Autacoids and anti-
inflammatory drugs
Dr. Hussain Addai Aljabery
M.B.Ch.B. M.Sc. ( Pharma.)
D.M.R.D. F.I.B.M.C ( Radiology)

Basic information
Inflammation is the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful
stimuli. Injury produces locally-acting substances that initiate inflammatory
response and activate the repair process. These substances are termed
'autacoids‘
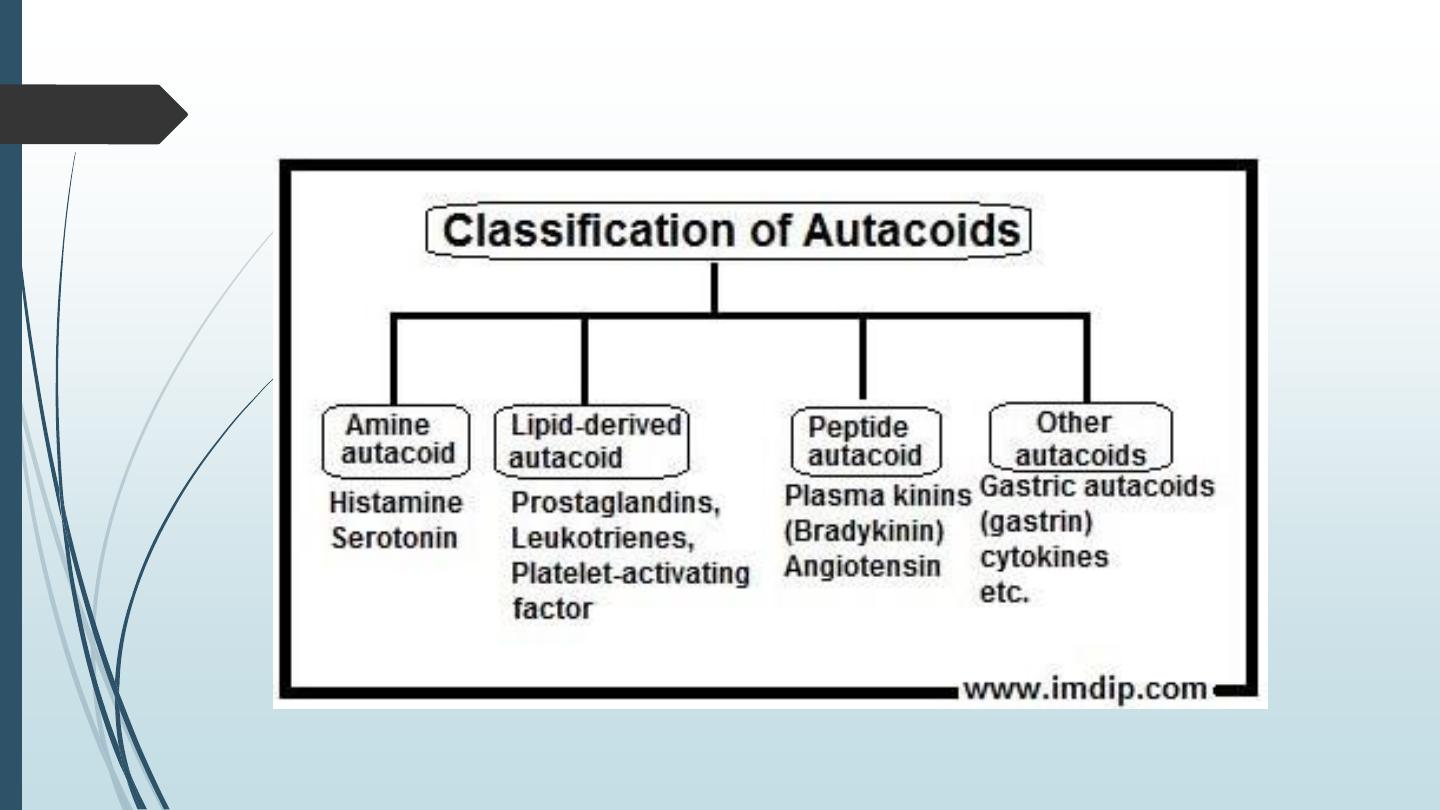
Examples of autacoids:
§ Amino acid derivative : e.g. histamine and 5-HT (serotonin).
§ Vasoactive peptides: e.g. angiotensin, kinins and endothelin's.
§ Fatty acid derivatives: e.g. prostaglandins, thromboxane's, leukotrienes, etc.
§ The family of cytokines: e.g. interleukins, interferones, TNF, growth factors, etc.
