Introduction intoHistology
By Dr.Alaa Al-sahlanyM.Sc. DermatologyBoston, USANov. 08, 2021Tissues are groups of cells organized to perform one or more specific functions
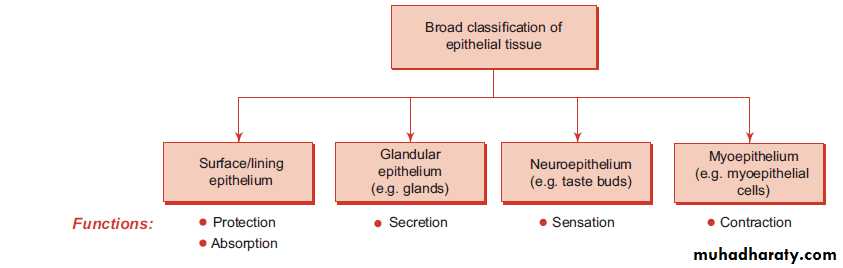
There are four basic types of tissue:Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body cavities, and forms glands.
Muscle tissue is made up of contractile cells and is responsible for movement
Nerve tissue receives, transmits information to control the activities of the bodyConnective tissue underlies or supports the other three basic tissues
Epithelial tissueEpithelium covers body surfaces, lines body cavities, and constitutes glands
The cells that make up epithelium have three principal characteristics:
(1)They adhere to one another by cell junctions
(2)They exhibit polarity: apical polarity, a lateral polarity, and a basal polarity.(3) Their basal surface is attached to an underlying basement membrane
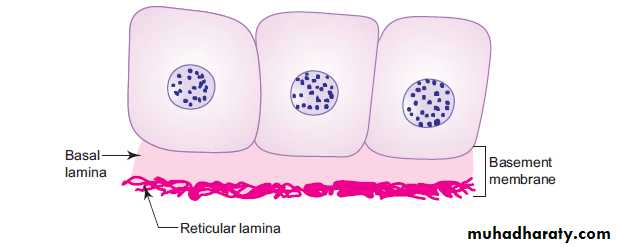
Basement membraneIs a specialized structure located next to the basal part of epithelial cells and the underlying connective tissue stroma.
Composed of:
(a) basal lamina (amorphous substance) – product of epithelium(b) reticular lamina
(reticular fibres) –product of connective tissue.
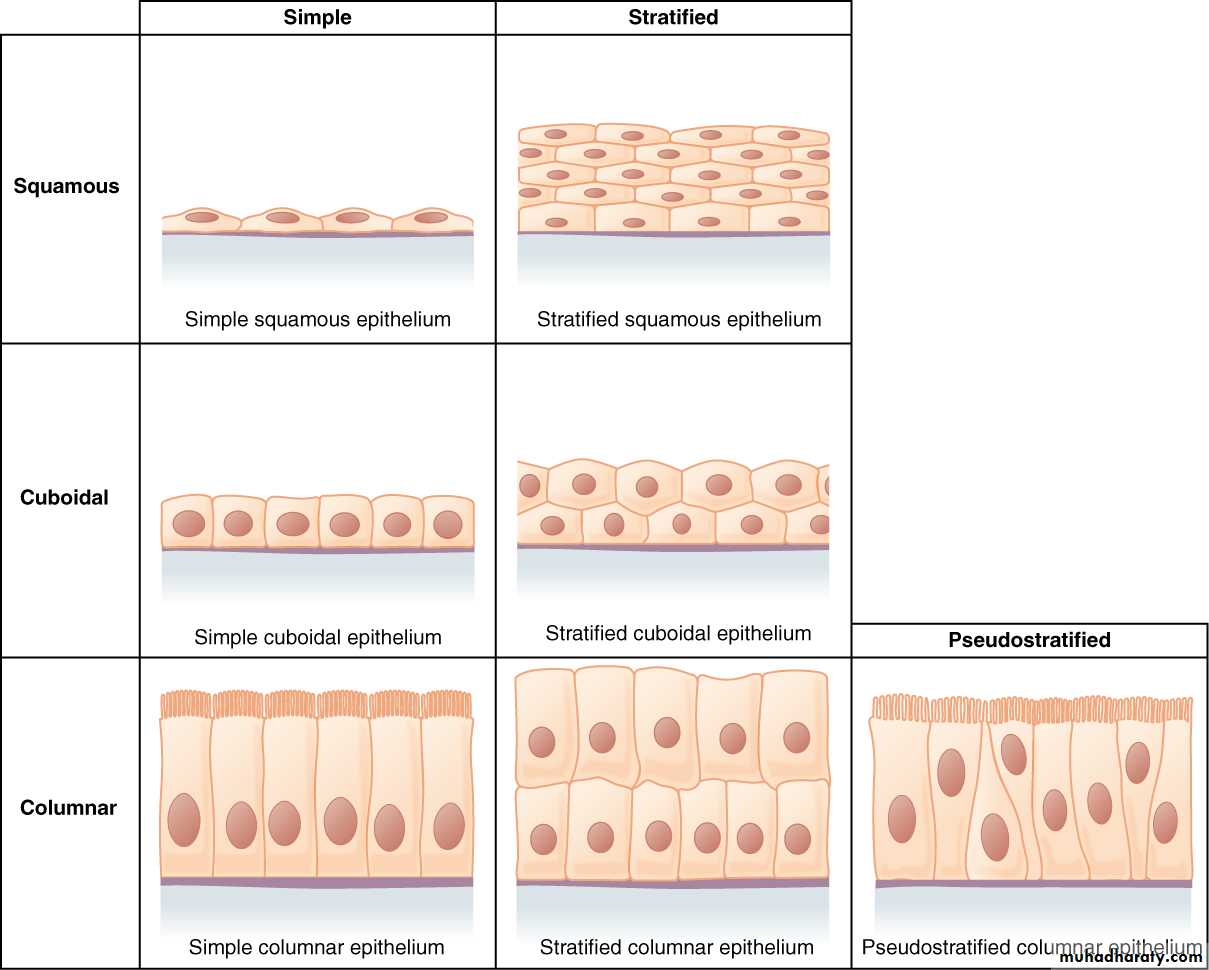
Epithelium is made of either single layer(simple) or many layers of cells(stratified).
