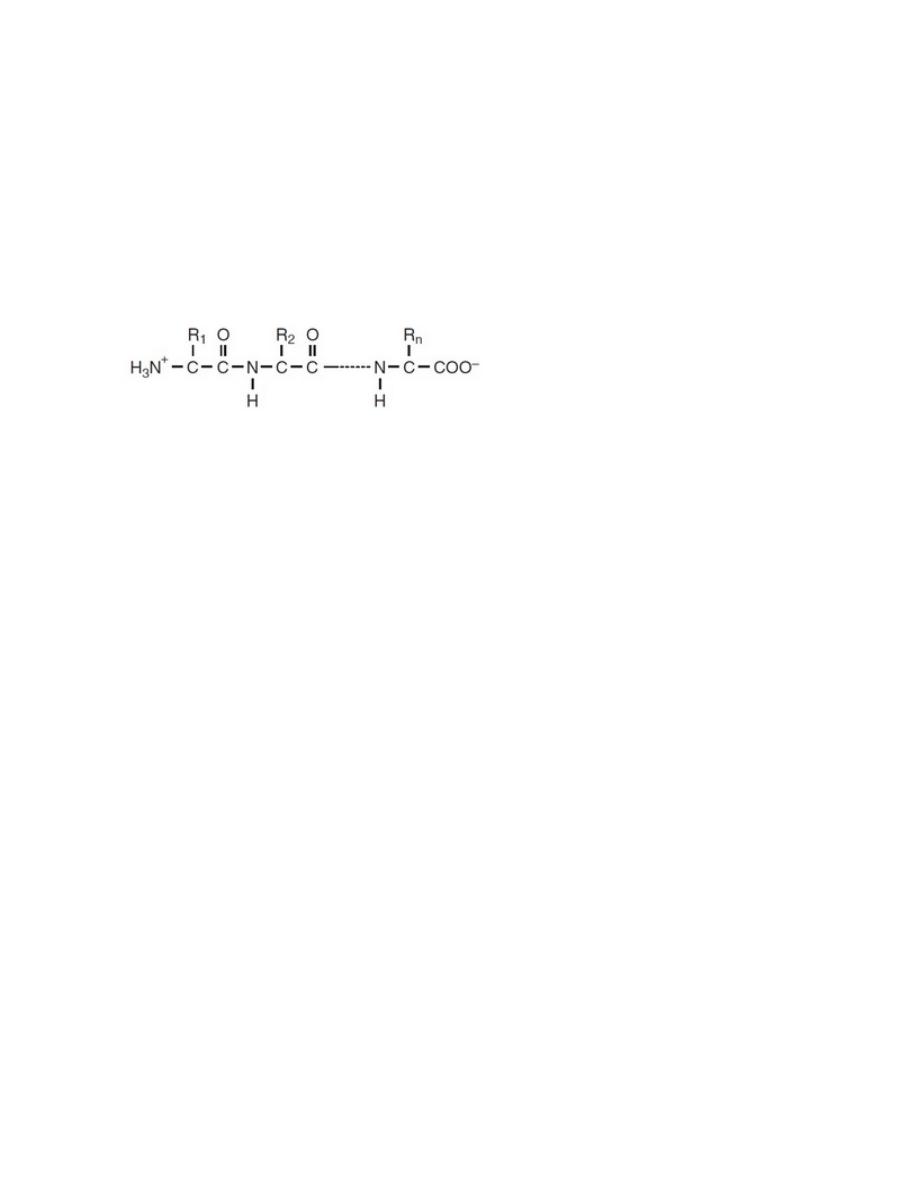
PROTEINS
Proteins consist of the elements carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur.
It is the fact that proteins contain nitrogen that sets them apart from pure
carbohydrates and lipids, which do not contain nitrogen atoms. Proteins are
polymers built from one or more unbranched chains of amino acids. A typical
protein contains 200 to 300 amino acids, but some are much smaller (peptides)
and some are much larger (e.g., titin, in muscle).
There are four distinct levels of a protein's structure:
1. Primary structure represents the number and types of amino acids in the specific
amino acid sequence.
2. Secondary structure refers to commonly formed structures stabilized by hydrogen
bonds between the amino acids within the protein. Common secondary structures
are the α-helix, β-pleated sheet
3. Tertiary structures are three dimensional and result from the interaction of side
chains, which are stabilized through the hydrophobic effect, ionic attraction,
hydrogen bonds, and disulfide bonds. The function and physical and chemical
properties of a protein are related to its tertiary structure
4. Quaternary structure is the shape or structure that results from the interaction of
more than one protein molecule, or protein subunits, held together by noncovalent
forces such as hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions.
