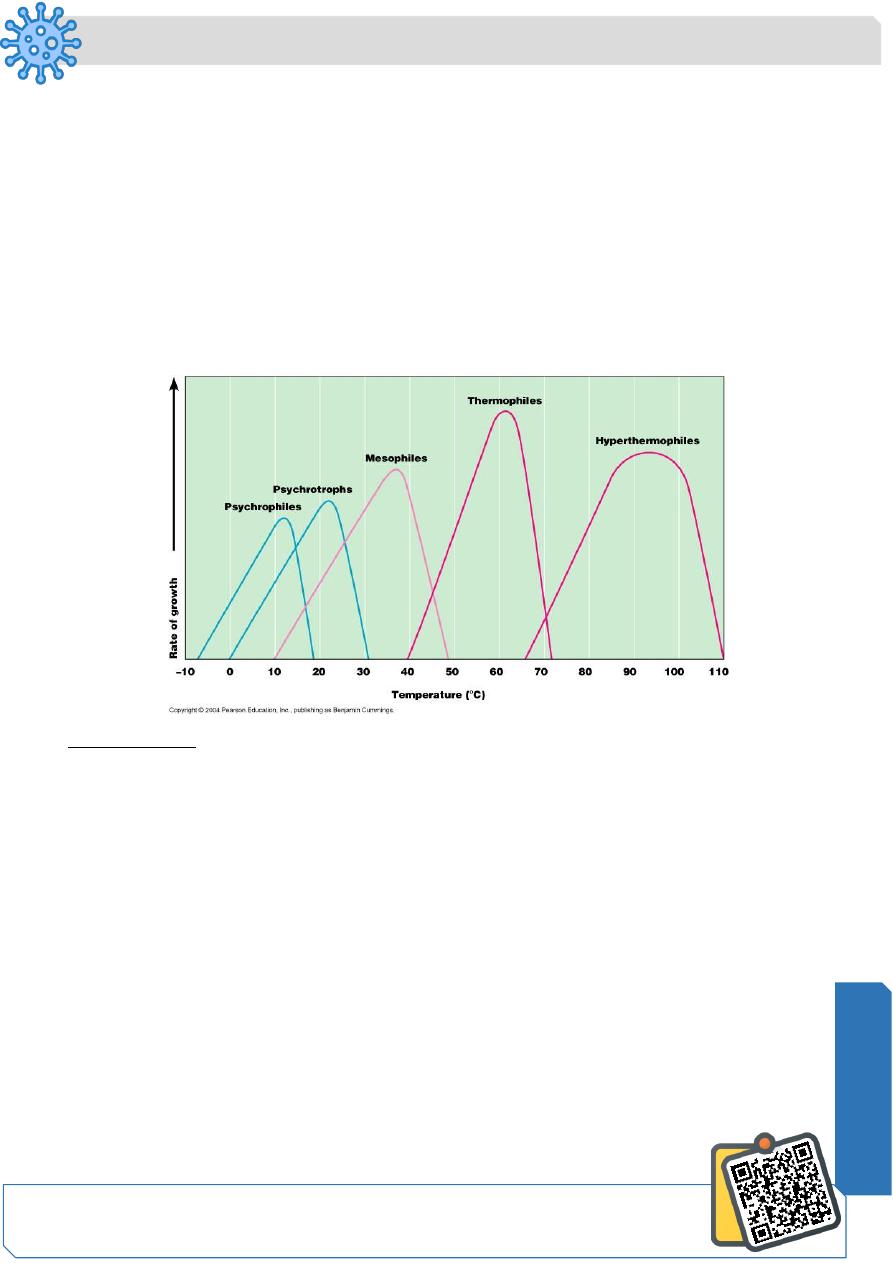
Temperature
✓ Minimum growth temperature
✓ Optimum growth temperature
✓ Maximum growth temperature
Psychrotrophs
Grow between 0°C and 20-30°C
Cause food spoilage
pH
✓ Most bacteria grow between pH 6.5 and 7.5
✓ Molds and yeasts grow between pH 5 and 6