Histamine
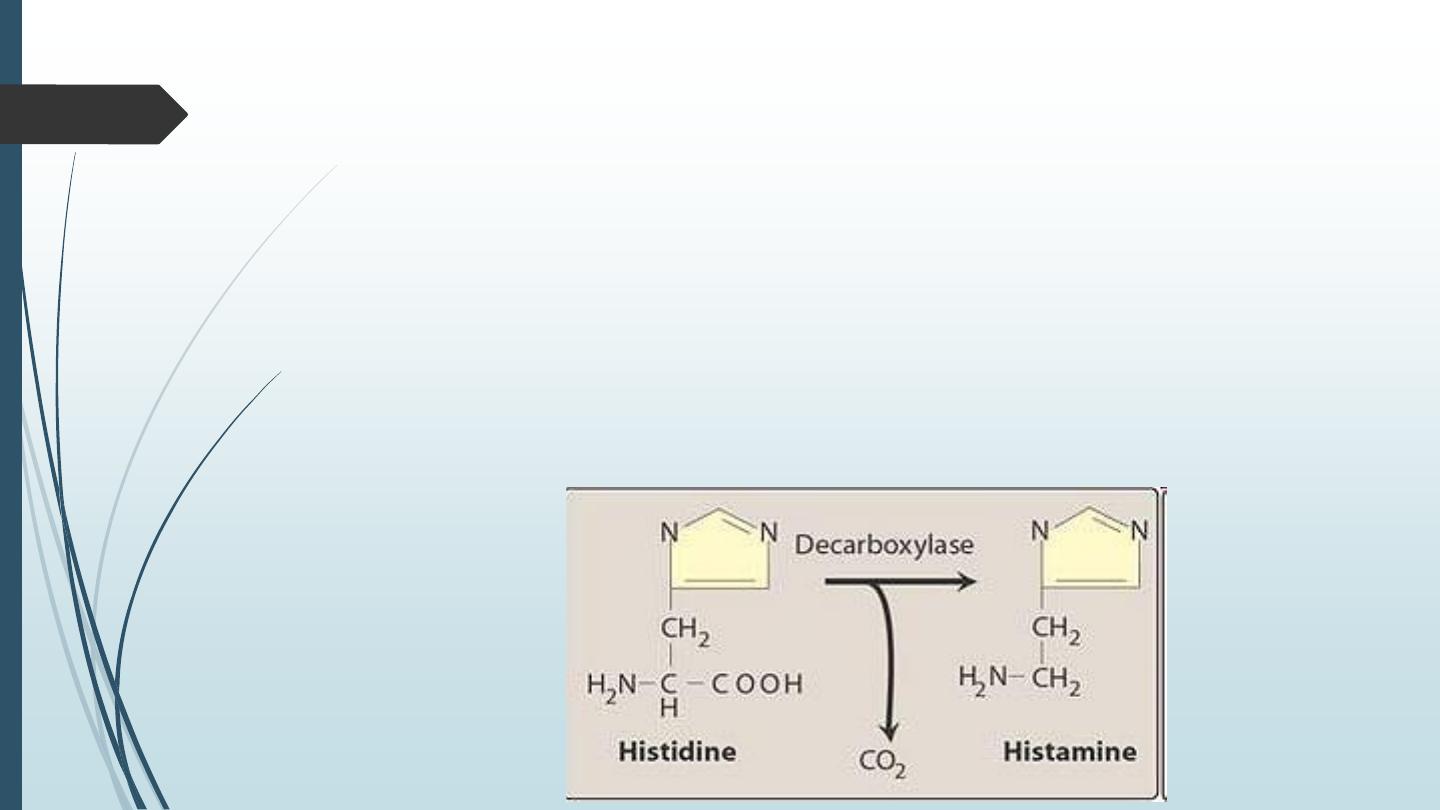
Histamine is formed from the amino acid histidine by the action of histidine
decarboxylase and stored mainly in mast cells. Non-mast cell Histamine is
found in several tissues including the brain.
§ No clinically useful drugs affect the synthesis or metabolism of histamine,
but certain drugs can cause release of histamine from mast cells as a side
effect.

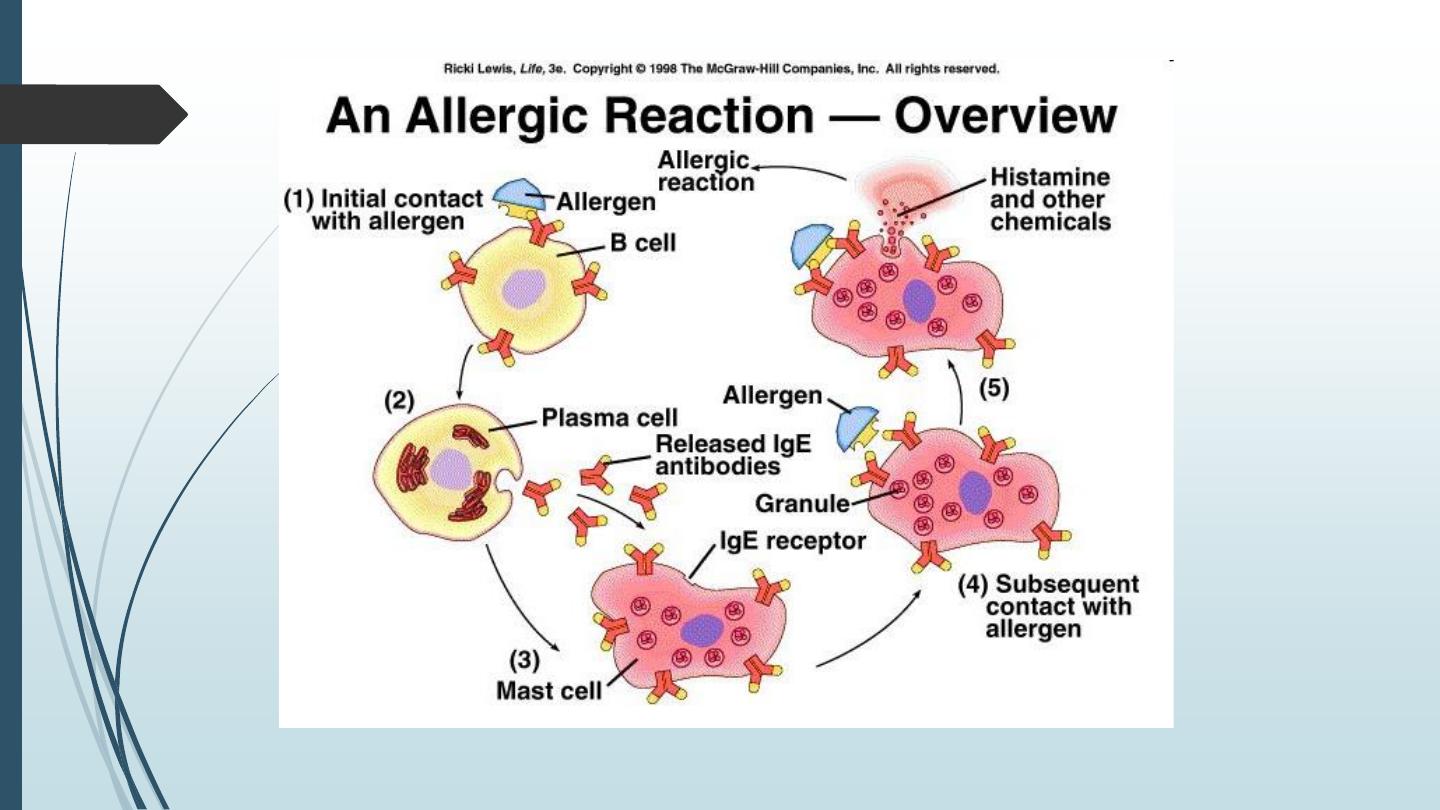
Histamine release:
can occur through 2 processes:
§ Ca2+ dependent mechanism: by fixation of Ig E to surface of mast cell with
subsequent activation of the complement, this causes Ca2+ influx and
degranulation of mast cells. Many drugs can induce this type e.g. penicillin.
