Dental Trauma
By:Assist Prof. Saba Hazim Hasan
أ.م صبا حازم حسن
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Department of
Pedodontics,
Orthodontics and Preventive Dentistry
Department of:
HERE
Pedodontics
5th academic year
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
History and examination
020-2021
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDental history
1. When did injury occur?
The time interval between injury and treatment significantly influences the prognosis of avulsions, luxations, crown fractures with or without pulpal exposures, and dento-alveolar fractures.
2. Where did injury occur? This may indicate the need for tetanus prophylaxis.
020-2021
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY3. How did injury occur? The nature of the accident can yield information on the type of injury expected. Discrepancy between history and clinical findings raises suspicion of physical abuse
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
4. Lost teeth/fragments? If a tooth or fractured piece cannot be accounted for when there has been, a history of loss of consciousness, a chest radiograph should be obtained to exclude inhalation.
5. Previous dental history? Previous trauma can affect pulpal sensibility tests and the reperative capacity of the pulp and/or periodon-tium.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
Medical history
Congenital heart disease, a history of rheumatic fever, or severe immunosuppression? These may be contraindications to any procedure that is likely to require prolonged endodontic treatment with a persistent necrotic/infected focus. Not all congenital heart defects carry the same risks of bacterial endocarditis, and the child’s pediatrician/cardiologist should be consulted before a decision regarding endodontic treatment is made.
Bleeding disorders? Very important if soft tissues are lacerated or teeth are to be extracted.
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
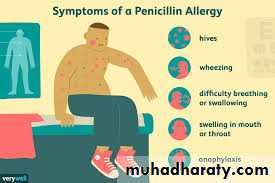
Allergies? Penicillin allergy requires alternative antibiotics.
Tetanus immunization status? Referral for tetanus toxoid injection is necessary if there is soil contamination of the wound and the child has not had a ‘booster’ injection within the last 5 years.
020-2021
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
Extra-oral examination
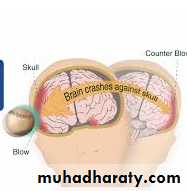
When there are associated severe injuries a general examination is made with respect to signs of shock (pallor, cold skin, irregular pulse, hypotension), symptoms of head injury suggesting brain concussion, or maxillofacial fractures.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
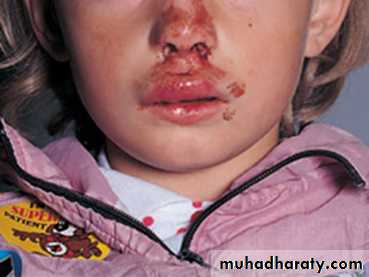
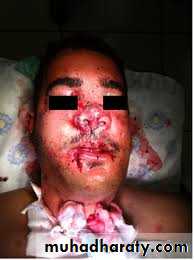
Facial swelling, bruises, or lacerations may indicate underlying bony and tooth injury.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Limitation of mandibular movement or mandibular deviation on opening or closing the mouth indicate either jaw fracture or dislocation.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
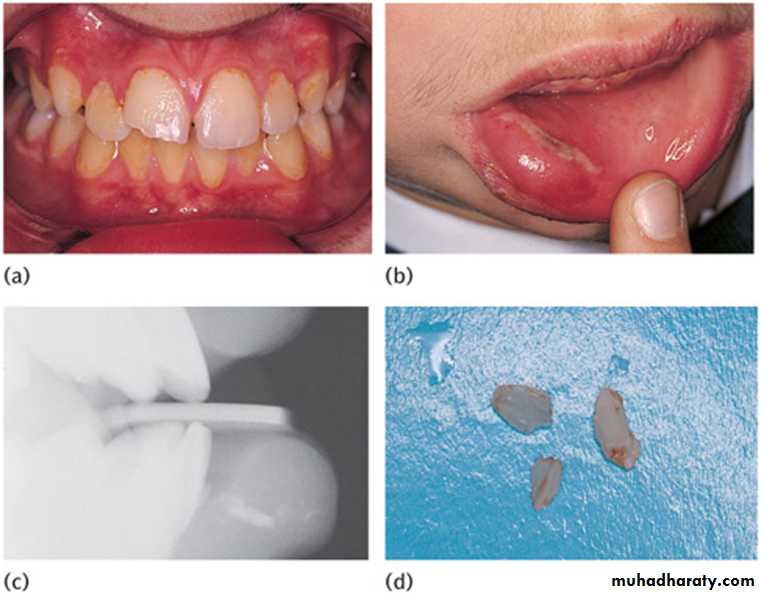
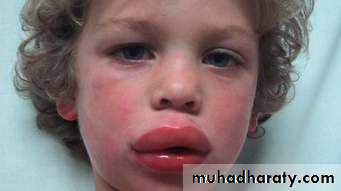
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYCrown fracture with associated swollen lip and evidence of a penetrating wound suggests retention of tooth fragments within the lip.:
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYIntra–oral examination
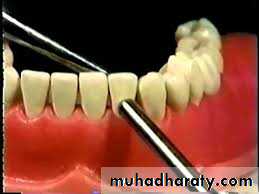
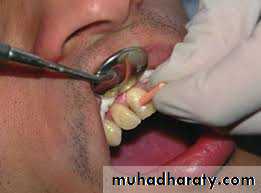
1. Mobility. Degree of mobility is estimated in a horizontal and a vertical direction. When several teeth move together en bloc, a fracture of the alveolar process is suspected. Excessive mobility may also suggest root fracture or tooth displacement.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
2. Reaction to percussion in a horizontal and vertical direction compared with a contralateral uninjured tooth. A duller note may indicate root fracture.