✓ Acidophiles grow in acidic environments
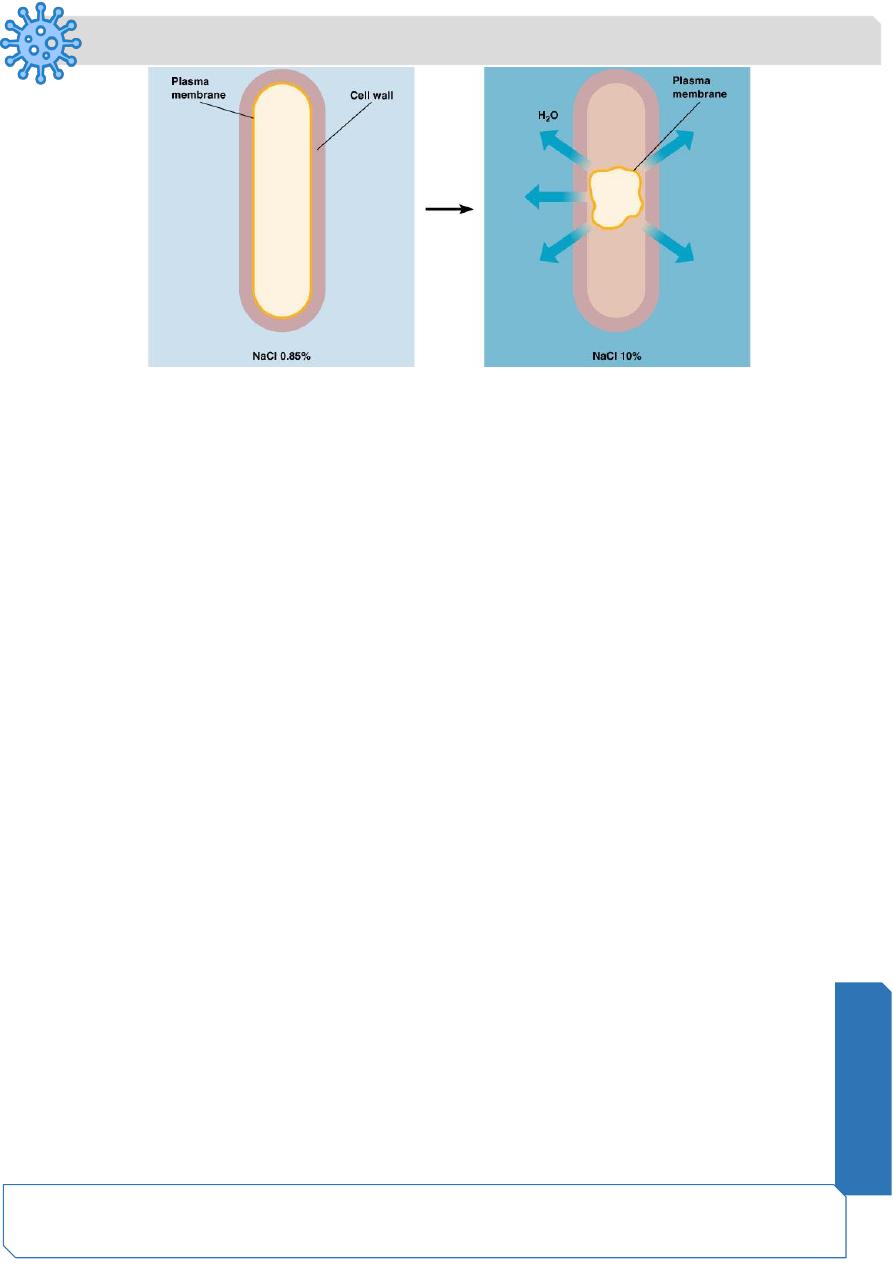
Osmotic Pressure
✓ Hypertonic environments, increase salt or sugar, cause plasmolysis
✓ Extreme or obligate halophiles require high osmotic pressure
✓ Facultative halophiles tolerate high osmotic pressure
N
eed S
om
e H
el
p?
