Microbiology
Notes…
1
Bacteriology Lecture.2
Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic Cells
Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
— Prokaryote comes from the Greek words for prenucleus.
— Eukaryote comes from the Greek words for true nucleus.
Prokaryote
One circular chromosome,
not in a membrane
No histones
No organelles
Peptidoglycan cell walls
Binary fission
Eukaryote
• Paired chromosomes, in
nuclear membrane
• Histones
• Organelles
• Polysaccharide cell walls
• Mitotic spindle
Average size:
0.2 -1.0 µm
2 - 8 µm
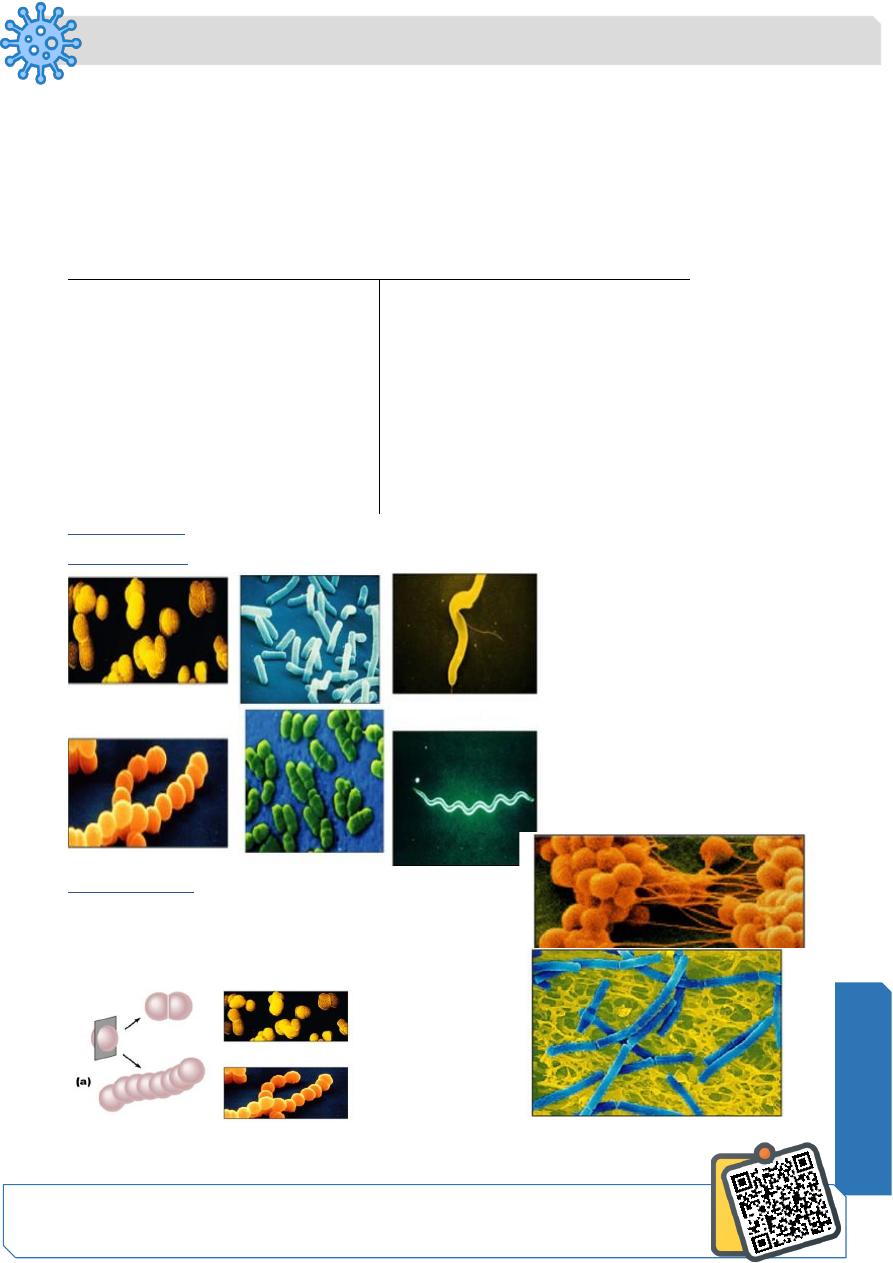
Basic shapes:
Arrangements
Pairs: diplococci, diplobacilli
Clusters: staphylococci
Chains: streptococci, streptobacilli
N
eed S
om
e H
el
p?
