
U N I V E R S I T Y O F M O S U L
C O L L E G E O F D E N T I S T R Y
2020-2021
Department of
Conservative
Dentistry
5 th YEAR
By: P.h.D. Lec. Maha Anwer Hussein
د
.
م
.
مها
أنور حسين

Patient aspirations and motivation.
Age and general health of the patient.
Ability and training of the dentist and technician.
Economic factors.
A-General factors
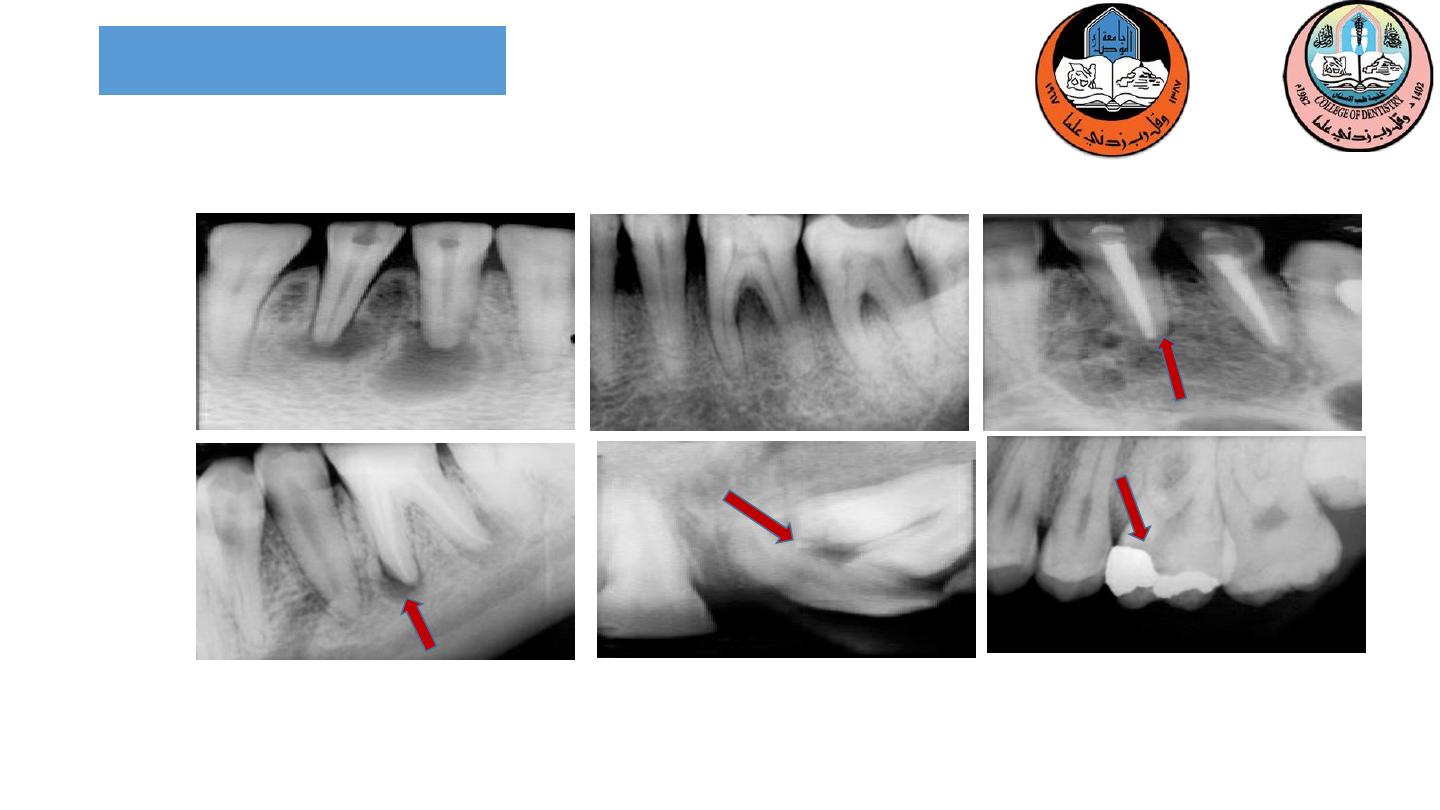
Evaluation of Abutment Teeth
1-Radiograph are made
B-Local factors
1
2
3
4
5
6

2
-pulpal health
is assessed by evaluating the
response to thermal and electrical stimulation.
3-
Existing restorations
,
cavity liners
, and
residual caries
are removed and a careful check is
made for possible pulpal exposure.
4-Teeth in which pulpal health is
doubtful
should be
endodontically treated before the initiation of fixed
prosthodontics.
