
1
FEMALE SEX HOEMONES :
1- Estrogens(E)
:- the commonest one called estradiol (E2, estradiol-17 beta ) , other include
estrone(E1) & estriol(E3) .
Synthetic E include following
:-
a- steroidal source like [ ethinyl-estradiol 0.0005-0.02 mg/day , micronized estradiol 1-2 mg/ds ,
estradiol cypionate 2-5 mg/d , estradiol valerate 2-20 mg/every other week , estropipate 1.25-2.5 mg/d
quinestrol 0.1-0.2 mg/ week , mixed estrogen orally 0.3-0.5 mg/d , as injection 0.2-2 mg/d ] .
b- non-steroidal source include [dienestrol , diethylstilbestrol 0.1-0.5 mg/d , benzestrol , hexestrol ,
methestrol , methallenestril3-9 mg/d , chlorotrianisene 12-25 mg/d ] .
in the circulation E binding to alfa 2 –globulin (sex hormones globulin) & to albumin at lower affinity . the
free part only of physiological activities . in the liver & other tissues converted into E1 & E3which are of
low affinity to estrogen receptors .the excreted via bile , the conjugated
form may be hydrolyze in the
intestine to active agent that is reabsorbable . small amount excreted in the milk . enter-hepatic circulation of
oral E cause a high ratio of hepatic( un-wanted effects) than peripheral effects .
the mechanism of action of E include 1- bounding to sex hormones binding globulin that then dissociate to
enter the cell & bind to the intra-cellular receptor that consist of alfa & beta units . the receptor bound to
stabilizing protein including two molecule of heat shock protein = HsP90 & several other , on binding of
estrogen the unstable complex created & HsP90 & associated molecules release , the remainder E-receptor
complex able to enter the nucleus to bind to E –response elements(ERE) , on the gene & regulate
transcription by RNA polymerase ІІ & associated transcription factors . a variety of factors may participate
in facilitating or inhibiting E – regulatory response . the result mRNA is edited & exported to cytoplasm for
production of protein that bring a bout the final hormones response . 2- rapid E- inducing effects such as
granulosa cell calicium uptake & increase uterine blood flow do not required gene activation , but appear to
be mediated via separated membranes receptors that differ than intracellular receptors .
Physiological Effects of E :-
1-female maturation 2-Endometrial effects 3-metabolic & cardio-vascular 4- on blood coagulation
5- other effects like synthesis of progesterone receptors , influence behavior & libido , may cause edema by
moving fluid from intra-0vascular compartment into extra-vascular compartment .
CLINICAL USES :
1- primary hypo-gonadism as a replacement therapy ( as in case of failure of development of ovary ,
premature menopause & menopause ), treatment should be star at age of 11-13 years old to stimulate
secondary sexual characters & menses .also stimulate optimal growth & prevent osteoporosis in dose of 0.3
mg conjugated E or 5-10 microgram ethinyl estradiol on day 1-21 of each month till the growth completed
then E & progesterone administrated together .
2- post-menopausal hormonal therapy [in case of loss of bone including hip –wrist – vertebra ,
atherosclerosis , genital atrophy , loss of period ] in case of ceases of normal ovulatory function cause
increasing in plasma level of cholesterol & LDL, decreasing LDL receptors while the effects on VLDL ,
HDL , & triglyceride not much affected . the mot common causes of death due to cardiovascular disorder .
E replacement decrease the incidence of myocardial infarction in about 50% & fatal stroke in 40% .
In patients undergo hysterectomy , E may be give for 5 days / week or continuously .
E is prescribe on first 21-25 day of each month , in dose of 0.3-1.25 mg /d of conjugated E or 0.01-0.02
mg/d ethinyl estradiol for sever case which develop osteoporosis while mild case which manifested as
atrophic vaginitis treated with topical preparation [ the benefit of topical form are escape first pass effects ,
for treatment of UT symptoms , to be completely absorbed .] .
E increase the risk of endometrial carcinoma , so to reduce the risk to 50% we give the patients
medroxyprogesterone 10 mg /d for the last 10-14 days of E period therapy .
Daily conjugated E in dose of 0.625 mg & 2.5-5 mg of medroxyprogesterone will eliminate [ cyclic bleeding ,
control vasomotor symptoms , prevent genital atrophy , maintain bone density ] .
2
3 other uses like[ combine with progesterone to suppress over function of ovary in case of amenorrhea ,
hirsutism , intractable dysmenorrhea ] .
adverse effects of E :
1- postmenopausal uterine bleeding , 2- nausea , 3- hyperpigmentation , 4- breast tenderness , 5- increase
frequency of migraine headache , cholesterol , hypertension , gall bladder disease , 6- increase the risk of
breast carcinoma on high prolong therapy . their contraindication : E-dependent neoplasm like endometrial
carcinoma or those at risk of breast cancer . 2-those with history of thrombo-embolic disorder.3- heavy
smoker .4-liver disease.5-undiagnosed vaginal bleeding .
