
Epidemiology and Control of Viral Hepatitis A infection Community Dr. Ali
Hepatitis A Infection (HAV) (Infectious Hepatitis)
• The Causative Agent:
• Hepatitis A Virus:
• 27 nm picornavirus single stranded RNA virus
• Nonenveloped, acid and heat stable
Reservoir of infection:
Humans are the only reservoirs of infection (Acute cases because there is No chronic carrier state)
Hepatitis A Transmission
• Close personal contact
• Household or sexual contact
• Daycare centers
• Fecal-oral contamination of food or water
• Food handlers
• Raw shellfish
• Blood-borne (rare)
• Injecting drug users
Incubation Period:15-50 days or (2-6 weeks)
Clinical Features:
Initially (pre-ecteric stage): Sudden onset of fever, anorexia, malaise, nausea, vomiting, &
abdominal discomfort. Some patients
• might develop mayalgia, arthralgia & alteration of smell & taste.
• Later (after several days to one week) : Jaundice with dark urine & clay stool.

• Asymptomatic (anicteric) infection is common especially in children.
• Symptomatic (Icteric) infection occurs in:
• <10% of Children under 6 years of age,
• 50-60% of Children from 6-14 years old,
• 70%-80% of adults and children over 14,
Consequences of hepatitis A infection
• Complete recovery without sequelae or recurrence in the majority of cases
• Immunity after infection lasts for life
• No chronic carrier state.
• Case fatality rate increases with increasing age
Age-specific Mortality Due to Hepatitis A
• Age group Case-Fatality
• (years) (per 1000)
•
• <5 3.0
• 5-14 1.6
• 15-29 1.6
• 30-49 3.8
• >49 17.5
• Total 4.1
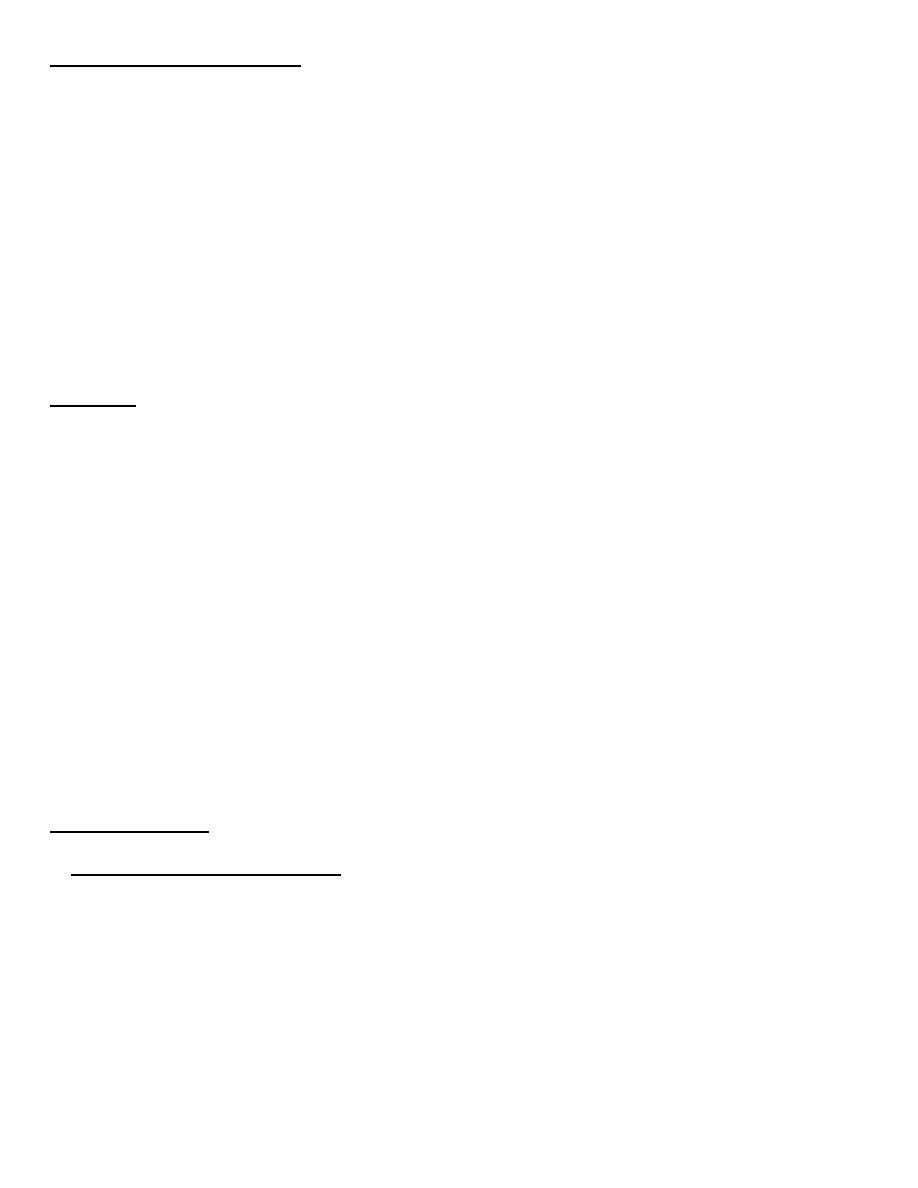
Period of Communicability:
• HAV is found in stool 2 weeks after exposure to infection reaching a peak levels the week or
two before onset of symptoms.
• Infectivity is higher towards the end of the incubation period.
• The number of viruses falls after the patient becomes jaundiced. Most cases are non-infectious
after the first week of jaundice.
• When the patient becomes jaundiced &comes under the care of the doctor he is probably no
longer excreting the virus & no longer infectious
Diagnosis
• Clinical features (The clinical course of acute hepatitis A is indistinguishable from that of other
types of acute viral hepatitis )
• Urine bilirubin in the pre-ecteric stage
• Liver function test
• Diagnosis is established by the detection of :
• IgM Anti HAV : appears 4 wks after exposure and may remain detectable for 4-6 months. It
