
ThiQar college of Medicine
Family & Community medicine dept
.
Biostatistics Practical
Third stage
by: Dr. Muslim N. Saeed
October 31
st
,2021

Presentation of Data
Mathematical Presentation of Data
Measures of Dispersion

3
Quintiles, Centiles & Quartiles
A quintile is a value below which a certain
proportion of observations occurred in the ordered
set of data values.
A centiles are values, in a series of observations,
arranged in ascending order of magnitude, which
divide the distribution into 100 equal parts
(10th
Percentile,
3rd,
97th,
and
the
50th
(median)
percentile).

4
Quintiles, Centiles & Quartiles
Quartiles are the observations in an array that divide
the distribution into four equal parts.
lower Quartile: the value below which 25% of
observations lie in an ordered array
2nd quartile = Median = 50th percentile
Upper Quartile = 75th percentile
Inter-quartile Range: is the middle 50% of all
observations

Distance travelled in miles
Villages
7.7
7.7
7.7
7.4
7.3
7.1
6.8
6.7
6.6
6.5
Village (1)
10
9.3
8.5
7.7
7.7
6.7
6.2
5.8
5.4
4.2
Village (2)
Distance travelled in Miles
Village (2)
Village (1)
Measures of
Central
Tendency
7.15
7.15
Mean
7.2
7.2
Median
7.7
7.7
Mode
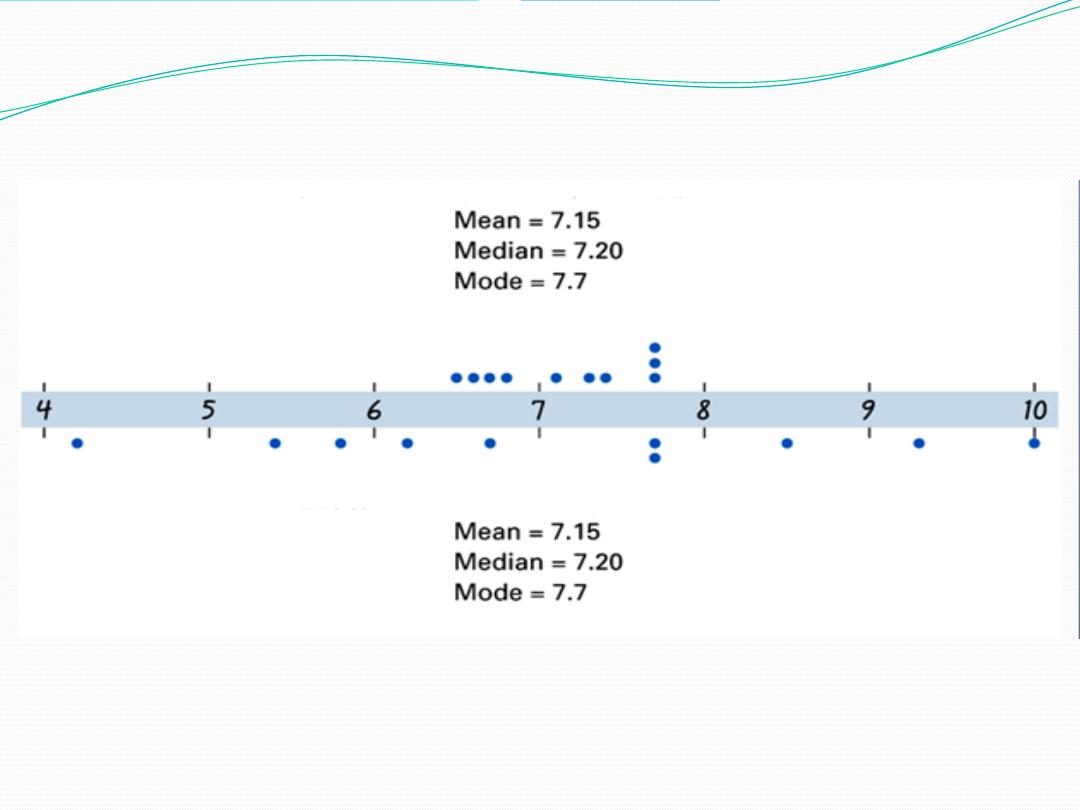
Dot plots of Distance Travelled
Even though the measures of center tendency are all the same,
it is obvious from the dot plots of each group of data that
there are some differences in the ‘spread’ (or variation) of the
data
Village (1)
Village (2)
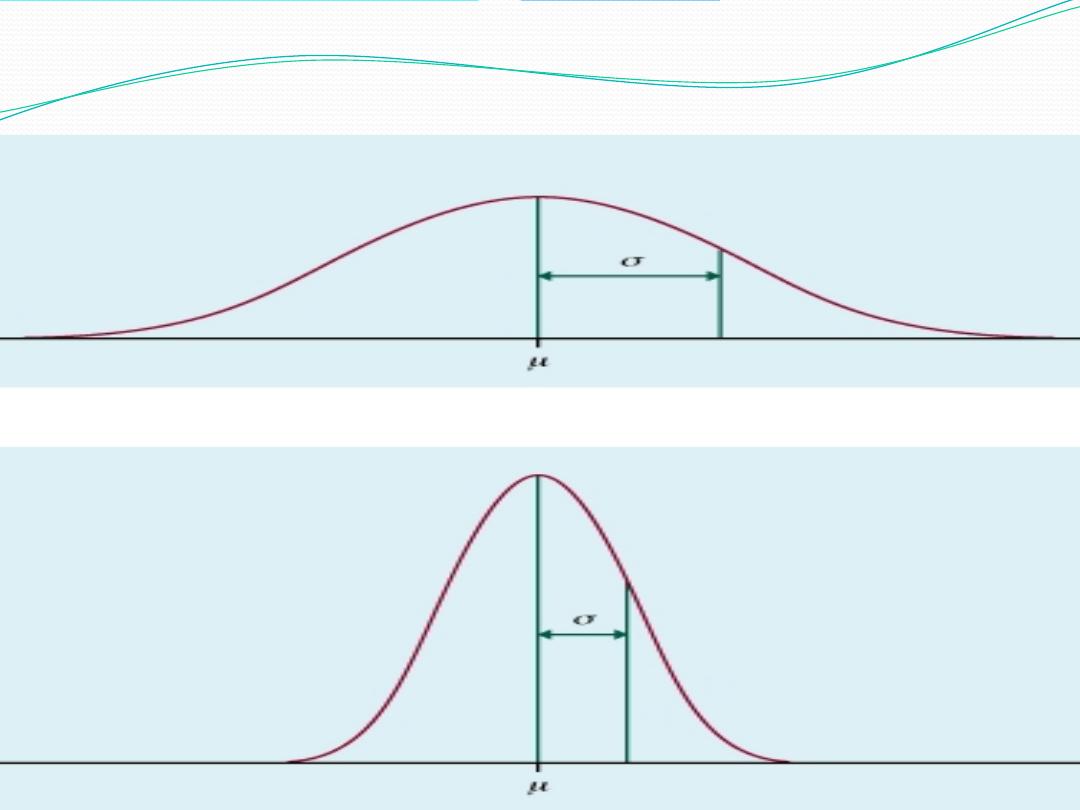
Consider these means for weekly candy bar consumption
Mean = {7, 8, 6, 7, 7, 6, 8, 7}
= (7+8+6+7+7+6+8+7)/8
= 7
Mean = {12, 2, 0, 14, 10, 9, 5, 4}
= (12+2+0+14+10+9+5+4)/8
= 7