2-Endodontically Treated Abutments
1-Unrestored Abutments
Abutment teeth and factors that
influence on selection
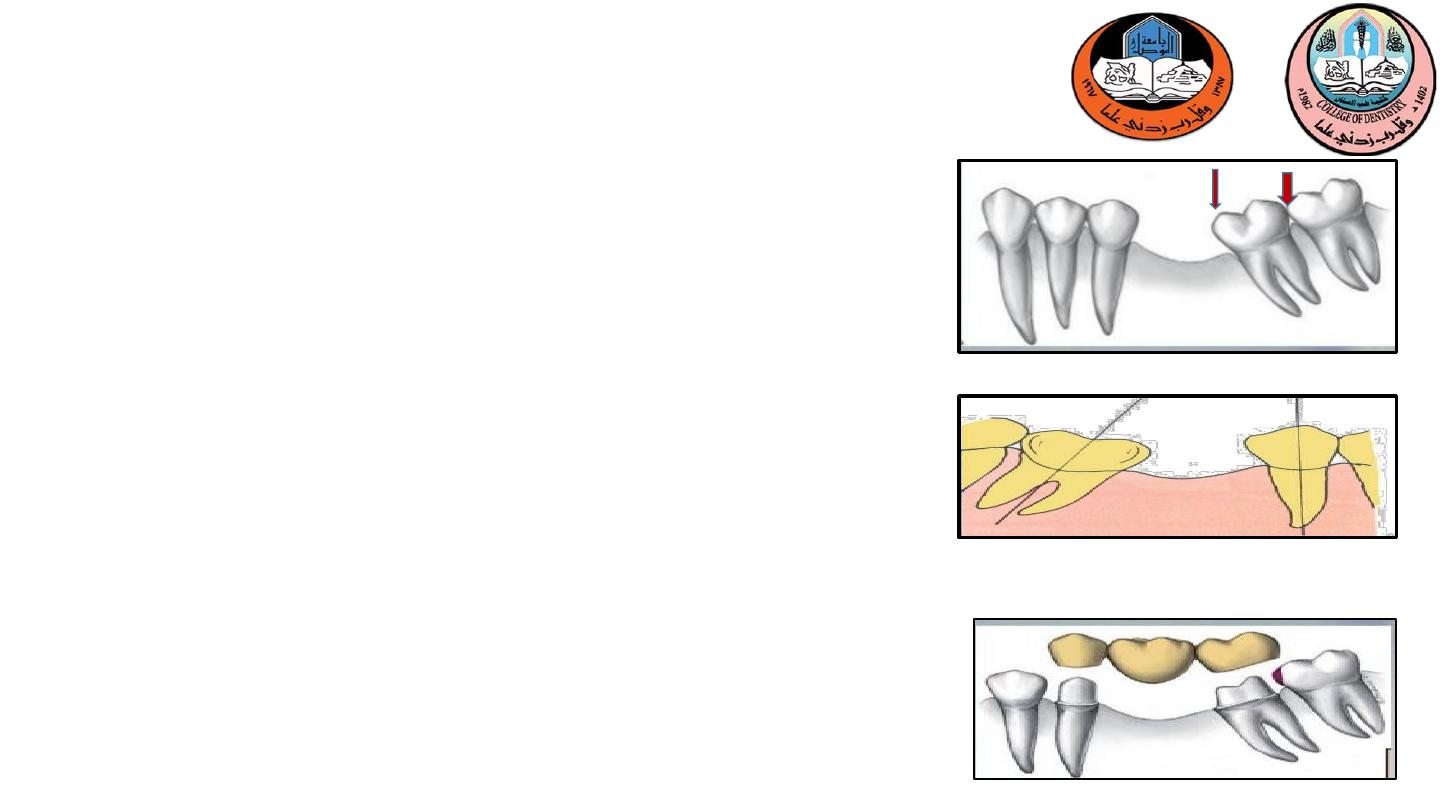
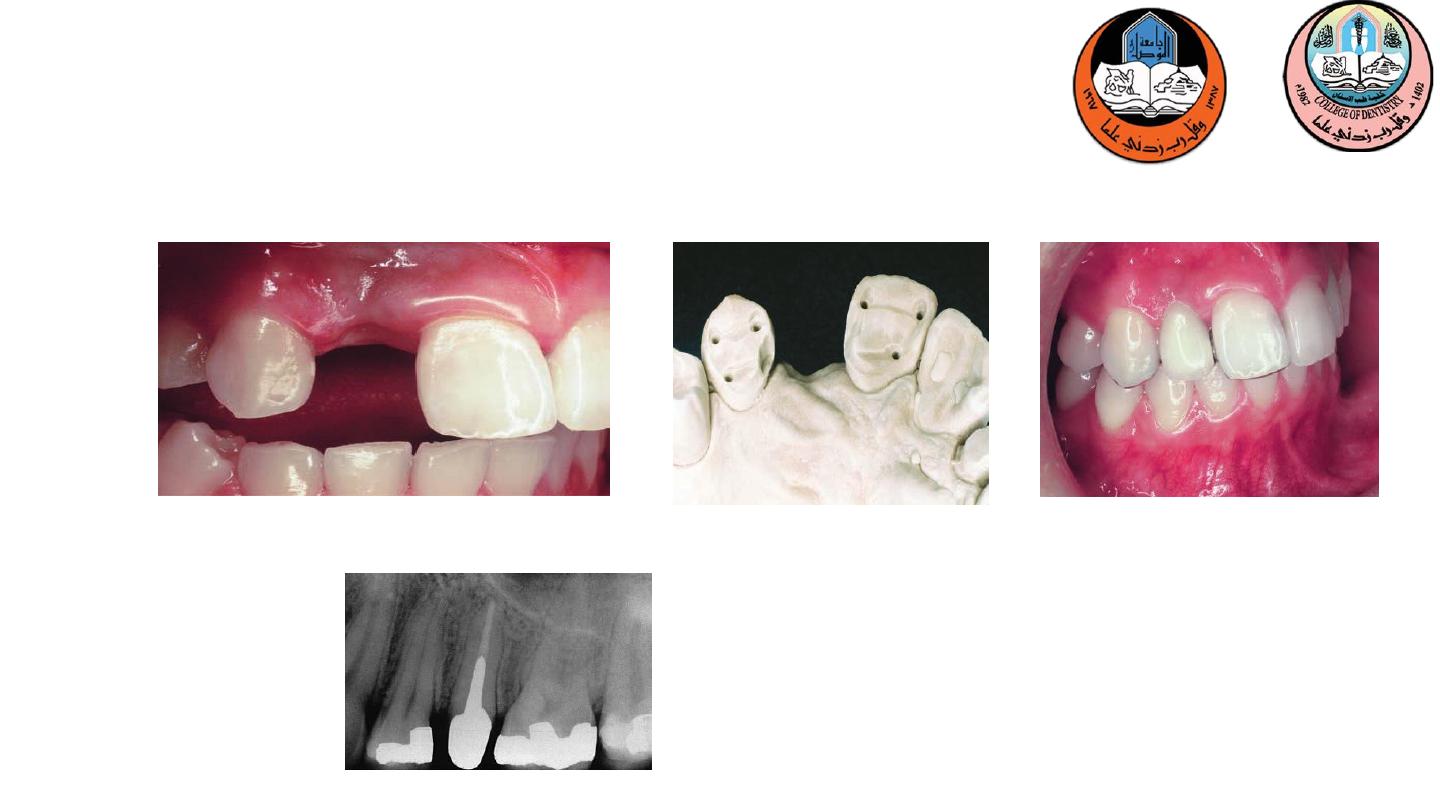
Early loss of a mandibular first molar ???
