Abnormal uterine bleeding
Fifth yearABNORMAL UTERINE BLEEDING
Definition: is a descriptive term applied to any alteration in normal pattern of menstrual flow
. excessive flow
. prolong flow
. intermenstrual bleeding
Classical nomenclature of abnormal uterine bleeding
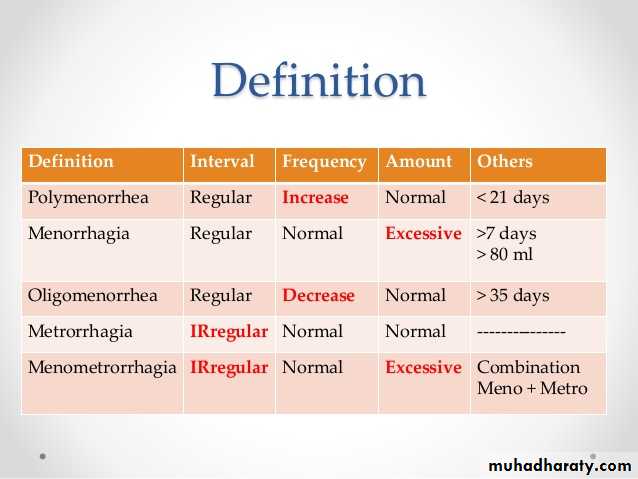
Menorrhagia: prolonged and increased menstrual flow
Metrorrhagia: regular intermenstrual bleeding
Polymenorrhea: menses occurring at less than 21 days' interval
Hypermenorrhea: excessive regular menstrual bleeding
Menometrorrhagia: prolong menses and intermenstrual bleeding
Amenorrheore a absence of menstruation for more than 6 months
Oligomenorrhoea: menses at intervals of more than 35 days
AETIOLOGY
1.organic causes
2. nonorganic causes this is called dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB)
ORGANIC CAUSES
General causeslocal causes
General causespsychological or emotional can lead to abnormal bleeding through the effect on hypothalamus effecting hormonal control of the ovary or it act on autonomic nerves system supplying genital organ
medication: exogenous steroid hormones neuroleptic. anticoagulant and cytotoxic drugs
endocrine disorder: abnormal thyroid function, pituitary gland disorder, adrenal disorder, prolactin disorder, Diabetes mellitusDisorder of hemostasis
liver and renal disease
local causes
pregnancy complication: implantation bleeding, all types of abortion, ectopic, trophoblastic diseasecongenital anomalies: double uterus increase surface area
Traumatic: local internal or external injuries, ring pessary
IUCD
PID: either local endometritis or sever pelvic infection may effect ovarian function and secondarily abnormal menstruation
hormonal producing tumor
tumor of the uterus: benign fibroid common cause or malignant endometrial carcinoma
end cervical polyp or hyperplasia
Cervical carcinoma
Rarities such as arteriovenous malformation in the uterus
NON-ORGANIC CAUSES
Known as dysfunction uterine bleeding
any abnormal bleeding for which no organic cause can be detected
responsible for 50% of abnormal bleeding
diagnosis by exclusion
classified to
An ovulatory causethis tend to occur in woman at the extremes of reproductive age and is typically irregular cycle .it is more common in obese women
Threshold bleeding: estrogen produce in amount enough to cause with drawl bleeding but not enough to produce proper proliferative endometrium (thin hypo plastic) this usually occur in adolescent and around menopause
Cystic glandular hyperplasia is the condition in which excessive and contiuos production of estrogen producing proliferative endometrium progress to hyperplasia so columnar epithelium become hypertrophy and stroma also proliferate with polymorph small haemorrgic area, necrosis and cystic dilation of the gland keeping the appearance of Suisse cheese appearance.