Microbiology
Notes…
2
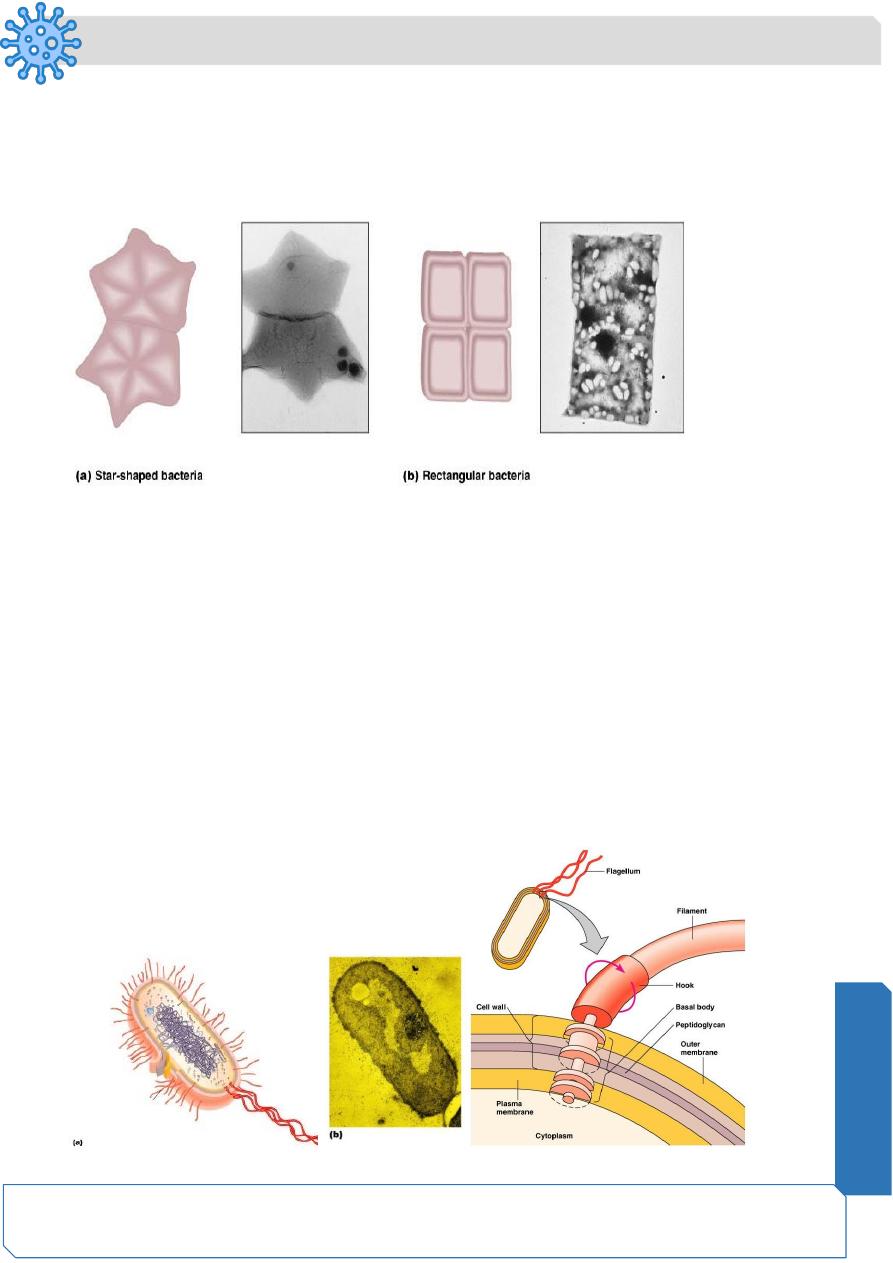
Unusual shapes
— Star-shaped
Stella
— Square
Haloarcula
Most bacteria are monomorphic
A few are pleomorphic
Glycocalyx
Outside cell wall
Usually sticky
A capsule is neatly organized
A slime layer is unorganized & loose
Extracellular polysaccharide allows cell to attach
Capsules prevent phagocytosis
Flagella
Outside cell wall
Made of chains of flagellin
Attached to a protein hook
Anchored to the wall and membrane by the basal body
Microbiology
Notes…
3
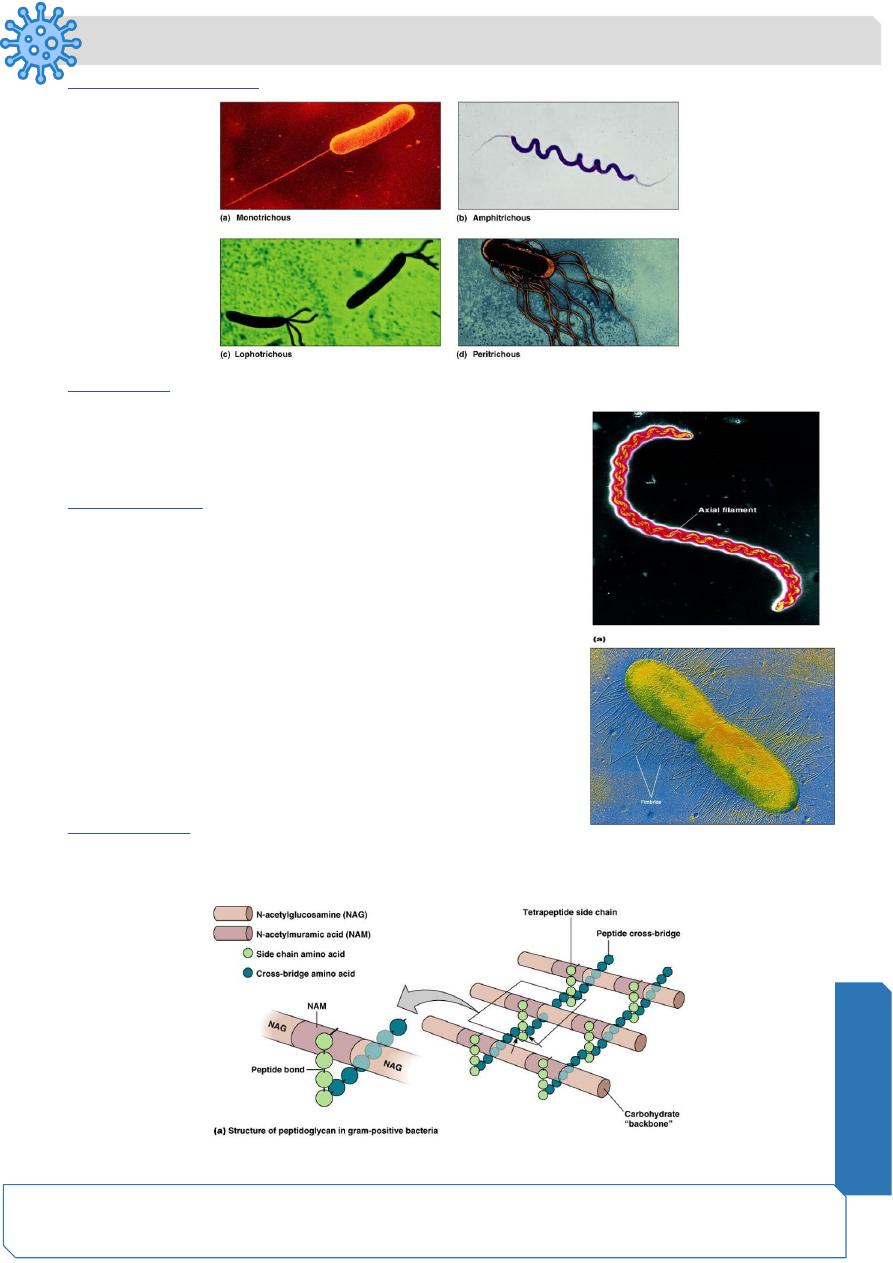
Flagella Arrangement
Motile Cells
Rotate flagella to run or tumble
Move toward or away from stimuli (taxis)
Flagella proteins are H antigens (e.g.,
E. coli
O157:H7)