Mesial tilting and drifting of the second and third molars.
Impossible to achieve common path of insertion.
In an attempt to do excessive preparation has to be done
or mesially tilted 3rd molar will not allow seating of
prosthesis
3-Tilted molar abutments
Path of insertion
1
2
3
1-Extract the third molar and upright the tilted 2nd molar
orthodontically
2-Fixed appliance – premolars and the canine are banded
and tied to a passive stabilizing wire .
3-A helical uprighting spring is inserted into a tube on the
banded molar.
4-activated by hooking it over the wire on the anterior
segment.
2-Modified preparation design if orthodontic
is impossible.
Proximal half crown : ¾ crown that has been rotated
90 degree the distal surface is uncovered.
Non-rigid connector on the distal aspect of the
premolar retainer compensates for the inclination of
the tilted molar.
A modified partial veneer crown
can be used when a single path of
insertion is required with minimal
tooth preparation
Non-rigid
1
2
Treatment modality
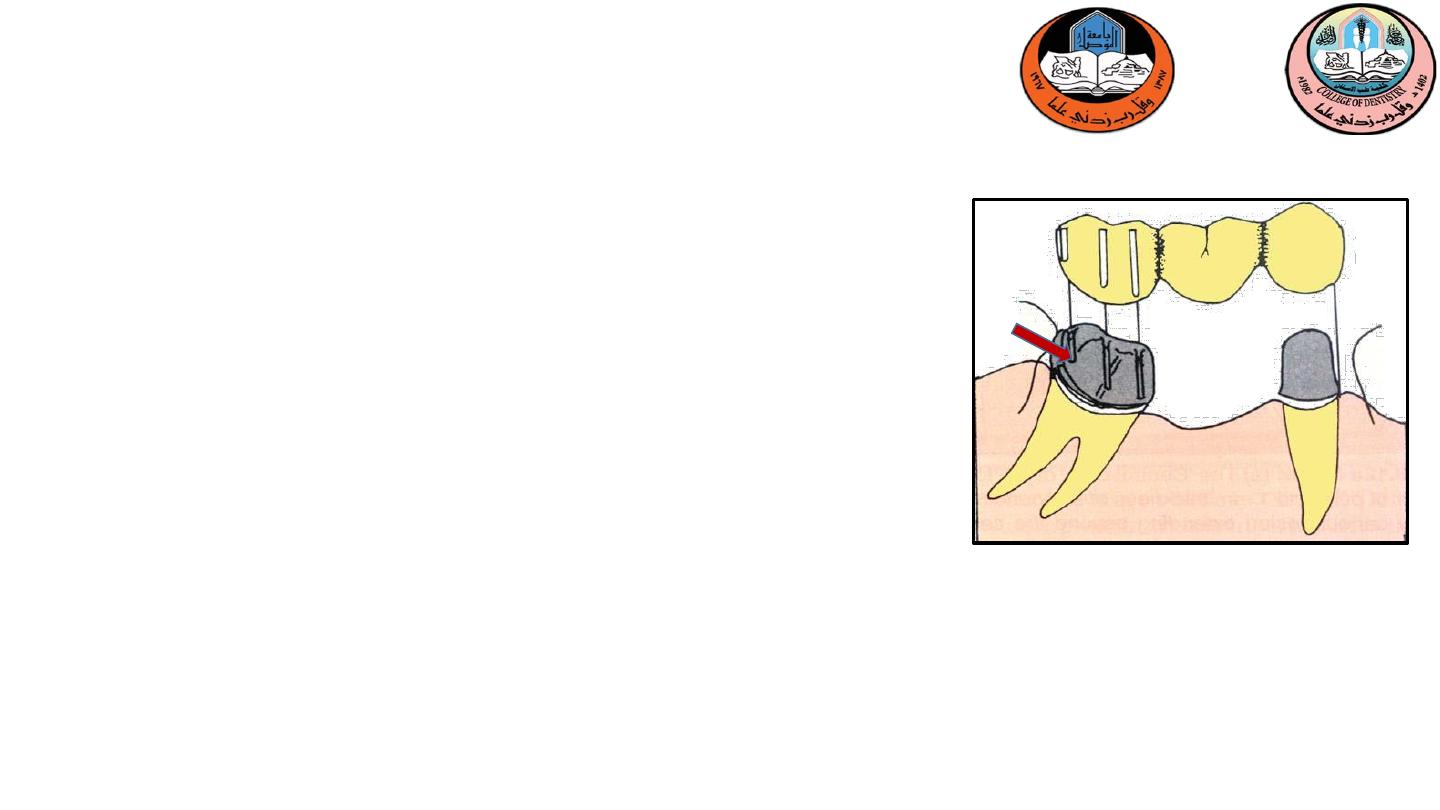
Telescopic crown
acoping or retainer is fabricated over
the tooth so that it alters the contour of the crown. This
crown should be fabricated with vertical slots so that it can
receive a second crown in a vertical direction,so
Telescopic
crown used as a retainer on the distal abutment .
