ThiQar college of MedicineFamily & Community medicine dept.
Nutrition Lecture 1Third stage by: Dr. Muslim N. SaeedDecember 5th ,2021NUTRITION AND HEALTH
Dietetics
The practical applications of the principles of nutrition.It includes “the planning of meals for the well and the sick people”
Classification of food:
-Classification by origin-Classification by chemical composition
-Classification by predominant functionClassification by origin:
-Foods of animal origin-Foods of vegetable origin
Classification by predominant function:1. Body-building foods: e.g. milk, meat, poultry, fish, egg, pulses ...etc.
2. Energy giving foods: e.g. cereals, sugars, fats and oils.
3. Protective foods: e.g. vegetables, fruits ... etc.
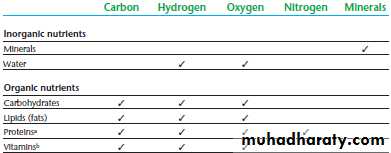
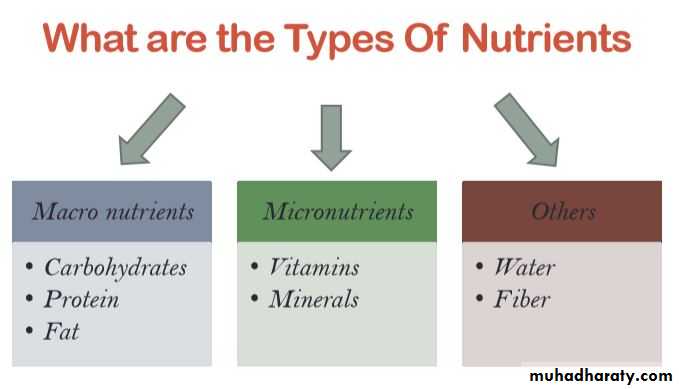
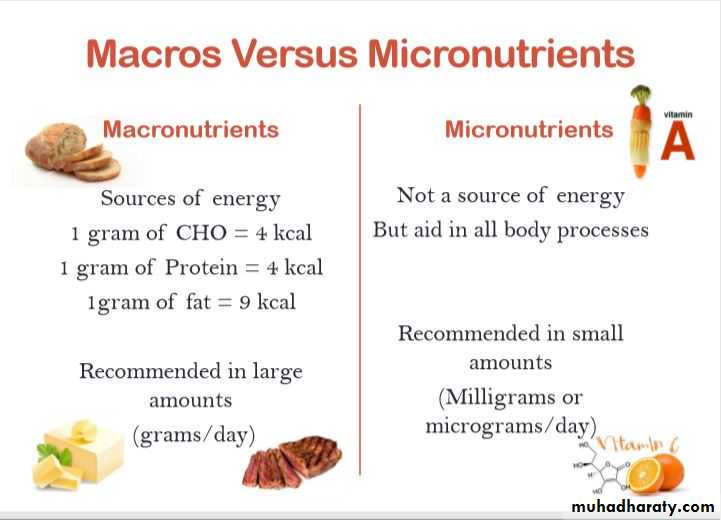
Elements in the Six Classes of Nutrients
Essential nutrients: nutrients a person must obtain from food because the body cannot make them for itself in sufficient quantity to meet physiological needs; also called indispensable nutrients. About 40 nutrients are currently known to be essential for human beings.
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)A set of nutritional reference values that applies
to healthy people.
The DRIs for most nutrients consist of four values:
• Estimated Average Requirement (EAR)
• Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
• Adequate Intake (AI)
• Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL)
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) The average daily amount of a nutrient considered adequate to meet nutrient needs of healthy individuals in a particular life stage and gender group.
Adequate Intake (AI)
the average daily amount of a nutrient that appears sufficient to maintain nutrient needs of healthy individuals.Its used as a guide for nutrient intake when an RDA cannot be determined.
The Estimated Energy Requirement (EER)
The Estimated Energy Requirement Is the Intake Predicted to Maintain a Healthy Weight.The Estimated Energy Requirement (EER) is defined as the average dietary energy intake that is predicted to maintain energy balance in a healthy adult.
This dietary intake is defined by a person’s age, gender, weight, height, and level of physical activity that is consistent with good health. Thus, the EER for an active person is higher than the EER for an inactive person even if all other factors (age, gender, and so forth) are the same.
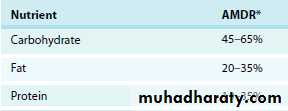
Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDR)A range of intakes for a particular energy source that is associated with reduced risk of chronic disease while providing adequate intakes of essential nutrients.
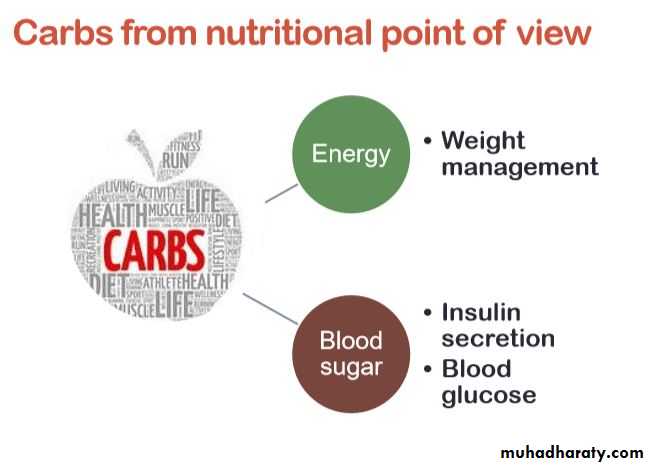
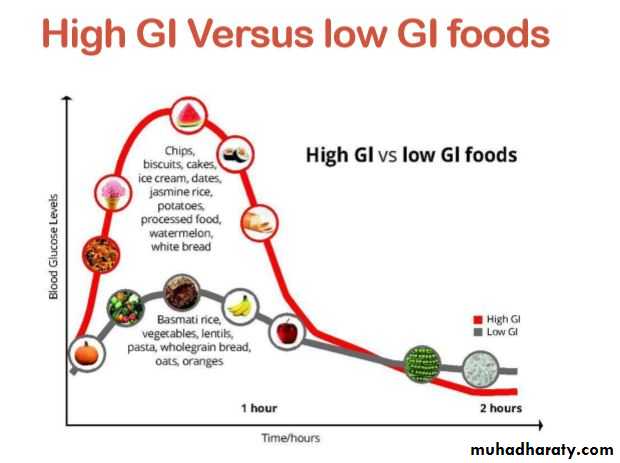
What is Glyceaemic index??• It is the variation in increase and fall in blood glucose level, following ingestion of carbohydrate containing food, this variation is known as The Glyceaemic index of food containing carbohydrates