Protein Metabolism
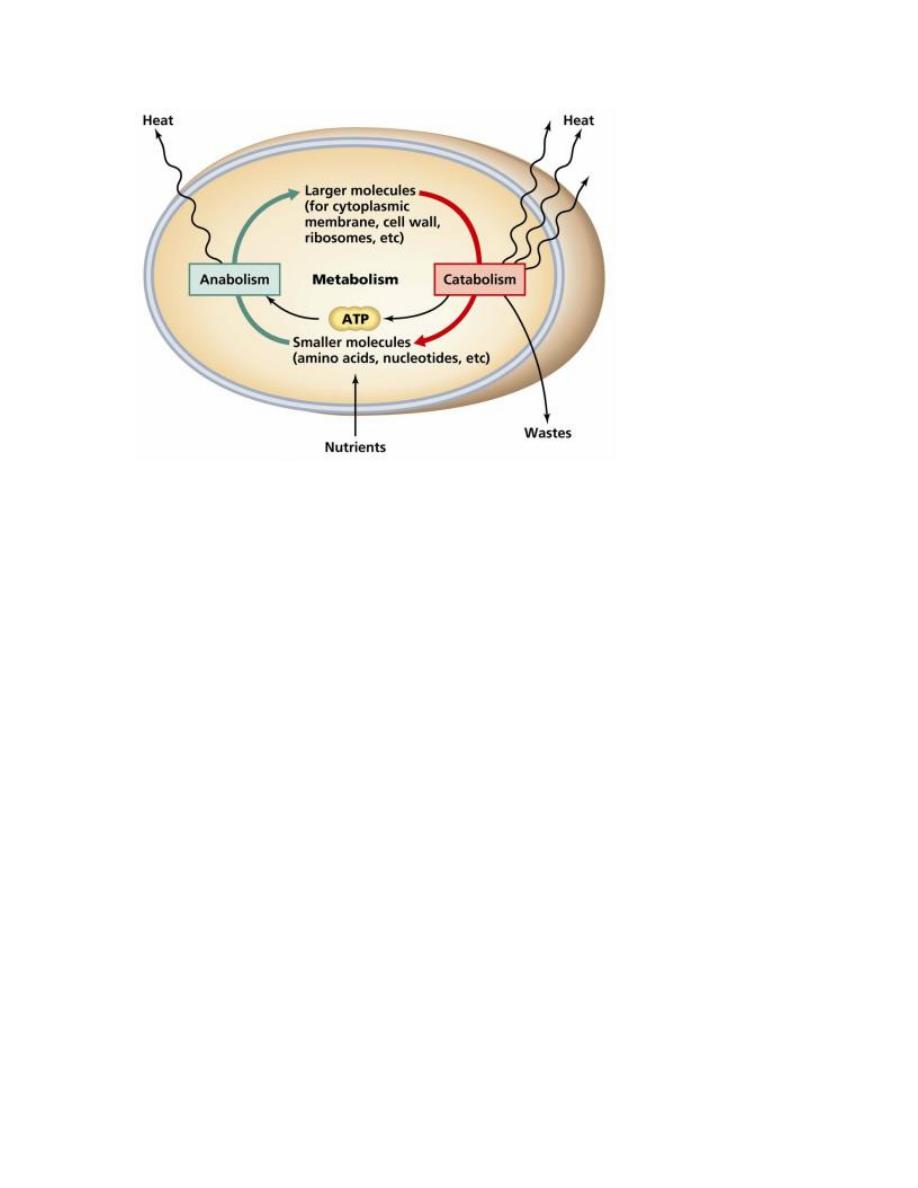
Metabolism is the chemical reactions that involved to maintain the cell and
organisms. For human, metabolism process is the very important because it require
the cellular metabolism which is involves the complex biochemical reactions that
called metabolic pathways.