A full crown preparation with heavy reduction is made to
follow the long axis of the tilted molar.
Inner coping is made to fit the tooth preparation
The proximal half crown that will serve as the retainer for
the fixed partial denture is fitted over the coping.
3-Telescopic crown
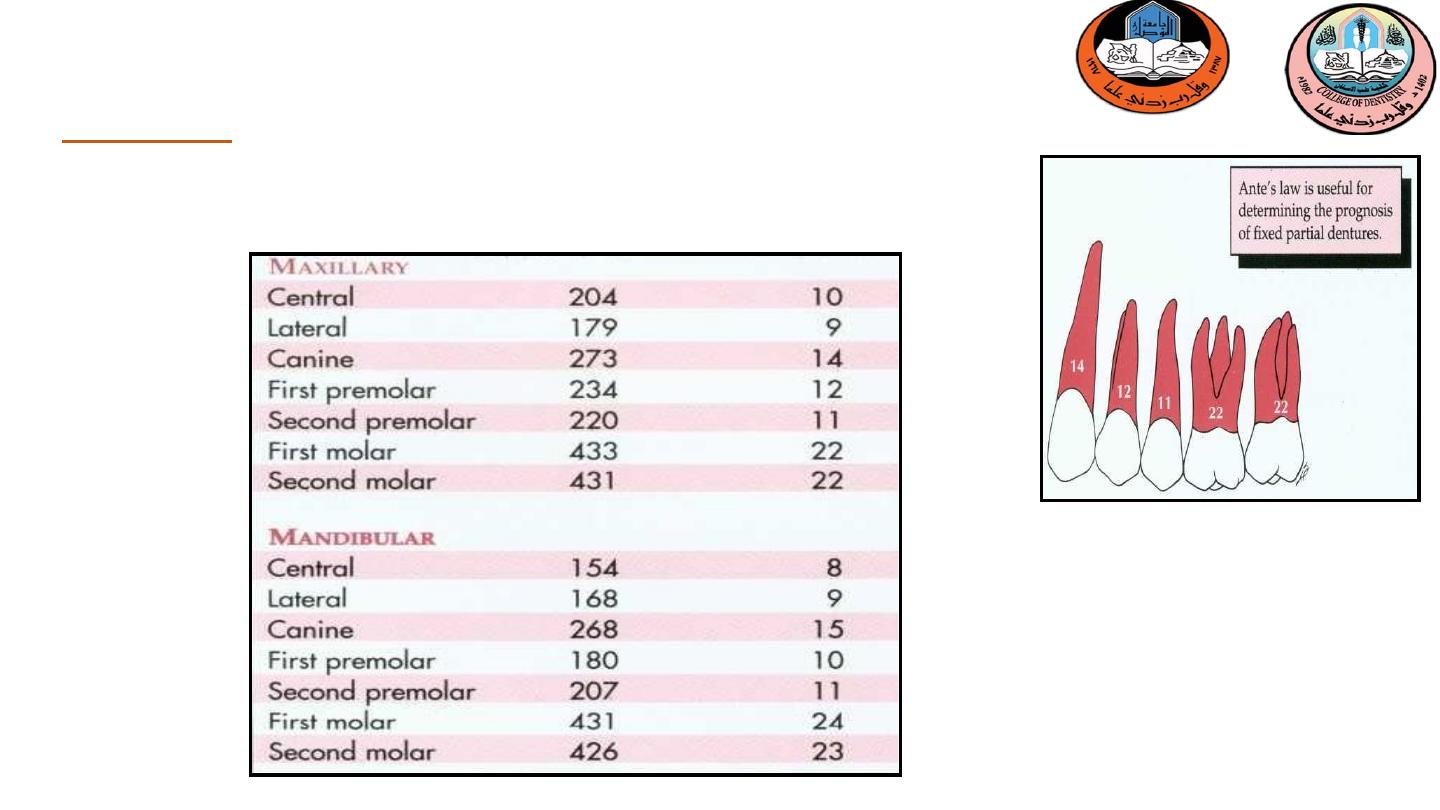
Area in quadrant
Root surface
area (nm)2
Percentage of
root surface
4-Root surface area of abutment
Ante’s law
''The abutment teeth should have a combined pericemental area equal to or
greater in pericemental area than the tooth or teeth to be replaced
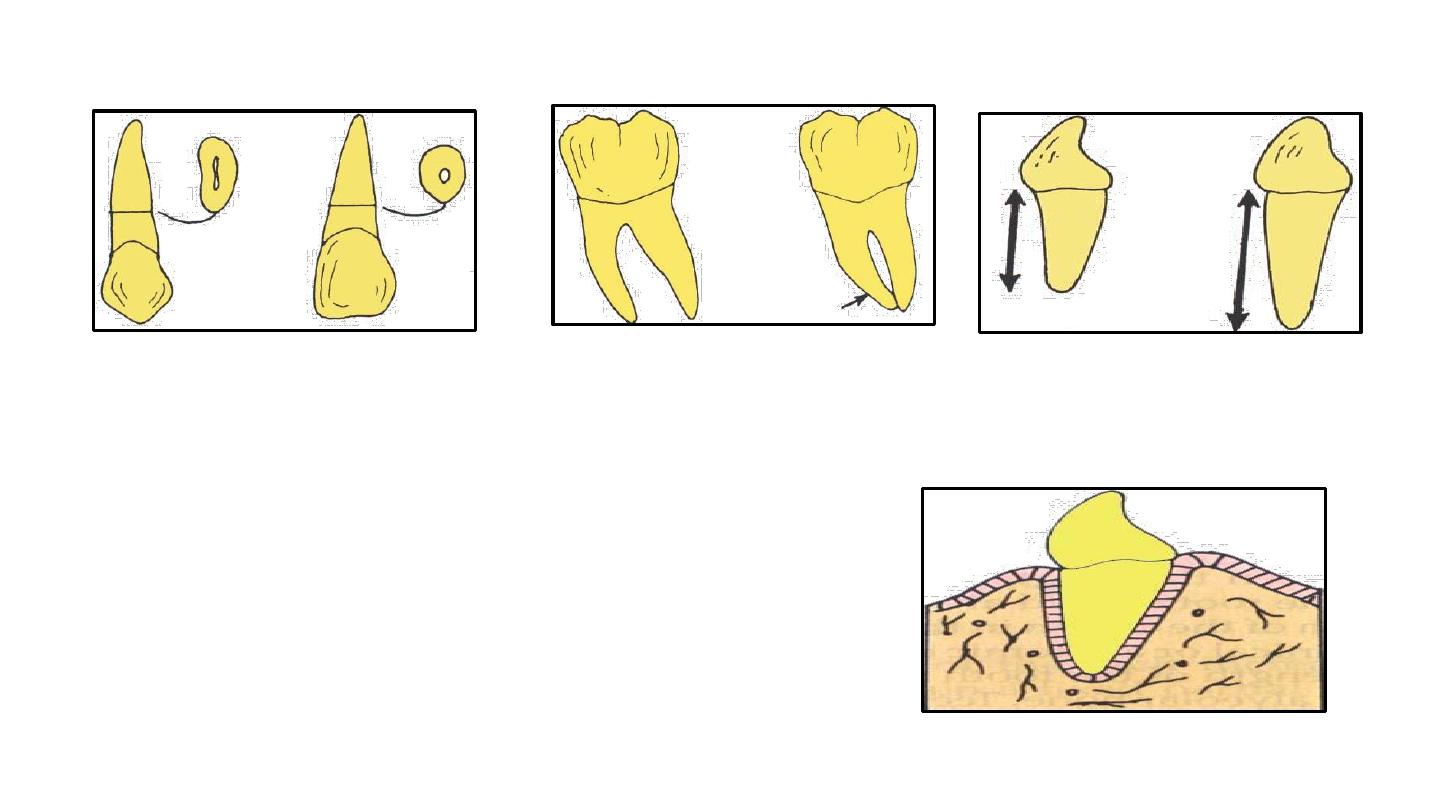
Roots with irregular curvatures are preferred
Teeth with longer roots
serve as better abutments
One third of the root length has been exposed, half
the supporting area is lost. In addition, the forces
applied to the supporting bone are magnified
because of the greater leverage associated with the
lengthened clinical crown
.
The abutment should have sufficient
bone support. The alveolar bone
should show good trabecular pattern
5-Root Shape and Angulation.
6-Root Support
Roots with greater labiolingual widths

The four mandibular incisors can usually be replaced by a simple FDP with retainers on each canine
tooth. It is not usually necessary to include the first premolars.
If a lone incisor remains, it should be
removed
because its retention unnecessarily complicates the
FDP design and fabrication and can jeopardize the long-term prognosis.Mandibular incisors, because
of their small size, generally are poor abutment teeth. It is particularly important not to have
overcontoured restorations on these teeth because plaque control may become nearly
impossible
.
The clinician may have to make a choice among :
(1) compromised esthetics from too thin a ceramic veneer.
(2) pulpal exposure during tooth preparation.
(3) selective tooth removal.
Because of the
curvature
of the dental arch, forces directed against a maxillary incisor pontic tend to
tip the abutment teeth outward. Unlike the mandibular incisors, the maxillary incisors are not
positioned in a straight line (particularly in patients with narrow or pointed dental arches). These
tipping forces must be resisted by means of additional abutment teeth at each end of a long-span
anterior FDP. Thus in general, when the four maxillary incisors are replaced, the canine teeth and first
premolars should be used as abutment teeth.
5-Replacing Multiple Anterior Teeth
.