OVULATARY DUB
This pattern is more common in woman aged 35 – 45 and is typically regular heavy and often painful menstruationCorpus luteum defect
corpus luteum slow to degenerate this cause prolong menstrual cycle and progesterone changes within the endometrium continue for longer time and there is premenstrual spotingcorpus luteum slow to develop (corpus luteum insufficiency )menstrual loss is prolong may last 15 days
MANGEMENT
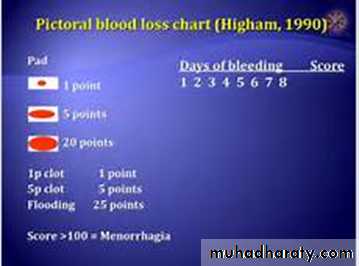
Patients will have different idea about heavy period so we have to confirm this is really heavy cycle
Soaked sanitary pad, presence of clots, blood spills over cloths or bedding, take any time off work due to this bleeding, treatment for anemia or blood transfusion
Type of abnormal bleeding whether continuous or regular or intermenstrual bleeding
Examination
Sign of anemia, sign of endocrine or medical disease that associated with heavy loss. abdominal and pelvic examination, cervix is visualized for polyp or carcinoma, cervical smear and swabINVESTIGATIONS
full blood count: assess severity and ascertain the need for treatment iron therapy or even blood transfusioncoagulation screen: especially if history consistent with coagulation disorder
pelvic ultrasound: mass fibroid, polyp, drug failure, endometrial thickness ,…………
high vaginal and endocevical swab
endometrial biopsy: should be performed
If age more than 45, irregular or intermenstrual bleeding, drug therapy has failed
Biopsy is performed either through outpatient Pipelle
Dilation and curettage
Outpatient hysteroscopy
Thyroid function test
Treatment
for some woman ,the demonstration that their blood loss in fact normal may be sufficient to reassure them and make further treatment unnecessary
when selecting appropriate management for the patient ,it is important to consider and discuss :.patients preference of treatment
risk \benefit of each treatment
contraceptive requirement complete family or not
past medical history
any contra indication to medical therapy
suitability of anesthetic
MEDICAL TREATMENT
Mefenamic acid and other NSAIDsreduce blood loss of 20 25 percent
effective analgesia
a number of contra indication like DU and asthma
Recommended dose 500 mg tds
Tranexamic acid
reduction blood loss by 50 percentrecommended dose 1 g qds to be taken when menstruating heavily
Combined oral contraceptive pills
benefit double up as very effective contraceptivelimited by side effect and contra indications ,age smoking ,obesity and family history
Norethisterone
cyclical from day 6 to day 26 of menstrual cycle
5 – 10 mg tds
Effective ,oral use but can cause break through bleeding
Levonogestrel intrauterine system (mirena )
reduce menstrual blood by 95 %effective contraceptive
disadvantages irregular menses and break through bleeding in the first 3 – 9 month after insertion
GnRH agonists
Act on pituitary to stop the production of estrogen which result in amenorrheafor short term use because its used limited due to hypo estrogenic state and can cause flushing and sweating
use for maximum 6 month unless addback HRT
effective in reducing dysmenorrhea
can cause irregular bleeding
Dose Zoladex 3.6 mg monthly or Decapeptyl 3 mg monthly
SURGICAL TREATMENT
failure of medical treatmentcomplete family
Endometrial ablation
destructive procedures employ the principle that ablation of endometrial lining of the uterus to sufficient depth prevents regeneration of the endometrium
reduction blood loss by 95 %
different method either resection of endometrium ,thermal ablation ,balloon thermal ablation ,microwave ablation
Hysterectomy
KEY POINT
PREGNANCY SHOULD ALWAYS BE CONSIDERED AND EXCLUDED
CONTRACEPTIVE HISTORY IS VITAL
REGULAR BLEEDING USUALLY INDICATE HORMONAL OR SYSTEMIC CAUSE WHILE IIREGULAR BLEEDING INDICATE LOCAL CAUSE
PATIENT AGE IMPORTANT AND MAY REFLECT THE UNDERLYING CAUSE
EXTREME REPRODUCTIVE AGE USUALLY BENIGN AN OVULATORY DUB WHILE MIDDLE AGE USUALLY BENIGN ORGANIC PATHOLOGY AND IF DUB USUALLY OVULATORY TYPE
COAGULATION DEFECT SHOULD BE EXCLUDED IN ANY ADOLECENT WITH ABNORMAL BLEEDING CAUSING SIGNIFICANT ANEMIA OR FAMILY HISTORY OF BLEEDING TENDANCY