indicates acute infection
• IgG Anti-HAV : peaks during convalescence and persists for life. Indicates immunity
acquired from past infection or immunization
Control measures
• General Preventive measures:
• Good sanitation & personal hygiene with special emphasis on hand washing particularly
among food handlers.
• Provision of safe water supply & proper sewage disposal.

Specific Preventive measures:
• Measures for patients :
• Isolation is not necessary
• Strict personal hygiene is required in homes where a case has occurred
• Treatment of patients
• - No specific treatment
• - Bed rest is essential
Measures for contacts
Investigation of contacts searching for other cases
Post-exposure prophylaxis:
Immune globulin 0.02 ml/kg IM within 2 weeks of exposure.
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is any prophylactic measure started immediately after exposure
to a disease (such as a disease caused by virus), in order to prevent the disease in healthy
individuals
Indications:
• Sexual contacts
• Close household contacts.
• Staff and children at day care center exposed to a patient with Hepatitis
A.
• Food handlers exposed to a patient with Hepatitis A.

Preexposure
• Immune Globulin
• VACCINATION
• Inactivated HAV Vaccine
• Parenteral
• Safe & well tolerated
• Protective efficacy rate 95-100%
• Protective antibodies are seen within 15 days of vaccination
• Protection for >10 years
• Dose & schedule
• Age: ≥ 2 years
• 2 doses at 6-12 months interval
Indications for Hepatitis-A Vaccine
• Persons with chronic liver disease (e.g. hepatitis B or C)
• Homosexuals
• Travelers to highly endemic areas
• Drug users( drug addicts), particularly injection drug users
• Persons at occupational risk for infection
Indications for Hepatitis-A Vaccine
• Persons with chronic liver disease (e.g. hepatitis B or C)
• Homosexuals
• Travelers to highly endemic areas
• Drug users( drug addicts), particularly injection drug users
• Persons at occupational risk for infection
Hepatitis B infection 2
nd
Lecture
Causative Agent
• Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
• Double stranded DNA genome
• Enveloped
• Virus contains 3 important HBV antigens
• HBsAg: Surface antigen
• HBcAg:Core antigen
• HBeAg:e antigen
Global Distribution of Chronic Hepatitis B Carriers
More than 2 billion people worldwide have been infected with HBV, and an estimated 350-400
million of those
people have become chronic carriers of the virus.