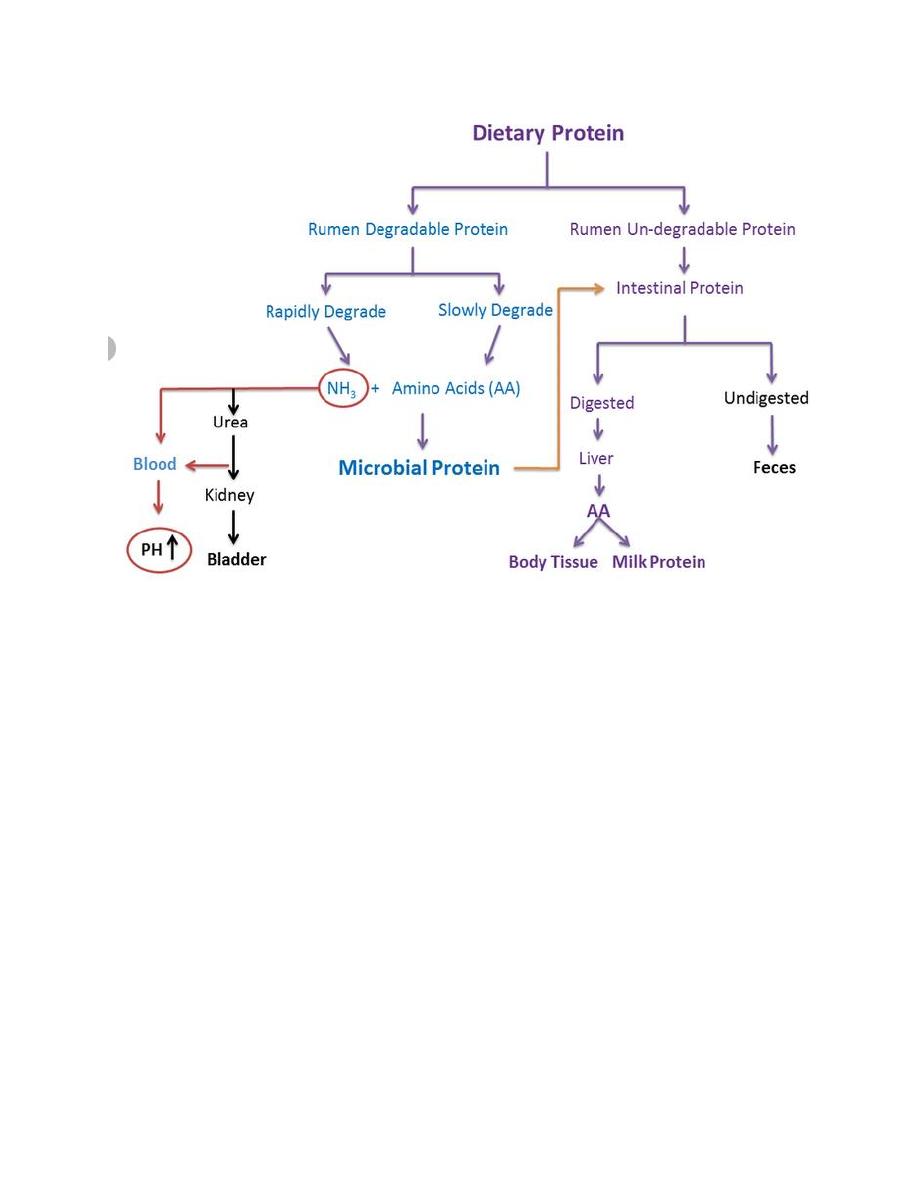
Protein metabolism is the process to breakdown foods are used by the body to gain
energy.
ANABOLISM (Synthesis)
Anabolism is Chemical reaction that synthesizes molecules from the smaller
components and usually require energy in process.
Most plasma proteins are synthesized in the liver and secreted by the hepatocyte
into circulation. Immunoglobulins are an exception because they are synthesized
in plasma cells. the information encoded in genes that provides each protein
with its own unique amino acid sequence. The amino acid sequence of a
polypeptide chain is determined by a corresponding sequence of bases (guanine,
cytosine, adenine, and thymine) in the DNA contained in the specific gene.
Protein synthesis occurs at a rate of approximately two to six peptide bonds
per second. Intracellular proteins are generally synthesized on free ribosomes,
whereas proteins made by the liver for secretion are made on ribosomes attached
to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. In some tissues, hormones, such as
thyroxine, growth hormone, insulin, and testosterone, may assist in controlling
protein synthesis.
CATABOLISM (breakdown)
Catabolism A series of degradative chemical reactions that break down complex
molecules into smaller units, and does not require energy because it is releasing
energy.
Unlike fats and carbohydrates, nitrogen has no designated storage, and dietary
proteins play an essential role in providing all the essential amino acids.
Insufficient dietary quantities of even one amino acid can quickly limit synthesis
of many essential proteins. Most proteins in the body are repetitively
synthesized and then degraded allowing for efficient recycling of amino acids. A
balance exists between protein synthesis (anabolism) and protein breakdown
(catabolism) and the turnover totals about 125 to 220 g of protein each day,
Nitrogen balance is maintained by equal intake and excretion of amino acids.