Axial Filaments
Endoflagella
In spirochetes
Anchored at one end of a cell
Rotation causes cell to move
Fimbrae
Fimbriae allow attachment
Pili are used to transfer DNA from one cell to another
Cell wall
Prevents osmotic lysis
Made of peptidoglycan (in bacteria)
Peptidoglycan
Polymer of disaccharide N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) & N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM)
Linked by polypeptides
Microbiology
Notes…
4
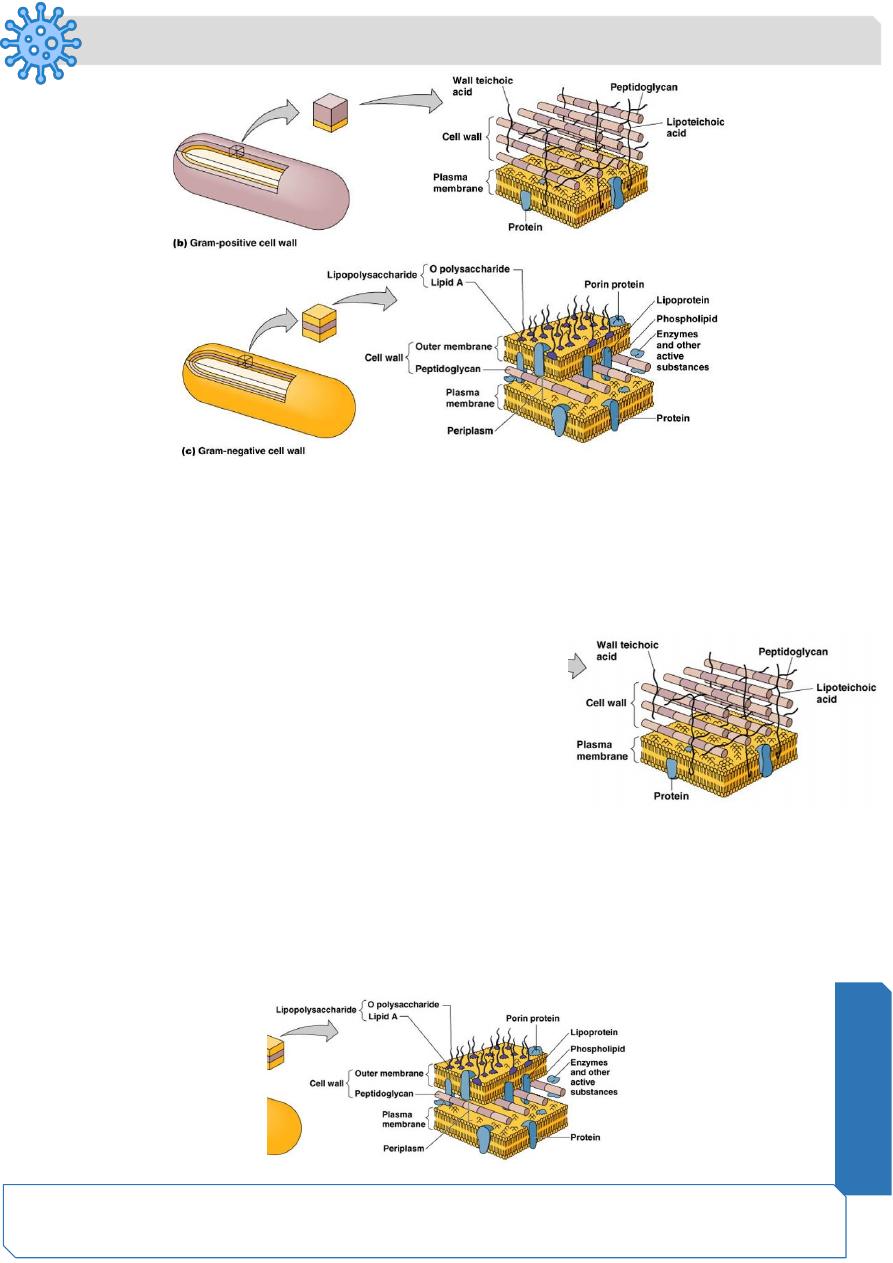
Gram-positive cell walls
Thick peptidoglycan
Teichoic acids
In acid-fast cells, contains mycolic acid
Gram-negative cell walls
• Thin peptidoglycan
• No teichoic acids
• Outer membrane
Gram-Positive cell walls
Teichoic acids:
— Lipoteichoic acid links to plasma membrane
— Wall teichoic acid links to peptidoglycan
May regulate movement of cations
Polysaccharides provide antigenic variation
Gram-Negative Outer Membrane
Lipopolysaccharides, lipoproteins, phospholipids.
Forms the periplasm between the outer membrane and the plasma membrane.
Protection from phagocytes, complement, antibiotics.
O polysaccharide antigen, e.g.,
E. coli
O157:H7.
Lipid A is an endotoxin.
Porins (proteins) form channels through membrane
Microbiology
Notes…
5
Atypical Cell Walls
Mycoplasmas
— Lack cell walls
— Sterols in plasma membrane
Archaea
— Wall-less, or
— Walls of pseudomurein (lack NAM and D amino acids)
Damage to Cell Walls
Lysozyme digests disaccharide in peptidoglycan.