Microbiology
Notes…
2
The Requirements for Growth: Chemical Requirements
Carbon
✓ Structural organic molecules, energy source
✓ Chemoheterotrophs use organic carbon sources
✓ Autotrophs use CO2
Nitrogen
✓ In amino acids, proteins
✓ Most bacteria decompose proteins
✓ Some bacteria use NH4+ or NO3
−
✓ A few bacteria use N2 in nitrogen fixation
Sulfur
✓ In amino acids, thiamine, biotin
✓ Most bacteria decompose proteins
✓ Some bacteria use SO42
− or H2S
Phosphorus
✓ In DNA, RNA, ATP, and membranes
✓ PO43
− is a source of phosphorus
Trace Elements
✓ Inorganic elements required in small amounts
✓ Usually as enzyme cofactors
Oxygen (O2)

Microbiology
Notes…
3
Toxic Forms of Oxygen
✓ Singlet oxygen: O
2
boosted to a higher-energy state
✓ Superoxide free radicals: O
2
−
✓ Peroxide anion: O
2
2
−
✓ Hydroxyl radical (OH
•)
Organic Growth Factors
✓ Organic compounds obtained from the environment
✓ Vitamins, amino acids, purines, pyrimidines
Culture Media
Culture Medium: Nutrients prepared for microbial growth
Sterile: No living microbes
Inoculum: Introduction of microbes into medium
Culture: Microbes growing in/on culture medium
Agar
Complex polysaccharide
Used as solidifying agent for culture media in Petri plates, slants, and deeps
Generally not metabolized by microbes
Liquefies at 100°C
Solidifies ~40°C
Culture Media
Chemically Defined Media: Exact chemical composition is known
Complex Media: Extracts and digests of yeasts, meat, or plants: Nutrient broth,
Nutrient agar
Microbiology
Notes…
4
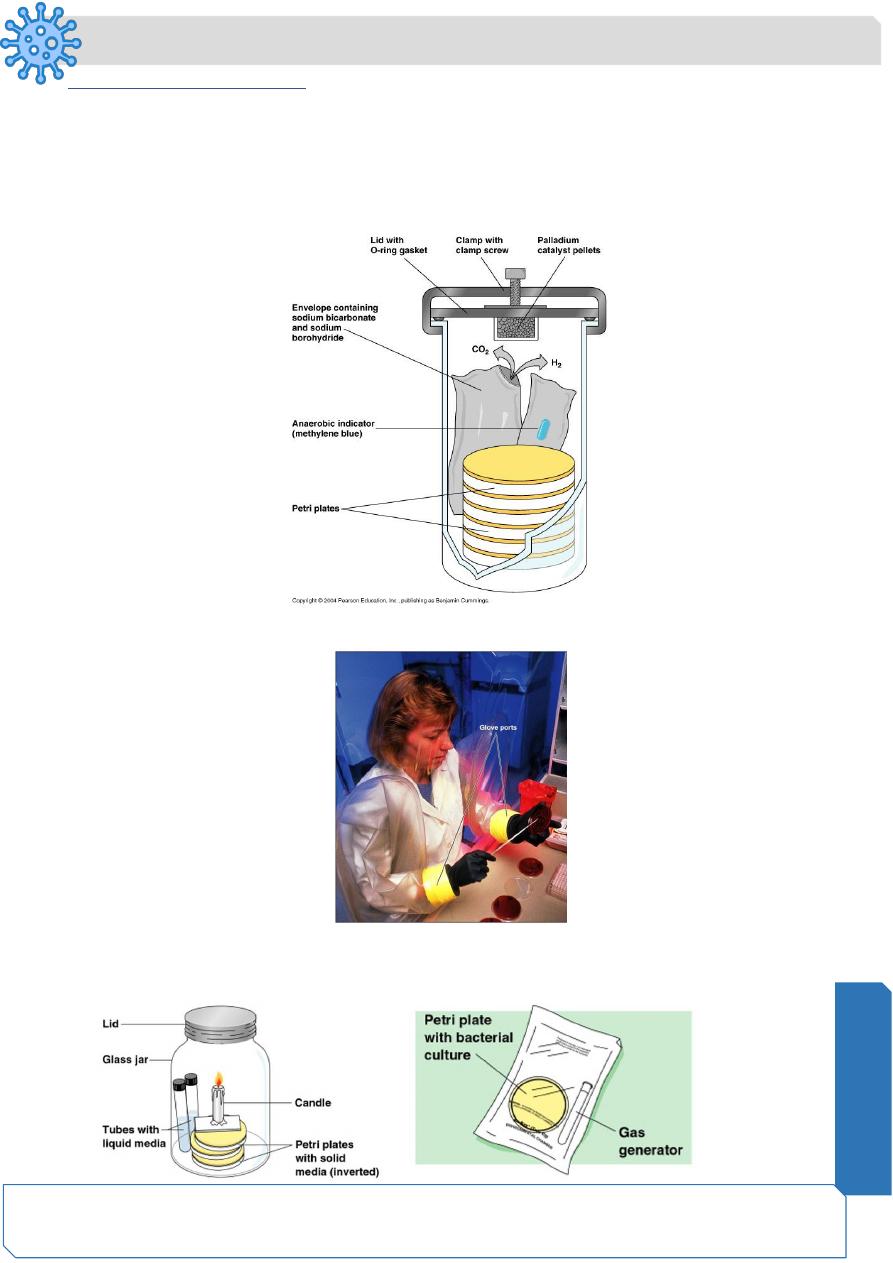
Anaerobic Culture Methods
Reducing media
✓ Contain chemicals (thioglycollate or oxyrase) that combine O
2
✓ Heated to drive off O
2
Anaerobic jar
Anaerobic chamber
Capnophiles require high CO2
Candle jar CO
2
-packet

Microbiology
Notes…
5
Selective Media
Suppress unwanted microbes and encourage desired microbes.
