By
Dr.Alaa Alsahlany
M.Sc. dermatology
Boston University
Nov. 11, 2021

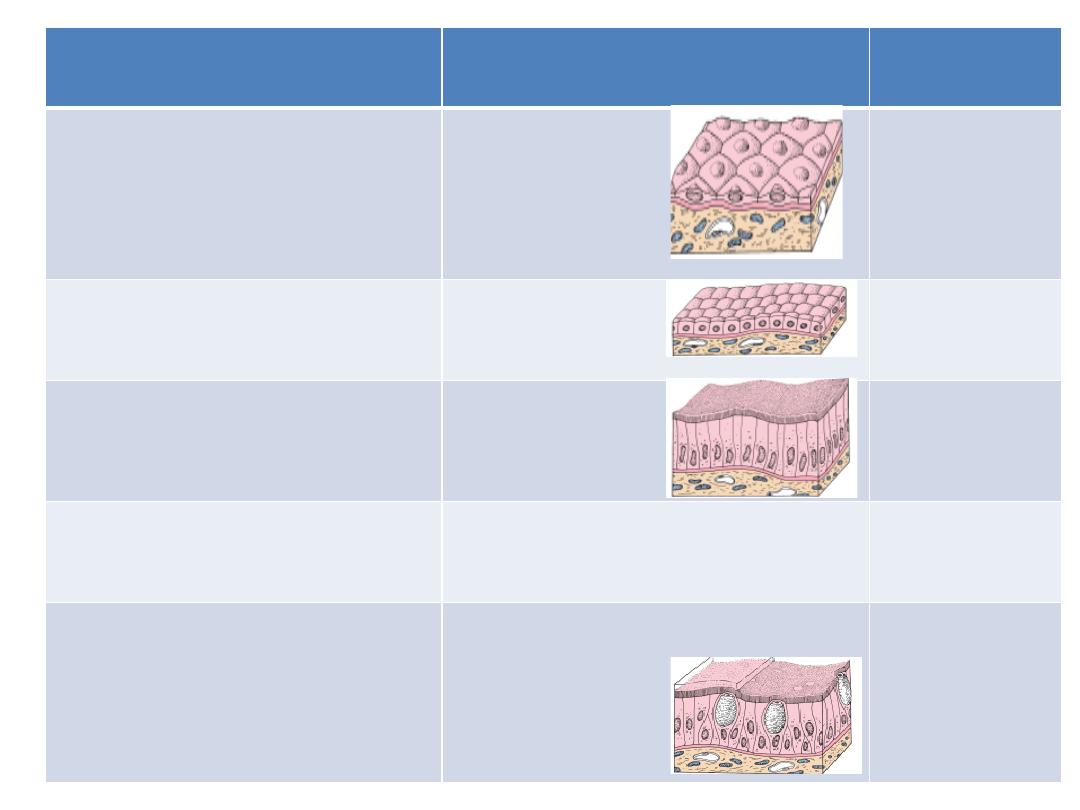
Classification of epithelium
Example
Based on cell shape
Based on cell layer
Endothelim (
lining of
blood vessels)
S. Squamous
(1) SIMPLE (S.)
One layer
Thyroid
follicles
S. Cuboidal
Stomach,
Intestine
S. Columnar
(non-ciliated)
Uterine tube
S. Columnar (ciliated)
Trachea
Pseudostratified columnar