Penicillin inhibits peptide bridges in peptidoglycan.
Protoplast is a wall-less cell.
Spheroplast is a wall-less Gram-positive cell.
L forms are wall-less cells that swell into irregular shapes.
Protoplasts and spheroplasts are susceptible to osmotic lysis.
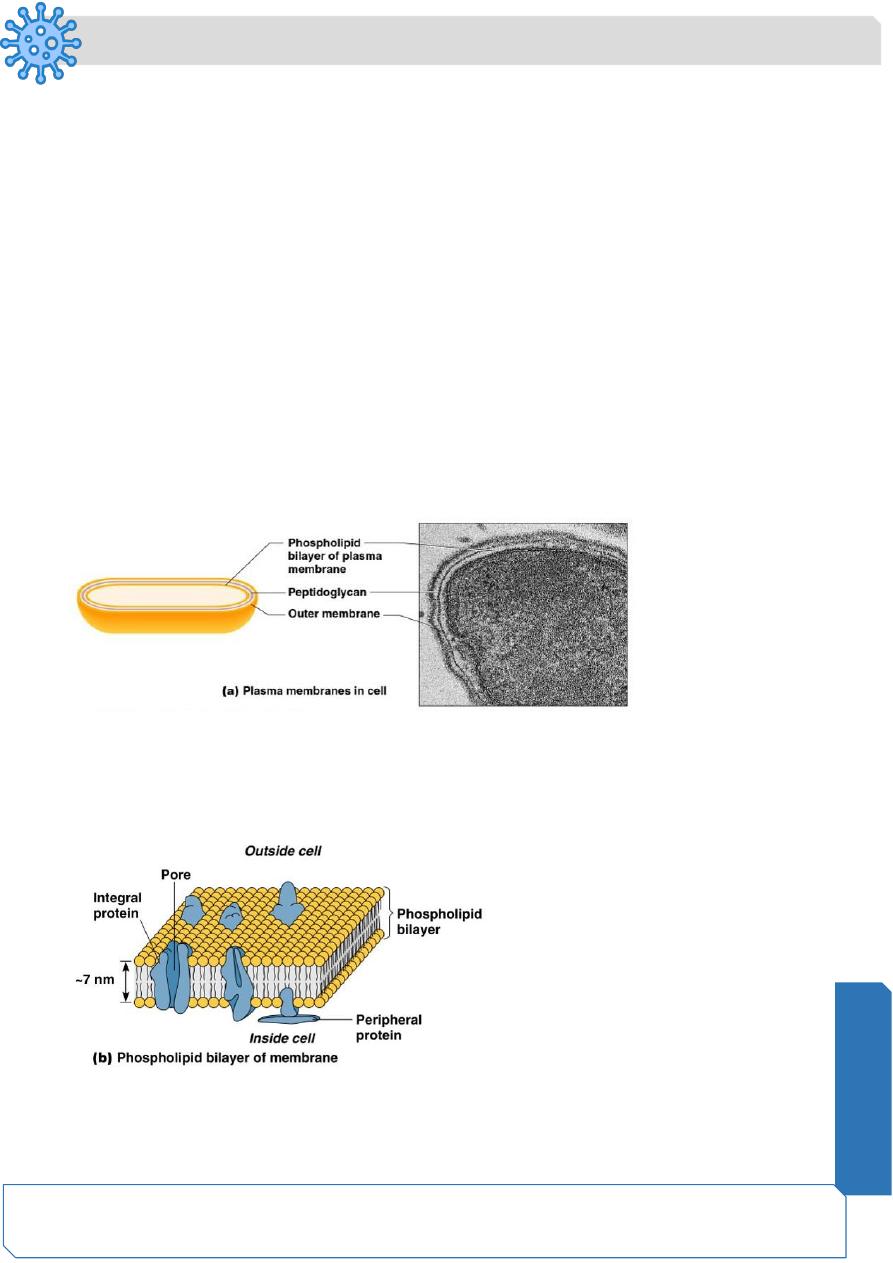
Plasma Membrane
Phospholipid bilayer
Peripheral proteins
Integral proteins
Transmembrane proteins
Selective permeability allows passage of some molecules
Damage to the membrane by alcohols, quaternary ammonium (detergents) and
polymyxin antibiotics causes leakage of cell contents.
