Temporomandibular joint disorders- II
Dr. Mohammed AmjedBDS, MSc, PhD
4.2.2021
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
1
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
2Objectives
Revision Of different TMJ Surgery
Rheumatoid arthritisSystemic Arthritic Conditions
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disorder associated with synovial membrane inflammation in several joints.
The TMJs are involved in approximately half of affected individuals.
Villous synovitis leads to the formation of synovial granulomatous tissue (pannus) (synovial hyperplasia).
The pannus releases enzymes that cause cartilage/ bone destruction.
WBC exudate inside the joint Collagenase ErosionDr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
3What is Still's disease?
Clinical features
• Pain over TMJs.• Tenderness over TMJs.
• Swelling over TMJs.
• Stiffness and limitation of opening.
• Crepitus.
• Developing anterior open bite and retrusion of chin in advanced disease.
• involvement of other joint is seen as Joints of hands, wrists, knees and feet.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
4
Radiology
it is not specific!
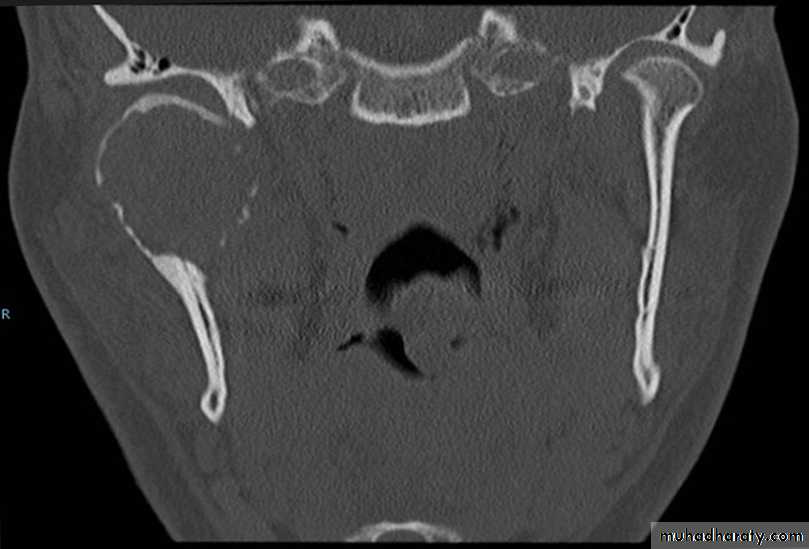
# Radiology demonstrates reduction in bone density in the TMJ.
# Marked erosion of the condylar head and articular fossa.
# Narrowing of the joint space.
In long-standing disease, there is:
• destruction of entire condyle• anterior open bite
• secondary osteoarthrosis
• ankylosis.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
5Management (Conservative)
• Physiotherapy + soft diet + avoid extreme joint movement
• Analgesics/anti-inflammatory drugs
• Steroids
• If steroid not effective, cytotoxic agent like methotrexate.