(2) PSEUDOSTRATIFIED
(They appear stratified but in
fact they are simple)
Example
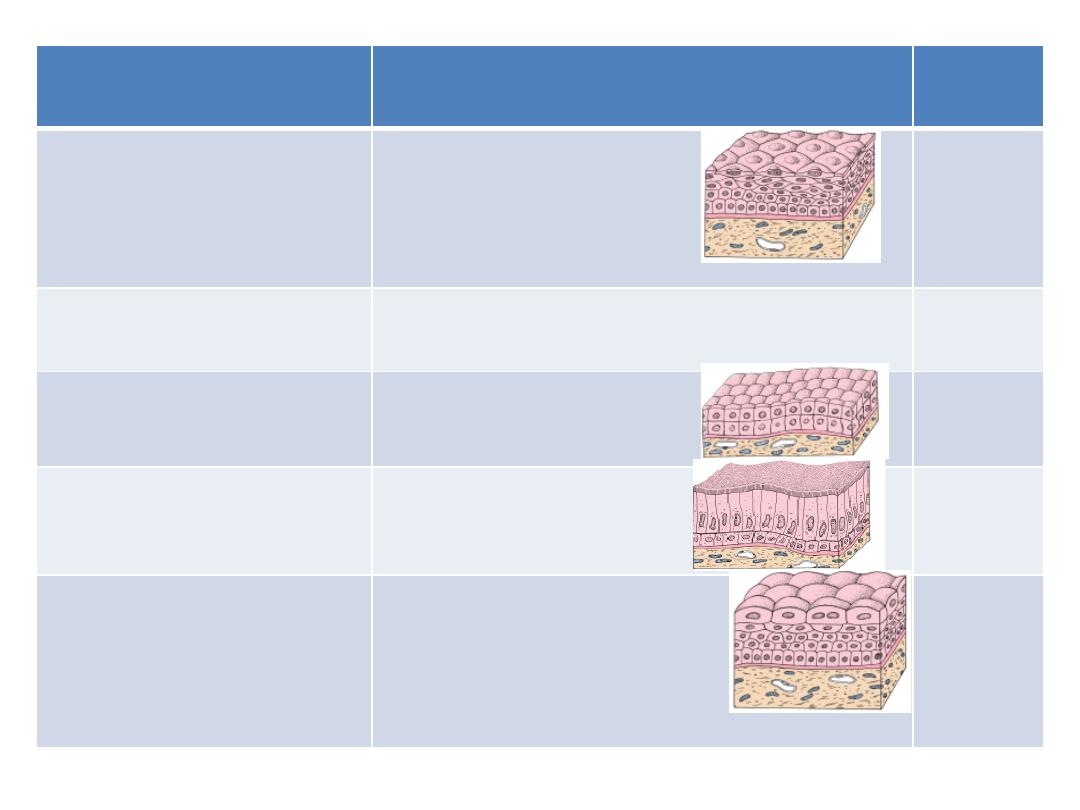
Based on cell shape
Based on cell layer
Mouth
cavity
Str. Squamous
Non-keratinized
(3) STRATIFIED (Str.)
More than one layer
Skin
Str. Squamous
Keratinized
Sweat
ducts
Str. Cuboidal
conjuncti
va
Str. Columnar
Urinary
bladder
Transitional (stratified
epithelium
with
characteristics that allow
it to Distend)

