2
nd
class Lab 1
-
:
route of drug adminstration
d
an
forms
Drug
Administration of drug is determined primarily by:-
- The properties of the drug .
- The therapeutic objective.
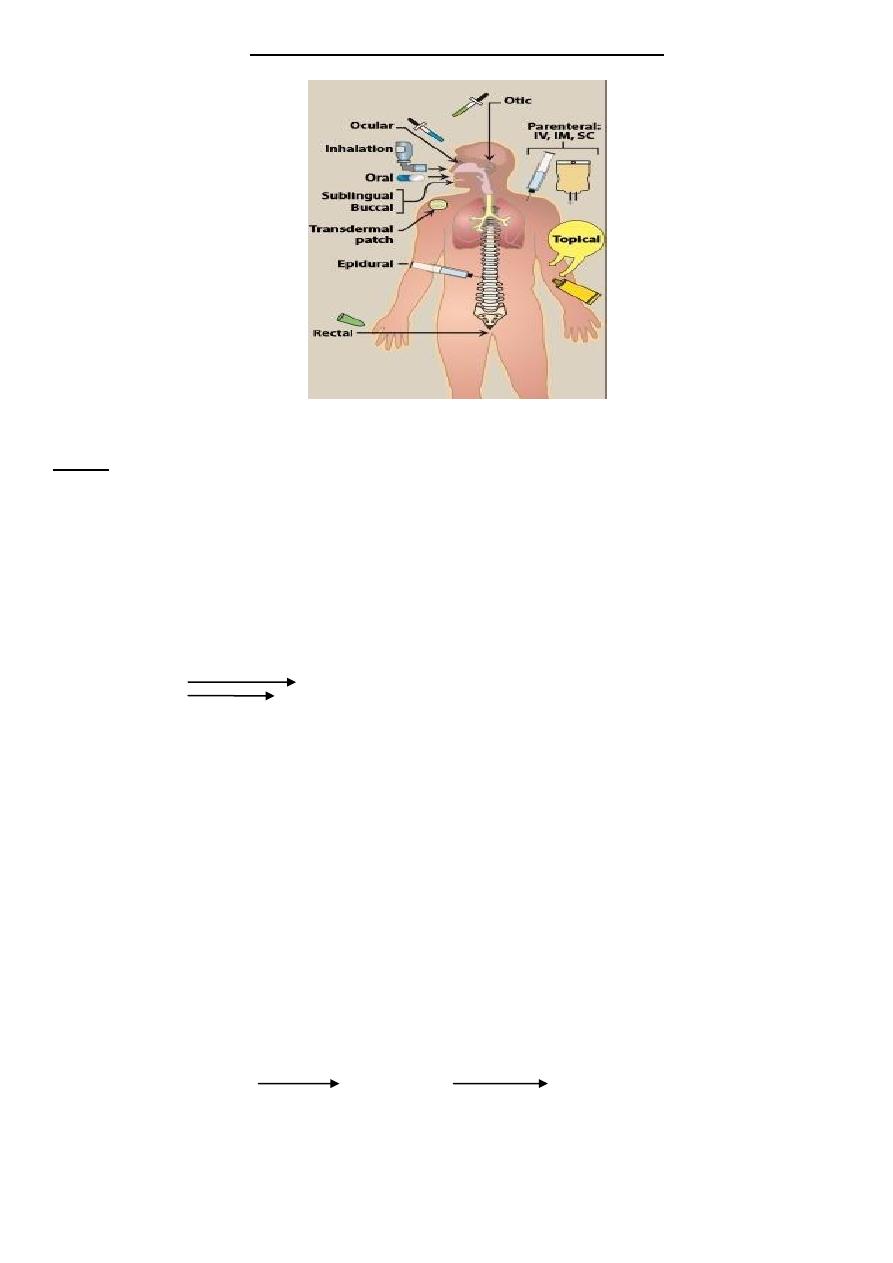
Major route of administration include enteral (oral and sublingual), parenteral and others
(oral inhalation, nasal inhalation, intrathecal / intraventricular, topical, transdermal and rectal).