• Intra articular steroid injection in acute phase
Rheumatoid arthritis
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
6
Management (Surgical)
Sever cases surgery is indicates in intractable pain or for correction of complication like micrognathia and ankyloses.
1. Arthroplasty for total joint replacement
2. High condylectomy in intractable pain
3. Synovectomy
Hyperuricemia: In this disorder, crystals of sodium urate in periarticular tissues increase which lead to, warmness, tenderness to palpation and pain in mandibular movement. Gout is a common hereditary disease in men. In laboratory tests, uric acid and ESR in blood is high. In radiography, punch-out bone erosions can be seen.
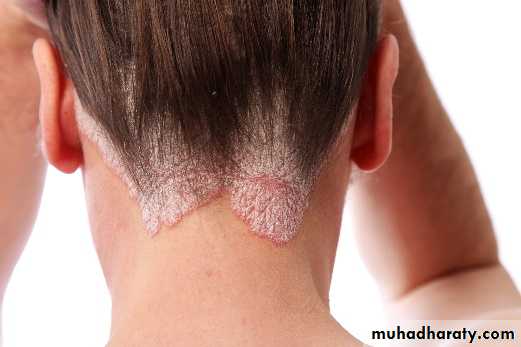
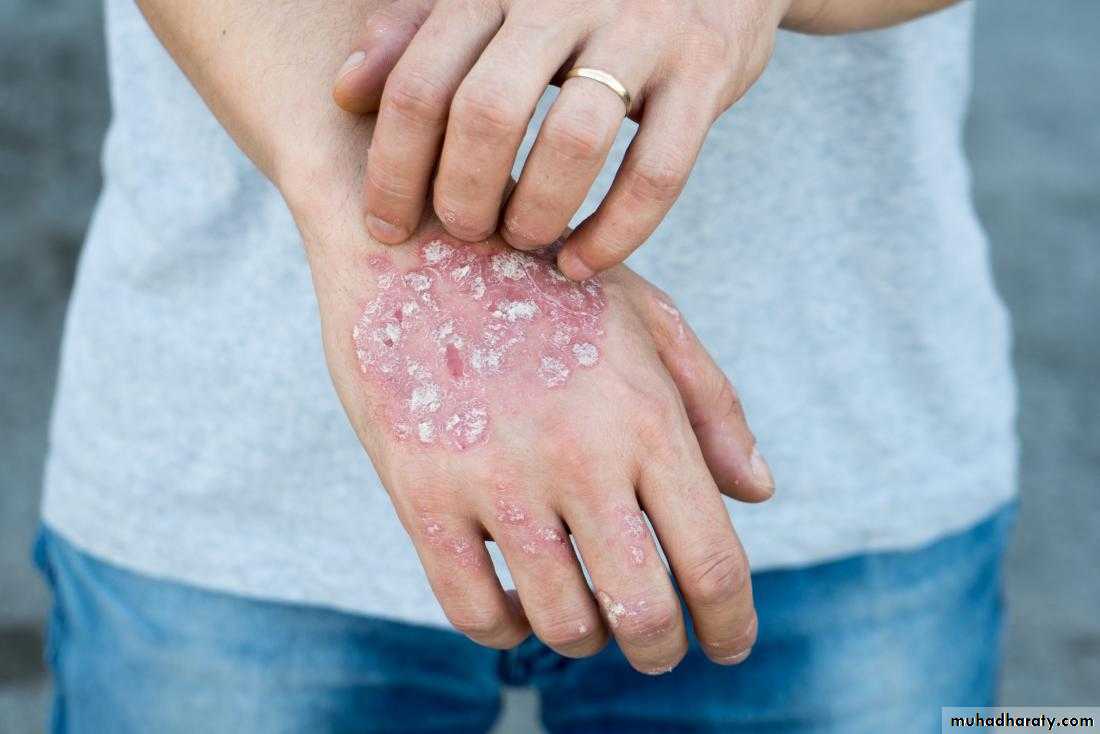
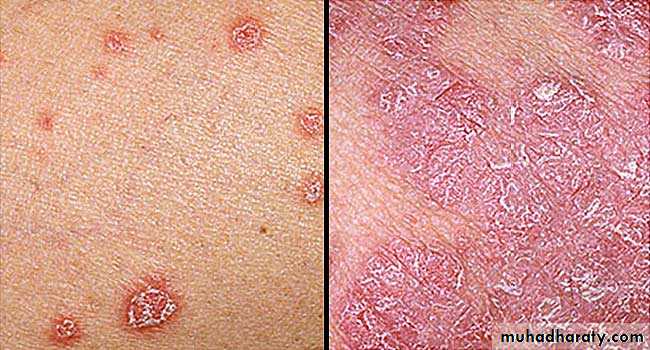
Psoriatic arthritis: It resembles the rheumatoid type, but it is associated with psoriasis, a dermatologic disease. Radiographic findings reveal osteoarthritis changes with erosion, osteoporosis and narrowing of articular space. This polyarthritis is asymmetric. –ve seriological test for Rh. fever.
Systemic Arthritic Conditions
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
7
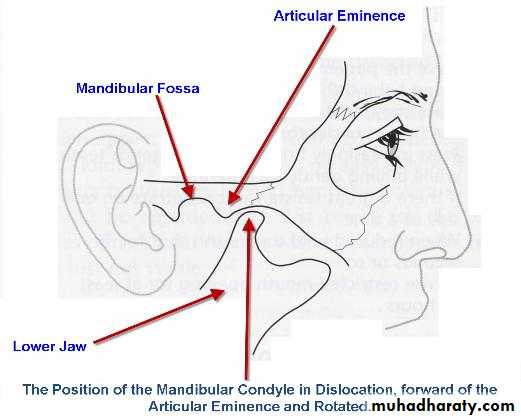
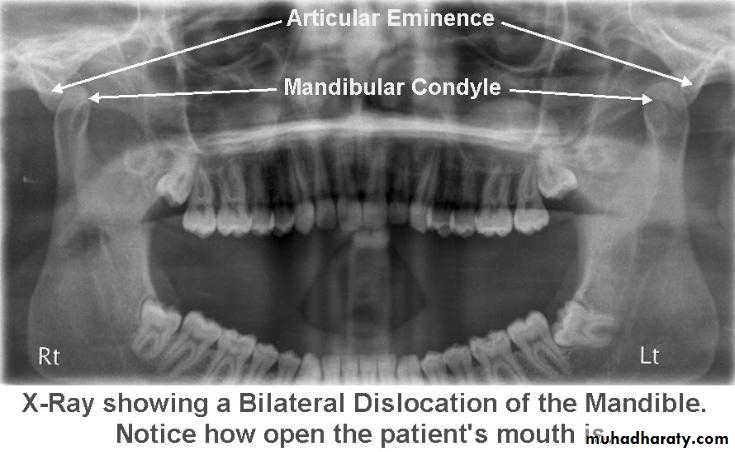
• The condyle is abnormally positioned outside the mandibular fossa but within the joint capsule.
• Dislocation may occur during trauma or be caused by failure of muscular coordination.
Dislocation
Clinical features
• Inability to close the jaw.
• Pain.
• Muscle spasm.
Anterior mandibular dislocation are:
I. Acute dislocation that is usually seen to occur post trauma or it may be spontaneous or may be associated with psychiatric illness.
II. Chronic recurrent : Happens many times
III. Subluxation or habitual dislocation is seen to occur in patients whose ligament
and capsule become flaccid with an associated flattening of articular eminence or sustained trauma.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
8Radiology
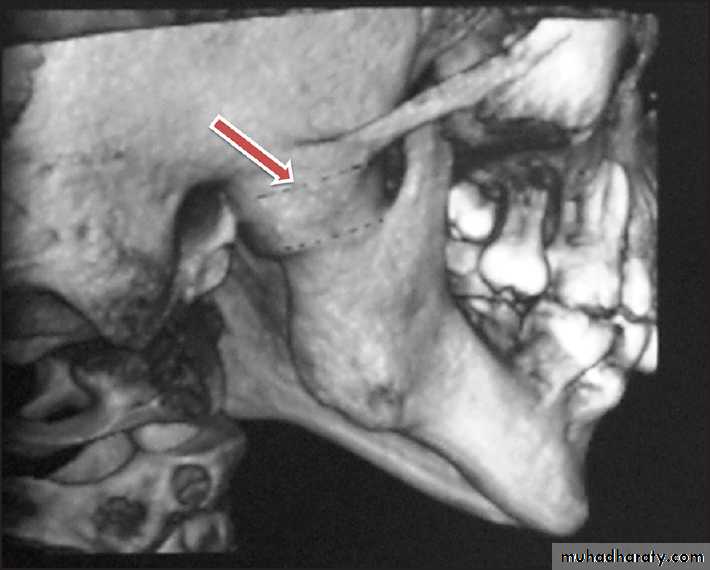
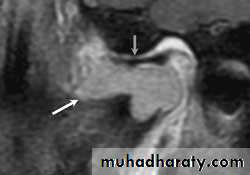
Radiography confirms a clinical diagnosis.The condyle may translate beyond the articular eminence normally, without a dislocation, so clinical information is essential. The condyle will be anterior and superior to the ‘summit’ of the articular eminence.
Dislocation
NB. Normally: the condyle may be translated anterior to the eminence as far as 5 mm.Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
9
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
10Dislocation is due to problem in
• Capsule and ligament
• Synchronization of muscle work
• Bony problems
• Disc displacement and its location settling between condyle and eminence
Treatment depend on each problem like cut lateral pterygoid muscle or inject botulinum toxin into it every 2-4 months.
Management
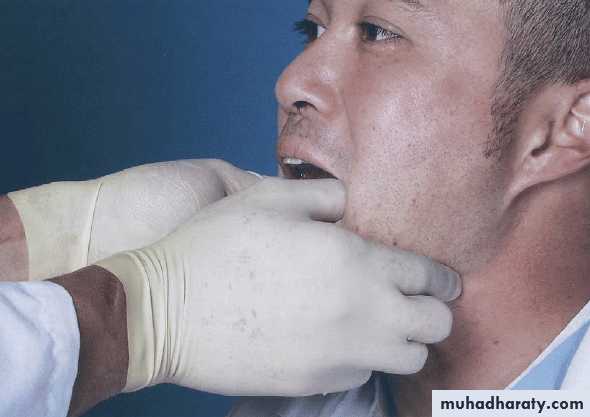
• non-surgical• Manual manipulation (for acute dislocation) to reduce the dislocation. Intravenous sedation with midazolam provides muscle relaxation and greatly facilitates this manoeuvre. The patient should avoid wide mouth opening for some days and use the hand to prevent this when yawning.
• Chemical Capsulorrhaphy: done in Pt. with recurrent dislocation. It produce fibrosis and tightening of the capsular ligament. Used sclerosing agent like (sodium morrhunate or sodium tetradecyl sulphate) into the ligament of the joint or the joint to produce fibrosis. Or prolotherapy (like dextrose) to regenerate the tissue and initiate healing
3. Occlusal equilibration
and splint therapy.
4. Exercise, physiotherapy and analgesia
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
11
Dislocation
ManagementB. surgical
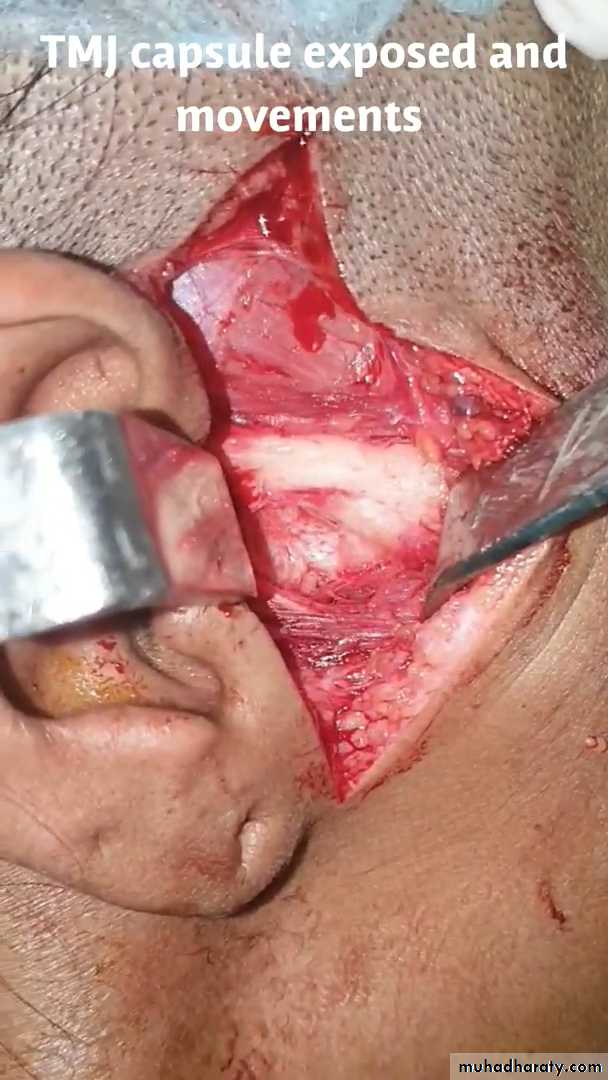
Directed to limit condylar translation, eliminate blocking, removal of obstacle, creating of mechanical obstacle in the condylar path of closure, or both procedures.