§ Ca2+ independent mechanism:
– Displacement of histamine from storage granules by drugs: e.g. morphine,
tubocurarine, vancomycin, and amine antibiotics.
– Mast cell damage: by venom , or mechanical trauma.
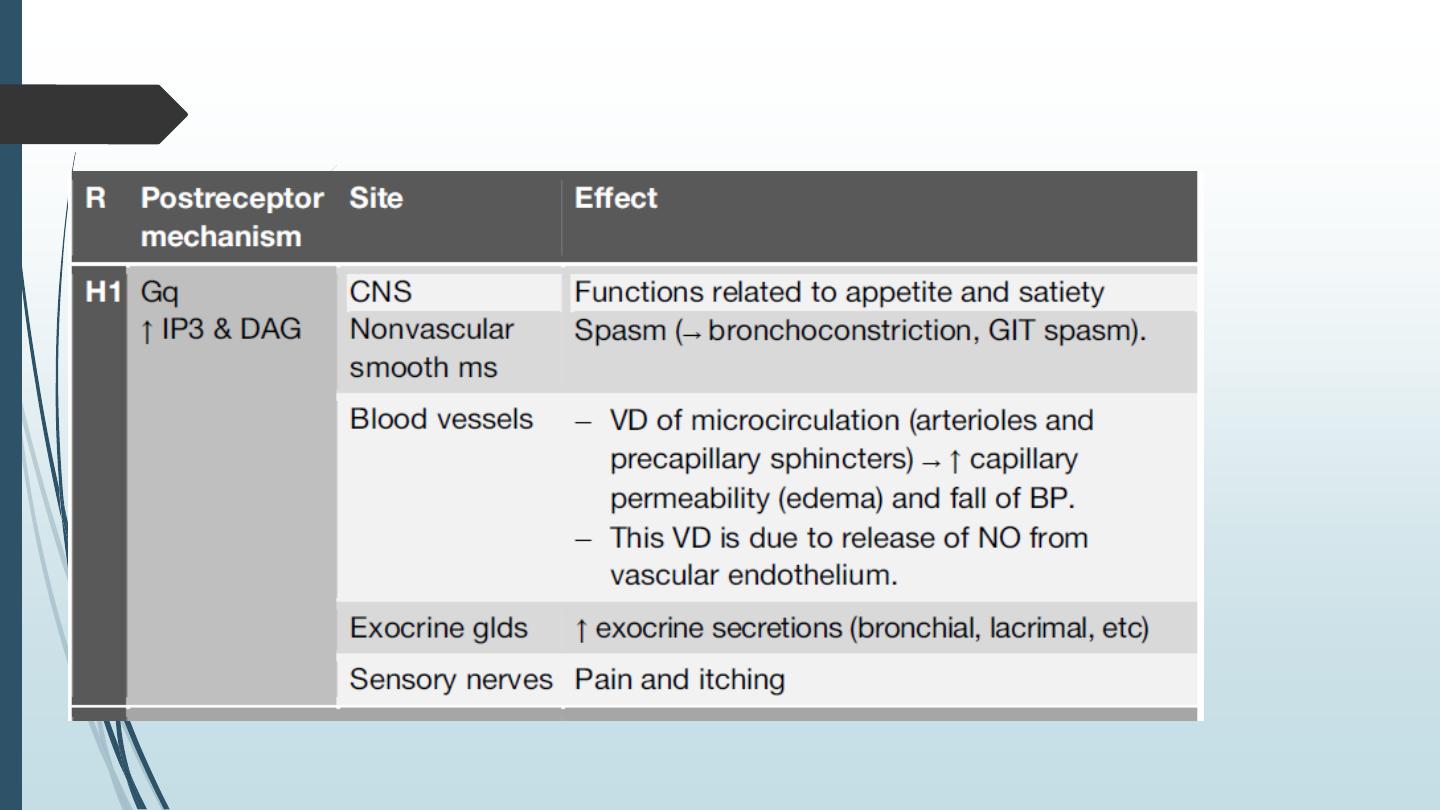