Epithelial cells are adherent to each other by means of intercellular junctions(junctional complexes) .The deep surface (basal) of the epithelium rests on a basement membrane, which separates it from the vascular connective tissue.
No blood vessels nor lymphatics are found in the epithelium; nourishment is provided by diffusion from the adjacent supporting connective tissues.
Epithelium has good regenerative capacity.
Its nuclear shape corresponds to cell shape (nuclei are oval in columnar cells, round in cuboidal , and flat in squamous cells).Epithelium can invaginate and subsequently grows into glands.
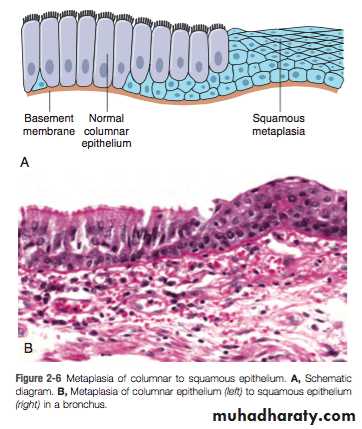
Epithelium may undergo morphological and functional changes from one type to another type(metaplasia)
Epithelium is derived from all three germ layers:
Skin – ectodermRespiratory and digestive systems – endoderm Cardiovascular system – mesoderm
Metaplasia
Smoking cause chronic irritation of respiratory epithelium and consequently cause metaplasia
The superficial surface (apical) of the epithelium is free and exposed to air or fluid and often shows modifications (i.e. presence of microvilli or cilia) depending upon the function it is destined to perform
Surface modifications are listed in the next table
• Functions• Surface modifications
• Surface coat over the absorptive epithelium of small intestine( rich in polysaccharides and hydrolytic enzymes) .
• Acts as receptor sites for hormones and enzymes .