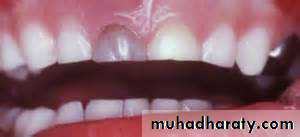
3. Colour of tooth. Early colour change associated with pulp breakdown is visible on the palatal surface of the gingival third of the crown.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
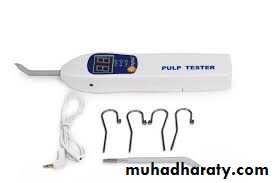
Reaction to sensitivity tests:
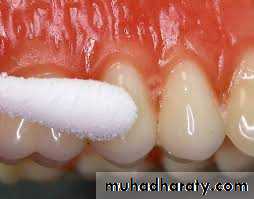
Thermal tests with warm gutta percha (GP) or ethyl chloride (EC) are widely used. However, an electric pulp tester (EPT) in the hands of an experienced operator is more reliable. Vitality test, immediately after trauma it does not give response to vitality test because the tooth is in state of shock, re – examine in the next appointment after 6 weeks, if the child does not give response then the tooth is dead. The vitality test needs cooperation and relaxed child, (child anxiety result in false response).
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Radiographic examination
• To approximate the size of pulp chamber.
• The stage of apical development; indicate the type of treatment.
• To see root fracture.
• To check alveolar bone.
• Any dislocation of the tooth.
• Periodontal condition.
• For comparing with record in the future.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
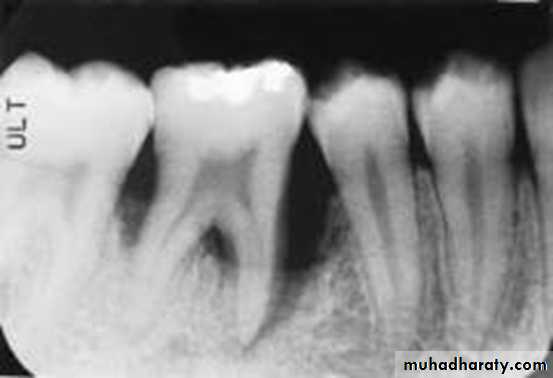
Periapical
Reproducible periapicals are the best for accurate diagnosis and clinical audit. Two radiographs at different angles may be essential to detect a root fracture. However, if access and cooperation are difficult, a single anterior occlusal radiograph rarely misses a root fracture. Periapical films positioned behind the lips can be used to detect foreign bodies.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
Occlusal
This view detects root fractures when used inta-orally and foreign bodies within the soft tissues when held by the patient/helper at the side of the mouth in a lateral view.UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
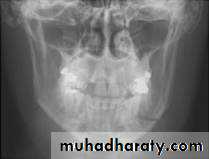
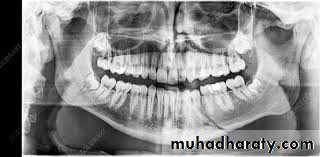
Orthopantomogram
This is essential in all trauma cases where underlying bony injury is suspected.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYUNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Photographic records
There are many reasons for using dental photography; the primary purpose of digital dental photography is recording accurately the clinical manifestations of the oral cavity., secondary uses include legal documentation, publishing, education, communication with patients. Each of these uses enhances and elevates the status of dental practice as well as improves delivery of care to patients.
Good clinical photographs are useful for assessing the outcome of treatment. Written consent must be obtained.
THE END
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
2020-2021
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE