Tumors ovary:-
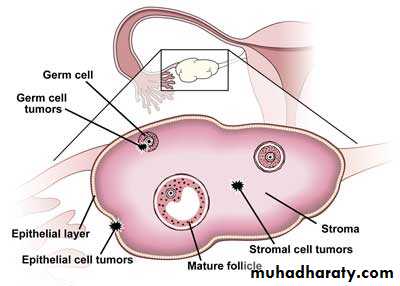
The 3 cell types of ovary form potential for large number of tumors and neoplasms and these types are:-1- Multipotential surface (coelomic) epithelial tumor.
2- Germ cells.
3- Sex-cord-stromal cells.
The surface epithelial – stromal cells are:
1- Serous tumor, which's subdivided into:
a-benign cystadenoma . b-borderline tumors (serous borderline tumor) . c-malignant (serous adenocarcinoma).
2- Mucinous tumor. which's subdivided into:
a-benign cystadenoma . b-borderline tumors (mucinous borderline tumor) . c-malignant (mucinous adenocarcinoma).
3- Endometrioid tumor. which's subdivided into:
a-benign cystadenoma . b-borderline tumors (endometroid borderline tumor) . c-malignant (endometroid adenocarcinoma).
4- Clear cells tumor. which's subdivided into:
a-benign . b-borderline tumors . c-malignant ( clear cell adenocarcinoma)
5- transitional cell tumors. which's subdivided into: a-Brenner tumor. b-Brenner tumor of borderline malignancy. c-malignant Brenner tumor. d-transitional cell carcinoma (non-Brenner tumor).
6-epithelial- stromal. a-adenocarcinoma. b-carcinosarcoma (formerly mixed mullerian tumor)
Germ cell origin are:
1- Teratoma. which's subdivided into : -immature. –mature. –solid. – cystic (dermoid cyst).
2- Dysgerminoma. 3- monodermal (struma ovarii, carcinoid) 4-yollk sac tumor. 5-mixed germ cell tumors.
Sex cord – stroma :
1- Fibroma.
2- Granulosa – theca cell tumor:- this tumor usually hormonally active and secrete large amount of estrogen so cause endometrial and breast cancer.
3- Sertoli – Leydig cell tumor.
Metastasis carcinoma:-
This occur in older age group and usually come from breast, lungs and GIT.Surface Epithelial Tumors:
Surface epithelial origin cells are the most common which's constitute over than 90% of ovarian neoplasms, arise from the fallopian tube or epithelial cysts in the cortex of the ovary, studies have shown that many of the tumors thought to arise from the coelomic epithelium that covers the surface of the ovary are now thought to arise from the fimbriated end of the fallopian tube, Important risk factors for ovarian cancer include nulliparity, family history, and germline mutations in certain tumor suppressor genes most of these are associated with mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 tumor suppressor genes which are also associated with hereditary breast cancer .
Serous tumor:-
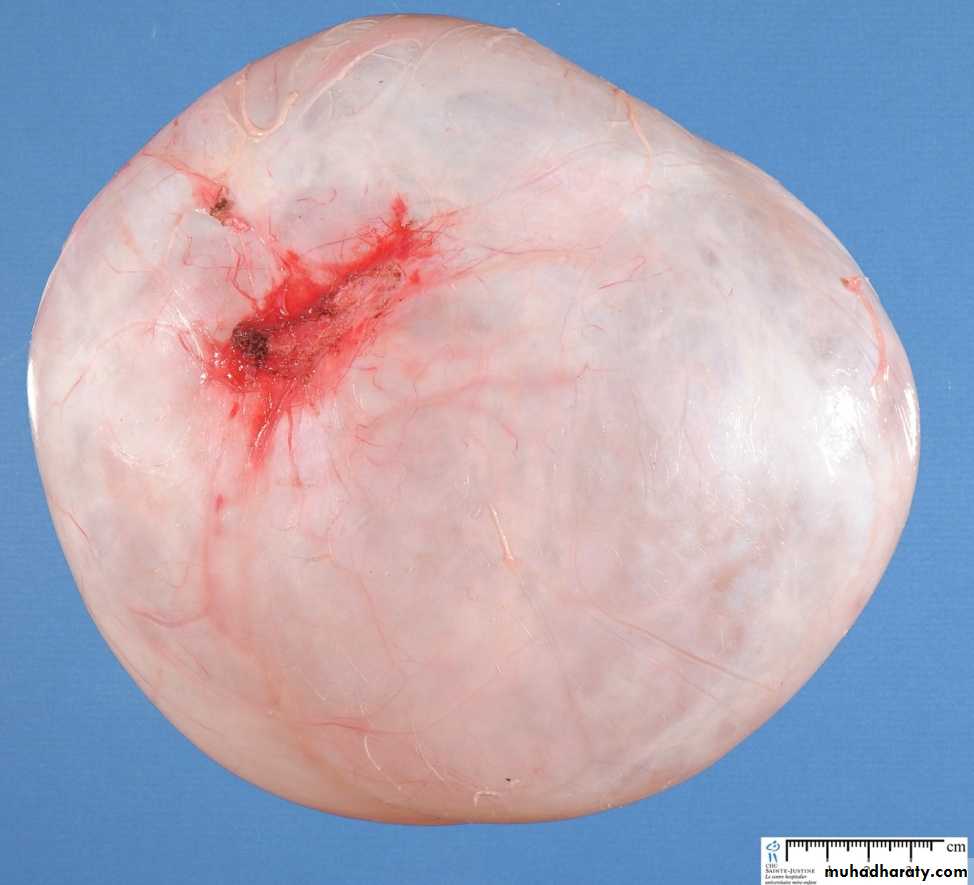