Cell death
(1) Necrosis
(2) Apoptosis

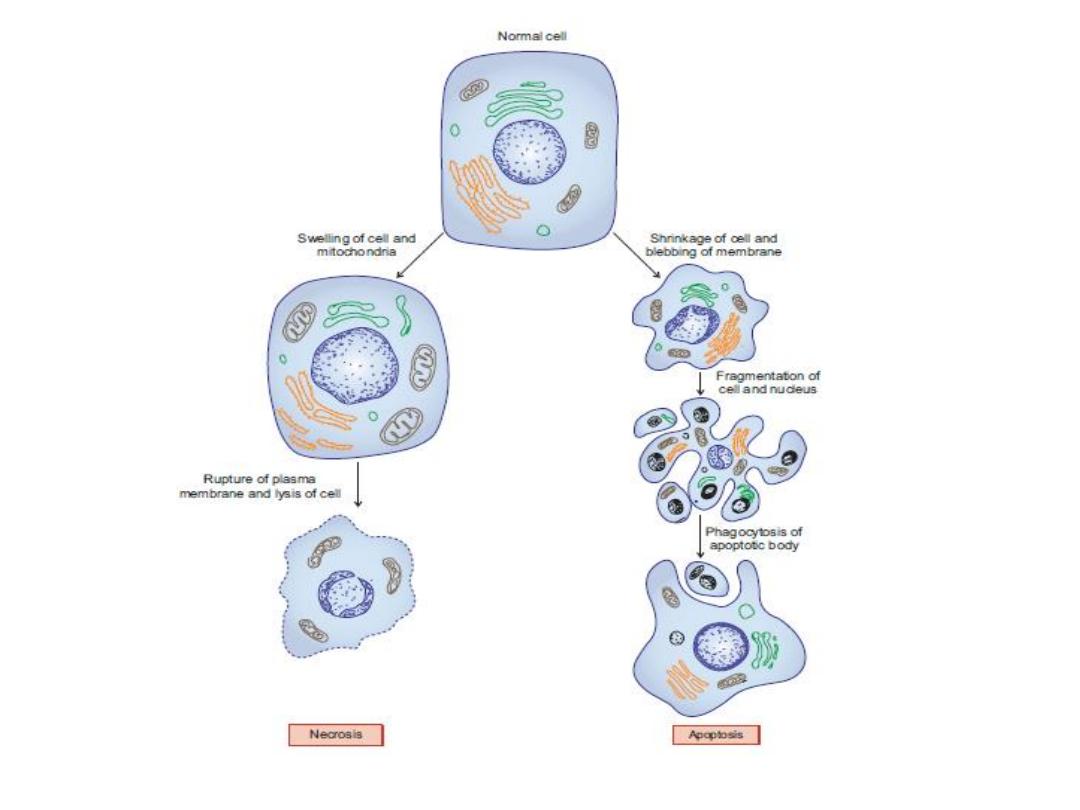
Necrosis

Death of the cells due to tissue injury
Necrotic cells swell and subsequently rupture
resulting in formation of cell debris.
This induces an
inflammatory response
at the site
of injury
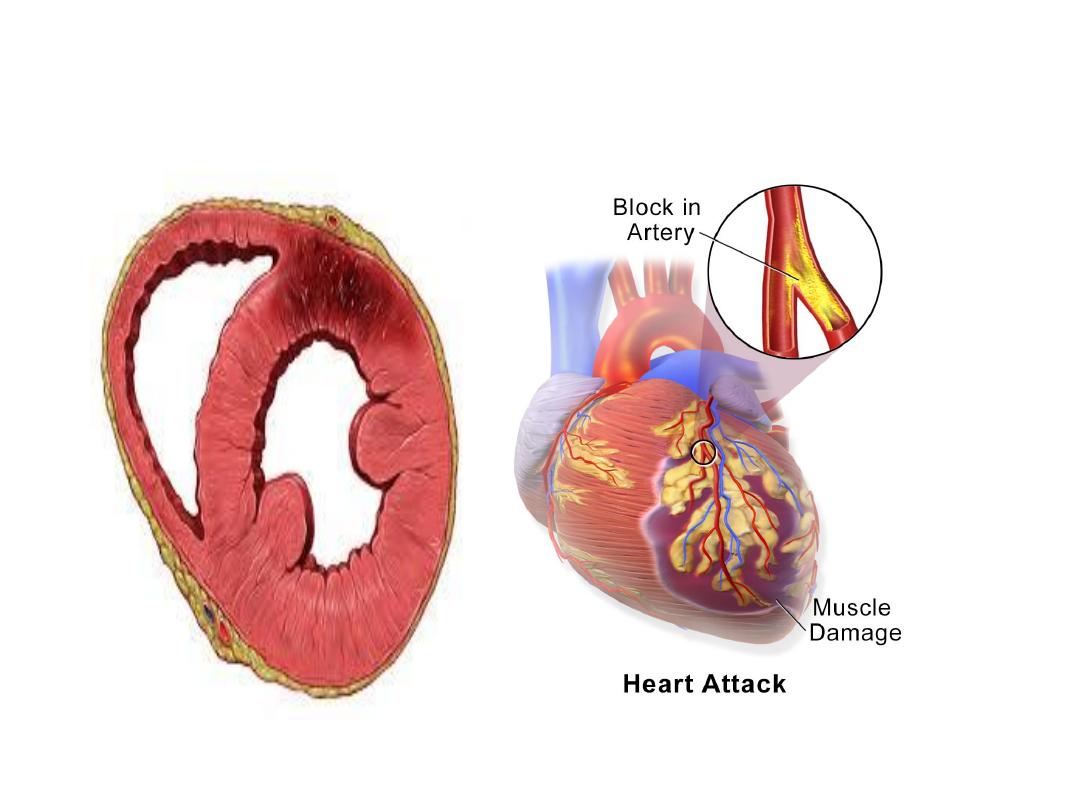
Necrosis of myocardium due to
ischemia

Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death
or Regulated Cell Suicide)

Apoptotic cells shrink.
Their plasma membranes undergo blebbing
without any loss (i.e. they are intact).
Their nuclei fragment forming apoptotic bodies.
Since the plasma membrane is intact, their
intracellular contents are not released into the
extracellular environment, so
no inflammation