The prevalence varies widely from region to region of the world. It is highly endemic in China,
Southeast Asia, and Africa, but occurs less frequently in North America, Western Europe, and
Australia.
>1 million people die annually of HBV-related chronic liver disease
• Reservoir :
• Man is the only reservoir of infection
• Source of infection:
• Acute symptomatic & A symptomatic cases
• Patients with chronic infection
Modes of Transmission:
• Hepatitis B is transmitted through exposure to body fluids containing the virus:
• Perinatal
• Sexual transmission
• Parentral/percutaneous,
• blood / blood products, needle stick, injection drug use, tattooing and piercing with
contaminated instruments, acupuncture.
• Non-sexual person-to-person contact,
e.g., household contact, Shared toothbrushes, razors, and towels
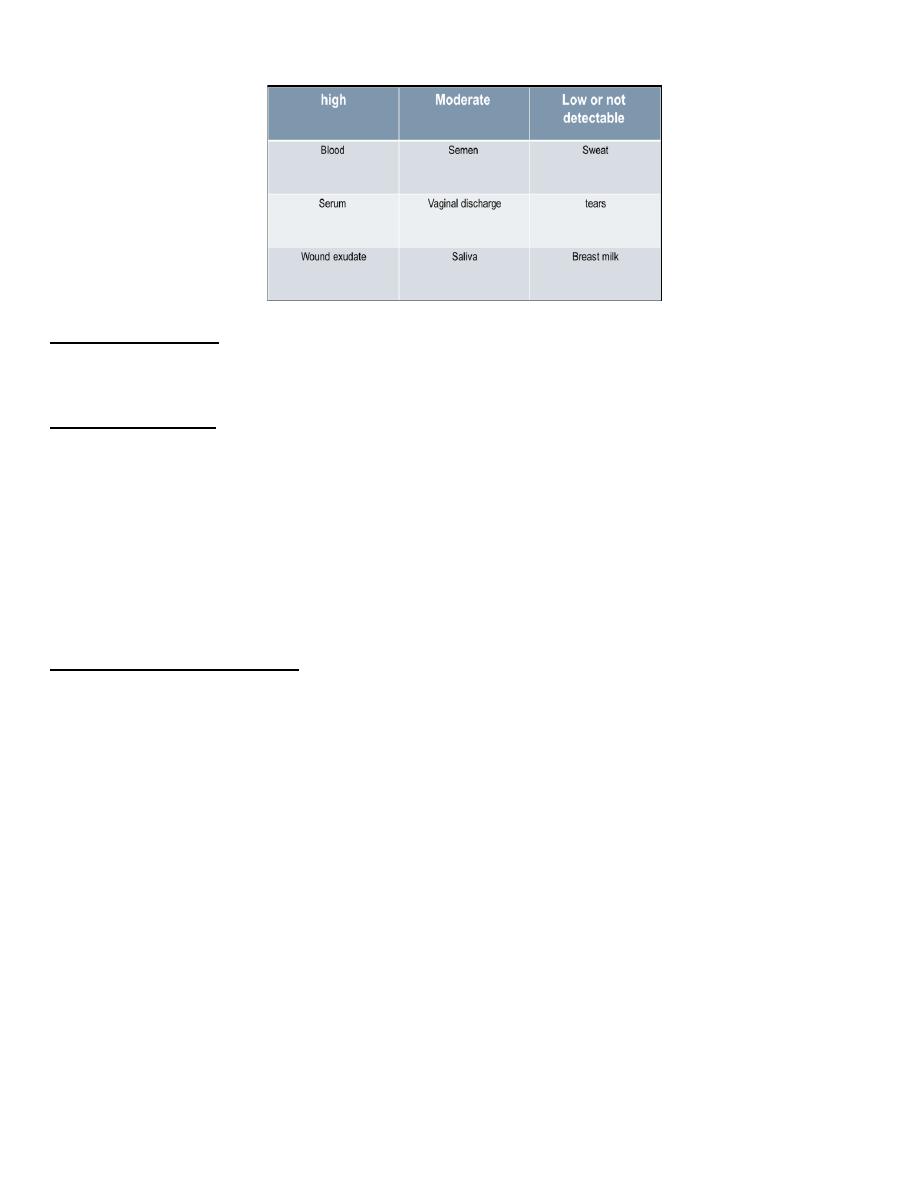