• Capsulorrhaphy: tighten the capsule
a. removing an edge of tissue from capsule and suturing the defect.
b. use dermal flap from occipital region or temporal fascia and augment the capsule.
c. capsular plication and ligamentopexy.
2. Anchoring sling:
3. Lateral pterygoid myotomy: (superior belly)
4. Blocking procedure: soft tissue and hard tissue.
5. Eliminating blocking factors in the condylar path of closure (discectomy and eminectomy)
6. Condylotomy and condylectomy.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
12
Dislocation
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
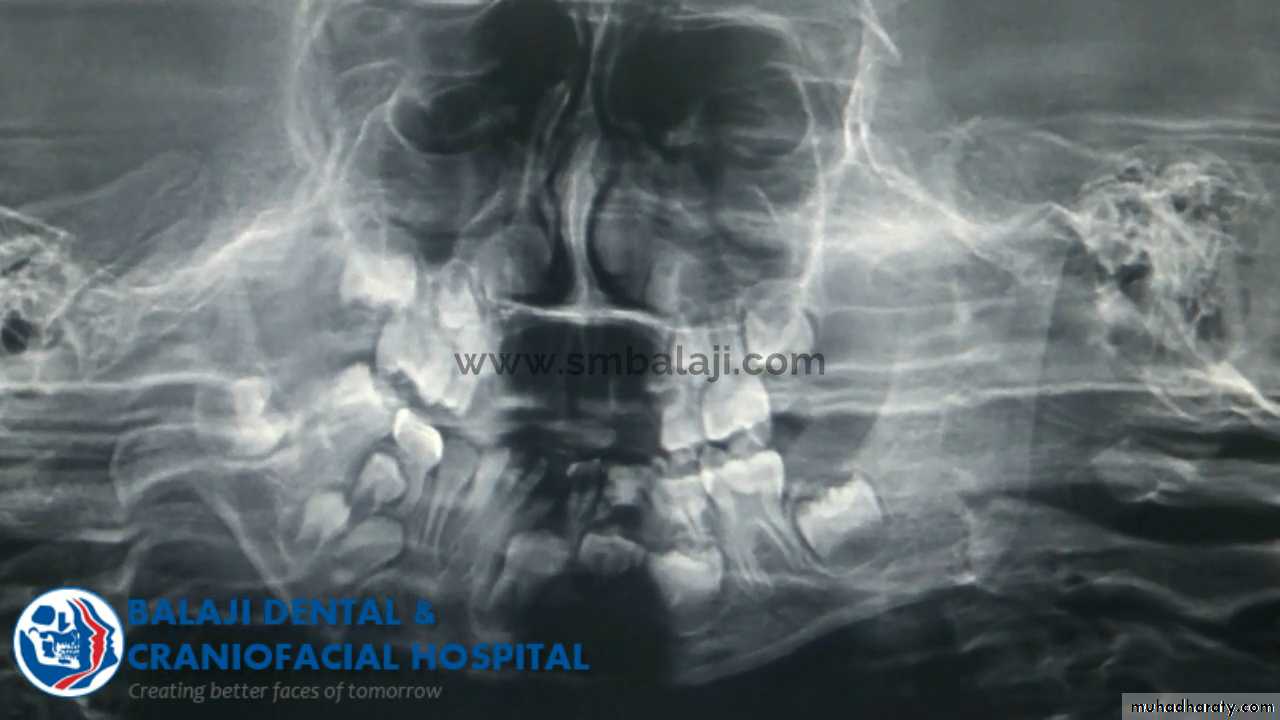
13Ankylosis
It is the union of two articulating surfaces of temporomandibular joint with fibrous or bone tissue leading to immobility or decreased mobilityDr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
14
Classification or Terms
• False or true ankyloses
• Extra- articular or Intra- articular
• Fibrous or bony
• Unilateral or bilateral
• Partial or complete
Ankylosis
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
15
False Ankylosis
It is one in which there is restricted mandibular movements due to extra-articular fibrosis, pathologic conditions or mechanical obstruction.It classified into the following groups.
1. Myogenic: It is the condition when the restriction in the movement of the joint is due to the muscles of mastication that have fibrosed due to the organization of an intramuscular haematoma.
2. Neurogenic: This group includes central nervous system lesions or cerebrovascular accidents, because of which the patient is unable to do masticatory activity.
3. Psychogenic: It refers to hysterical trismus.
4. Bone impingement: This is seen in untreated fracture of zygomatic complex, exostosis of the coronoid process.
5. Fibrous scar tissue: This is formed in any tissue due to trauma, as is seen in burn cases.
6. Tumors: This interferes with condylar movements.
7. Submucous fibrosis: Patients, specially in the Indian subcontinent, due to their betel nut chewing habit, develop submucous fibrosis. These are tough fibrous bands in the submucosa of the oral cavity, that restrict the opening of the mouth.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
16
True Ankylosis
It is one in which there is restriction of mandibular movements due to some intraarticular causes. That is there is a union of the articulating surfaces of the joint byfibrosis, fibro-osseous, osseous or osteocartilage.
Causes
1. Trauma
2. Repeated infections around temporomandibular joint like parotitis, otitis media, tonsillitis, osteomyelitis of the jaw, abscess around the joint as in suppurative arthritis and actinomyosis.
3. Systemic arthropathy like Rheumatoid arthritis.
4. Others
i. Irradiation therapy
ii. Scleroderma
iii. Osteochondroma
iv. Post surgery
v. Idiopathic.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
17
Ankylosis
Clinical Features
They vary according to the:
• Time of onset of ankylosis
• Unilateral or Bilateral
• Severity of ankylosis
• Duration
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
18
Ankylosis
Time of Ankylosis
The time of ankylosis is very important as the clinical features as well as treatment planning is different for the patients in whom ankylosis takes place after the growth of the patient or in those whom growth is not complete.Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
19
Ankylosis
Before Completion of Growth
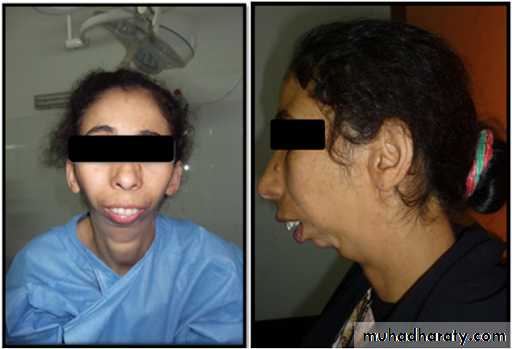
Destruction of the condyle and absence of proper function produces• Typical 'bird facies'
• Micrognathia
• Restricted somatic growth
• Malocclusion
• Dental caries
• Periodontal diseases
• Psychological trauma
• Restricted diet
• Antegonial notching and angular exostoses as a result of bone apposition beneath the pterygo-massetric sling.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
20
Ankylosis
Ankylosis after Growth Completion
The patient has a restricted mouth openingthat may in a long time cause
• Dental caries
• Periodontal problems due to lack of hygiene
• Restricted diet.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
21
Ankylosis
Unilateral Ankylosis
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202122
Unilateral Ankylosis
1. The patient has an obvious facial asymmetry.2. There is a deviation of the mandible and the chin to the affected side.
3. The chin on the affected side is receded with hypoplastic mandible.
4. The face of the patient on the affected side is rounded.
5. The face appears flattened and elongated on the unaffected side.
6. The antigonial notch on the affected side of the mandible is well defined and concave.
7. Condylar movements are absent on the affected side.
8. In unilateral ankylosis some amount of oral opening may be possible. Interincisal opening will vary depending on whether it is fibrous or bony ankylosis.
9. Class II Angles malocclusion on the affected side with unilateral posterior cross bite on the ipsilateral side is seen.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
23
Bilateral Ankylosis
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
24
Bilateral Ankylosis
1. The mandible is symmetrical but micrognathic.2. The patient develops a typical bird face deformity with receded chin.
3. Inability to open the mouth.
4. The neck chin angle is greatly reduced. The defect can be so grievous that sometimes the neck chin angle is absent.
5. Antegonial notch is well defined bilaterally.
6. Upper incisors are often protrusive with anterior open bite. Maxilla may be narrow.
7. Multiple carious teeth with bad periodontal health can be seen.
8. Severe malocclusion.
9. Crowding with many impacted teeth is seen on a radiograph.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
25
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
26Ankylosis
Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint ankylosis
Surgery is the only form of treatment for a patient of ankylosis.
• The aims of surgery are to remove the ankylosed mass and create a gap so that mobility of the joint is restored.
• Care has to be taken to prevent re-ankylosis.
• To try to restore the height of the ramus that was lost due to ankylosis.
• If the patient is young, costochondral grafts can be placed to encourage the growth of mandible.
• And most of all to help the patient, to have a chance to live a normal life.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
27
Ankylosis
Different Surgical Procedures
i. Condylectomyii. Gap Arthroplasty
iii. Interpositional Arthroplasty includes:
a. Autogenous grafts, e.g. Temporalis muscle and fascia, conchal cartilage, full
thickness skin graft, etc.
b. Alloplastic material, e.g. Silicon, tantalum plate, etc.
iv. Interpositional Arthroplasty to allow the growth to continue, e.g. Costochondral graft.
Any suitable incision of the surgeon’s choice can be used for these open joint surgery surgeries.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
28
Ankylosis
Condylectomy
• Condylar head of a fibrosed joint is removed.