Pregnant women, growing children, and adults recovering from major illness are
often in positive nitrogen balance, which means that their nitrogen intake exceeds
their loss as net protein synthesis proceeds. When more nitrogen is excreted than is
incorporated into the body, an individual is in negative nitrogen balance. A negative
nitrogen balance may occur in conditions in which there is excessive tissue
destruction, such as burns, wasting diseases, continual high fevers, or starvation. The
breakdown of protein occurs in the digestive tract and kidneys, but
primarily in the liver. Nitrogen elimination begins intracellularly with protein
degradation. There are two main routes for converting intracellular proteins to
free amino acids: a lysosomal pathway and a cytosolic pathway.

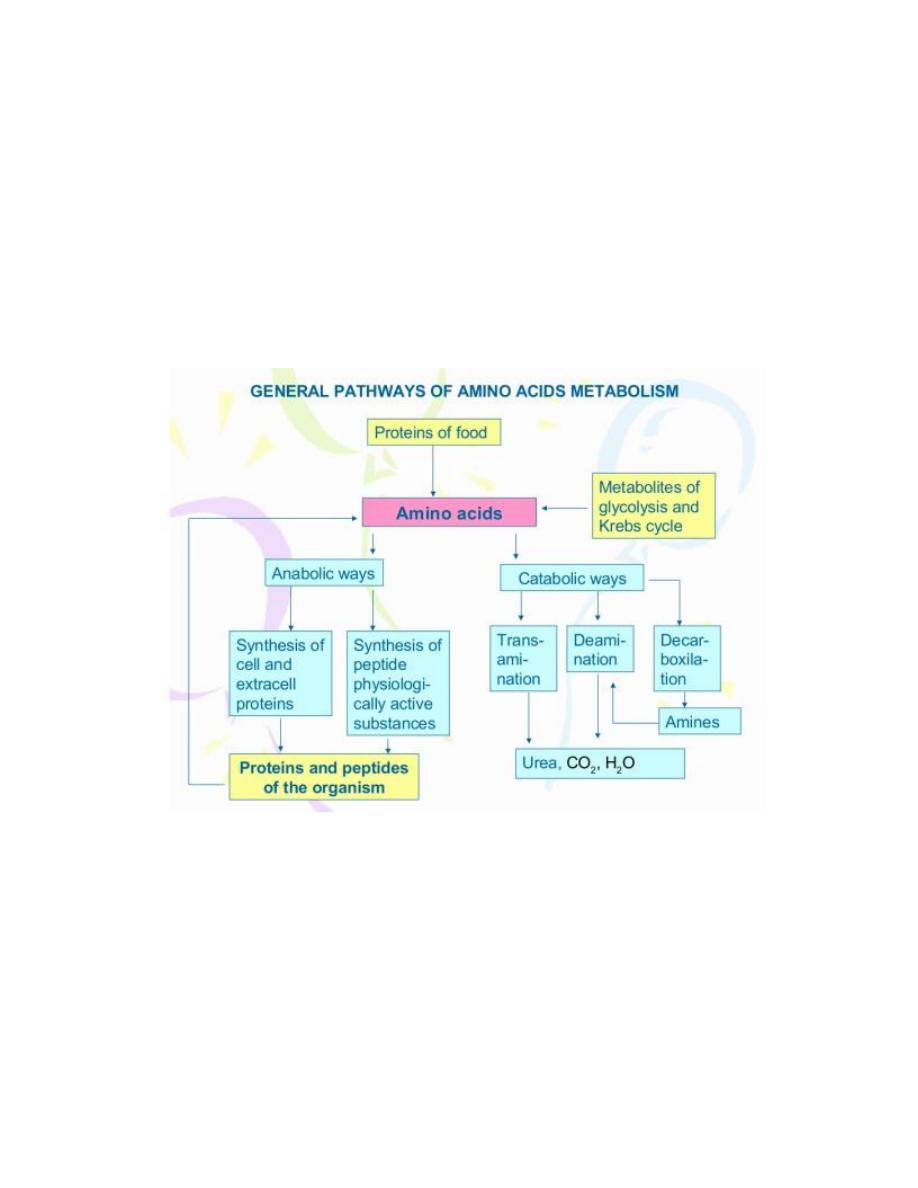
The general ways of amino acids degradation:
1. Deamination
- Elimination of amino group from amino acid with ammonia formation.