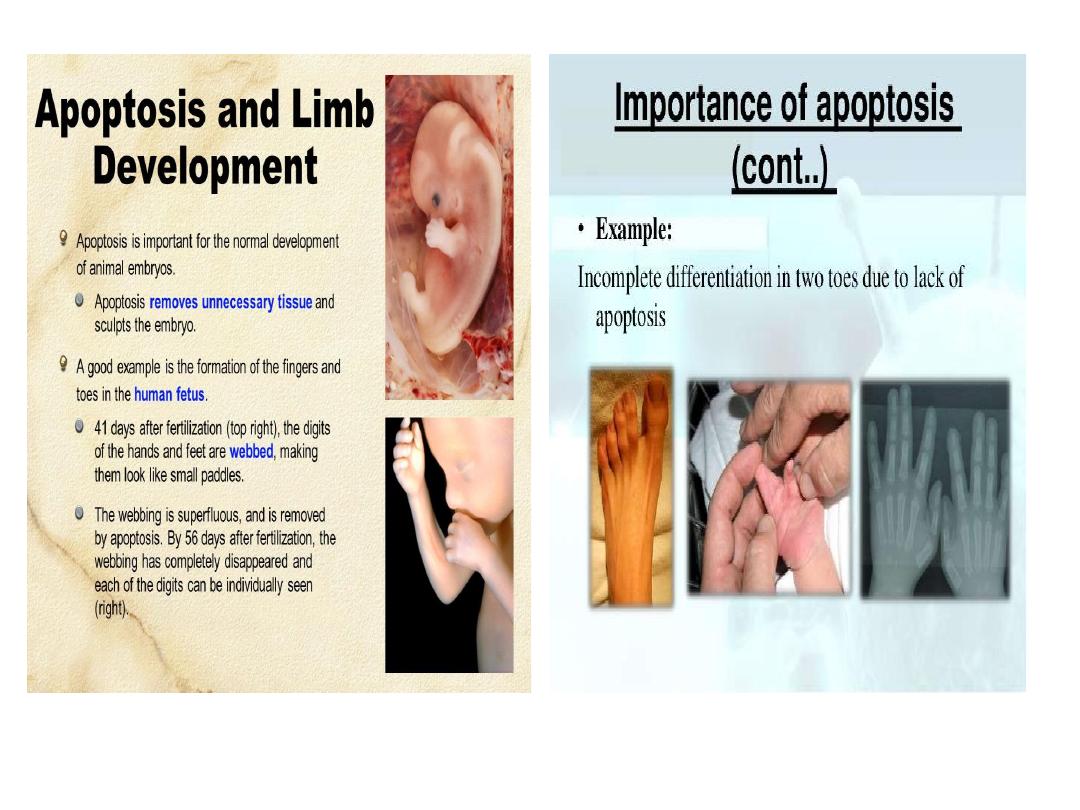
Apoptosis is a central mechanism controlling
development in regulating the number of cells
that mediate a particular activity (e.g. separation
of the developing fingers and toes during
embryogenesis).

Adipose tissue

General Features
A special type of connective tissue formed by
aggregation of fat cells (adipocytes). It constitutes
15–20% of body weight in men and 20–25% in
women.
Two types
(1)Parietal : It is found subcutaneously (under the
skin) throughout the body
(2)Visceral: around viscera

Function
(1) Is a reservoir of energy.
(2) Gives shape to the body
(3) Gives thermal insulation to the body
because it is a bad conductor of heat