PROGESTIN :-
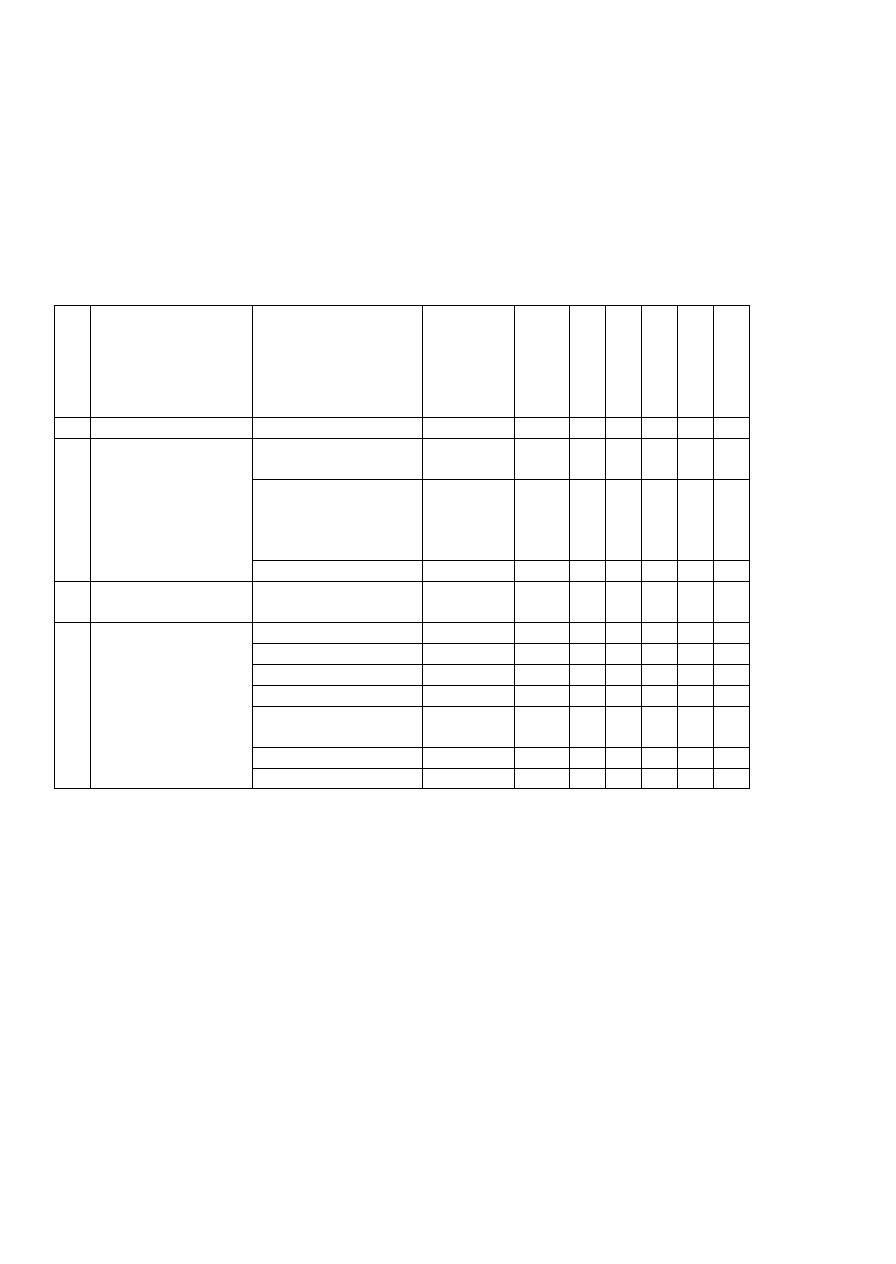
No
Group
Agents
Duration
Route
A
es
tr
ogen
A
nd
ro
gen
A
n
ties
tr
o
ge
-n
A
n
tiand
rog
-ni
c
A
nab
ol
ic
1
progesterone
--------
1 day
IM
+
2
21-carbon
compound
Hydroxyprogesterone
caproate
8-14 day
IM
Sl
Sl
Medroxyprogesterone
acetate
Oral-1-3
day,
injection4-
12 week
IM,
PO
+
+
Megestrol acetate
1-3 day
PO
+
+
3
17-
ethinyltestosterone
dimethisterone
1-3 day
PO
Sl
4
19-nortestosterone
Desogestrel
1-3 day
PO
Norethynodrel
1-3 day
PO
+
Lynestrenol
1-3 day
PO
+
+
+
Norethidrone
1-3 day
PO
Sl
+
+
+
Norethindrone
acetate
1-3 day
PO
Sl
+
+
+
Ethynodiol diacetate
1-3 day
PO
Sl
+
+
L -norgestrel
1-3 day
PO
+
+
+
=Progesterone is the most important progestin in human body , it is of both hormonal & as precursor of E ,
androgen ,adrenocorticoid steroid .the site of synthesis include ovary , testis & adrenal from circulation
cholesterol,large amount synthesize by placenta during pregnancy,female normally secrete about1-5 mg /day .