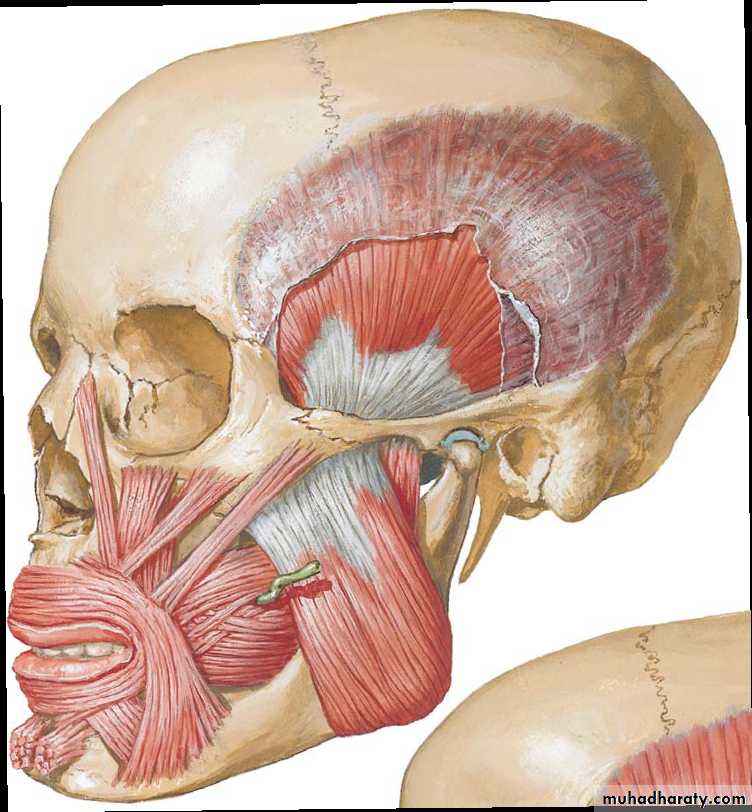
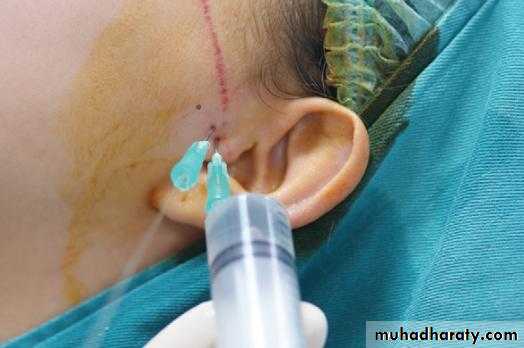
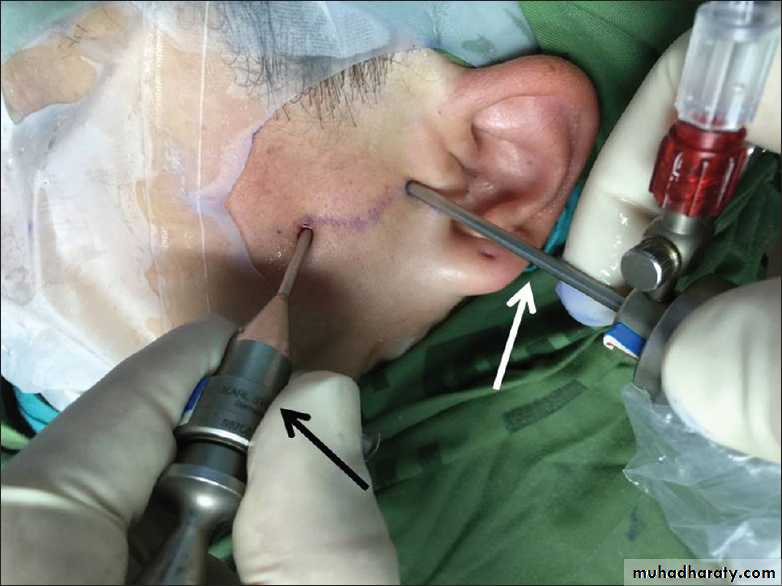
• Approached through a preauricular incision.
• Once the neck of the condyle is cut, the cut condylar head is removed, pressure pack is given
• IMF is done for a few days followed by active mouth opening exercise.
• Care should be taken to avoid injury to the maxillary artery, as it lies just below the neck of the condyle.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
29
Ankylosis
Gap Arthroplasty
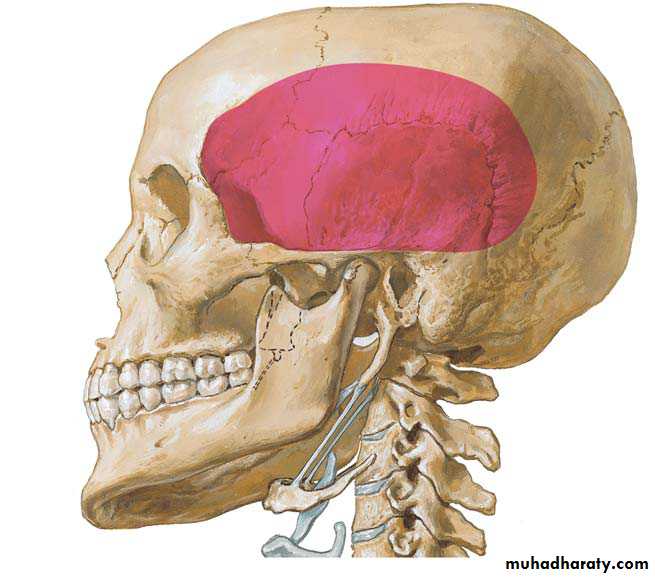
• a gap of minimum 2 cm• it is very important to make two horizontal osseous cuts in such a way that the gap is equal on the mesial as well as the distal ends of the cut joint.
• This procedure is very often accompanied with unilateral or bilateral coronoidectomy, i.e. excising the coronoid.
• care has to be taken to do vigorous physiotherapy for at least 1 yr. postoperatively.