A – Enteral:-
-
Oral:
I.
Drug form which contains dried
he most common preparation for oral use.
T
-
Tablets:
=
powdered active drug and also contains binders to provide bulk and proper size. A tablet before
being absorbed should disintegrate into granules & then dissolute into primary drug particles.
Many different types of tablets:
Can easily be broken into two
.
ablet
t
Indented line running across the
:
Scored Tablets
-
a
pieces with a knife to produce two doses.
ists stomach acid
that res
film coat design
Covered with a special
:
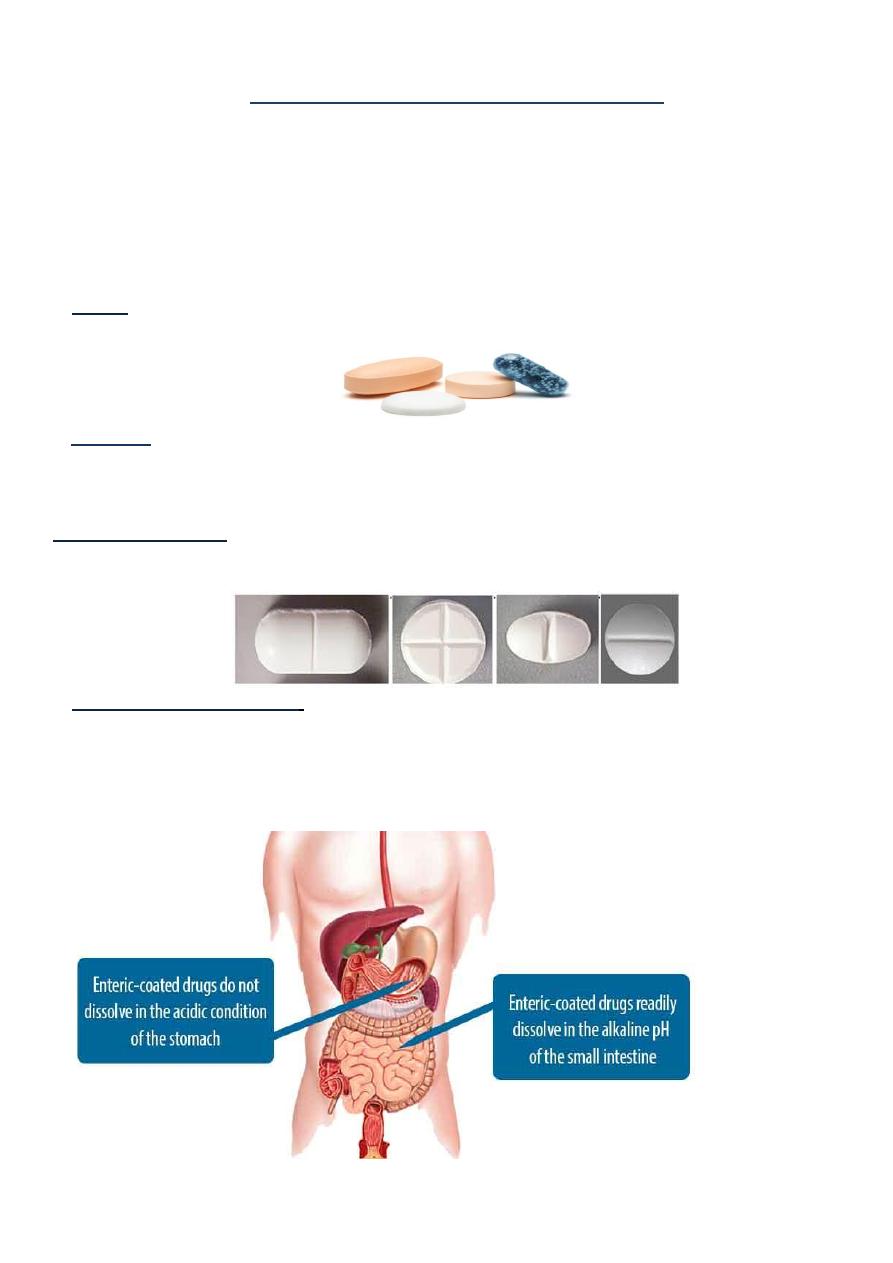
Tablets
coated
-
Enteric
-
b
but dissolves in the alkaline environment in small intestines. These are different type.