Microbiology
Notes…
6
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is the substance inside the plasma membrane
Nuclear Area
Nuclear area (nucleoid)
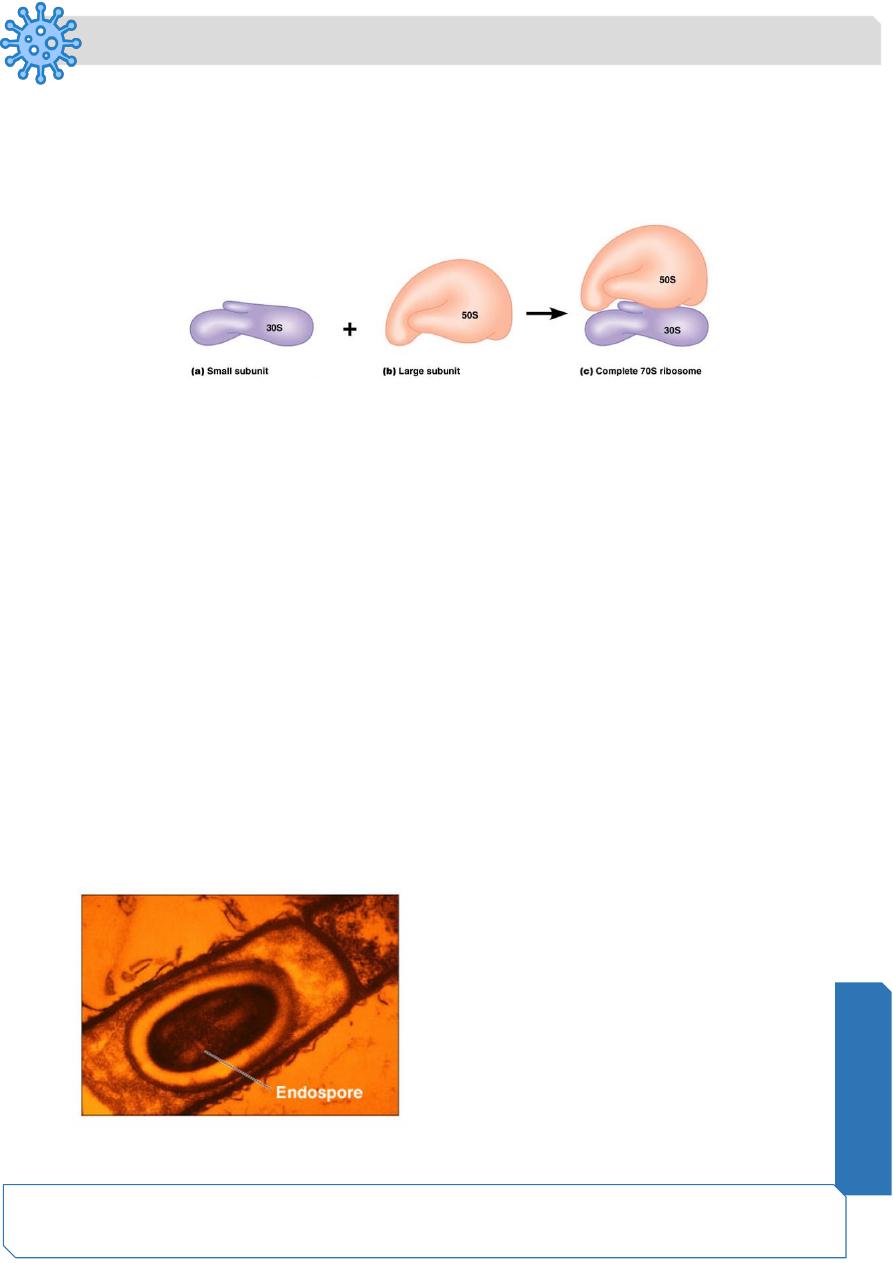
Ribosomes
Inclusions
Metachromatic
granules
(volutin)
Polysaccharide granules
Lipid inclusions
Sulfur granules
Carboxysomes
Gas vacuoles
Magnetosomes
• Phosphate reserves
• Energy reserves
• Energy reserves
• Energy reserves
• Ribulose
1,5-diphosphate
carboxylase for CO
2
fixation
• Protein covered cylinders
• Iron
oxide
(destroys H
2
O
2
)
Endospores
Resting cells
Resistant to desiccation, heat, chemicals
Bacillus, Clostridium
Sporulation: Endospore formation
Germination: Return to vegetative state