• Though this procedure is simple and requires a short operating time, it is not the best option. There is a great chance of re-ankylosis after the surgery. Very often the patient is a young child and is not co-operative for the physiotherapy, which is extremely painful.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
30
Ankylosis
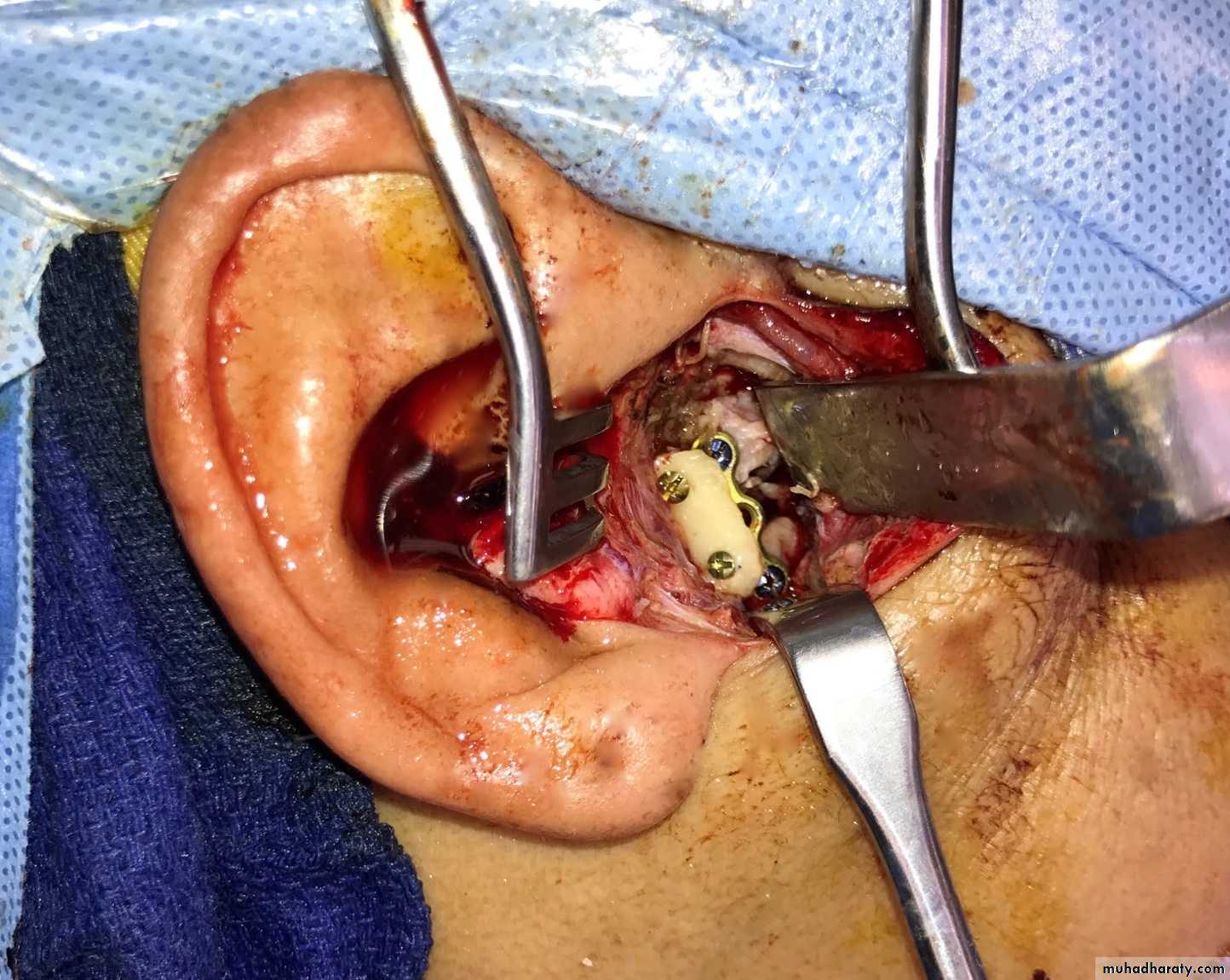
Interpositional Arthroplasty
To prevent re-ankylosis, interposition of alloplastic or autogenous graft is placed between the cut ends of the joint.Temporalis Muscle and Fascia
Full Thickness Skin Graft
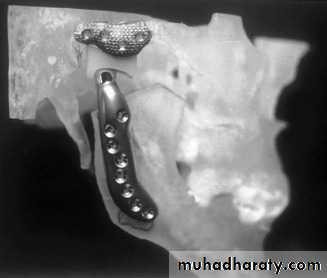
Alloplastic Materials like silicon
Once the gap arthroplasty has been accomplished, the alloplastic material is molded to the right size and secured into position before closure of the surgical site.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
31
Ankylosis
Joint Reconstruction
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202132
Ankylosis
21. What are the indications for total joint reconstruction?
• Fibrous or bony ankylosis with severe anatomic abnormalities• Severe inflammatory disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis, that results in anatomic mutilation of the joint components and functional destabilization
• Failed autogenous grafts in multiply operated patients
• Destruction of autogenously grafted tissues by pathology
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
33
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
34
Ankylosis
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202135
Ankylosis
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
36- Young children with TMJ Ankylosis growth develop mandibular micrognathia.
This is because, the growth center that is present in the condyle is lost.
- To overcome this problem, the joint is reconstructed in a - - way that there is replacement of the growth center with another center. Also there is restoration of balanced mandibular function.
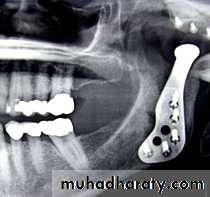
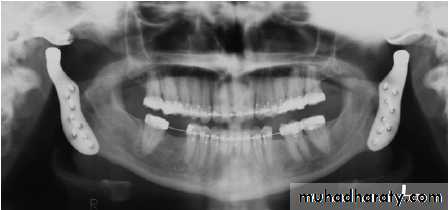
For this purpose, a costochondral graft is harvested.