Measures of Dispersion
⚫
As well as measures of central tendency we need
measures of how variable the data are.
⚫
Dispersion is a key concept in statistical thinking.
⚫
The basic question being asked is how much do the scores
deviate around the Mean?
Measures of Dispersion; These are
⚫
The range
⚫
The Variance
⚫
Standard Deviation
⚫
Standard Error
⚫
Coefficient of Variation
Measures of Dispersion; The Range
⚫
The range is an important measurement
Range
Highest
Value
Lowest
Value
However, they do not give
much indication of the
spread of observations about
the mean
Simple to calculate
Easy to understand
It neglect all values in the center and depend on the extreme value,
extreme value are dependent on sample size
It is not based on all observations
It is not amenable for further mathematic treatment
should be used in conjunction with other measures of variability

Variance
:
The mean sum of squares of the deviation from the mean.
e.g. if the data is: 1,2,3,4,5.
The mean for these data=3
the difference of each value in the set from the mean:
1-3= -2
2-3= -1
3-3= 0
4-3= 1
5-3= 2
⚫
The summation of the differences =zero
⚫
Summation of square of the differences is not zero
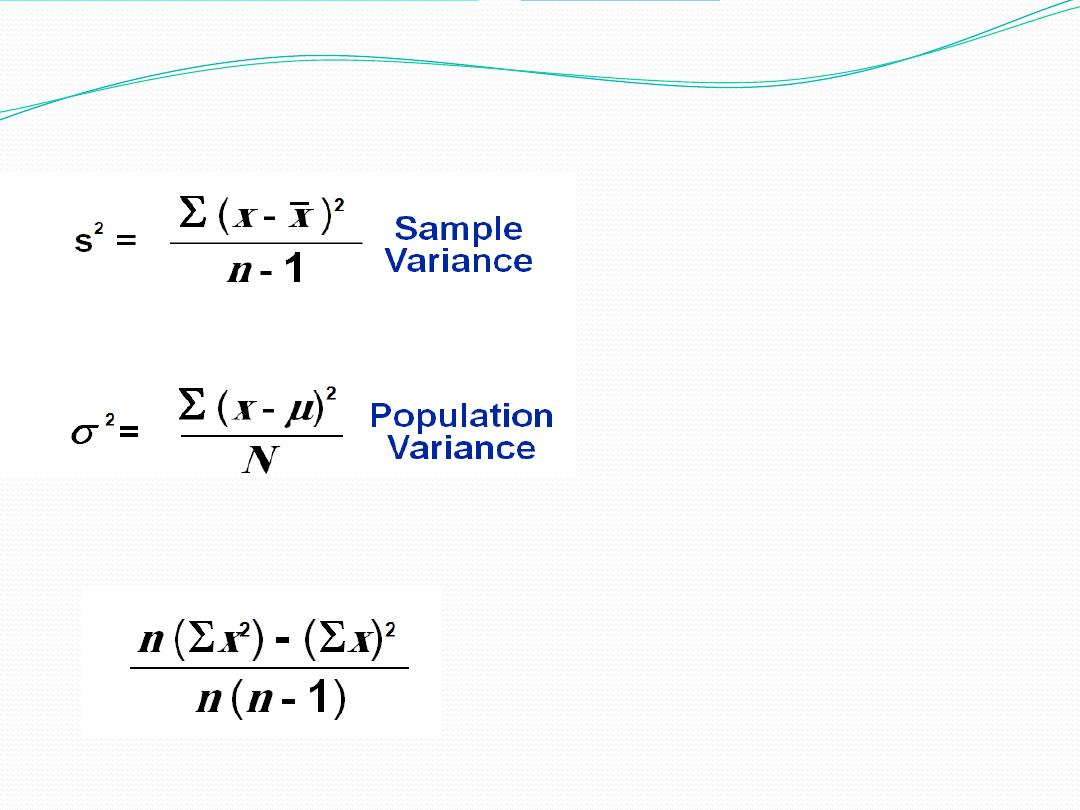
The Variance
Another formula for the variance
Variance can never be a
negative value
All
observations
are
considered
The problem with the
variance is the squared
unit
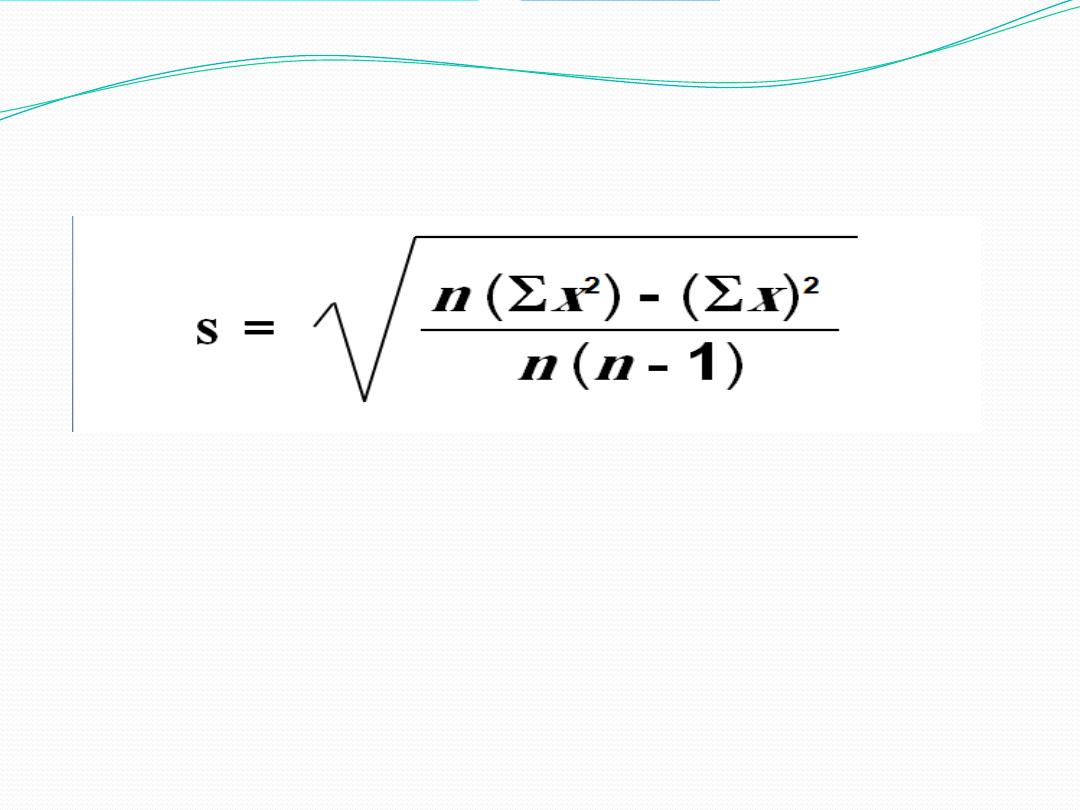
The standard deviation is the square root of the
variance
The
standard deviation measured the variability between
observations in the sample or the population from the mean of that
sample or that population.
The unit is not squared
SD is the most widely used measure of dispersion