- Types of deamination:
i) Oxidative
ii) Reductive
iii) Hydrolytic
iv) Intramolecular
2. Transamination
3. Decarboxylation
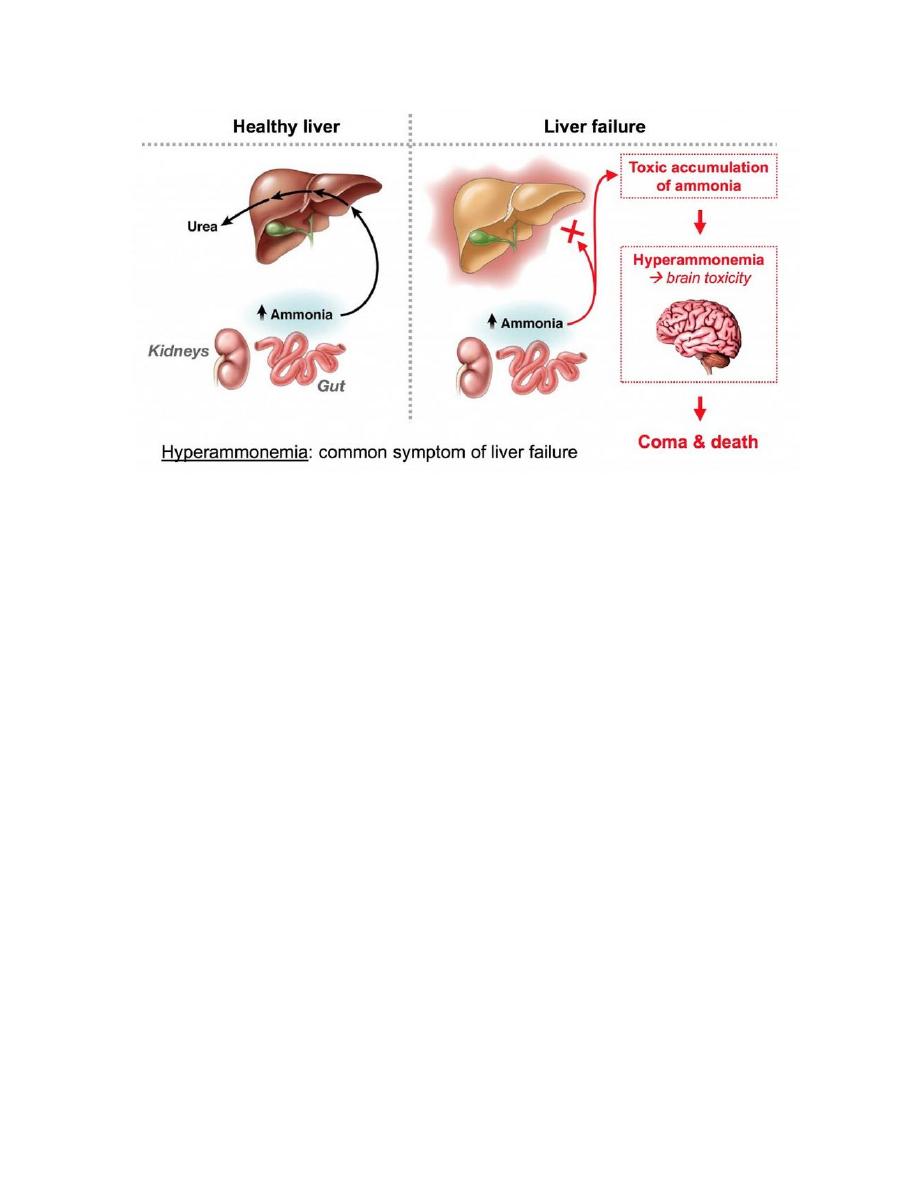
THE EFFECTS OF AMMONIA INTOXICATION:
The ammonia intoxication happens when blood containing ammonium rises because
of the capacity to detoxify it by the formation of glutamate and glutamine has been
exceeded. There also can occur in infants where some of their blood ammonium has
risen extreme high only can undergo the emergency treatment. Tryptophan is the
precursor of Serotonin, whereas the Serotonin act as the neurotransmitter. If the
quantity of Serotonin is excess so it will causes a state of hyper excitation.
At the end, the patient having symptoms of ammonia intoxication like blurring of
vision, tremor, slurring when she speech, convulsions, coma and even can cause a
death. The biochemical basis of this symptoms is depletion and hyper excitation due
to the excess of serotonin production and the decreasing of GABA synthesis.
Therefore, when a person have Cirrhosis of liver, the conversion of ammonia to urea
is impaired and it she might or will has hyperammonemia other than the liver
disorders blood and CSF Glutamine levels are increasing when she undergo a feature
diagnostic of hepatic encephalopathy.
CASE: DETOXIFICATION OF AMMONIA
A 60 year-old-woman suffers from cirrhosis of liver. Toxins such as ammonia are
not properly metabolized by the liver and can damage brain. Which of the following
compounds should be in highest concentration in brain as result of detoxification of
ammonia?
1. Alpha ketoglutarate
2. Glutamine
3. Glutamate
4. Gamma amino butyric acid
5. Asparagine