Ankylosis
Costochondral Graft
This is harvested from the 5th, 6th or the 7th rib. The harvested portion should at least contain 3-4 cm of bone and 1.5 cm of cartilage. Perichondrium and periosteum at the bone-cartilage junction is carefully preserved.• A pre-auricular incision is made.
• The ankylosed mass is removed and the mandible is checked for mobility. Care has to be taken that there is no obstruction in the mandibular movements.
• Then in unilateral cases, the mandible is swung anteriorly and laterally until it correlates with the midline. In bilateral cases, the mandible is advanced until a symmetric face and harmonious profile is achieved.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
37
Ankylosis
The costochondral graft is then inserted. For doing this, the submandibular incision is made. The graft is fixed using mini-screws or wires. Intermaxillary fixation is maintained for 3-4 weeks. Post-operative exercise is to be done routinely.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
38
Ankylosis
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
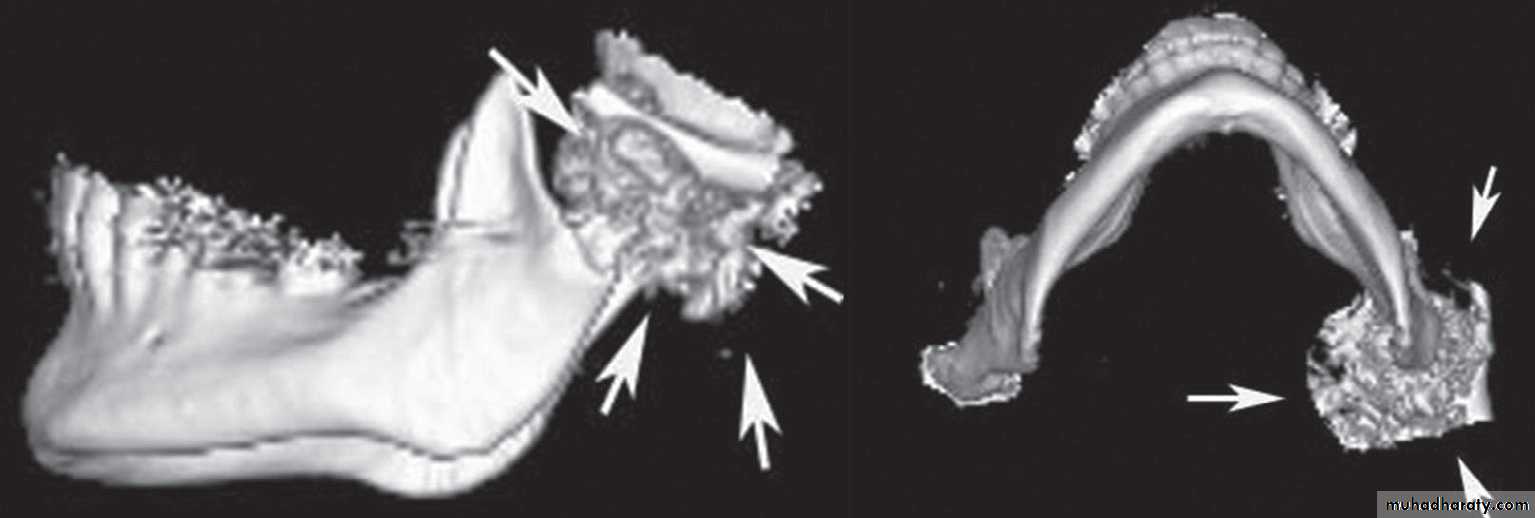
39Neoplasia
Neoplasms in the TMJ are rare. Neoplasms can occasionally result inrestriction of opening and joint pain. Tumors within the TMJ may result in an abnormal condyle and fossa relationship or an intracapsular ankylosis.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
40
1. Eminectomy: It is the removal of the eminence
2. Condylectomy: It is the total removal of the condyle3. Modified condylectomy: It is a vertical ramus osteotomy, whereby the condylar process is detached from the mandibular ramus
4. High condylectomy or condylar shaving: It is limited bony reconditioning of the head of the condyle
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
41
Synopsis of surgical treatments of the temporomandibular joint
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
425. Plication: It is folding or taking a tuck to reduce the size of disk
6. Gap arthroplasty and coronoidectomy: It is a process of removing a section of bone to create a gap of 1 - 1.5 cm [ or not less than 2 cm in other opinion] between the condylar head and eminence. The glenoid fossa may be re-contoured if needed. Coronoid process is removed also
SURGICAL TREATMENTS OF THE TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT
7. Costochondral grafts: These are graft materials, commonly used (5,6,7) the Rib bone of about to replace the resected condylar process. It is fixed to the ramus of mandible by stainless steel wiring or screws
8. Arthrocentesis: It is a process of needle puncture of the joint space; usually this is combined with lavage, which is irrigation of the joint
9. Arthroscopic surgery: It is an operative procedure performed with fine instruments during telescopic penetration of a joint cavity for diagnosis and therapeutic reasons. The surgery is performed using a rigid endoscope (arthroscope) and is less invasive than arthrotomy.
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
43
SURGICAL TREATMENTS OF THE TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 2021
44
Summary
Revision of the TMJ surgery
The End
Dr. Mohammed Amjed Alsaegh, 202145