Concentration of Hepatitis B Virus in Various Body Fluids
Incubation period:
1-6 months) )Average 2-6 months
Clinical Features :
Similar to hepatitis A
Symptomatic infection increases with the increase in age
In children < 5 yrs: <10% develop clinical jaundice
5 yrs and above : 30%-50% develop clinical jaundice
Outcomes of HBV Infection
Three outcomes:
Recovery from symptomatic & asymptomatic infection
Death from fulminant acute hepatitis
Chronic carrier, usually for life
Age is the major risk factor in determining the carrier state, the younger the age , the higher the
risk of becoming a carrier:
neonates and infants ; 80-90%
1-4 year olds ; 30-50%
adults ; 2-5%
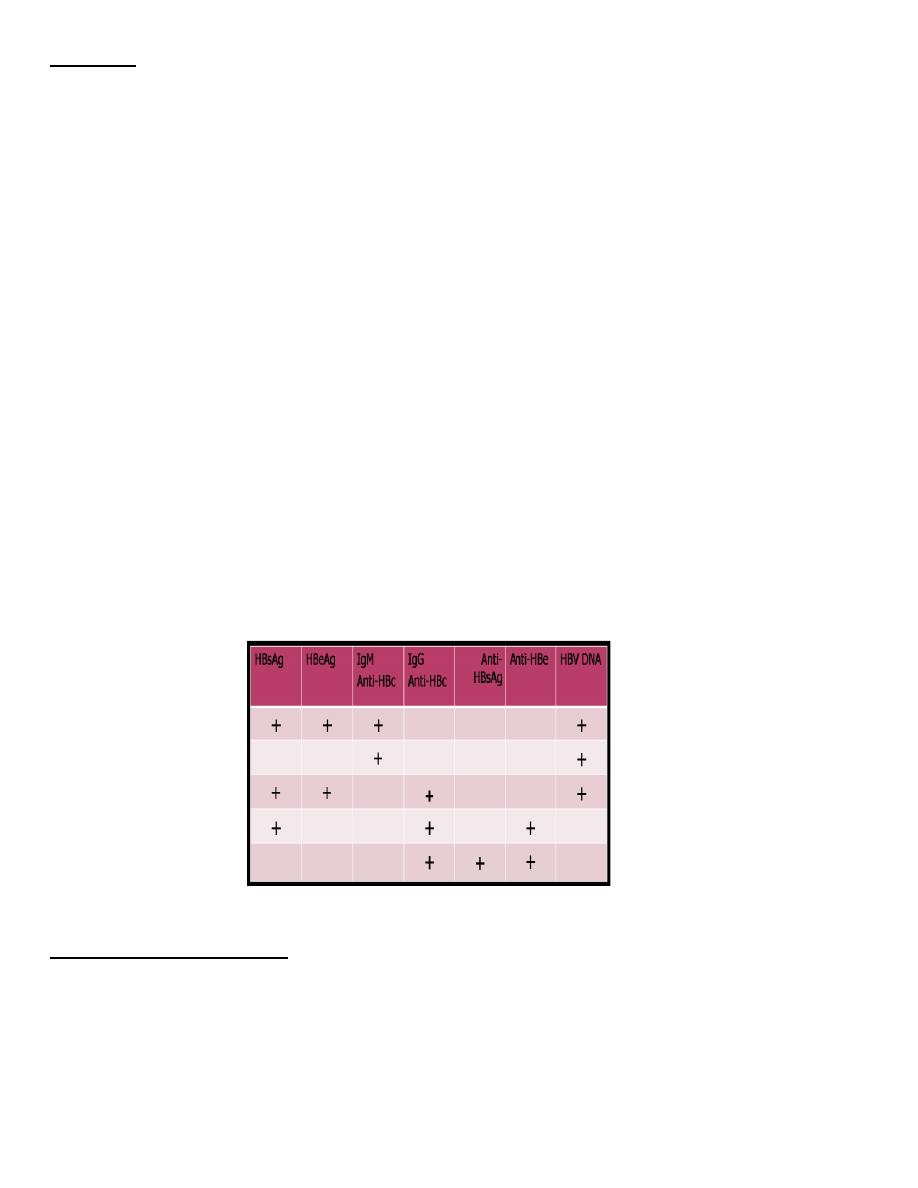
Diagnosis
Abnormal liver function test
Serological tests: many serological tests are used for the diagnosis of acute and chronic hepatitis
B infection.