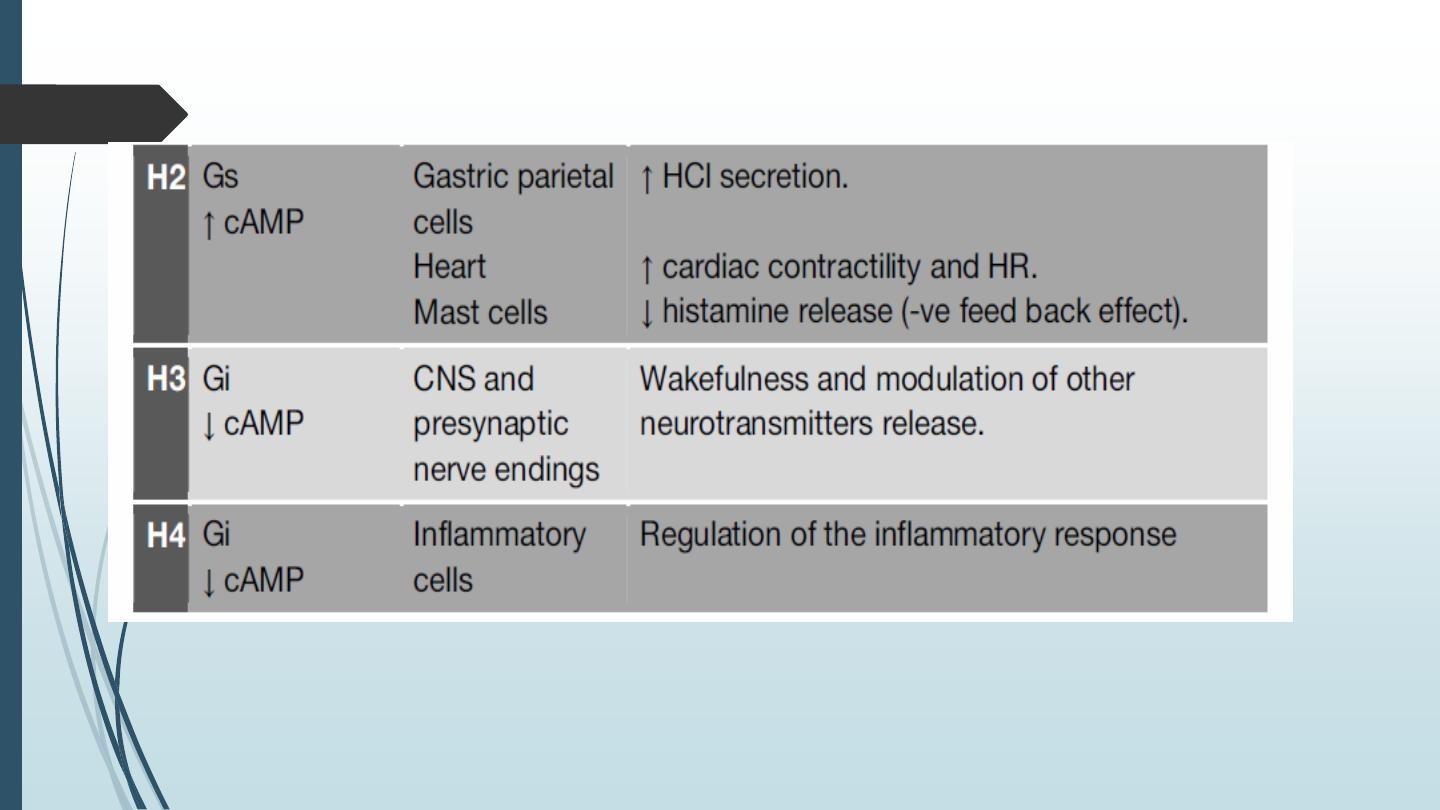
Pharmacological effects of histamine : Histamine acts on at least 4 types of receptors

Clinical uses of histamine
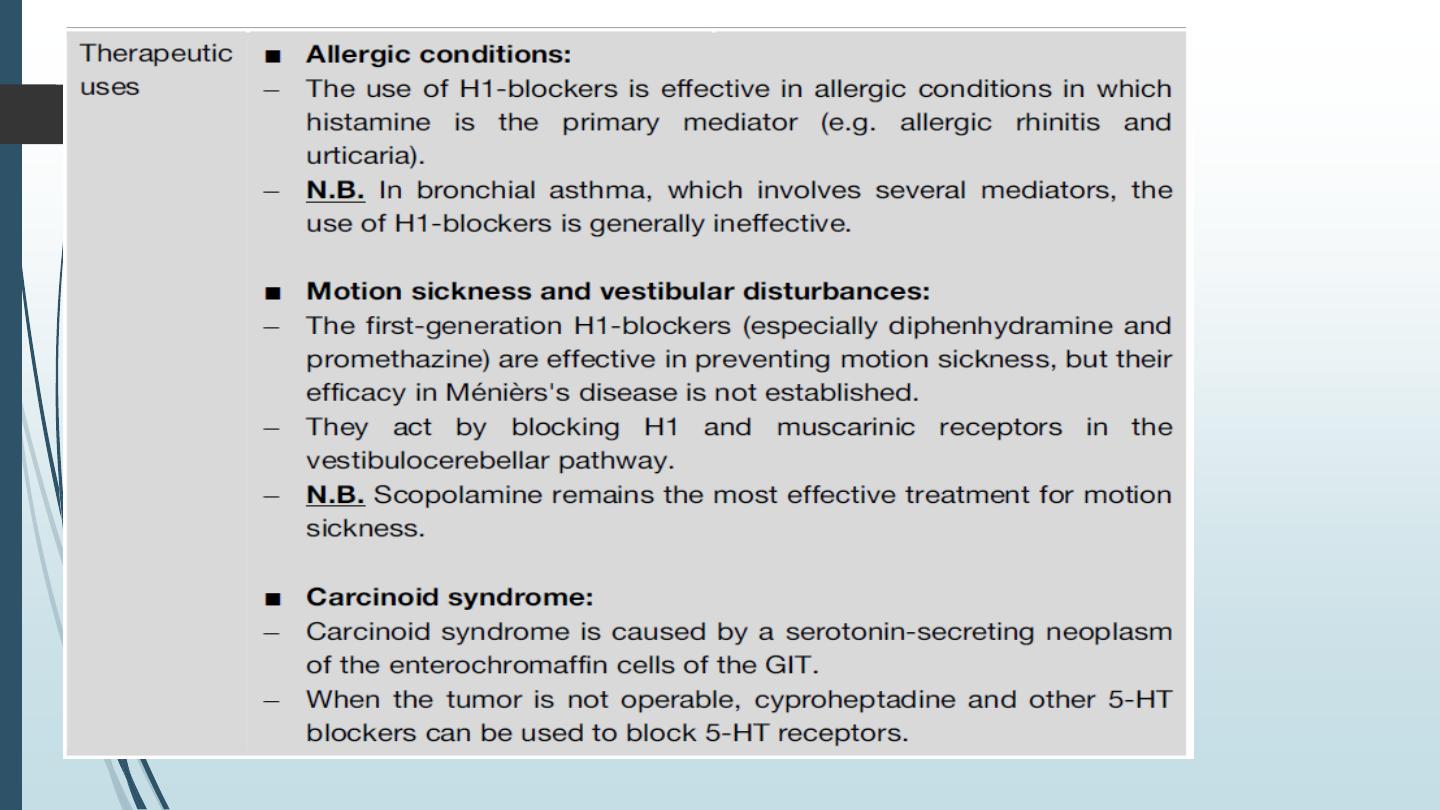
Histamine itself has no clinical applications.