=Progesterone rapidly absorbed after any route of administration , their plasma half life 5 minutes , small
amount store temporally in body fat tissues , it is completely metabolize on one passage through liver , , their
metabolite into pregnanediol then conjugated with glucuronic acid & excrete in the urine as pregnanediol
glucuronide .all other compound extensively metabolize & excreted in the urine .
Their mode of action like estrogen .
A- therapeutic application like :-
1- hormonal replacement & hormonal contraceptive .
2- long term ovarian suppression , IM medroxyprogesterone in dose of 150 mg every 90 days cause prolong
anovulation & amenorrhea results , this treatment employed in treatment of dysmenorrhea , endometriosis ,
bleeding disorder when estrogen contraindicated , as contraceptive ( such treatment phase a problem that is a
long time required to restore ovulation ) .
3- relief hot flushes in some menopausal females .

3
4-medroxyprogesterone acetate in dose 10-20 mg twice weekly every 1-2 weeks orally , or IM 100 mg every
1-2 weeks prevent menstruation but not arrest accelerated bone maturation in children with precocious
puberty .
5-their administration decrease the risk of abortion(threaten & habitual) in about 20% .
6-treatment of slow rise basal body temperature of women .
7-treatment of pre-menstrual symptoms .
B- diagnostic uses like as a test of estrogen secretion in dose of 150 mg /day progesterone or 10 mg
medroxyprogesterone for 5-7 days withdrawal bleeding in amenorrheic patient only when the endometrium
stimulated by estrogen .
Their advers effects include increase blood pressure , androgen type reduce plasma level of HDL on female ,
increase risk of breast cancer in female .Progestin compound include following agents :-
=================================================================== .
ESTROGEN & PROGESTERONE INHIBITORS – ANTAGONIST :-
1-Tamoxifen& related partial agonist estrogen :- tamoxifen it is a competitive partial agonist inhibitor of
estradiol at the E receptors , use in treatment of advance breast cancer in post menopausal women as
palliative therapy , it is non-steroidal agent give orally , their half life 7-14 hours , excreted via liver , their
dose 10-20 mg x2/day , their adverse effects like hot flush , nausea , vomiting in 25% of patients , it reduce
incidence of contra-lateral development of breast cancer in 35%, Toremifene structurally similar to
tamoxifen .
-Raloxifene it is also partial agonist at some , but not all E receptors , their half life 24 hours , so use once
daily , use to prevent post menopausal osteoporosis .
- Clomiphene it is a weak estrogenic , partial agonist agent , acts as a competitive inhibitor of endogenous
E , use as ovulation inducing agent .
2-Mifepristone it is a 19-norsteroid that strongly bind to progesterone receptor & inhibit their activity , it is
of luteolytic properties in 80% of women if give in the mid-luteal period , it use as a contraceptive agents , of
long half-life , a single daily dose of 600 mg is effective as emergency postcoitus contraceptive , it uses
include a majorly for termination of early pregnancy in dose of 400-600 mg /day for 4 days or 800 mg /day
for 2 days , it terminate pregnancy in about 85% . combination of single dose of 600 mg orally + vaginal
pessary of 1 mg PGE1- misprostol cause a termination of pregnancy in about 95% within 7 weeks of
pregnancy . their adverse effects include [prolong bleeding , pelvic or abdominal pain , vomiting , diarrhea ].
3-Danazol ; it is a isoxazole derivative of ethisterone with a weak progestational , androgenic &
glucocorticoid activity , it is use to suppress ovarian function , it bound to a receptors like glucocorticoid
receptor , androgenic receptor & progesterone receptor , it is able to translocate androgen receptor to nucleus
to initiate androgen specific RNA synthesis . slowly metabolize of half life about 15 hours , highly
concentrate in liver , kidney & adrenal gland , their excretion via kidney & feces . their major (a-)use include
in treatment of endometriosis in a dose of 600 mg /day reduce to 400 mg /day within 1 month then to 200 mg
within 2 months, their improvement rate 85% within 3-12 months .(b-) fibrocyctic disease of breast ,
hematologic condition or allergic disorder including hemophilia , ITP , Christ man disease & angion-
neurogic edema .
their adverse effects include weight gain , deeping of voice , increase hair growth , acne , decrease breast
size . oily skin , change the libido , hot flush , headache, muscle cramps . their major contraindication
pregnancy & breast feeding . use with sever precaution in liver dysfunction since it may cause a mild to
moderate hepato-cellular damage .
