White & Red Lesions of The Oral Mucosa
By:Dr. Ahmed Salih KhudhurBDS, MSc, PhD Newcastle University/ UK
دكتور احمد صالح خضر
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Department of:
HERE
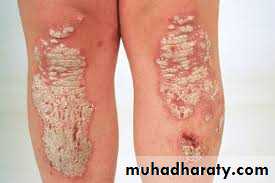
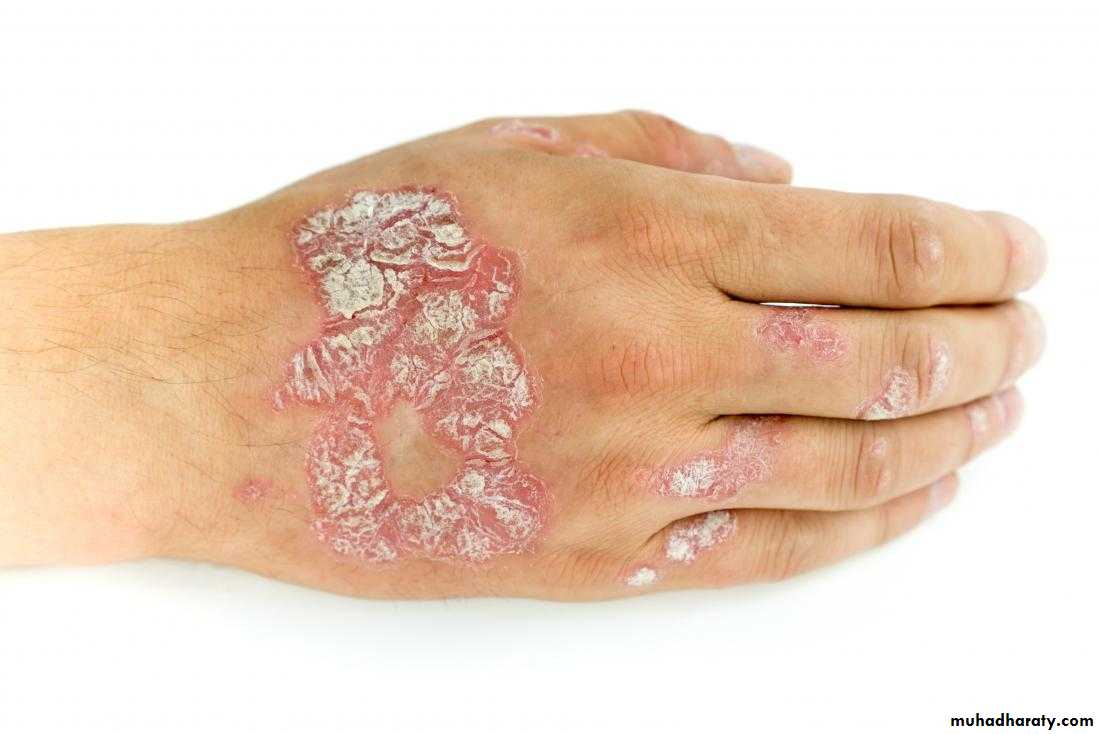
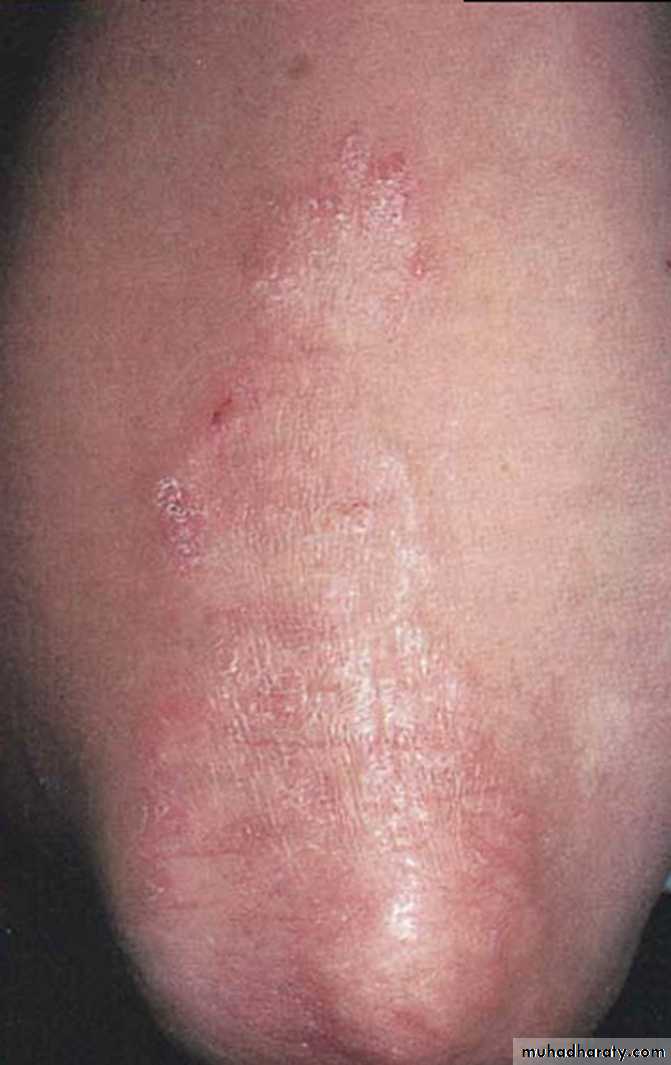
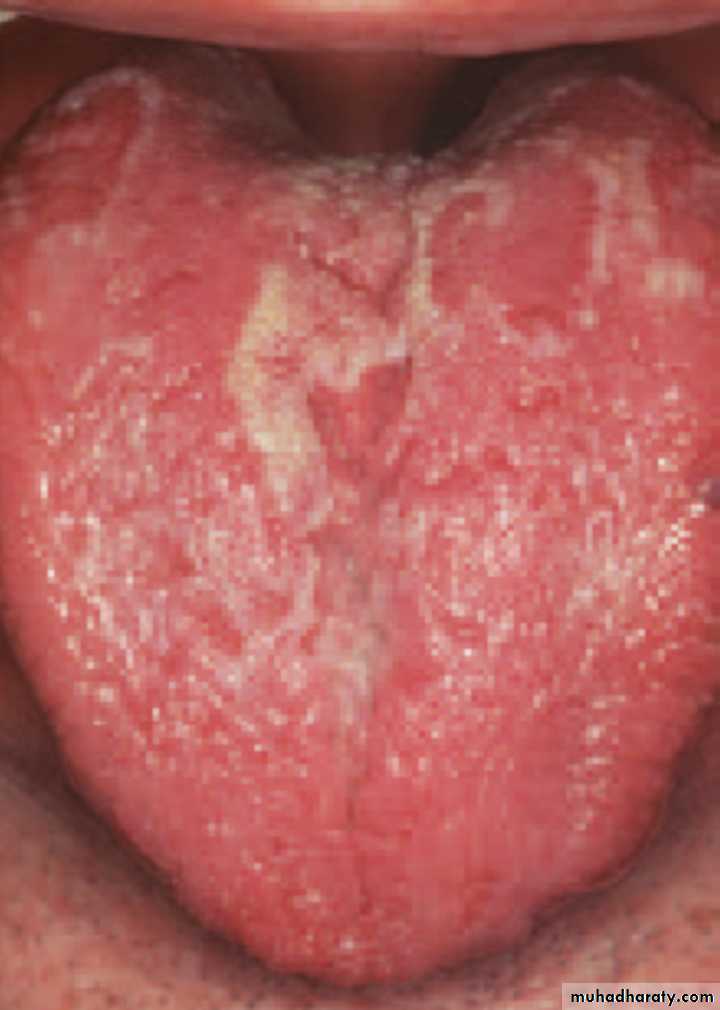
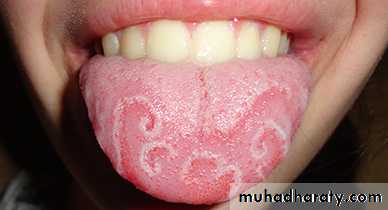
Psoriasis
•
Oral Psoriasis
•Oral Psoriasis
Leukoplakia• Leukoplakia (Leuko=white & Plakia= patch): It’s defined as a white patch which cannot be wiped of the oral mucosa or ascribed to any specific disease process
• _______________________________________________________________
Clinical features:
Sites of oral leukoplakia:
• _______________________________________________________________
• Etiology of Leukoplakia
Local factors:
Systemic factors:
Subtypes of Leukoplakia
• Varieties of OLK have been identified:Homogeneous leukoplakia or thick leukoplakia (LK or HLK)
Nodular (speckled) leukoplakia (NLK, or SLK)
Verrucous leukoplakia or verruciform leukoplakia (VL)
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL)
Other types such as candidal leukoplakia & syphilitic leukoplakia (discussed previously)
Homogeneous leukoplakia or thick leukoplakia
Refers to a usually well-defined white patch, localized or extensive, which is slightly elevated and may have a fissured, wrinkled, or corrugated surface•
Homogeneous leukoplakia or thick leukoplakia
White, thick plaque with a corrugated surface on the floor of the mouth. A biopsy showed hyperkeratosis with moderate epithelial dysplasiaHomogeneous leukoplakia or thick leukoplakia
Large white plaque on the right buccal mucosa. The lesion exhibits thick and thin areas. A biopsy showed hyperkeratosis with moderate epithelial dysplasiaHomogeneous leukoplakia or thick leukoplakia
A diffuse, corrugated white patch on the right ventral surface of the tongue and floor of mouth
Homogeneous leukoplakia or thick leukoplakia
Extensive buccal mucosal lesion with uneven whiteness and fissures. Moderate epithelial dysplasia was noted on histopathological evaluation, and squamous cell carcinoma later developed in this areaHomogeneous leukoplakia or thick leukoplakia
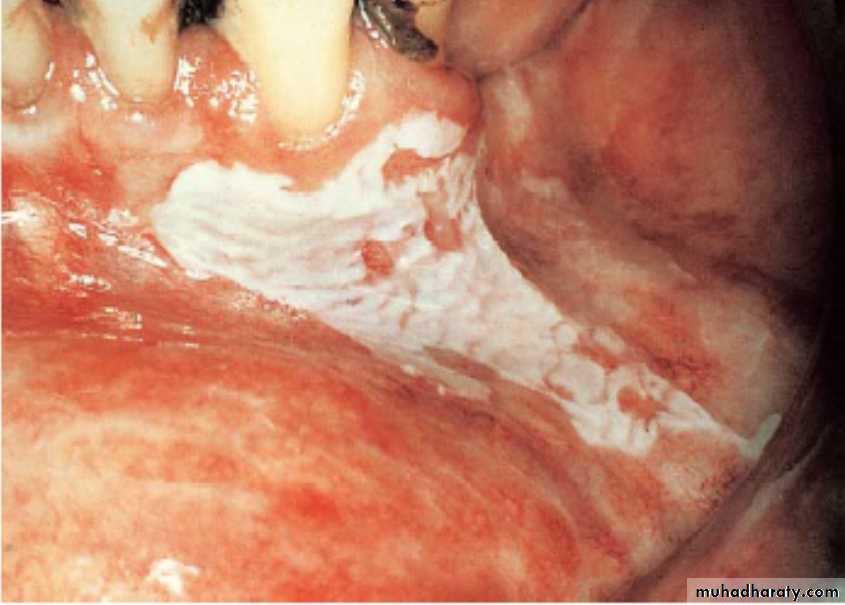
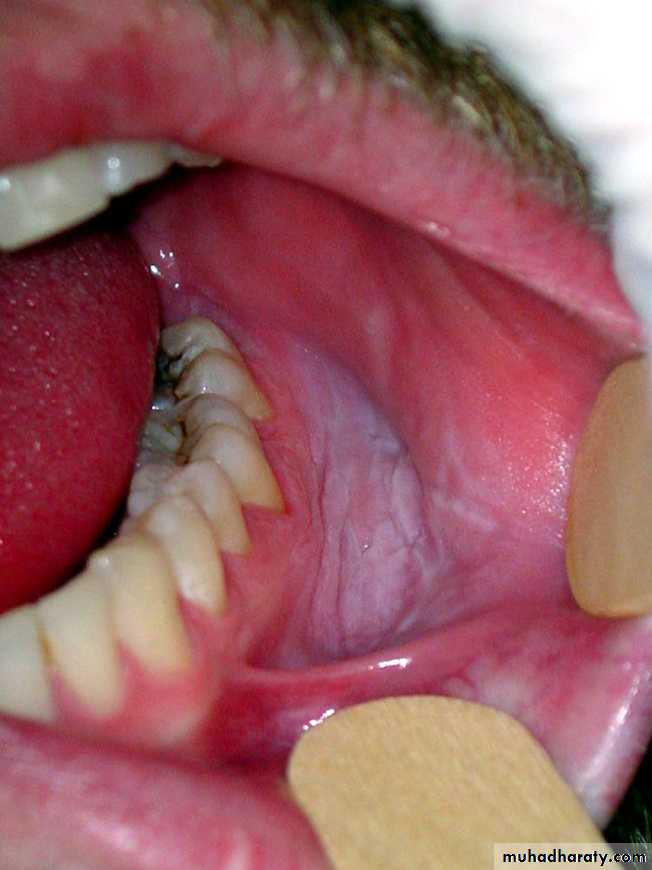
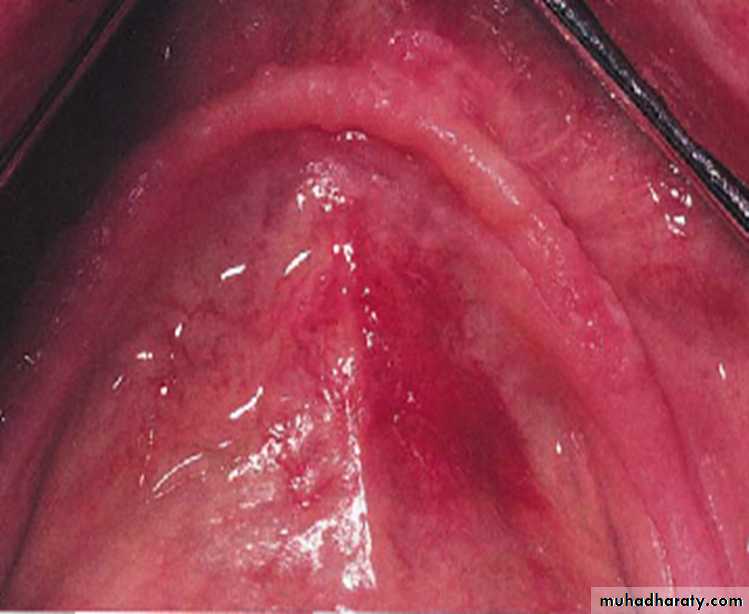
Thick white patch with corrugated surface on the attached (alveolar) gingivae of the lower anterior teeth•
Homogeneous leukoplakia or thick leukoplakia
Oral Leukoplakia in the buccal sulcus of a• Tobacco chewing patient
•
Homogeneous leukoplakia or thick leukoplakia
Poorly defined leukoplakia on the right latero-dorsal side of the tongue, this innocent looking lesion showed dysplasia in histopathology with malignant transformation later•
Homogeneous leukoplakia or thick leukoplakia
White patch with dysplsaia. Post-commissural lesion is poorly defined and comprises of both white and red areas•
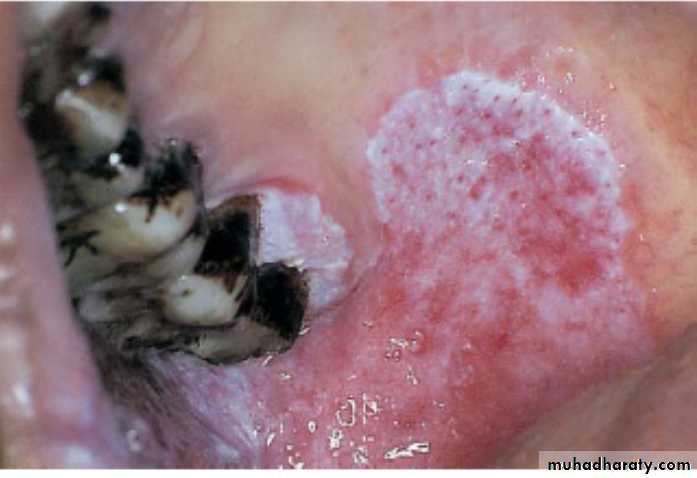
Nodular (speckled) leukoplakia
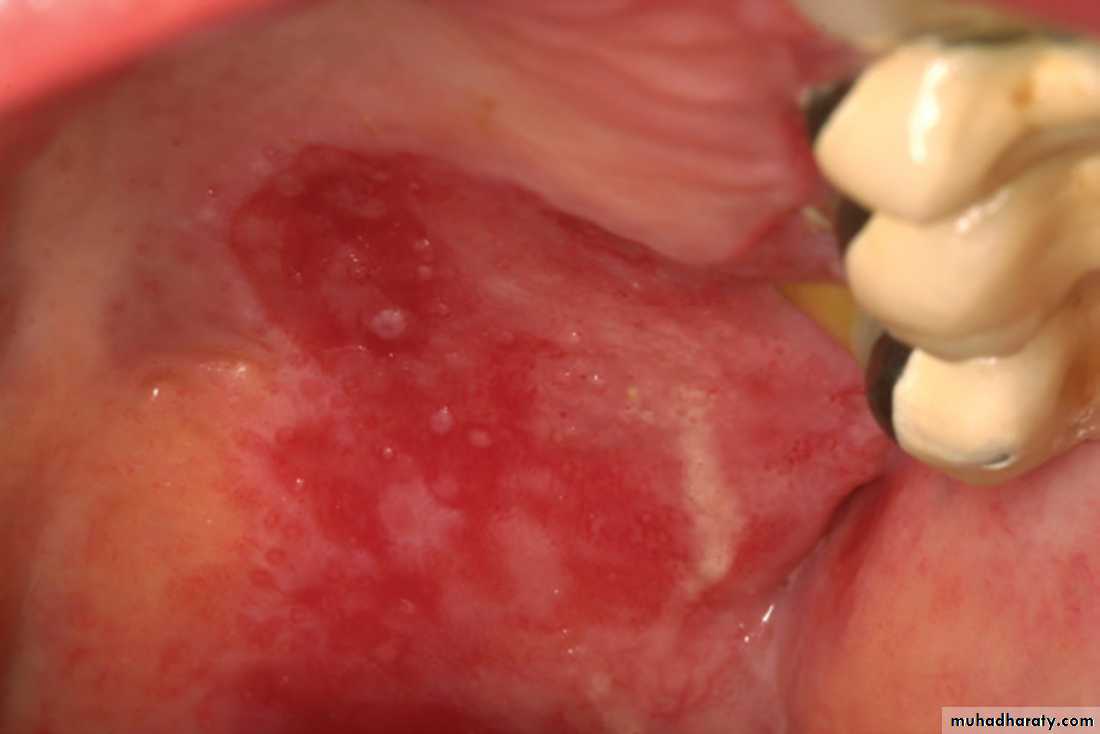
White and red plaque with a granular surface on the buccal mucosa extending to the commissureNodular (speckled) leukoplakia
White and red plaque with a granular surface on the buccal mucosa
•
Nodular (speckled) leukoplakia
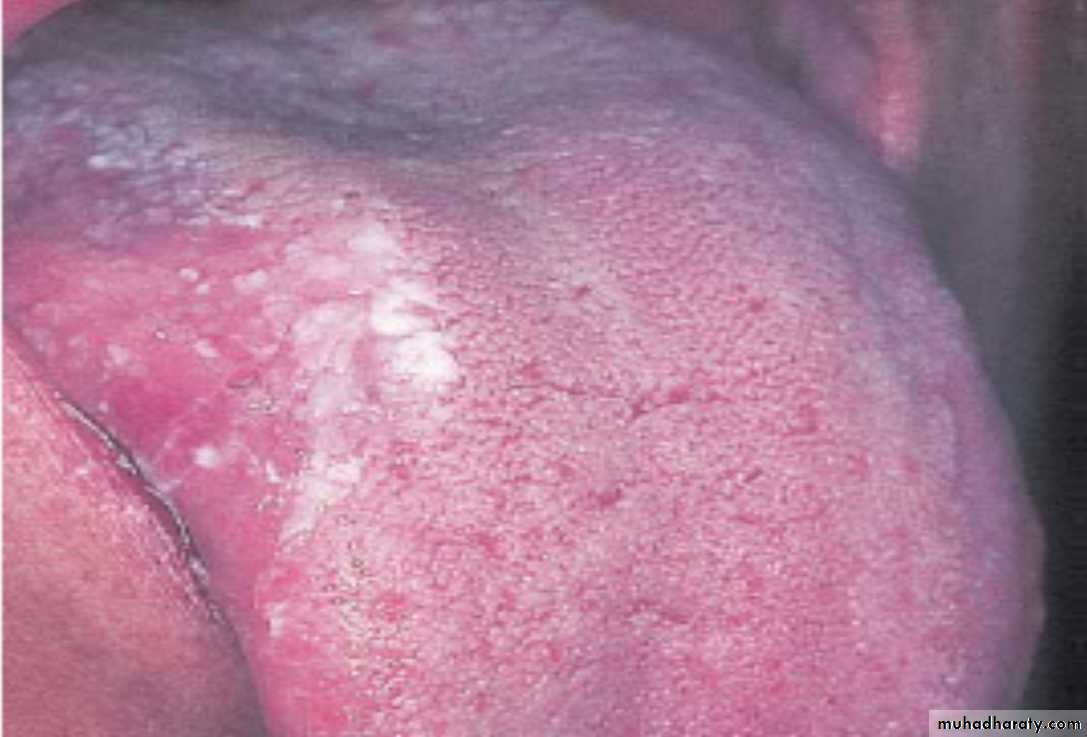
Granular Leukoplakia. Focal leukoplakic lesion with a rough, granular surface on the posterior lateral border of the tongue. Biopsy revealed an early invasive squamous cell carcinomaNodular (speckled) leukoplakia
Speckled (granular) leukoplakia on the posterior part of the palate extending to the palatal gingivae adjacent to the upper molar teeth, maxillary tuberosity and posterior part of the buccal mucosa•
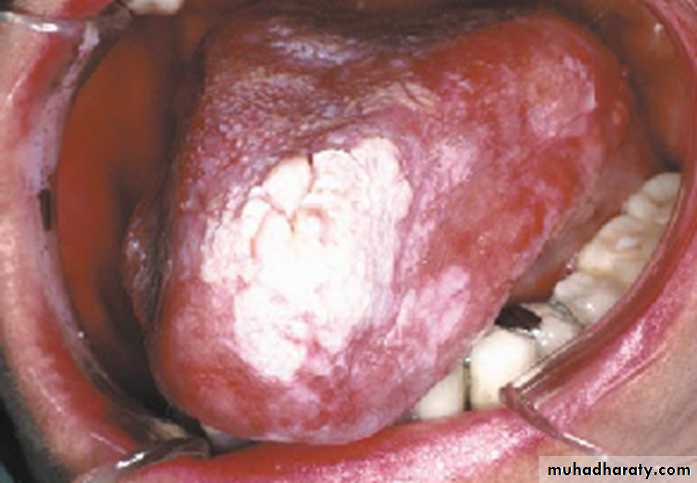
Verrucous leukoplakia or verruciform leukoplakia
VL on the dorsum of the tongue•
Verrucous leukoplakia or verruciform leukoplakia
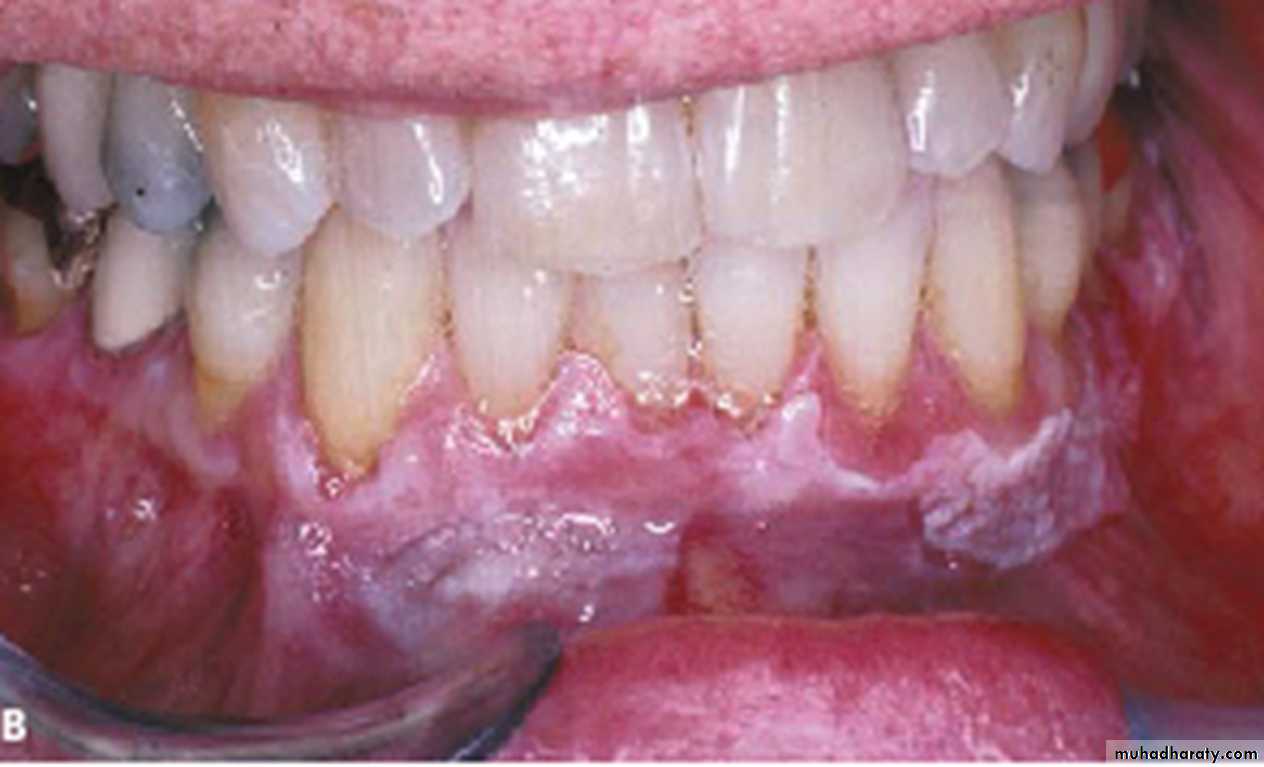
VL white linear plaque involving the labial marginal gingiva of the lower anterior teeth
Verrucous leukoplakia or verruciform leukoplakia
Patient with extensive white plaque on the buccal mucosa (VL)Verrucous leukoplakia or verruciform leukoplakia
• Diffused, corrugated, white lesions of the buccal andpalatal mucosa
• Thickened, corrugated, white lesion involving thepalate, alveolar ridge, and palatal marginal gingiva
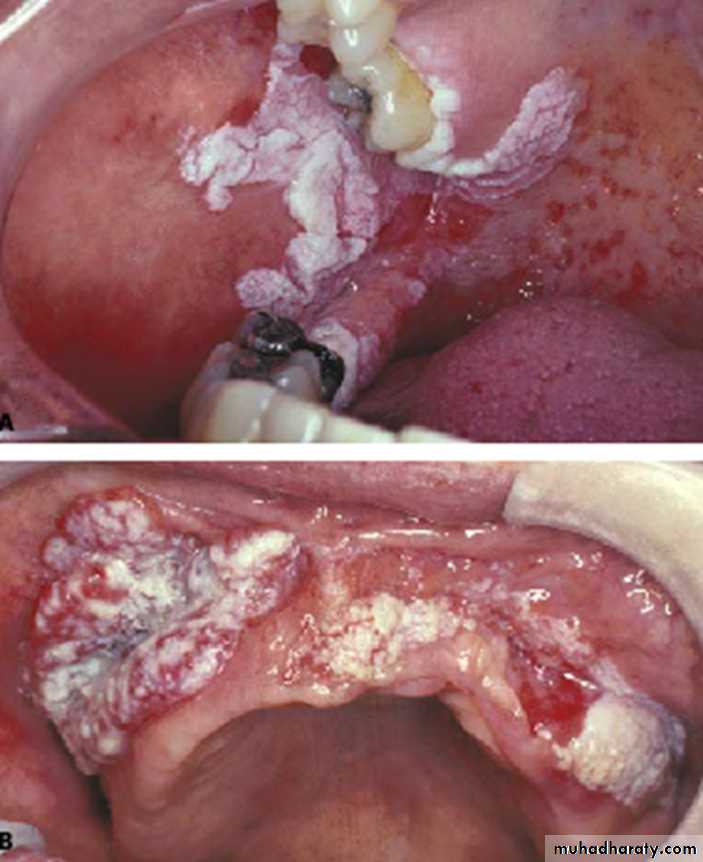
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
• PVL with malignant transformation•
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
• An elderly white female developed extensiveleukoplakia with rough surface projections on the
buccal mucosa and mandibular alveolar ridge• After failing to comply with a recommendation for
biopsy, the same patient returned 2 years later with averrucous carcinoma
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakiaDiffused, thick, white plaque with verrucous surface involving the labial mandibular gingiva and adjacent vestibule
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
An extensive proliferative verrucous leukoplakia in an 80 year old womanProliferative verrucous leukoplakia
Ventral surface of the tongue exhibiting a large, white plaque with a rough, warty surface
Leukoplakia
• Diagnosis of leukoplakia:• 1.History & Clinical examination 2.Biopsy
• Treatment of leukoplakia:
Elimination of etiological factors
Vitamin supplement & therapy (Vitamins A ,E and B complex)
Conventional surgery (Excision)Cryosurgery
Laser therapyFollow up
Sublingual keratosis• The term ‘sublingual keratosis’ is applied to white lesions on the floor of mouth
• and ventral surface of the tongue
• It’s unclear whether this lesion is a different entity from other leukoplakias
• Clinical features:
• Pathology:
• Treatment: Same as leukoplakia
Sublingual keratosis
Sublingual keratosis. This white patch involving the entire ventral tongue and floor of mouth has a uniformly wrinkled appearance. No red areas are associated but the site alone may possibly indicate a high risk of malignant transformation
Sublingual keratosis
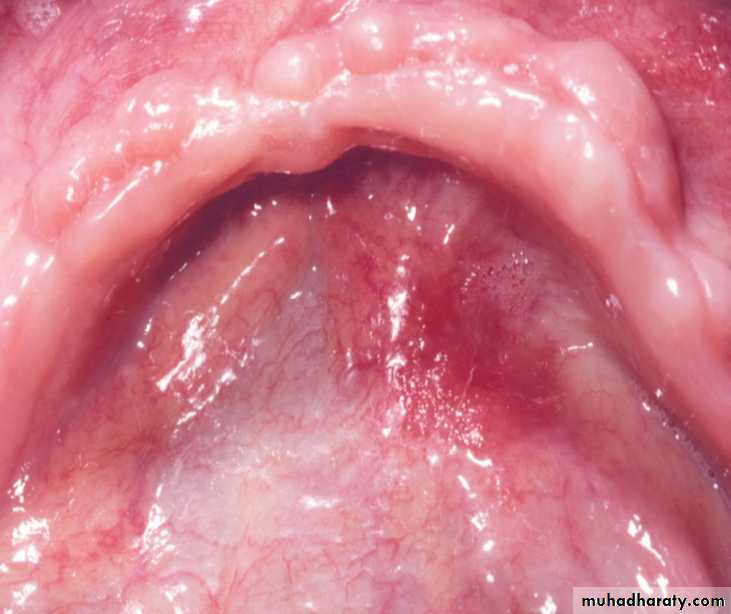
Sublingual keratosis. This more irregular white patch is associated with some reddening in the floor of the mouth, which may have a high risk of malignant transformationErythroplakia (Erythroplasia)
• It’s defined as a red lesion, patch or plaque that cannot be characterized clinically• or pathologically as any other condition
• The prevalence of oral erythroplakia ranges from 0.01% to 0.83% of population
• Though it’s uncommon in the oral cavity, but it possesses high risk for malignant
• transformation and half of the lesions often show malignancy on the first biopsy
• Major risk factors include tobacco and alcohol use
• Clinical features:
• Homogenous Erythroplakia, Erythroleukoplakia & Granular or speckled
• erythroplakia
Erythroplakia (Erythroplasia)
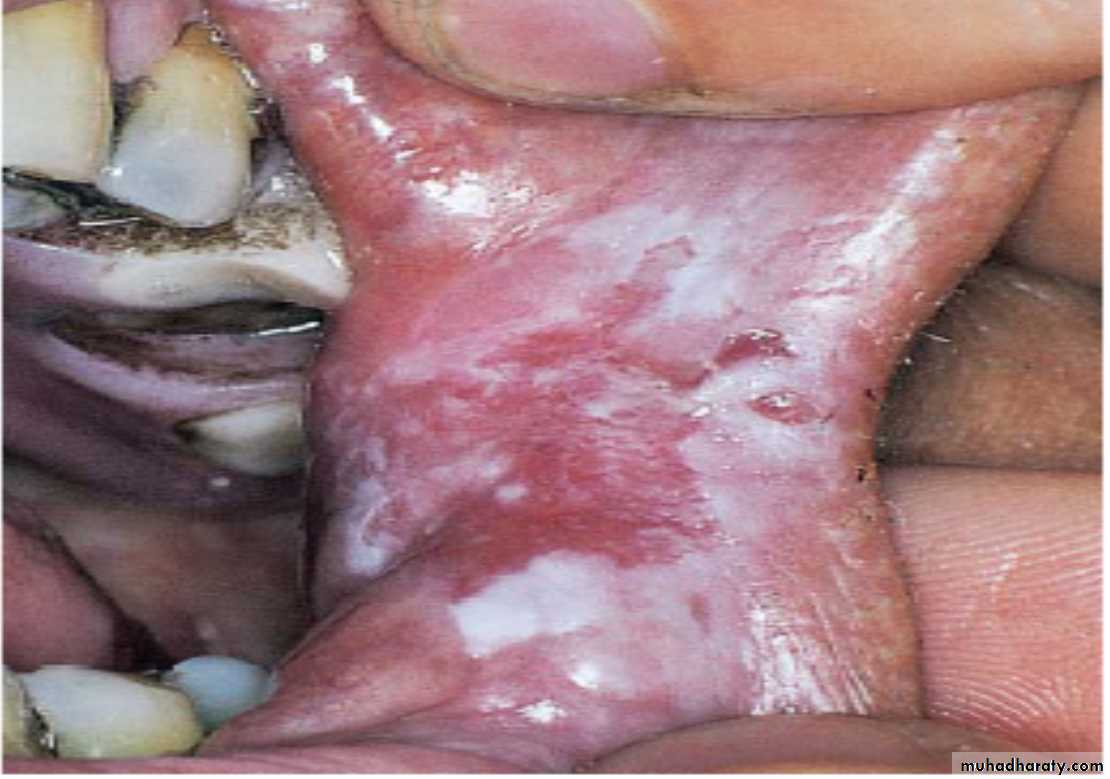
Erythroplakia. This slightly depressed, well-defined red patch on the dorsolateral tongue showed squamous cell carcinoma on biopsyErythroplakia (Erythroplasia)
Erythroplakia at the alveolar ridge. The patient later developed a squamous cell carcinomaErythroplakia (Erythroplasia)
Erythroplakia. Erythematous macule on the right floor of the mouth. Biopsy showed early invasive squamous cell carcinoma
Erythroplakia (Erythroplasia)
Erythroplakia. Well-circumscribed red patch on the posterior lateral hard and soft palateErythroplakia (Erythroplasia)
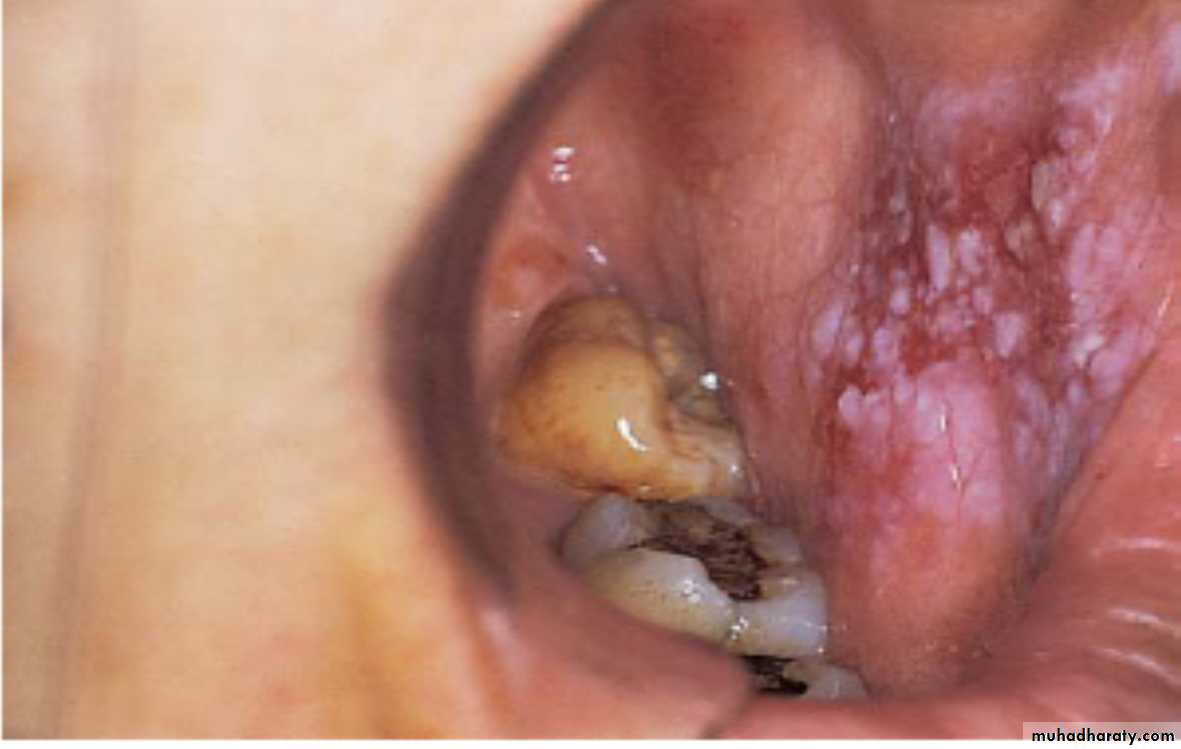
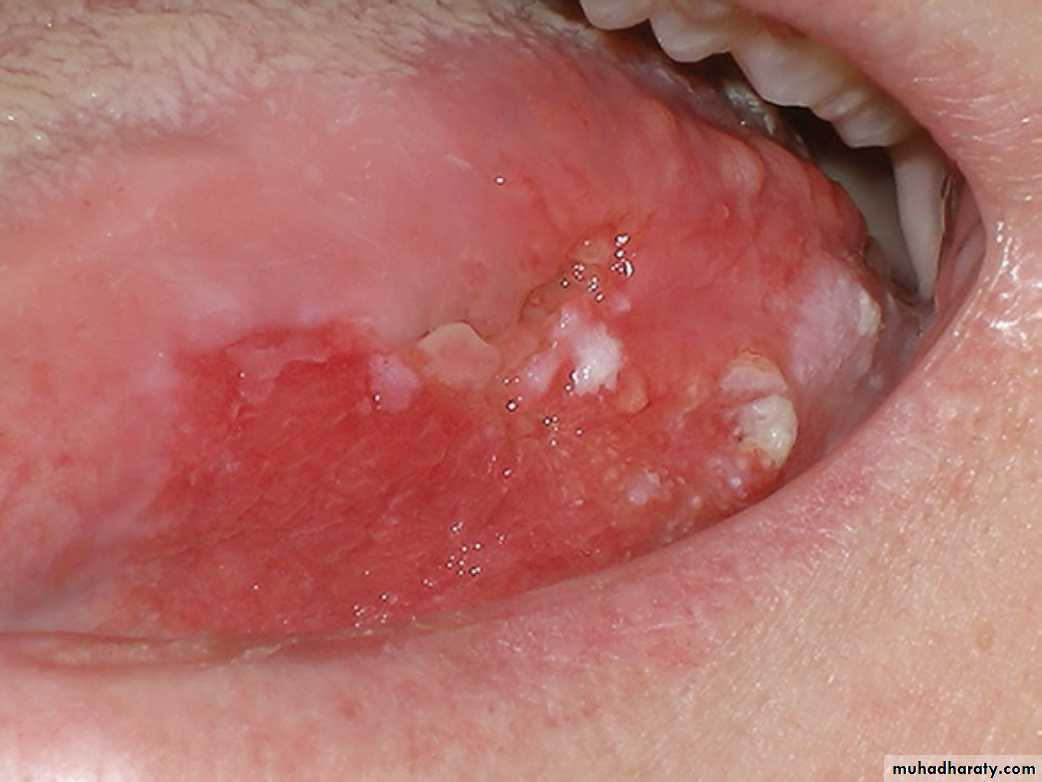
Erythroplakia. Right posterior buccal mucosa showing an erythematous lesion with ulceration. A biopsy showed carcinoma in situErythroplakia (Erythroplasia)
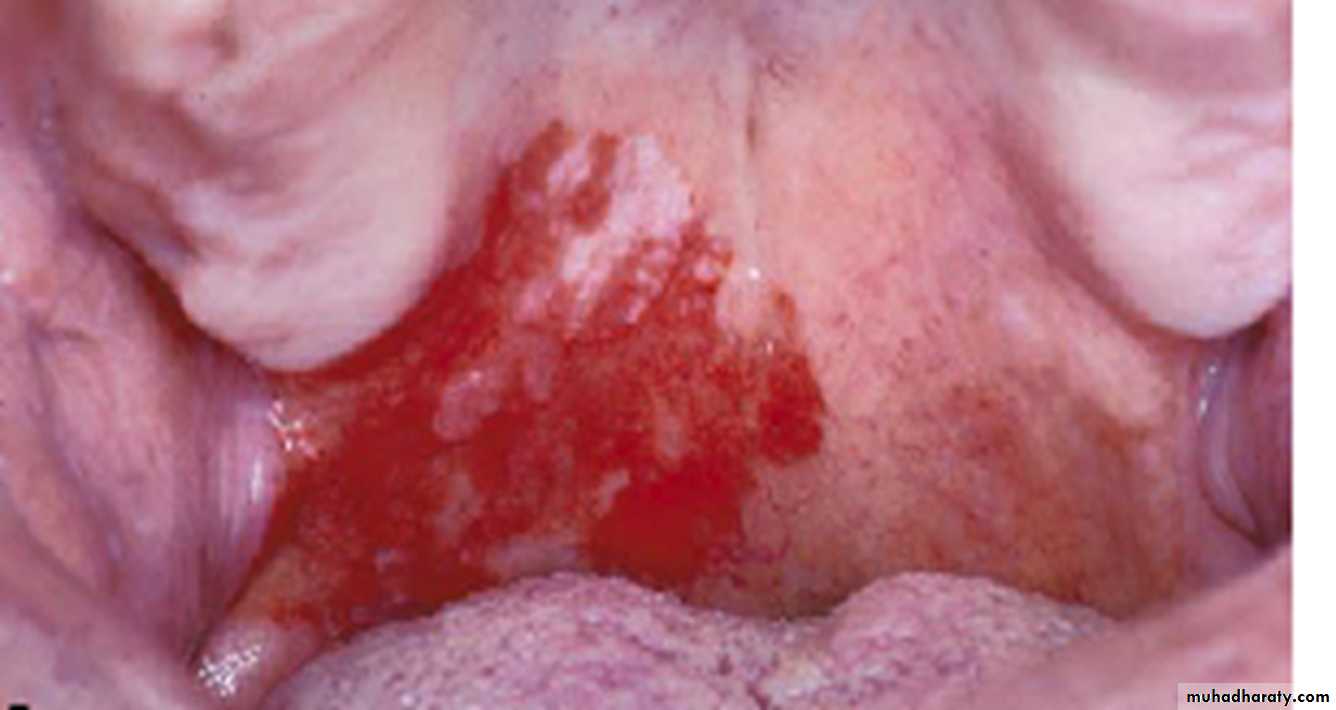
Erythroplakia. Erythematous plaque on the soft and hard palateErythroplakia (Erythroplasia)
Erythroplakia. Red and white plaque involving the left posterior ventrolateral tongue. A biopsy showed squamous cell carcinoma.Erythroplakia (Erythroplasia)
An erythroleukoplakia on the hard and soft palate with malignant transformationErythroplakia (Erythroplasia)
• Diagnosis of erythroplakia• 1.History & Clinical examination
• 2.Toluidine blue test (stain the lesion with 1% to demonstrate areas with possible
• premalignant or malignant changes)
• 3.Laboratory diagnosis (Especially Biopsy)
• Treatment of erythroplakia
• Removal of the a suspected irritants
• Surgical excision
• Laser ablation
• Cryotherapy
• Long-term clinical follow up (Every 3months for 1st postoperative year, then every
• 6months for an additional 4 years)
THE END
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021