Differential Media
Make it easy to distinguish colonies of different microbes.
A pure culture contains only one species or strain
A colony is a population of cells arising from a single cell or spore or from a group
of attached cells
A colony is often called a colony-forming unit (CFU)
Streak Plate
Preserving Bacteria Cultures
Deep-freezing: -50°to -95°C
Lyophilization (freeze-drying): Frozen (-54° to -72°C) and dehydrated in a vacuum
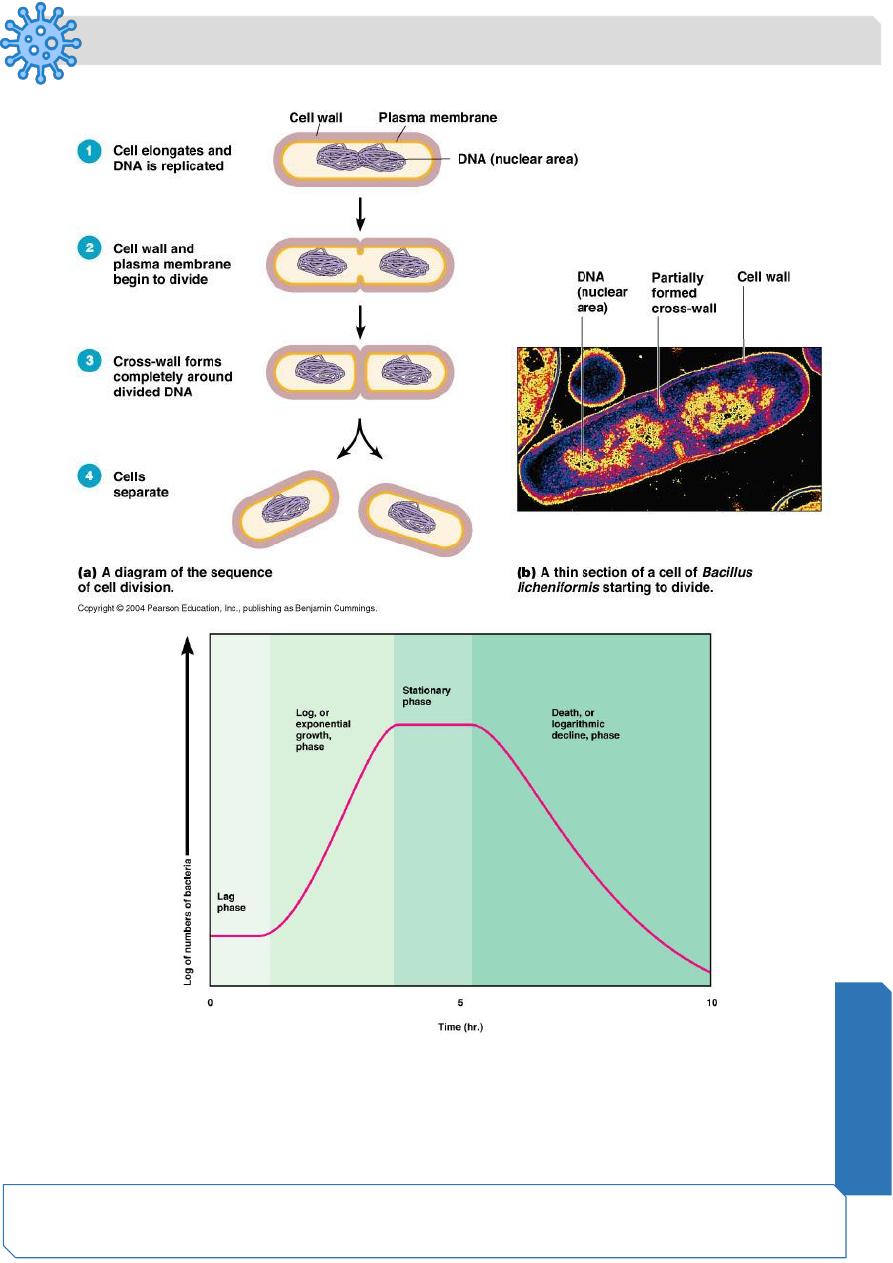
Reproduction in Prokaryotes
Binary fission
Budding
Conidiospores (actinomycetes)
Fragmentation of filaments
Microbiology
Notes…
6
Binary Fission
Microbiology
Notes…
7
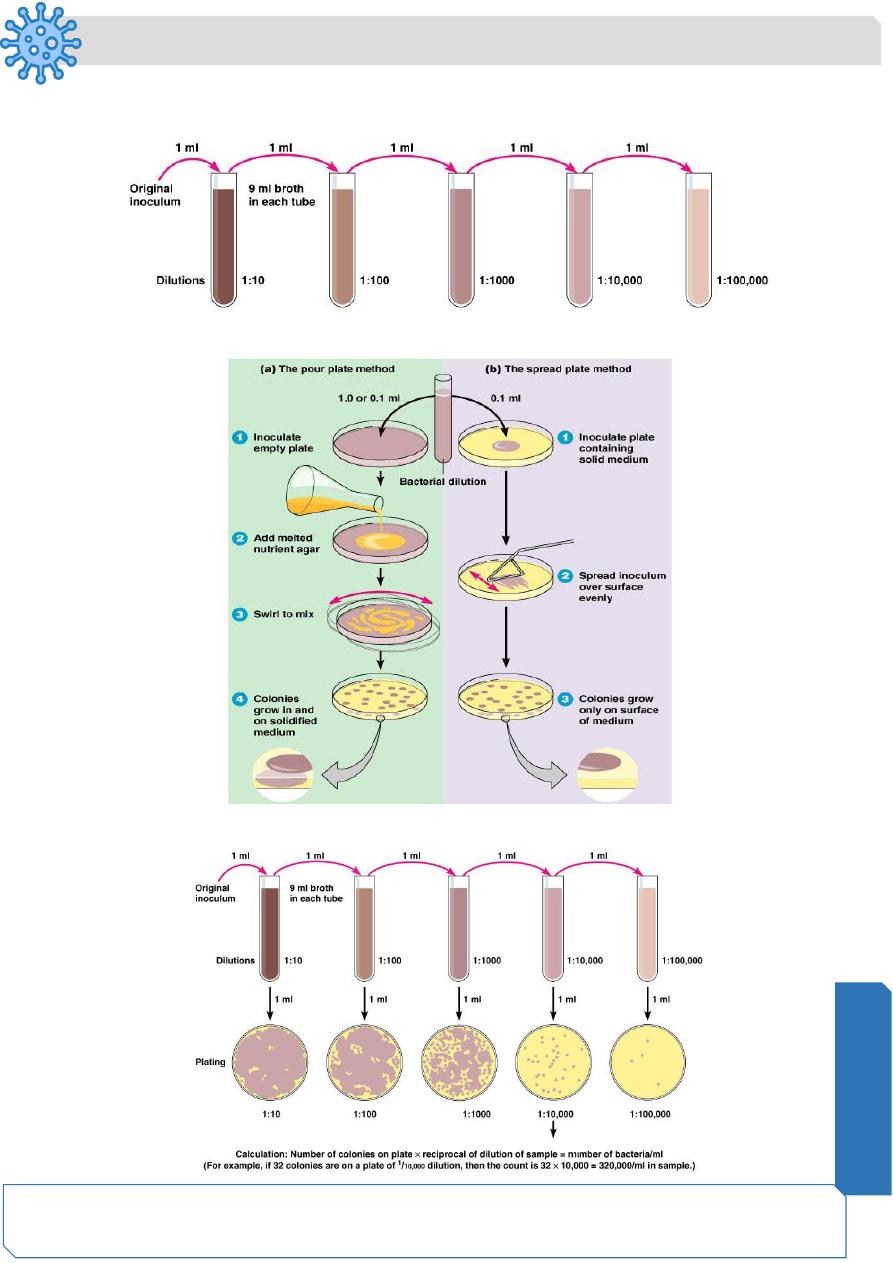
Direct Measurements of Microbial Growth