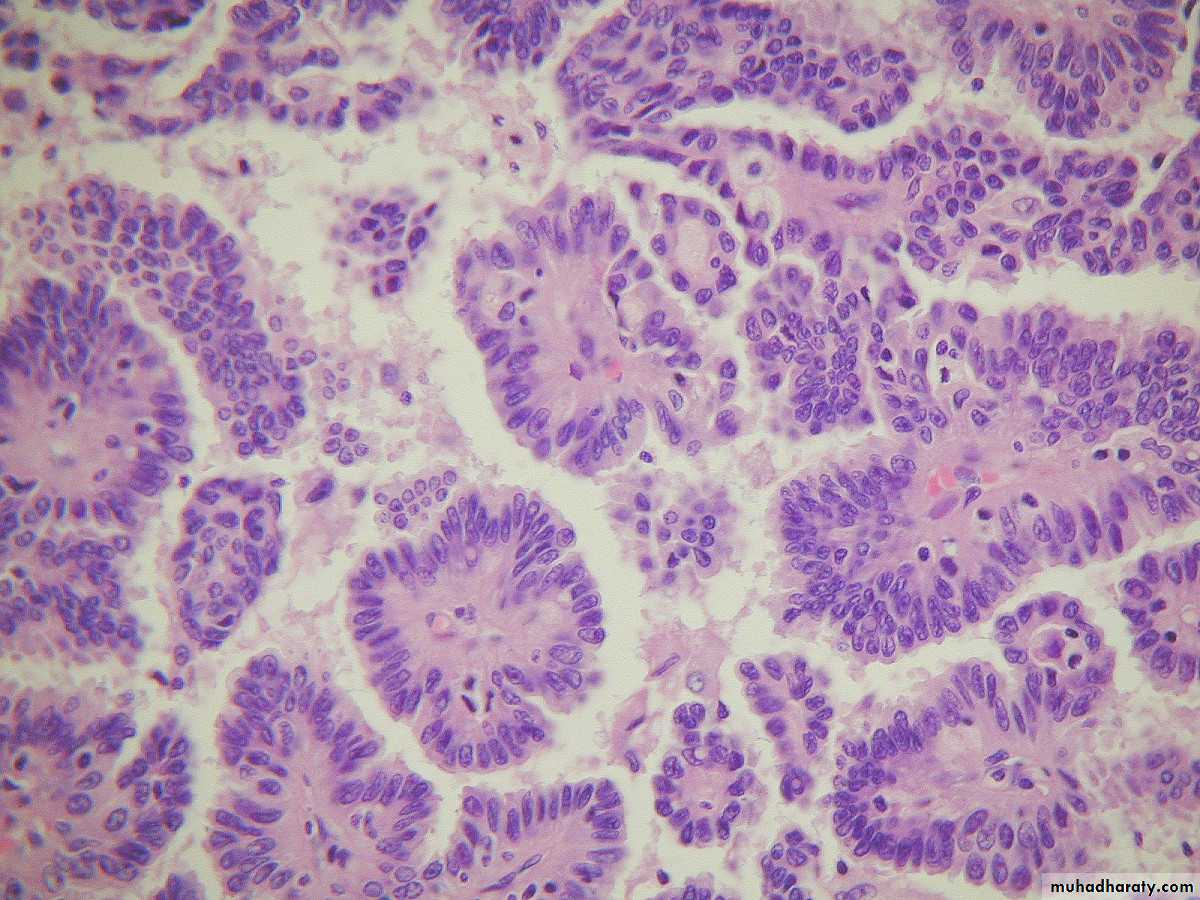
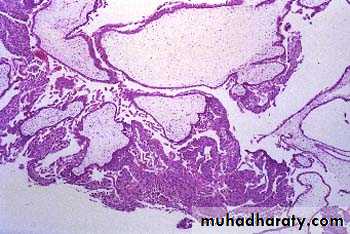
These are most frequent of the ovarian tumors, it's usually cystic so known as cystadenoma for benign tumor and cystadenocarcinoma for malignant one and borderline or recently named as tumor of low malignant potential for borderline tumor between benign and malignant.Morphology:-
Grossly: serous tumor may be small 5 to 10 cm or may reached even 40 cm in diameter, the surface in benign one is smooth and glistening while in malignant one is irregular, cut section reveal unilocular or more multilocular cysts filled by serous fluid and smooth inner surface in benign one while in malignant tumor the inner surface usually contain polypoid and papillary growth.
Microscopically: in benign one usually consist of thin wall lined by single layer of tall columnar serous epithelial cells.
While in malignant one usually composed of complex papillae lined by multilayring atypical malignant cells with invasion of stroma, in borderline the atypia of lining papillae are present but no stromal invasion seen.
The metastasis of this tumor is usually by local invasion of wall and implant itself in peritoneal cavity so associated with ascetis.