• 1. Glycocalyx (cell coat)
• minute finger-like projections of the cell membrane
• Increase the surface area for absorption (intestine)
• 2.Microvilli (brush border)
• Very long, thick microvilli, non-motile,
• Increase the surface area (inner ear)
• 3. Stereocilia
• long hair-like projections of cell membrane
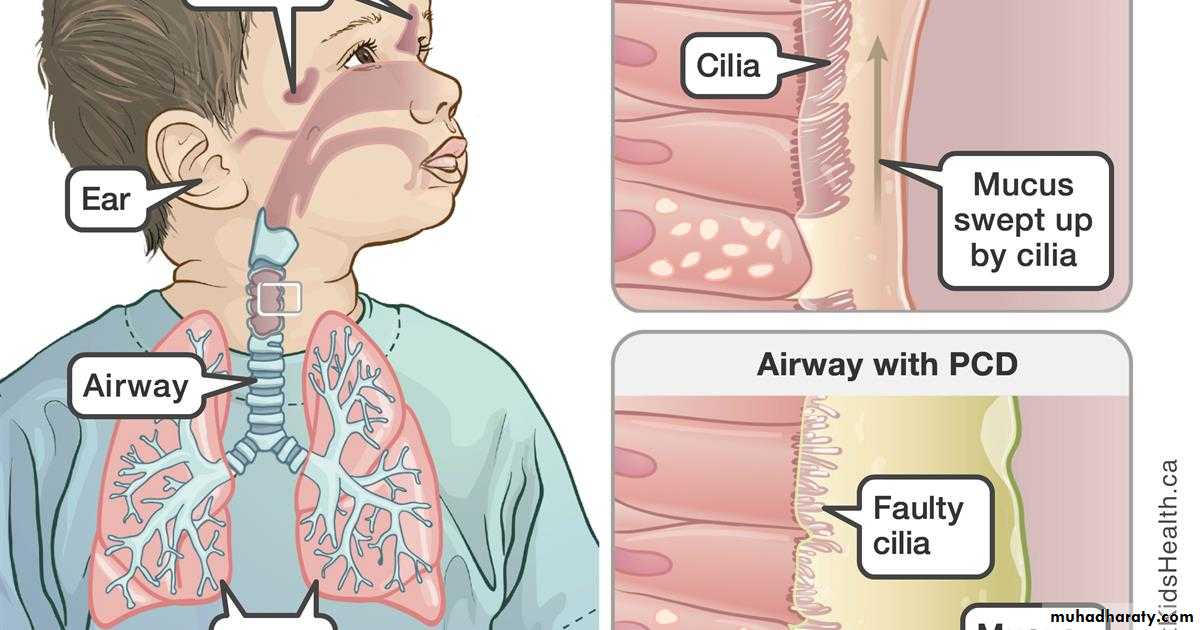
• Move towards one direction, thereby moving the entangled particles (beat towards pharynx in respiratory tract and towards uterus in uterine tube)
• 4. Cilia
Cilia
Microvilli
MotileNon-motile
Motility
Composed of microtubules
Composed of microfilament
Composition
Moving the particles in one direction
Absorption
Function
Respiratory tract
Uterine tube
Intestinal epithelium
Kidney
Example
Primary ciliary dyskinesiaNot included in the exam
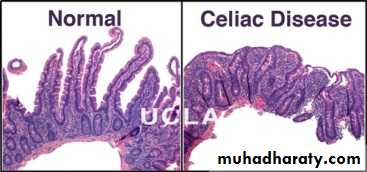
Celiac diseaseGluten sensitivity
Atrophy of microvilli cause decreased intestinal
absorption and chronic diarrheaNot included in the exam
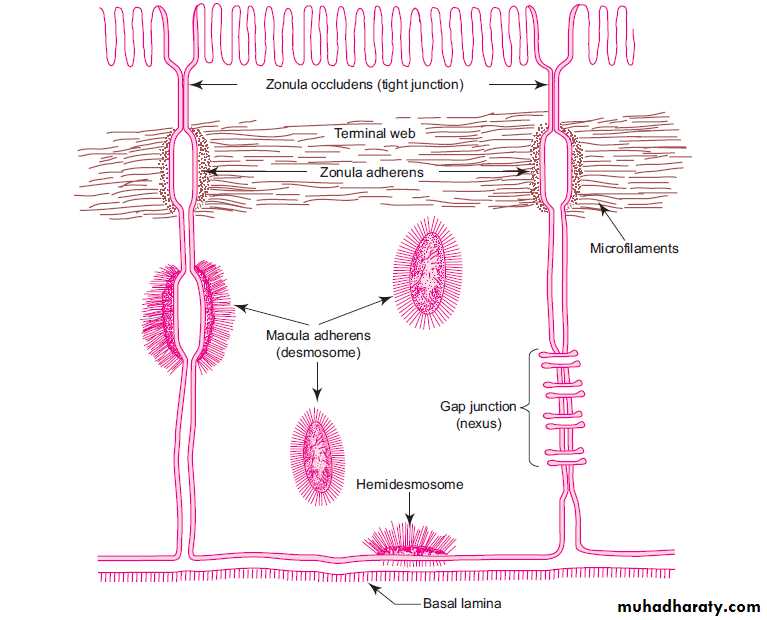
INTERCELLULAR JUNCTIONS (JUNCTIONAL COMPLEXES)
FunctionType of junction
Name of junction
Seals adjacent cells together
Occluding junction between cells
Zonula occludens (tight junction)
Couple microfilaments to basement membrane at site of cell-cell adhesion
Anchoring junction between cells
Zonula adherens
Function
Type of junctionName of junction
• Couple the intermediate filaments to basement membrane at site of cell-cell adhesion
• Anchoring junction between cells
• Macula adherens (desmosomes)Create a conduct for passage of ions and molecules between adjacent cells
Communicating junction between cellsGap junction(nexus)