1-They are used to protect a drug from degradation in the stomach.
2-To minimize gastric irritation caused by some drugs.
3-To improve the appearance of the tablet.

se their contents over extended
elea
his is designed to r
T
-
release tablets (SR):
-
Sustained
-
c
period of time.
.
Easier to swallow
.
Coated tablets in the shape of a capsule
Tablets:
Caplets
-
d
never
,
, water and flavorings
sugar
Formed with a harden base of
Tablets:
Lozenges
-
e
swallow,
dissolve slowly in mouth. They are used to medicate the mouth and throat.
. However,
o high compression
t subjected t
Drug particles in the capsule are no
-
Capsules:
2.
drug bioavailability from capsule isn't always better than a tablet. The capsule comes in two
varieties, generally easier to swallow
a- Soft gelatin- Capsule: Manufactured in one piece in which the drug is in a liquid form inside
the soft shell
b- Hard shell-
Capsule: Manufactured in two pieces that fit together and hold the drug which is
in a powder or granular form.
taking.
stirred in water before
r particles of drug, sugar &
ll irregula
A
-
Granules:
3.
he basis of the effervescence is a mixture of citric acid & tartaric
T
-
:
Effervescents tablet
4.
acid with sodium bicarbonate. When dissolve in water, the acid & bicarbonate react together to
produce carbonic acid. The carbonated water partly disguises the unpleasant taste of drug & has
refreshing properties.
5- Powder
: Finely ground form of an active drug, can be contained in a capsule, glass vials-
sterile water, Packaged- water.

Solution or suspension
-
2 forms
Comes in one of
:
Liquids
-
6
Solution:-.
= Types of Solutions:
1- Elixirs: alcohol & water base with added sugar & flavoring.
2- Syrups: sugar, water & flavoring thicker.
3- Tinctures: alcohol & water base used topically.
Suspensions:-
- Contain fine, un dissolved particles of a drug suspended in a liquid base.
- Important to always shake before use.
11- Sublingual:-
Placement under the tongue allows the drug to diffuse into capillary network and, therefore,
to enter the systemic circulation directly. The buccal route between check and gum is similar to
sublingual route.
-
:
and route of drug adminstration
Drug forms
1- Enteral:-
-
Oral:
1- Oral therapy:
- Advantages:
a- Swallowing (tab, cap, syrup) is by far the most acceptable, and usually the cheapest.
b- Easy, safe, and convenience.
.
- Disadvantage:
a- Absorption may be delayed, reduced or enhanced by the presence of food or with drugs
that inhibit gut motility (ex. antimuscarinic).
b- Some drugs ulceration.
c- Most drugs undergo first pass metabolism.
d- Variation in drug effect,.
e- Patient compliance is necessary.
Sublingual and buccal therapy
11-
- Advantage:
a- Bypasses first pass metabolism involve giving the drug by sublingual and buccal route.
The drugs are absorbed by oral mucosa in both methods.
b- Bypasses destruction by stomach acid.
c- Rapid absorption and efficacy.
d- Drug stability maintained because the pH of saliva relatively neutral.
- Disadvantages:
a- Irritation of mucosa membrane.
b- Limited to certain types of drugs.
c-Limited to drugs that can be taken in small doses.
c- Excessive salvation swallowing loss part of the drug dose.