Some selective agonists are available for diagnostic purposes only e.g. test
for gastric secretion.

Histamine antagonists
■ Physiological antagonists (adrenaline): adrenaline reverses all the effects of
histamine by action on different receptors (see ANS).
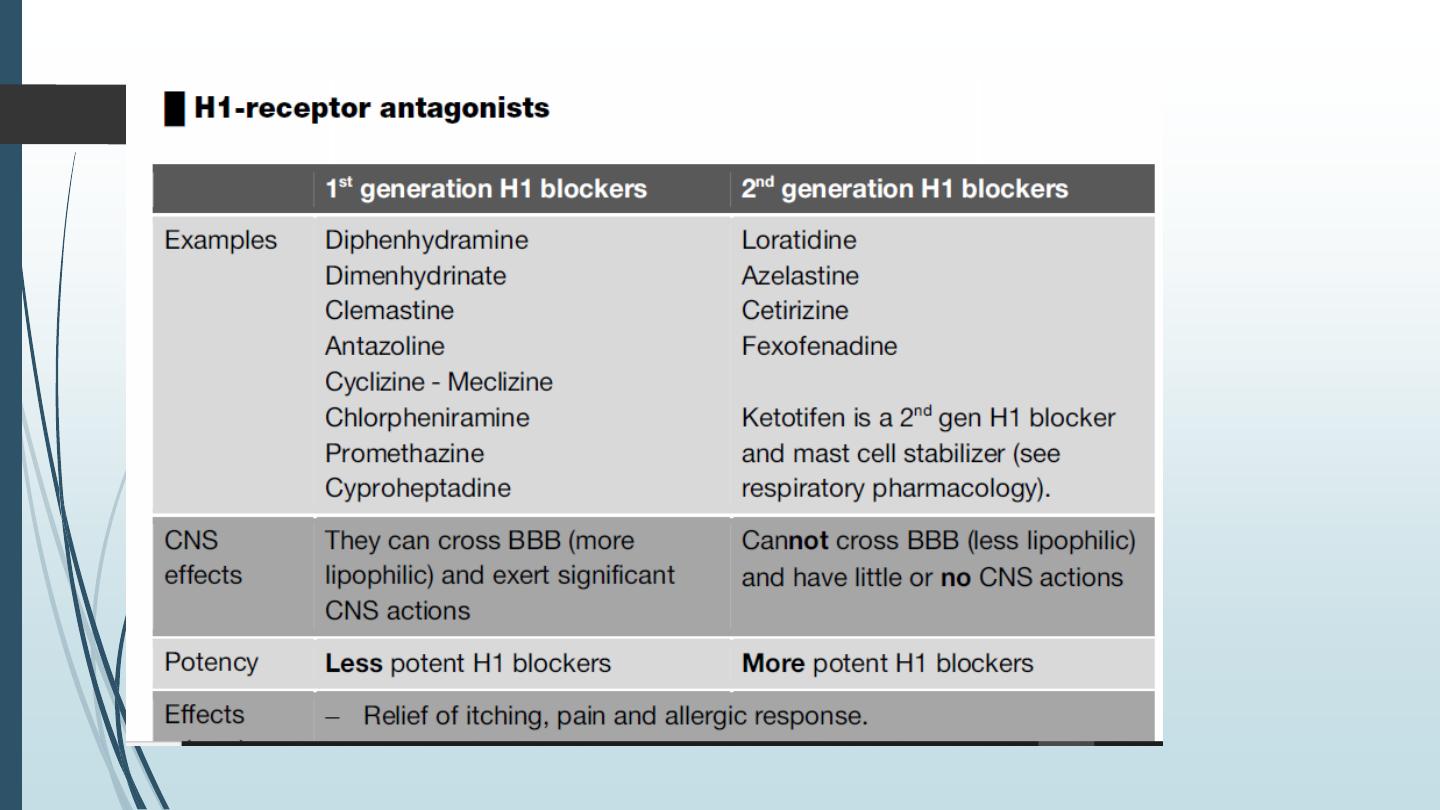
■ Histamine receptor antagonists:
– H1-blockers: e.g. diphenhydramine, loratidine, etc. (see below)
– H2-blockers: e.g. cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine, etc. (see GIT)
– H3 and H4 -blockers: are not yet available for clinical use.
■ Histamine release inhibitors (mast cell stabilizers): ketotifen and
cromoglycate
They inhibit Ca2+ influx into mast cells and prevent mast cell degranulation.

Desensitization therapy (immunotherapy):
Immunotherapy is a process in which an allergic patient can become
desensitized to antigens that trigger allergic responses. Small doses of the
allergic substance are injected weekly. Each week the dose is increased.
Gradually a protective antibody (IgG) is formed to block the allergic reaction.
Many patients notice an improvement within 6 months.



█ Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT)
5-HT is formed from the amino acid tryptophane and stored mainly in the
enterochromaffin tissue of the GIT (90%) and platelets (10%). Serotonin is found
also as a transmitter in many areas within the CNS. Like histamine, no clinically
useful drugs affect the synthesis or metabolism of 5-HT, but many drugs can
act on 5-HT receptors as agonists or antagonists.