4- other inhibitors :- the prototypical steroidal inhibitor of aromatase (enzyme required for E synthesis ) like
a-Testolactone it is a weak inhibitor of enzyme & need in large dose to achieve clinical effects .
b-Anastrozole it is a selective non-steroidal inhibitor of aromatase , effective in some women when their
breast tumor become resistance to tamoxifen .
c-Letrozole .

4
d-Exemestane it is steroidal agent , it is irreversibly inhibit aromatase use in women with advance breast
cancer .
e-Fadrozole it is newer oral non-steroidal (triazole) inhibitor of aromatase activity , its potency like that of
tamoxifen.
g- GnRH- & its analog (nafarelin,buserelin,goserelin , histrelin ) important as both stimulant & inhibitors
of ovarian function , GnRH it is stimulant pituitary function , use to treated infertility caused by
hypothalamic –hypogonadotropic hypogonadism .
nafarelin,buserelin,goserelin , histrelin = all GnRH analogthat induce hypogonadism if use continuously , use
in treatment of prostate cancer , uterine fibroid , polycystic ovary syndrome , precocious puberty .
CONTRACEPTIVE AGENTS :-
Contraceptive of two type female & male contraceptive .
Female contraceptive include two types a- oral contraceptive which either in form of 1- combine
preparation of both estrogen& progesterone {can be monphasic or diphasic or triphasic } or 2- in form of
progesterone alone without estrogen . both adequately absorbed, combine form their preparation component
each one alter the pharmacokinetic of the other / b- implantable contraceptive only one form available for
clinical uses called NORGESTREL (6 tubes of 36 mg each & be effective when release from subcutaneous
implant to suppress ovulation ) .
--- large dose of IM medroxy-progesterone provide contraceptive effect for long period .
--- their mode of action :-as selective inhibitor of ovulation via inhibition of pituitary function , combine form
produce a changes in cervical mucus , uterine endometrium , & motility& secretion of uterine tube , all
decrease conception , progesterone alone does not always prevent ovulation but other factor play a role .
failure rate of contraceptive 0.5-1 % .
their clinically used in treatment of endometriosis in addiution to their indication to prevent conception .
Their adverse effects divided in to 3 type according to their degree as follows :-
A- mild adverse effects including [nausea , edema( due to the effect of estrogen) , increase sedimentation
rate (due to increasing of fibrinogen ) headache * increase frequency of migraine , etc . ] .
B-moderate adverse effects include [bleeding(in case of progestin alone reach upto 25%) , weight gain ,
increase skin pigmentation( after 1 year upto 5% , after 8 years upto 40%) , exacerbation of acne in combine
form while estrogen improve acne on large dose , hirsutism in female( especially in case of combine one &
19-nortestosterone) , sever resist& difficult vaginal infection , amenorrhea in some patients ] .
C- sever adverse effects include [1- vascular disorder in form of venous thrombosis( superficial & deep ) ,
pulmonary embolism , myocardial infarction (especially in obese , or hypertensive , or diabetic or pre-
clampsic , smoking patients due to increase or acceleration of atheroseclerosis , decrease HDL , increase
LDL , increase platelet aggregation ) , cerebrovascular disorder in form of stroke , subarachenoid
hemorrhage depending on medication dose & patient age ,./ 2- GIT disorder in form of cholestatic jaundice ,
cholecystitis , cholangitis , increase incidence of hepatic adenoma , ischemic bowel disease ../ 3- depression
in6% ./ 4- cancer by increase risk of breast carcinoma ] .
Their contraindication are thrombophelitis , thromboembolic phenomena , adolescent age female , cerebro-
vascular disorder , breast cancer & estrogen dependent neoplasm . they use in caution in case of liver
disease , asthma , eczema , migraine , neuritis , convulsive disease , CHD .
MALE CONTRACEPTIVE :-
Include :
1- testosterone or testosterone enanthate in dose of 400 mg / month cause in 50% of treated men
azoospermia .
2-testosterone + danazole .
3- androgen + medroxyprogesterone .
4- IM testosterone 100 mg / week + 500 mg of Levonorgestrel daily orally cause azoospermia in 94% .
5-cyproterone & cyproterone acetate cause oligospermia .
6- Gossypol & Gossypol acetic in dose 20 mg /d for 2 months then maintenance dose of 60 mg / week cause
azoospermia in 99% .
