
[1]
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
BPH
*BPH is the most common benign tumor in men.
*Its age related disease.
For Pathology mean cellular proliferation of stromal and epithelial
elements of prostate
For Radiologist mean an enlarged prostate > 30cm
For Urologist represent collection of lower urinary tract symptoms
(LUTs) that develop in male population in
association with aging and prostatic enlargement
Pathology.
The prostate composed of
-stroma (smooth muscle & fibrous tissue) and
-epithelium.
BPH can arise from any one of them or in combination
Etiology. BPH need both age +androgen to developed
Increase in cell number
• Epithelial and stromal proliferation.
[2]
• Impaired programmed cell death (apoptosis)
Proposed factors that play role in aetiology include
✓ Androgens
✓ Estrogens
✓ Stromal-epithelial interactions
✓ Growth factors
✓ Neurotransmitters
✓ Genetic(autosomal dominant) family history usually effect
younger age group
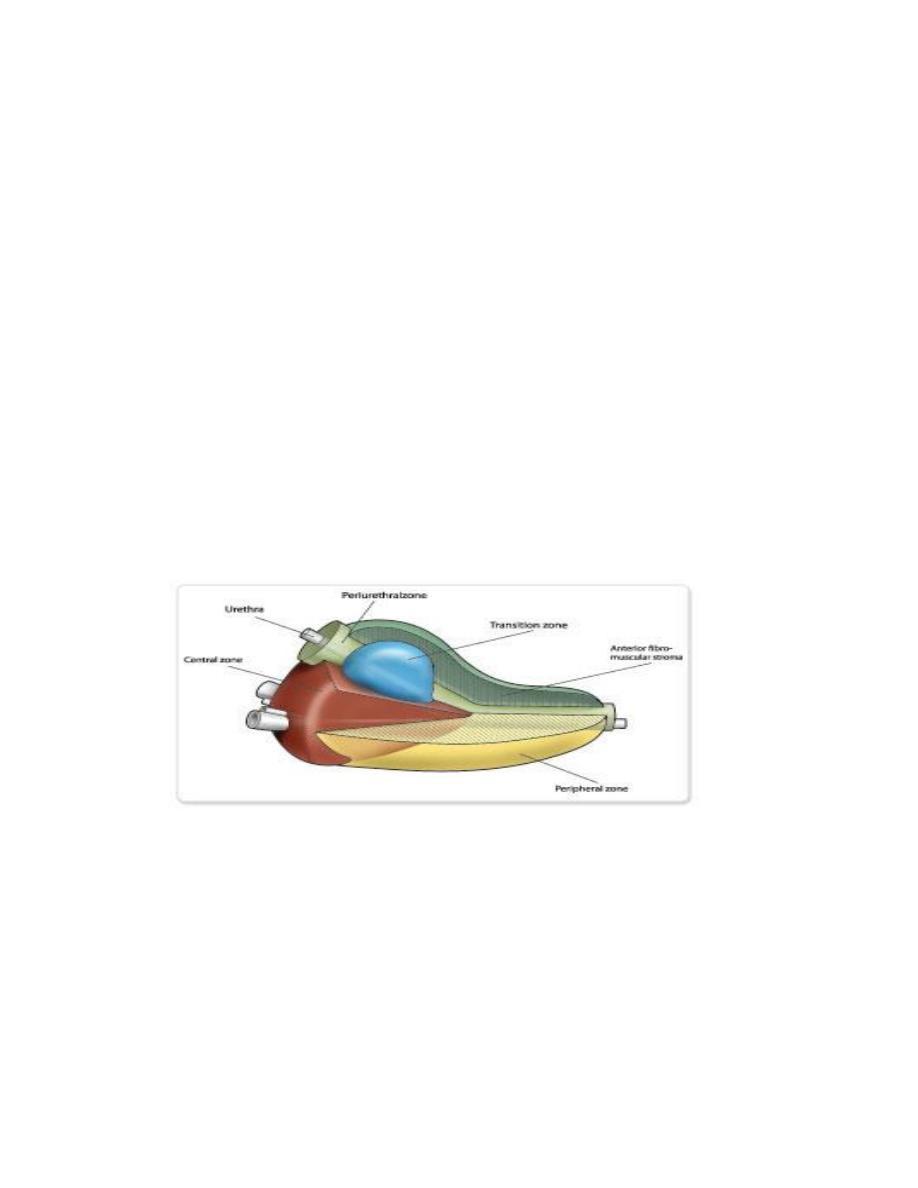
Anatomically
the prostate had 3 zones
-peripheral (70%) commonest site for Ca,
-central (25%) around ejaculatory duct, &
-transitional (5%) periurethral.
[3]
BPH uniformly originate from the transitional zone & as the
nodule enlarge compress the outer zones of the prostate
resulting in surgical capsule.
Pathophysiology
Increase urethral pressure lead to bladder wall hypertrophy so
First : the changes that lead to decrease compliance
causing frequency and urgency
Second :changes associated with decreased contractility
causing
decrease
force
of
urinary
stream,hestancy,intermittency and increase resudial volume
Clinical features :-
Either obstructive or irritative.

[4]
obstructive symptoms
-hesitancy,
-decrease force & caliber of stream,
-sensation of incomplete bladder emptying,
-double voiding
-straining to urinate, & post void dribbling
Irritative symptoms
Urgency, Frequency, & Nocturia.
* The amount of post void residual urine is extremely variable
in sequential evaluation of same patient.
DRE,
used to determine the size, consistency of the prostate
-a smooth firm usually BPH while
-induration signify the possibility of Ca & need further
evaluation.
-retention may occur usually precipitated by prostatic
infection or infarction, ingestion of diuretic, anticholenergic,
antidepressant
Symptom not related to prostatic size
Investigation
❑ GUE, infection & hematuria.
❑ Renal function : b.urea & s.creatinine.
❑ PSA : is optional .prostatic tumor marker
❑ Imaging : IVU &U/S is some time recommended.
❑ Cystoscopy. Used to choose surgical approach when surgery
is indicated.
D.Dx.

[5]
Obstructive condition of lower tract like
-urethral stricture,
-bladder neck contracture,
-bladder stone, &
-Ca prostate.
irritative
-UTI,
-CIS, &
-neurogenic bladder
Treatment Options
❖ Watchful waiting
❖ Medication
❖ Surgical approaches
TURP
Invasive open procedures
Minimal invasive
A-Watchful waiting
Idea is Only 5%of BPH patients will develop retention
• Mild symptoms with not very active life style
• Follow up every 3-6 months
• Offer suggestions that reduce symptoms
Like avoid caffeine , night time excessive fluid and
decongestant,antihistamine anticholinergic
B-Medical therapy.
1-Alpha blocker:
The human prostate & bladder neck contain alph-1a
receptors.

[6]
Alpha blocker lead to smooth muscle relaxation & dilatation
of bladder neck.
Alpha blocker either nonselective act on alpha like
phenoxybenzamine
Selective which either
short acting e.g prazosin or,
long acting e.g terazosin & doxazosin .
These need dose titration to decrease their side effect
side effect include
-orthostatic hypotension,
-dizziness,
-tiredness,
-retrograde ejaculation,
-rhinitis, &
-headach .
Highly selective act on alpha 1a receptors like
tamsolusin and Silodosin in both no need for dose titration
because it had fewer side effect.mostly causing retrograde
ejaculation ,not effect blood pressure.
2- 5-alpa reductase inhibitor
Finasteride and dutasteride are 5 alpha reductase inhibitors
that
block
the
conversion
of
testosterone
to
dihydrotestosteron. This drug act on epithelial component
(adenoma) of the prostate reduce the size of the gland
(20% reduction of weight in 6 months).

[7]
side effect
-decrease libido &
-reduce PSA level to 50% complicating cancer detection.
B-Surgical management.
Absolutetely Indicated in
1-refractory retention (after at least 1 trial of catheter
removal),
2-recurrent UTI due to PBH
3-recurrent gross hematuria, due to PBH
4-bladder stone,
5-renal insufficiency
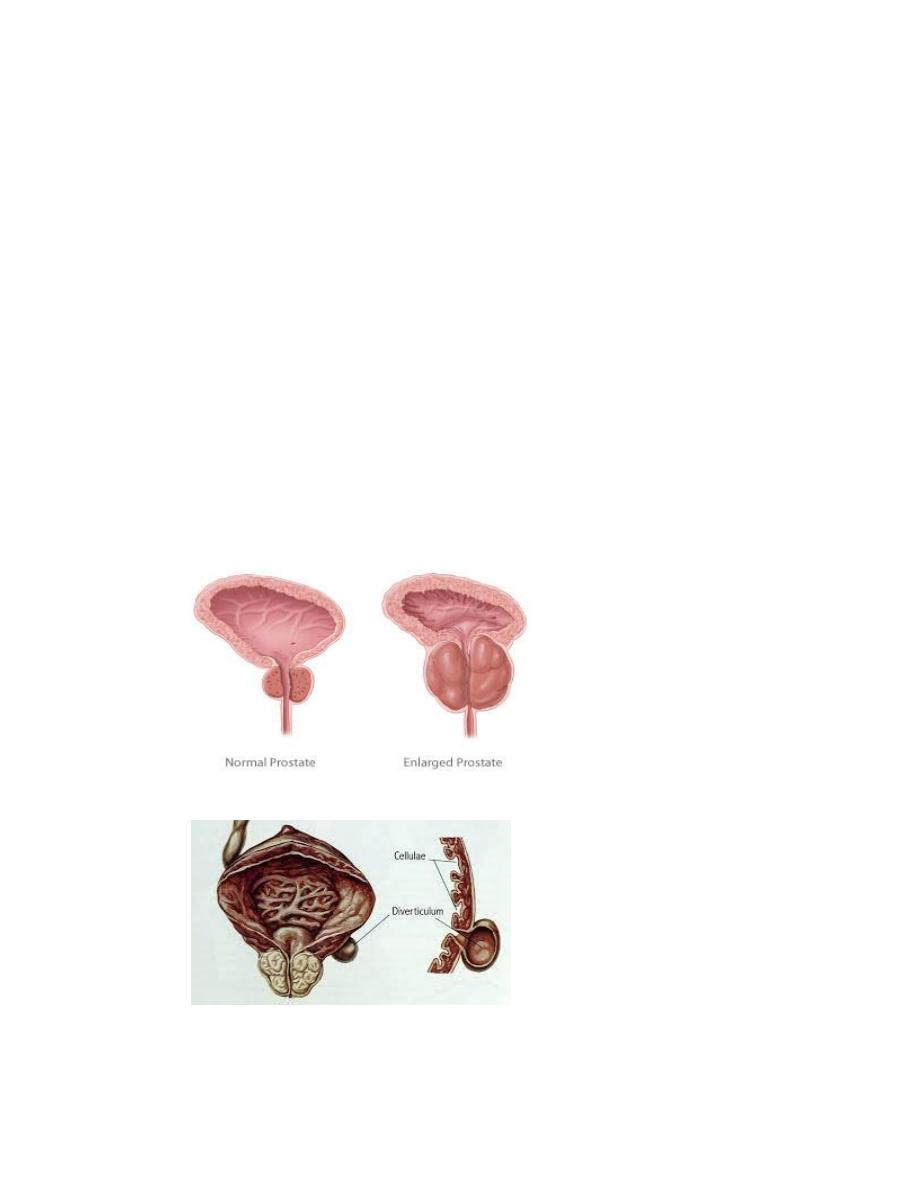
6-bladder diverticulum
7- failure of medical treatment (medication not improving the
quality of life)
*provide these are from BPH.
1-TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate)
-resection of the prostate endoscopically into small pieces
which removed by bladder wash.
-Used in 95% of BPH.
complications. Immediate
-Bleeding
-Capsular perforation with fluid extravasation
-Infaction
-TURP syndrom
TURP syndrome : resulting from hypervolemic hyponatremic
state due to absorption of hypotonic irrigating solution.
Manifested by nausea, vomiting, confusion, hypertension,
bradycardia,& visual disturbance

[8]
Late complication
• Urethral stricture
• Bladder neck contracture
• Retrograde ejaculation
• Impotence
• Incontinence
2-open simple prostatectomy.
Indicated when TURP not performed due to
1- large prostate >100g.
2- concomitant bladder pathology like stone or diverticulum, &
3- when dorsal lithotomy positioning is not possible.
Its either transvesical or retropubic
3-minimal invasiae therapy.
1- laser therapy,
2- electrovaporization of the prostate,
3- transurethral needle ablation,
4- high intensity focused ultrasound,
5- intraurethral stent,
6- balloon dilation of the prostate