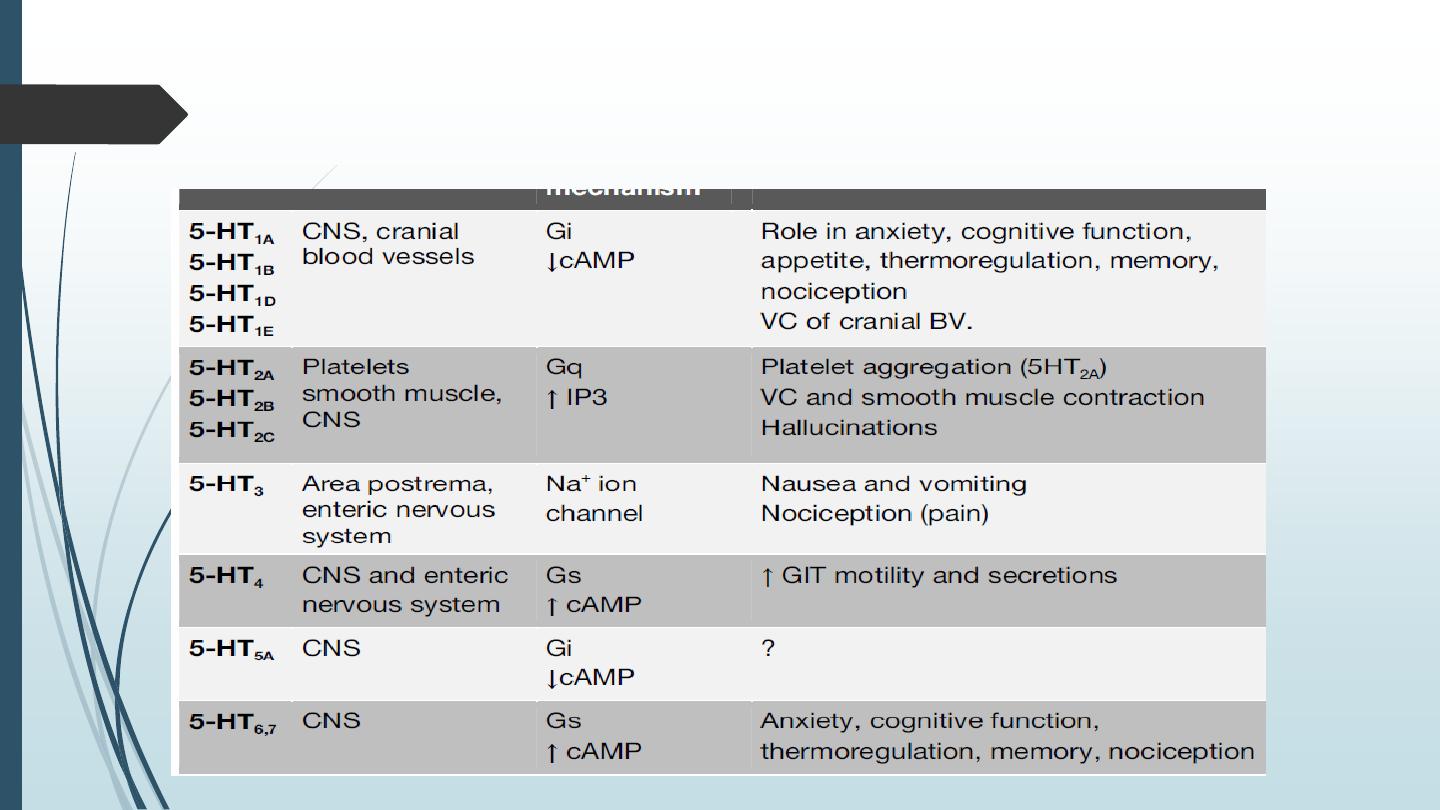
Pharmacological actions of 5-HT
5-HT acts on at least 7 types of receptors:

Some 5-HT agonist and antagonists in clinical
use
▌
5-HT agonists
■ Bupirone:
– It activates central 5-HT1A receptors. It is used for treatment of anxiety disorders especially in elderly patients.
– Therapeutic effect may take as long as 2 weeks to appear.
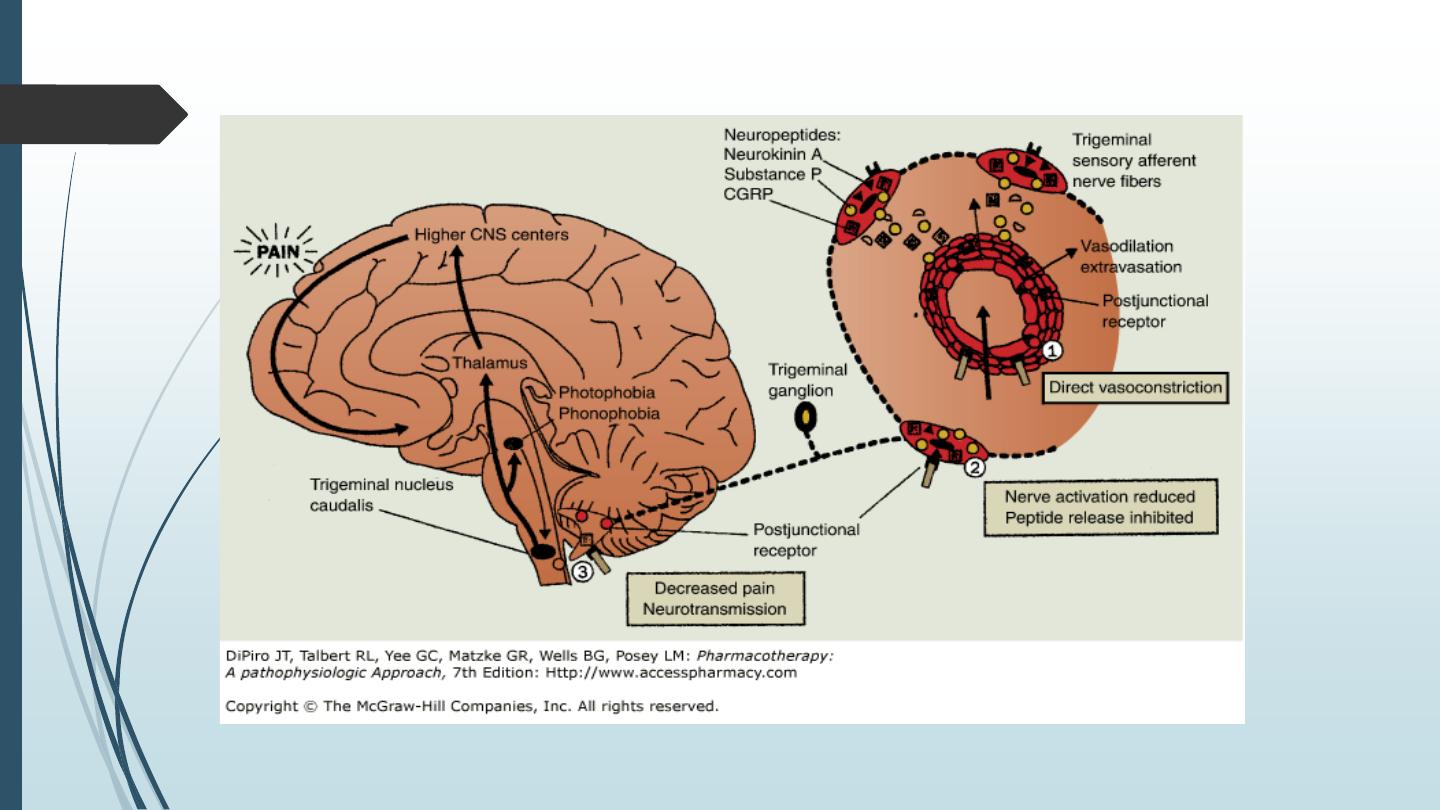
Triptans: sumatriptan, zolmitriptan, naratriptan
– They activate 5-HT1B/1D receptors.