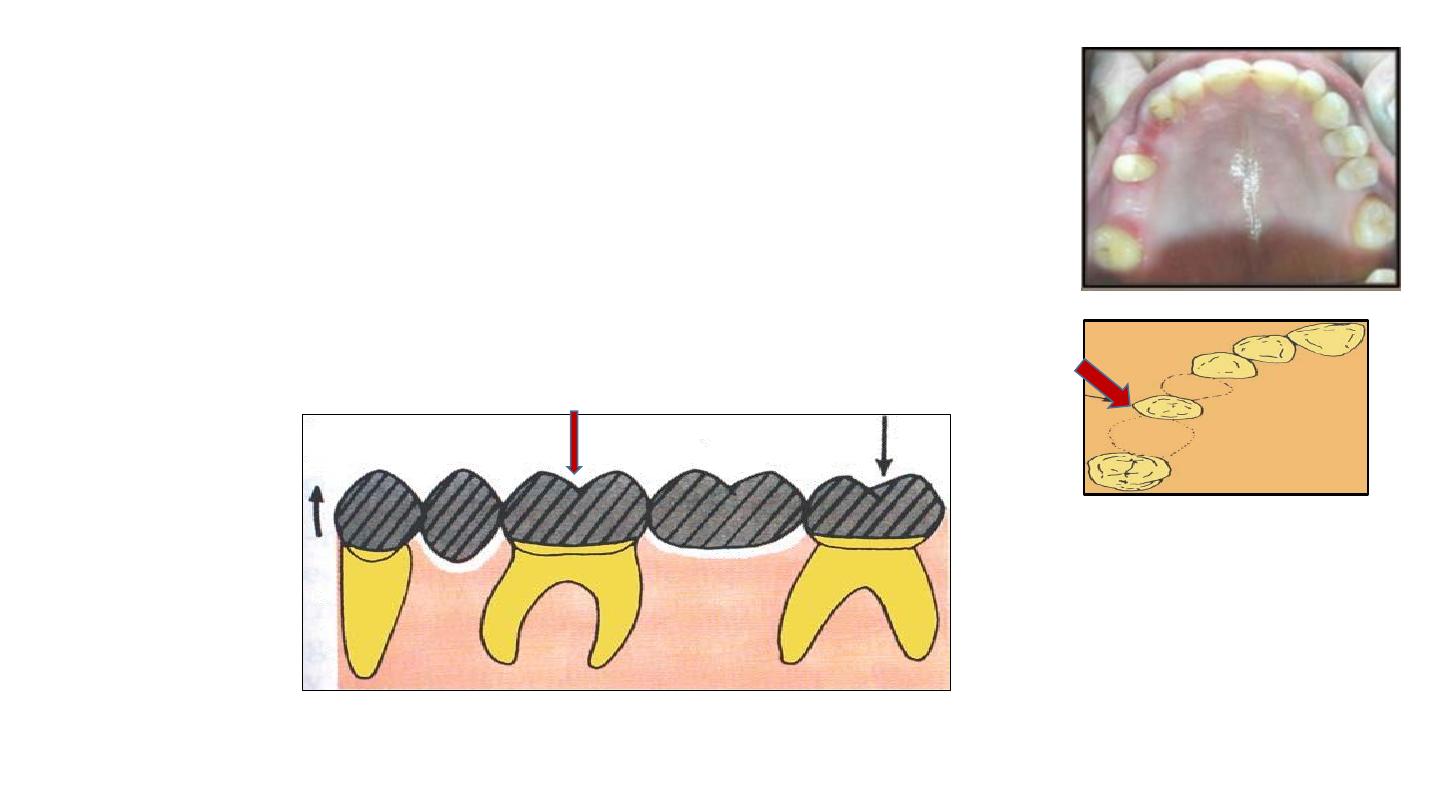
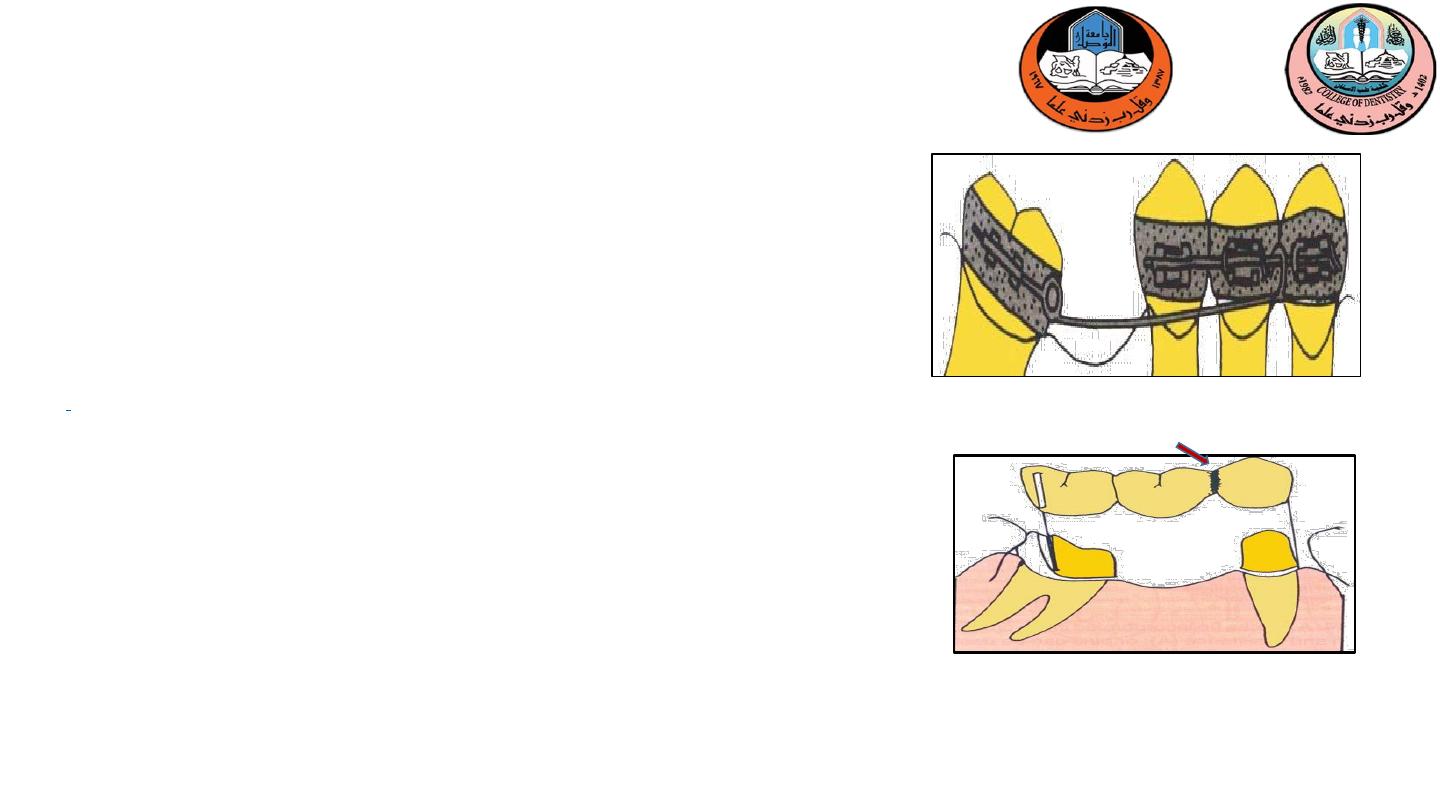
A Pier abutment is a single tooth with two adjacent
edentulous spaces on either side. In this case, the single tooth
will have to act as an abutment for both the edentulous
spaces
6-Pier abutment

Rocking of retainer
Bending of retainer
Tension between abutment and retainer
Intrusion of retainer on abutment
What are the problem???
