Cytosis: Exocytosis or Endocytosis
Phagocytosis (cell eating)Pinocytosis (cell drinking)
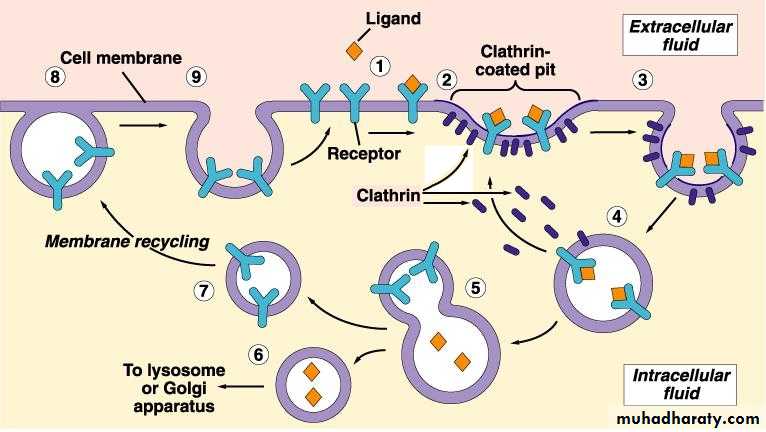
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Formation of Interstitial Fluid and Lymph
Types of Capillaries: Type 1, 2, and 3.Starling Forces that determine fluid movement through the capillary membrane
The capillary hydrostatic pressureThe interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
The plasma colloid osmotic pressure
The interstitial fluid colloid osmotic pressure
Capillary permeability
Main functions of Lymph:
1. Return of proteins to blood from tissue spaces.2. Fat from intestine are mainly absorbed through lymph.
3. Maintain fluid distribution in body.
90%
10%
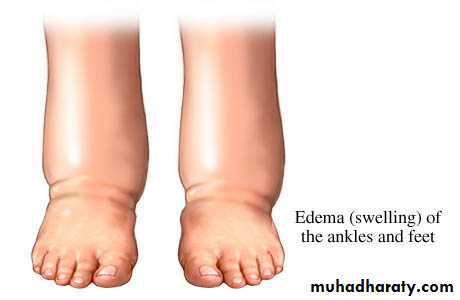
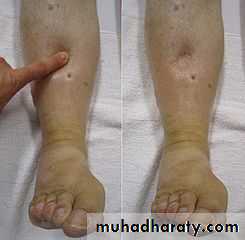
Edema: Disturbance of water balance in which there is an excess of fluid (a 10% increase in tissue spaces and serous cavities of the body.
The factors that cause edema are:
1. Increase in capillary hydrostatic pressure.2. Decrease in plasma oncotic pressure or an increase in interstitial oncotic pressure.
3. Obstruction of lymphatic drainage (lymphedema).
Protection factors against edema: An increase in interstitial fluid volume lead to:
ʘ An increase in lymphatic flowʘ A decrease in interstitial oncotic
ʘ The increase in interstitial fluid volume will cause the interstitial hydrostatic pressure to rise..