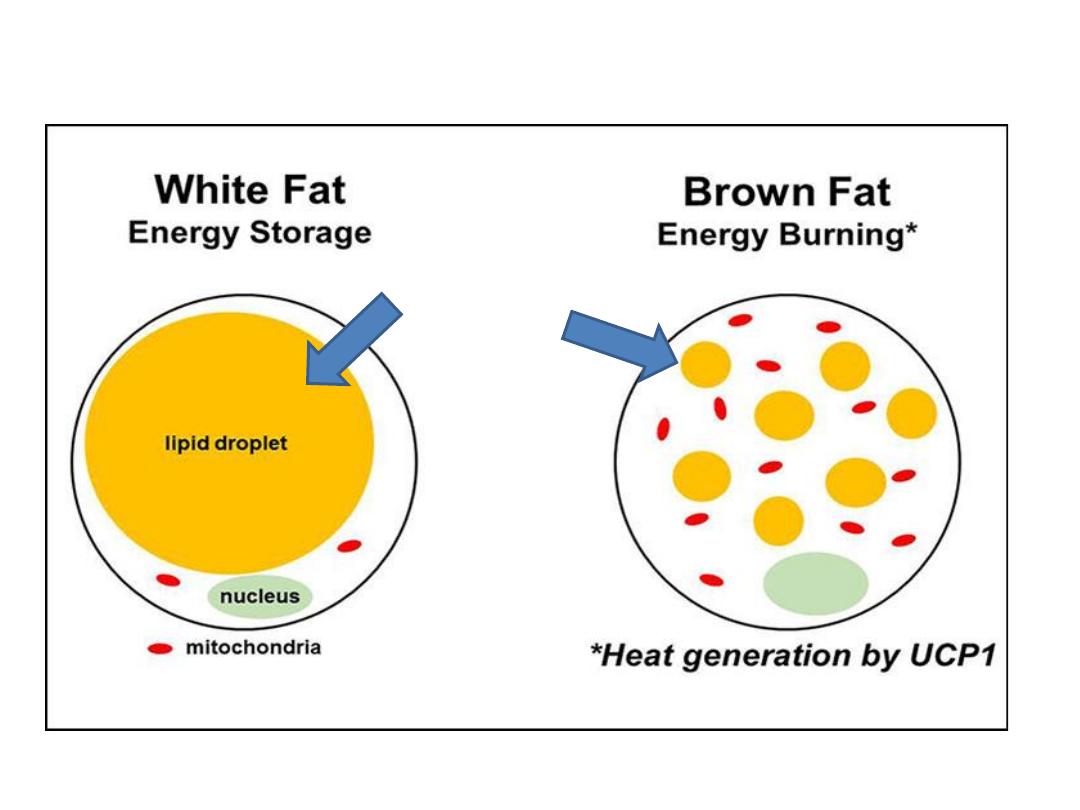
Histological types of fat
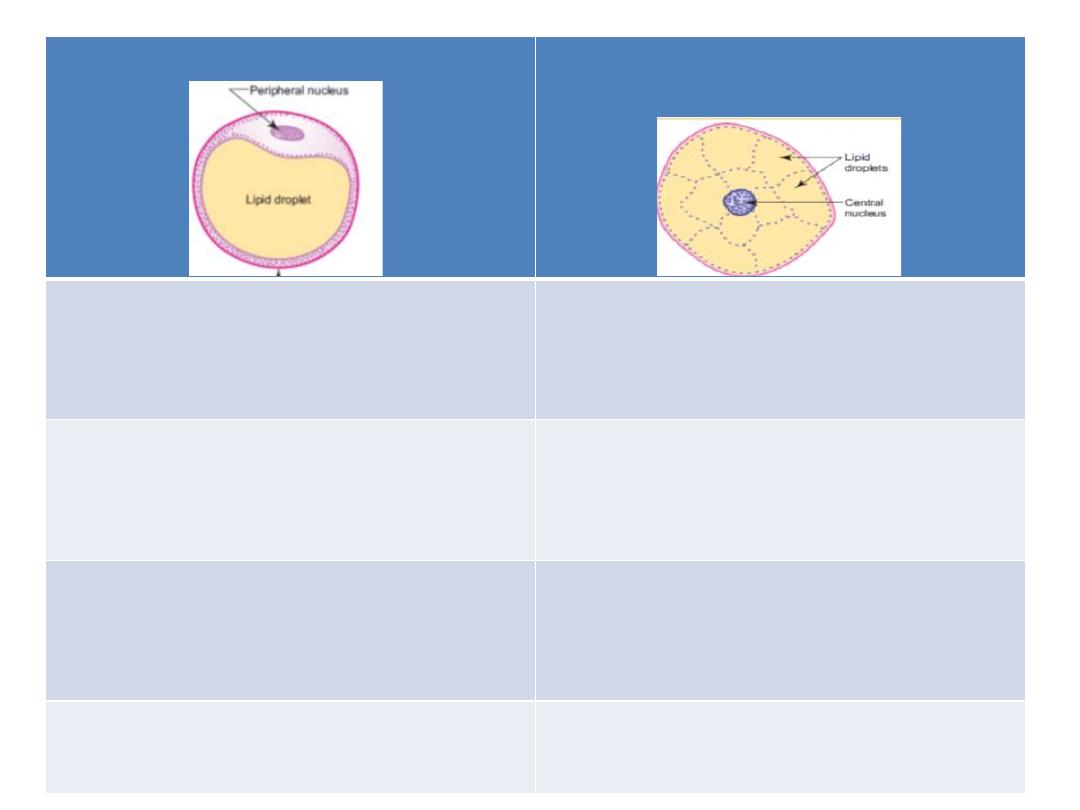
Brown adipose tissue(embryonic
type)
Yellow adipose tissue(adult type)
Multilocular (contain many lipid
droplets)
Unilocular (contain single lipid
droplet)
Small polygonal with central nucleus
Big round with peripheral nucleus
Found in fetus and newborn
Found in adult
Production of heat that protect the
fetus against cold
Store house of energy
Lipid droplets