Plate Counts: Perform serial dilutions of a sample
Inoculate Petri plates from serial dilutions
After incubation, count colonies on plates that have 25-250 colonies (CFUs)
Microbiology
Notes…
8
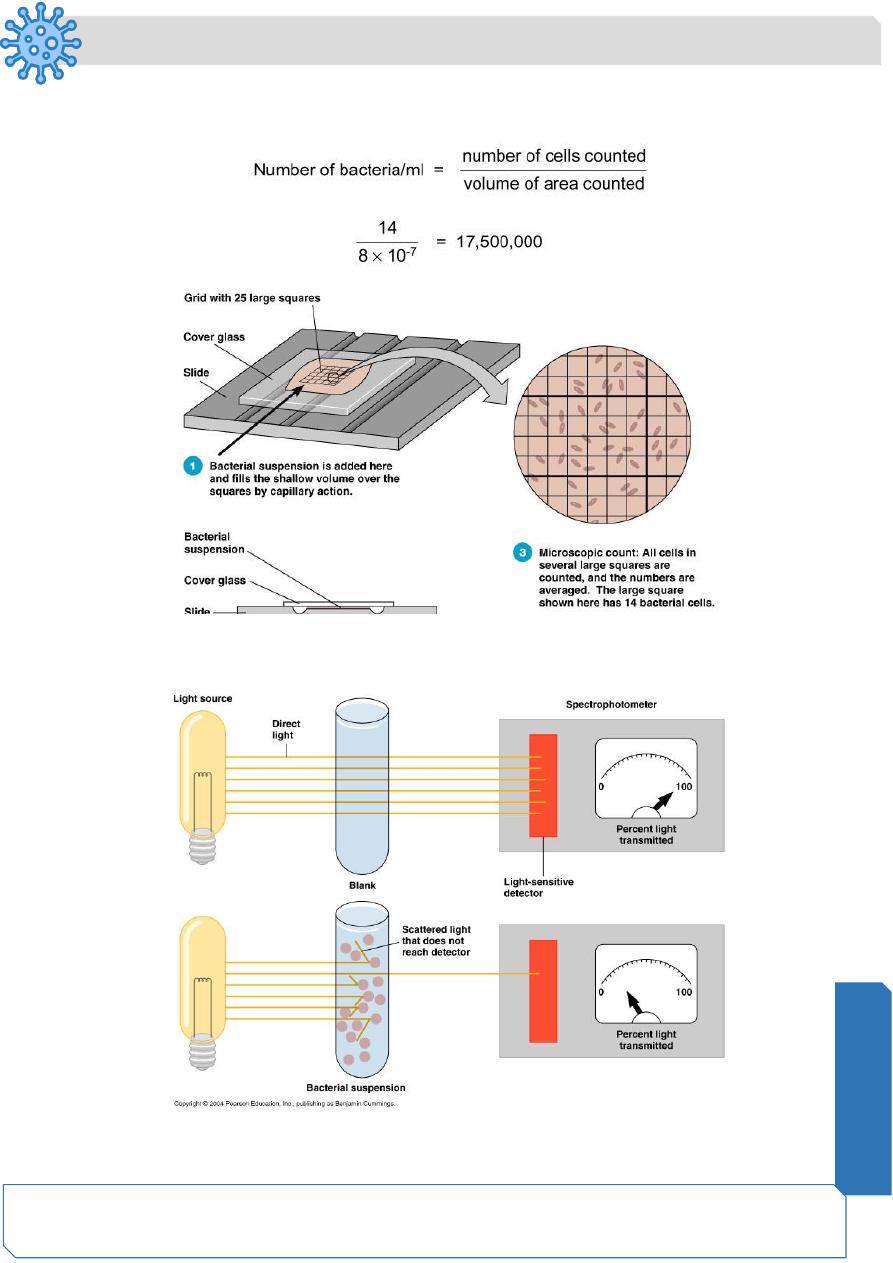
Direct Measurements of Microbial Growth
Direct Microscopic Count
Estimating Bacterial Numbers by Indirect Methods
Turbidity