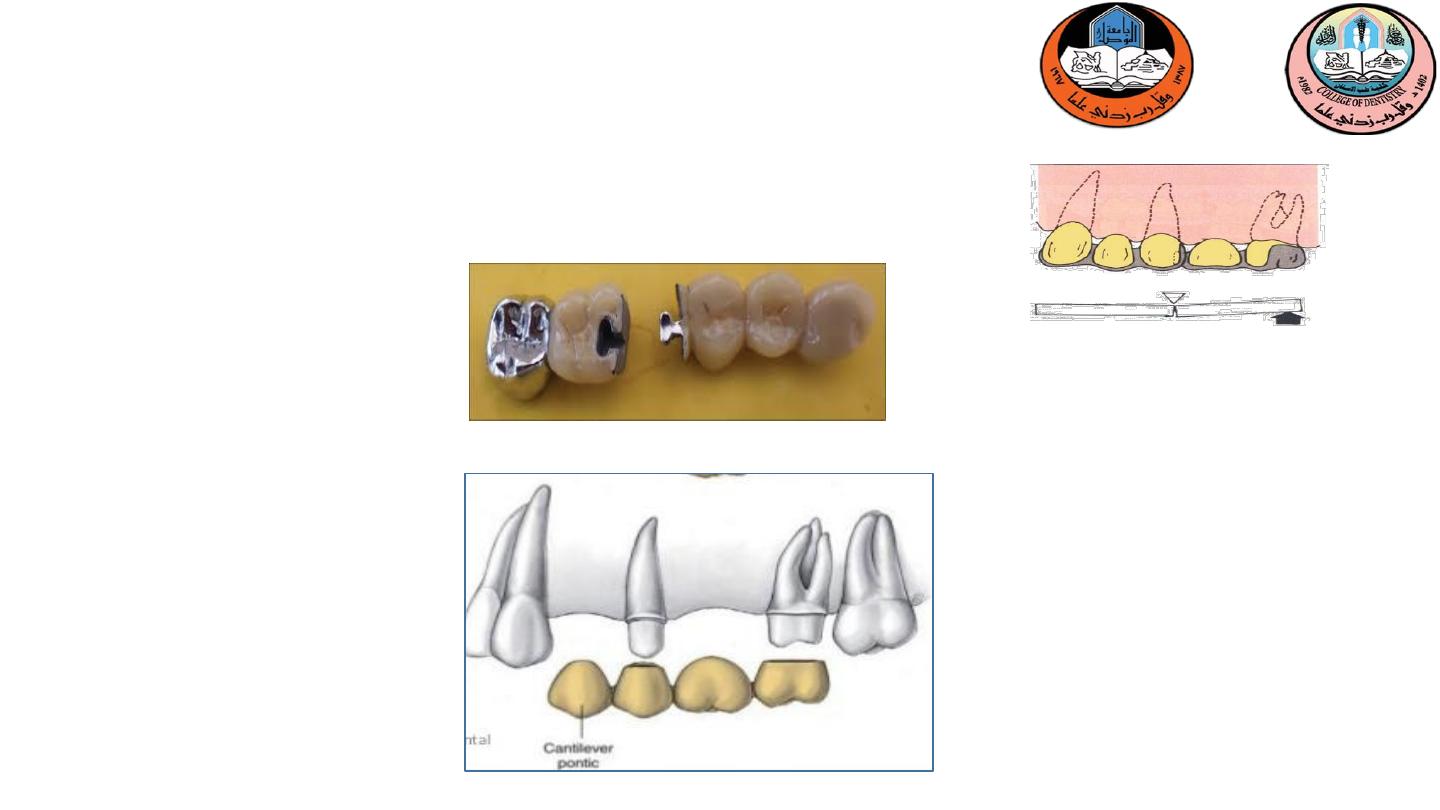
a. Non rigid connector
:
broken stress mechanical union
of retainer (dovetail keyway) and pontics (T -shaped key).
b
.