– The major use of triptans is the treatment of acute migraine. Activation of 5-HT1D receptors inhibits inflammation of
meninges, pain transmission, and release of VD substances e.g. calcitonin gene-related peptide in trigeminal
neurons. Activation of 5-HT1B receptors causes VC of the dilated cerebral vessels. About 50%–80% of patients report relief
from pain within 2 hours.
– 5-HT1B activity can cause coronary spasm so; these drugs are contraindicated in patients with ischemic heart disease
(IHD).
Tegaserod: It is aspecific 5-HT4 agonist. It increases GIT motility of irritable bowel syndrome with constipation.

▌5-HT antagonists
■ Cyproheptadine:
– It is blocks 5-H 2, H1, & muscarinic receptors.
- it is used for treatment of symptoms of carcinoid tumor and as anti allergic.
■ Atypical antipsychotics: Olanzapine, risperidone
– They block 5-HT2A and dopamine D2 receptors CNS leading to improvement of
the negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
■ Ondansetron, granisetron:
– They selectively block 5-HT3 receptors centrally (CTZ) and peripherally (GIT).
– It is used for treatment of nausea & vomiting associated with cancer
chemotherapy.

█ Kinins (bradykinin)
§ Kinins are potent vasodilator peptides formed from protein substrates called kininogen
by the effect of kallikrein enzyme.
§ Kinins act on at least 2 subtypes of receptors: B1and B2. Activation of B2 receptors
causes VD and ↑ capillary permeability,
smooth ms contraction
(bronchoconstriction, GIT colic, etc.), and stimulation of sensory nerves causing pain.
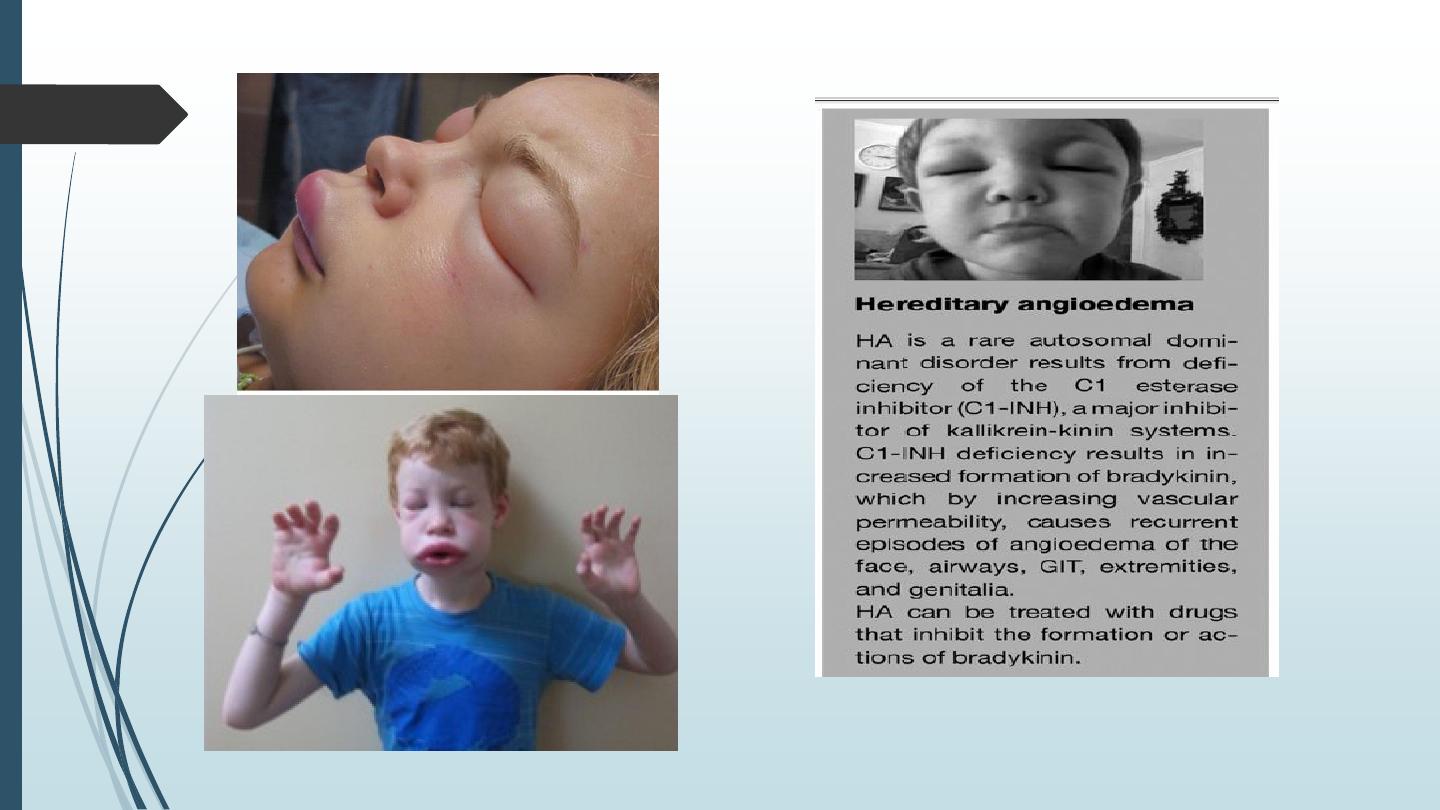
§ Icatibant is a 2nd genration decapeptide which acts as a selective antagonist at
bradykinin B2 receptors. It is given by s.c. injection for the symptomatic treatment of
acute attacks of hereditary angioedema. It may also be useful in drug-induced
angioedema, ascites, and pancreatitis.