Standard Error of the mean(SE)
It measures the variability or dispersion of the
sample mean from population mean
It is used to estimate the population mean, and to
estimate differences between populations means
SE=SD/√ n

Coefficient of variation (CV)
:
It expresses the SD as a percentage of the mean
CV= (S /mean) x 100 (mean of the sample)
It has no unit
It is used to compare dispersion in two sets of data
especially when the units are different
It measures relative rather than absolute variation
It takes in consideration all values in the set
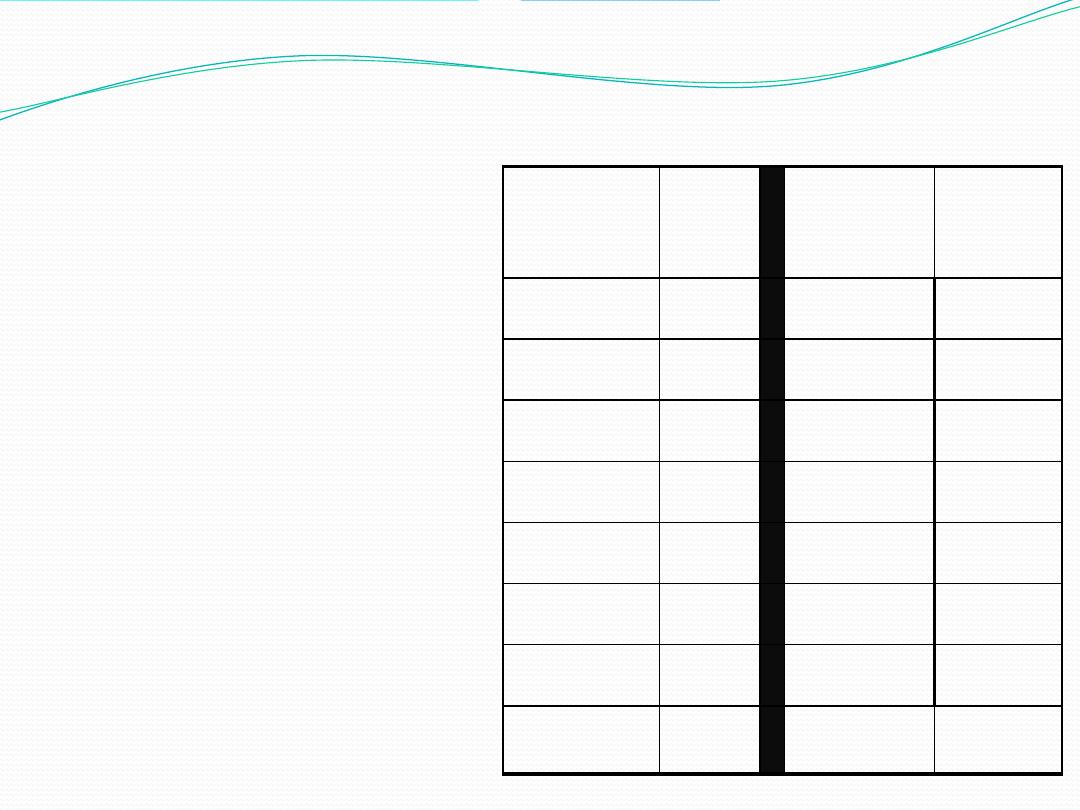
A sample of 15
patients
making
visits
to
a
health
center traveled these
distances in
miles,
calculate
measures
of Dispersion.
Distance
(mile)(X)
Pat.
no
Distance
(mile)(X)
Pat.
no
13
9
5
1
7
10
9
2
3
11
11
3
15
12
3
4
12
13
12
5
15
14
13
6
5
15
12
7
141
T
6
8
Exercise (1)

End