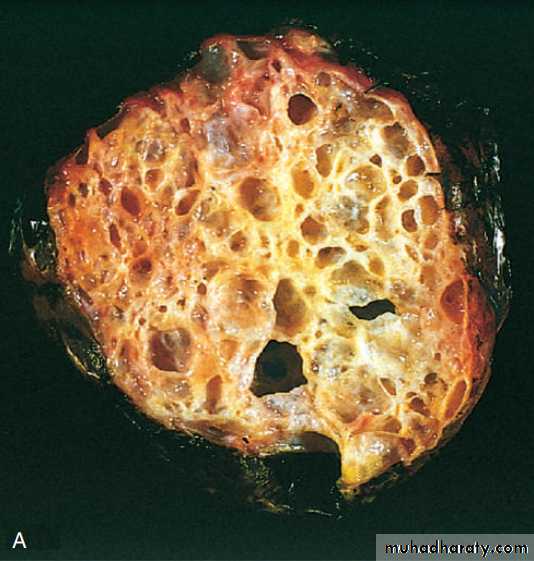
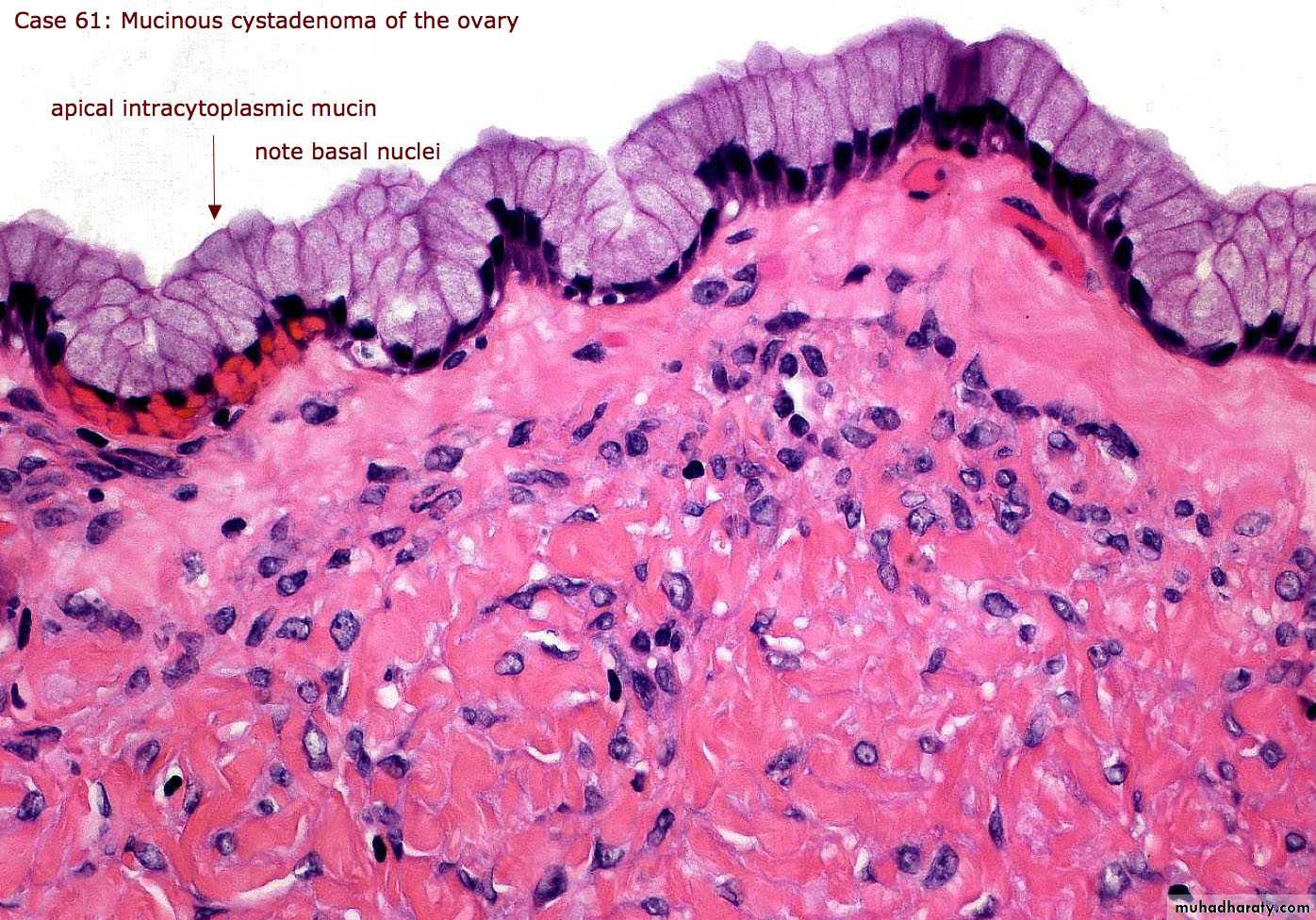
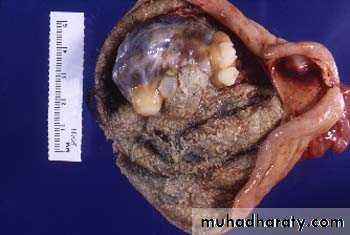
Mucinous tumor:-
This usually analogous to serous tumor but it's usually larger than serous cyst and multilocular, it's lined by mucous secreting cells as endocervical cells.Grossly: it can't be differentiated from serous cysts but on cut section reveal mucinous thick material.
Microscopically: in benign tumor, it consist of thin wall lined by single layer of mucous secreting cells which consist of apical vacuoles and basal located nuclei, in malignant one also consist of complex papillae lined by multilayering malignant cells with stromal invasion which's not seen in borderline tumor.
The metastasis or rupture of mucinous cystadenocarcinoma may give rise to pseudomyxoma peritonii, that the peritoneal cavity becomes filled with mucinous material with multiple implants on serosal surface so abdominal viscera become matted together.
Other ovarian tumors:
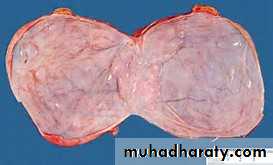
Many other types of tumors of germ cell and sex cord– stromal origin also arise in the ovary, the most common are:Teratomas
It's divided into:-
1- Mature (benign teratoma).
2- Immature (malignant teratoma).
Benign (Mature teratoma) these tumors arise from totipotential germ cells to give origin of 3 embryonal layers:
1- Ectodermal 2- Mesodermal 3- Endodermal
The more common take the differentiation of ectodermal totipotential germ cells, which also this teratoma can contain teeth, bone, cartilage, nests of bronchial or gastrointestinal epithelium even brain tissue.
Immature teratoma:-
It usually occur in younger age group than mature, it's bulky and solid.Micrscopically consist of different tissues as undifferentiated and immature may be in one element only especially in neuroepithelial cells.
Diseases of pregnancy:-
Ectopic pregnancy:-
Defined as implantation of fertilized ovum in any site other than normal uterine location, this condition occur in 1% of pregnancy.
Location:-
1- Over 90% of the implantation occur in oviduct (tubal pregnancy).2- Other sites are ovaries, abdominal cavity and intrauterine portion of oviducts.
This occur because of retards passage of the ovum along its normal course through the oviducts to the uterus.
In half cases the delay passage of ovum have no anatomic causes.
But other 50% occur due to:
1- Chronic inflammation.
2- Intrauterine tumor.
3- endometriosis.
Morphology:-
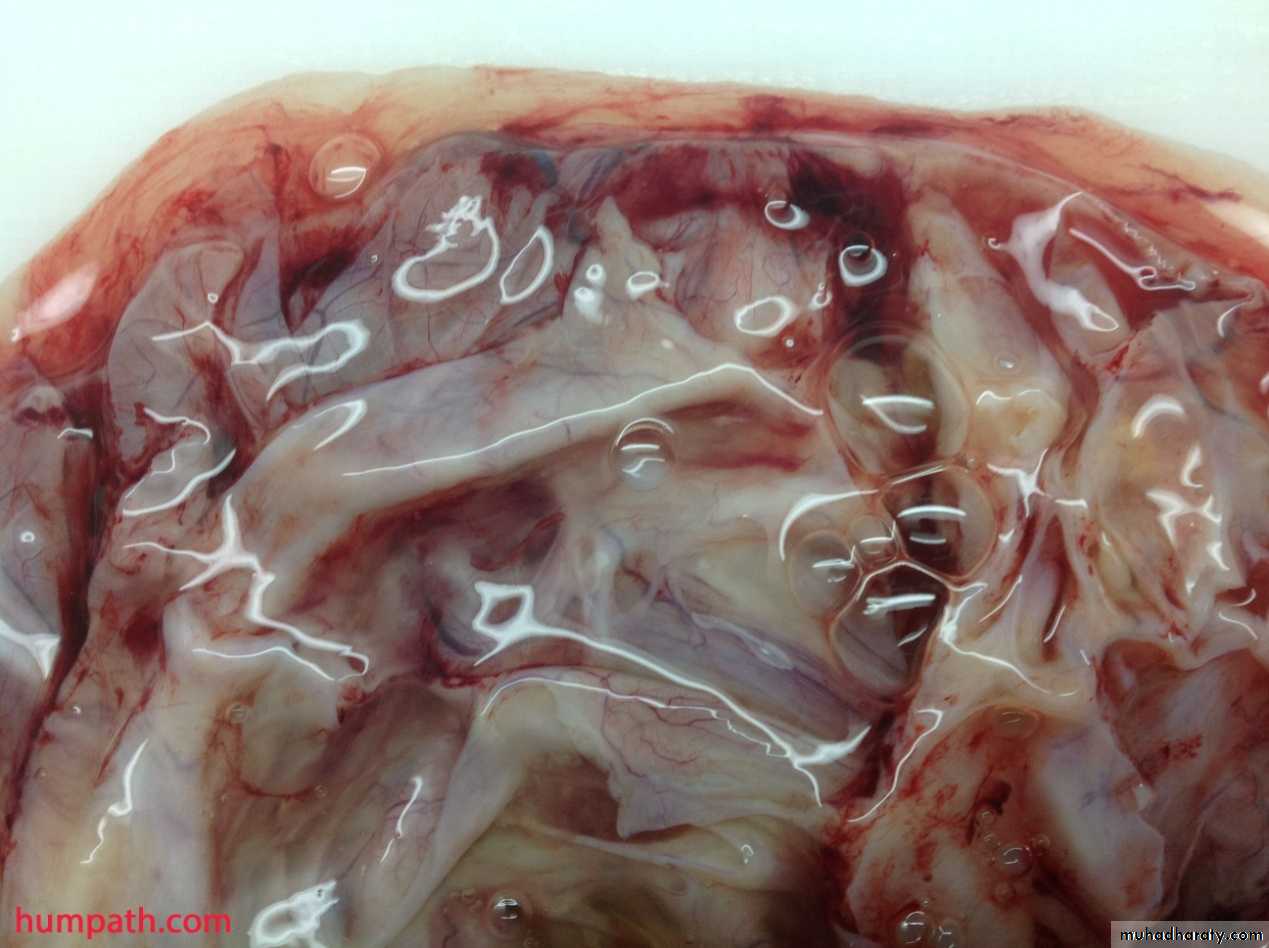
In tubal pregnancy there's usually dilatation of F.T which's may reach 3 to 4 cm in diameter cut section show blood clot with bits of grey placental tissue and fetal parts.Microscopically:-
There's decidual reaction of stroma with presence of placental villi and rarely can be seen fetal parts because the poor attachment of the placenta to the tubal wall result in death of the embryo and proteolysis.
Gestational trophoblastic disease:-
The gestational trophoblastic tumor divided into 3 categories arrange according to level of aggressiveness:
1- hydatiform mole complete and partial.
2- Invasive mole.
3- Choriocarcinoma.
1- Hydatiform mole:-
It's known a swollen, cystically dilated, chorionic villi appear grossly as a grape like structures. The complete mole does not perm it embryogenesis and therefore never contain fetal parts or normal villi and this cause by empty egg fertilized by 2 spermatozoa.So the epithelial cells carry diploid karyotype (46, xx or 46 xy).
While partial mole contain fetal parts and normal villi with abnormal one, which is resulting from a normal egg is fertilized by 2 spermatozoa so it carries triploid karyotype (69 xxy).
Morphology:-
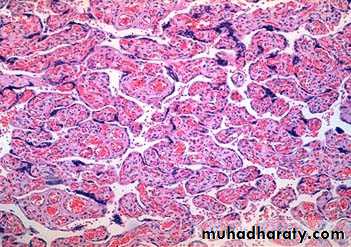
Grossly: the uterine cavity it's filled by thin- walled translucent cystic structures grape-like.Microscopically: in complete mole all the villi are showing hydropic dilatation with absence of vascularization and lined by proliferate cyto and syncytial trohoblast.
While in partial mole some of villi are normal other are dilated with less proliferation of trophoblastic cells.
Invasive mole:-
The mole retains the hydropic villi with hyperplastic and atypical changes of epithelium, the villi invade deeply the muscular layer of uterus and can reach the vagina or broad ligament by local spread but metastasis do not occur.
Choriocarcinoma:-
This is a very aggressive malignant tumor arise from gestational chorionic epithelium or less frequently from totipotential cells within the gonads.
This neoplasm occur in female below age of 20 and over age of 40.
Usually occur 50% after complete mole and less partial mole, 25% after abortion and remainder percentage after normal pregnancy.
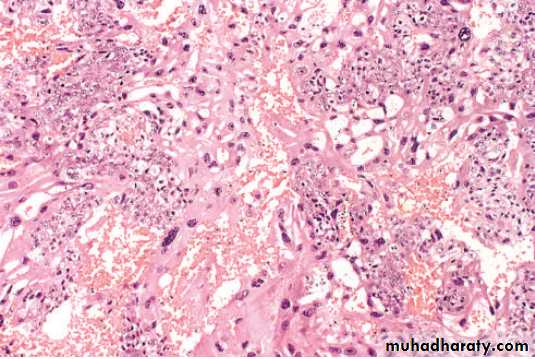
Microscopically: it's seen as very hemorrhagic necrotic masses within the uterus, sometimes the necrosis is complete to destruct the primary neoplasm and remain only the metastasis, in contrast to H.mole chorionic villi are not formed and consist from only malignant cyto and syncitiotrophoblast and this tumor is wide spread by blood but lymphatic invasion is not common.
This tumor has very good response to chemotherapy. Nearly 100% of cases have been cured and even healthy infants born to the survivors.