§ Recently, a 3rd generation of orally active B2-receptor antagonists was eveloped
and currently under study

█ Endothelin
Endothelin is a vasoconstricting peptide produced by the endothelium.
There are 3 isoforms. Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is one of the strongest vasoconstrictors currently
studied.
Endothelins act on at least 2 subtypes of receptors: ETA and ETB.
§ Most of ET-1 effects are mediated through ETA receptors present in vascular smooth ms
and other tissues. Its activation leads to potent VC, vascular smooth ms proliferation, cardiac
hypertrophy, and elevation o blood pressure.
§ Increased production of ET-1 have been implicated in a variety of CVS diseases including
primary pulmonary hypertension, cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, atherosclerosis, and
coronary artery disease .
§ Boentan is orally active nonselective blocker of ETA and ETB receptors, while ambrisentan
is a selective ETA blocker. Both drugs are approved for treatment of pulmonary
hypertension.

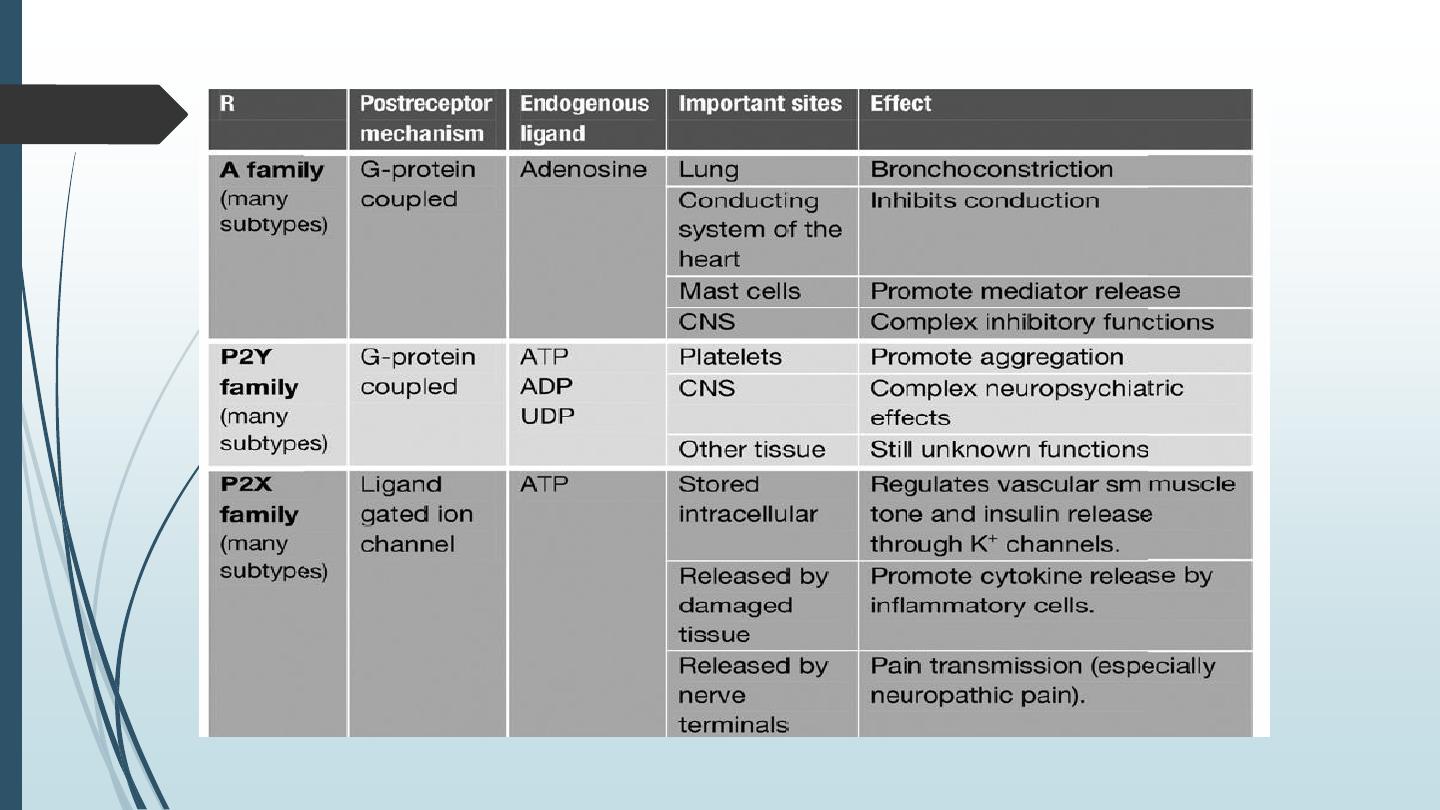
█ Purines as mediators
Nucleosides (adenosine) and nucleotides (AD and ATP) are extracellular
chemical mediators. ATP is stored in vesicles and released by exocytosis or
through tissue damage. Released ATP is rapidly converted to ADP and
adenosine. The three purine act on three main families of purine receptors
and exert a wide range of functions.

▌Drugs acting on purine receptors:
Adenosine
It is a short acting purine A receptor agonist. It is given by i.v. route to inhibit AV conduction
and converts supraventricular tachycardia to the sinus rhythm in non- asthmatic patients .
Methylxanthines
Caffeine, aminophylline and theophylline are purine A1 receptor antagonists. They are us d as
bronchodilators and CNS stimulants .