HBsAg - used as a general marker of infection (acute and chronic infection).
Anti-HBc IgM - marker of acute infection.
Anti-HBcIgG – a marker of past or chronic infection.
HBeAg - indicates active replication of virus and therefore infectiveness.
Anti-Hbe – indicates that the virus no longer replicating. However, the patient can still be
positive for HBsAg .
Anti-HBs- used to indicate recovery and/or immunity to HBV infection.
HBV-DNA - indicates active replication of virus, more accurate than HBeAg . Used mainly for
monitoring response to therapy.
Serological Markers for HBV Infection
EarlyAcute
infecion
Window period
Chr, repl
Chr, non-rep
Recovery
Period of communicability
Body fluids &blood of affected individuals are infective several weeks before onset of symptoms
& remain infective throughout the acute clinical stage & during the chronic carrier state.
The infectivity of chronic carriers varies from highly infectious ( HBeAg +ve ) to relatively
lack infectivity ( Anti-HBe +ve

Treatment
No specific treatment for typical acute viral hepatitis.
Symptomatic treatment is recommended.
Patient isolation or hospitalization is rarely necessary.
Preventive and control measures
Vaccination
Screening of high risk populations
ٍScreening of blood products
Health education to:
• Avoid sharing of items that might get contaminated with blood like toothbrush, razor, &
nail clippers).
• Avoid getting tattoos because transmission may occur through unsterilized tattoo or
piercing instruments.
• Avoid sharing needles or syringes
Vaccination (pre-exposure prophylaxis)
Highly effective recombinant vaccine is available:
Protective efficacy rate 85-95%
Immunogenic in healthy subjects( >95%)
Safe and well tolerated
Vaccination is recommended for:
high risk groups only (In areas of low-endemicity).
• All Neonates as universal vaccination in many countries (In hyper-endemic &moderately
endemic areas ).
• Recommended dosage & schedule

• 3 IM doses 0,1,6 months
• Dose 0.5ml for children from birth - 10 years
• 1 ml for older children and adults.
• In Iraq
• 3 IM doses to infants at birth, 2 months, and 6 months.
Hepatitis B Risk groups
People exposed to blood as a result of their occupation or of medical treatment; health care
workers; recipients of blood products; haemodialysis patients & staff.
Household contacts & sexual partners of infected persons.
Homosexuals & sexually promiscuous
Injecting drug users (IDUs); drug addicts
Babies born to HBsAg-positive mothers.
Post-exposure prophylaxis
Include :
Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin (HBIG)
Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin (HBIG) may be used to protect persons who are exposed to
hepatitis B. It is particularly effective within 48 hours of the incident.
Protective efficacy exceeds 95%
Dose
Post-exposure prophylaxis
• - 0.06 ml/kg as early as possible after exposure
• - Infants 0.5 ml
• Indications
• Neonates of HBsAg-positive mothers (should be given within <12 hours
• Accidental needle brick (within 24 hours)
• Susceptible sexual contacts of cases (within 14 days)
• Household contacts
• Post exposure prophylaxis for accidental needle brick
• The measures depend on the vaccination status of the exposed person :
• Unvaccinated exposed person:
• Hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) 0.06 ml/kg IM immediately . Initiate
hepatitis B vaccination series within 7 days
• Previously vaccinated exposed person:
• HBIG 0.06 ml/kg IM immediately plus HB Vaccine booster
• OR HBIG 0.06 ml/kg IM immediately and repeat it after 1 month.
• Post exposure prophylaxis for houshold contacts:
• For Infants (<1 year) : HBIG & vaccination (3 doses)
• Others: Vaccination only (3doses)