Cantilever
A nonrigid connector on
the pier abutment isolates
force to that segment of
the fixed partial denture
to which it is applied
1
2
Two alternatives are there to minimizes the stress

Span length
is the distance between abutments affects the viability of
placing fixed prostheses
7-Span length
Ideal for one missing teeth
loss of 2-3 adjacent teeth requires careful evaluation
of other factors (crownroot ratio, root length and
form, periodontal health, tooth mobility, occlusal
force and biomechanical factor)
Excessive flexing under occlusal loads may cause
1-Failure of a long-span FDP. It can lead to fracture of a
porcelain veneer
2-Breakage of a connector
3-Loosening of a retainer, or an unfavorable soft tissue
response and thus render a prosthesis useless.
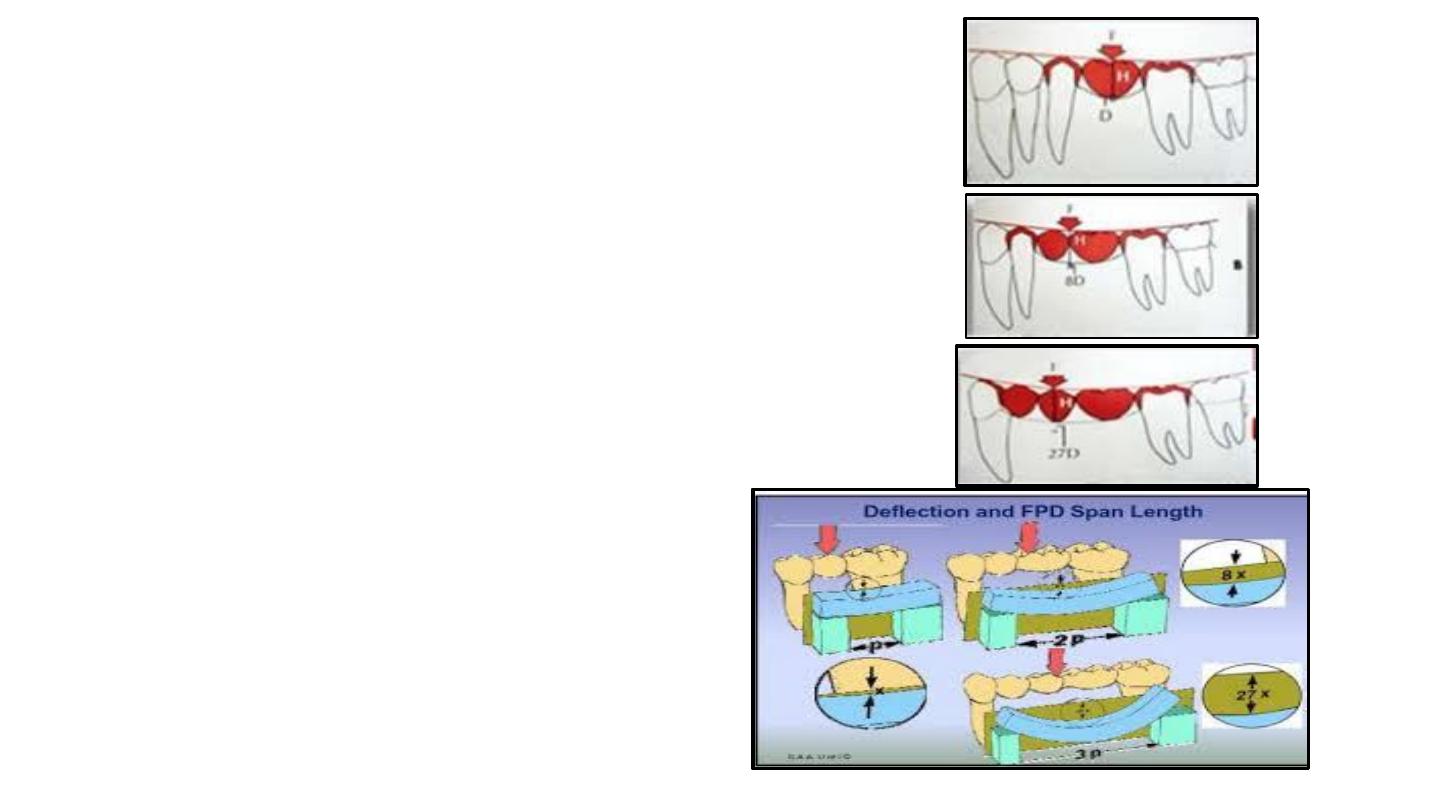
The
longer
the span, the greater the
flexing
. The relationship
between deflection and length of span is not simply linear but
varies with the
cube
of the length of the span .
Bending or deflection varies directly with the cube of the length
and
inversely
with the cube of the occlusogingival thickness of
the pontic. more toruquing forces on the abutment.
If a span of a
single
pontic is deflected a certain amount, a span
of
two
similar pontics will move
eight times
as much, and a span
of
three
will move 27 times as much.
(Length of the Fixed Partial Denture)3
Flexion=______________________________________
(Occlusogingival Height of the Pontic)3

When long span F.P.D. fabricated:
1) Using
double abutments
to enhance retention and support
for long span FPD (anterior & posterior abutments should
have nearly the same retention and resistance ).
2) Pontics & connectors should be made as bulk as possible
to ensure optimum rigidity without jeopardizing gingival
health.
3) The prosthesis should made be of a material that has high
strength & rigidity
.
U N I V E R S I T Y O F M O S U L
C O L L E G E O F D E N T I S T R Y
2020-2021
1-Contemporary fixed prosthodontics
2-Textbook of Prosthodontics
References
:
Thank you for your nice attention