Abnormal fat
Obesity
Lipodystrophy

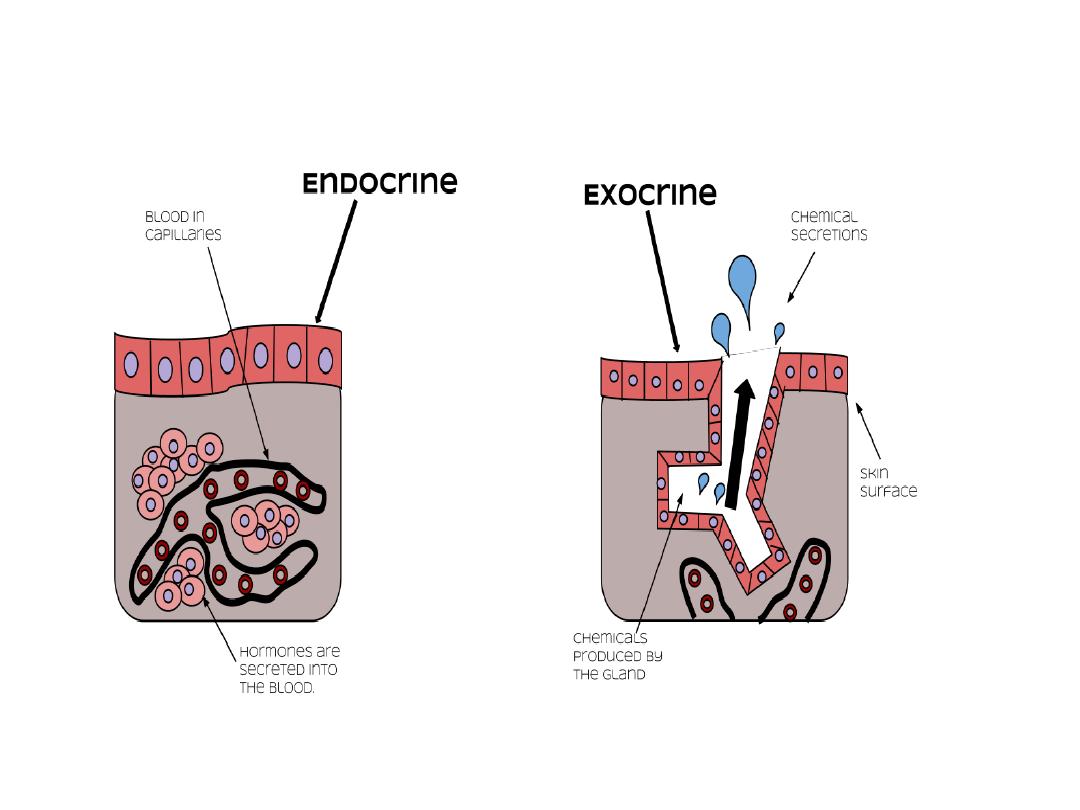
Glands
Exocrine glands secrete their products onto a
surface directly or through ducts that are
connected to a surface e.g. sweat glands
Endocrine glands lack a duct system. They secrete
their products into the connective tissue, from
which the products enter the bloodstream to
reach their target cells. They produce hormones
e.g. thyroid