Assessment of the Musculoskeletal System
The skeleton proper (bones & joints)Skeletal muscles
TendonsLigaments
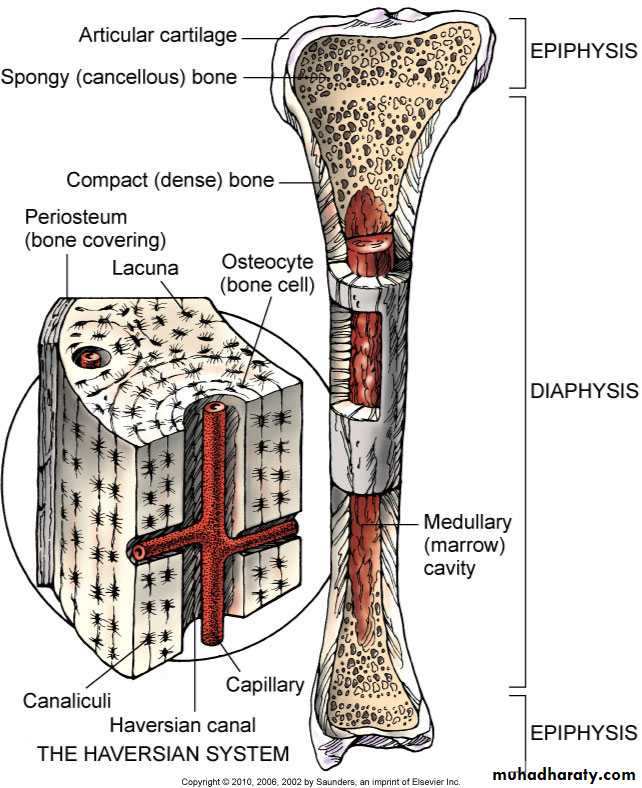
Composition of the Musculoskeletal SystemBone Structure
Types include synarthrodial, amphiarthrodial, diarthrodial.
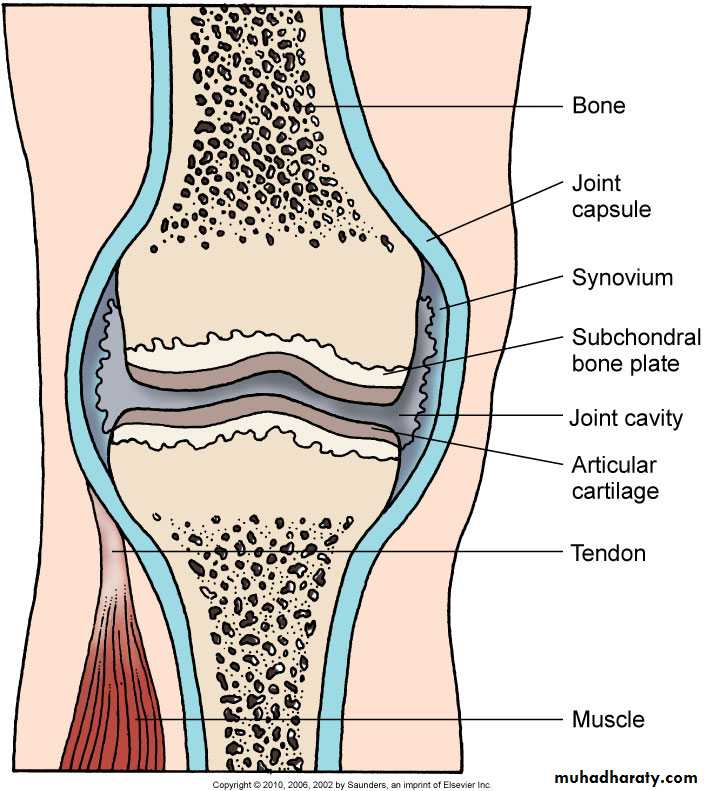
Structure synovial joint.Subtyped by anatomic structure:
Ball-and-socket
Hinge
Condylar
Biaxial
Pivot
Joints
Structure Diarthrodial Joint
History-taking
Inspect & Palpate jointsAssess range of motion
Assess muscle strength
1
2
3
4
5
Assessment of the musculoskeletal system
Face and neckSpine
Hand
Hip
Ankles, feet
Neurovascular assessment
Psychosocial assessment
Specific Assessments
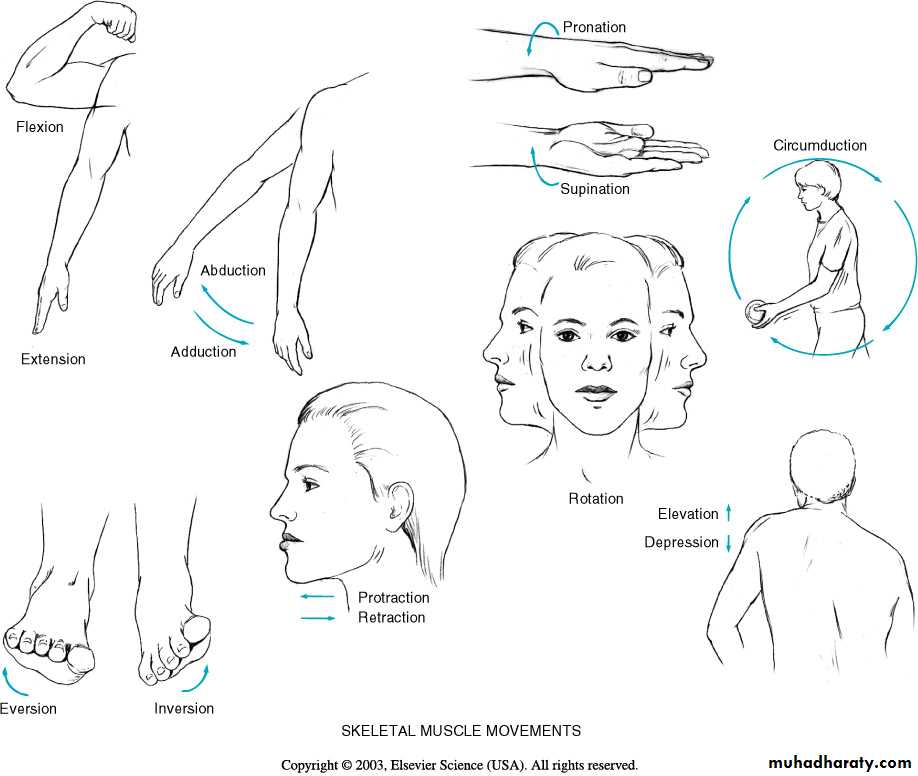
Flexion
Extension
Dorsiflexion
Plantar flexion
Adduction
Abduction
Joint motion - a review of terms
Inversion
Eversion
Internal rotation
External rotation
Pronation
Suppination
Measuring Range of Motion
If any limitation or increase in ROM is noted, use a ___________ to measure the angles preciselyDifferential diagnoses - what is the primary problem
FractureSprain
Dislocation or subluxation
Joint or muscle inflammation
Age specific abnormality
Systemic illness (examples)
neuropathy
myopathy
connective tissue disease
Laboratory tests—serum calcium and phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase, serum muscle enzymes
Radiographic examinations—standard radiography, bone density, tomography and xeroradiography, myelography, arthrography, and CT
Other diagnostic tests—bone and muscle biopsy
Diagnostic Assessment
EMG aids in the diagnosis of neuromuscular, lower motor neuron, and peripheral nerve disorders; usually with nerve conduction studies.
Low electrical currents are passed through flat electrodes placed along the nerve.
If needles are used, inspect needle sites for hematoma formation.
Electromyography
Fiberoptic tube is inserted into a joint for direct visualization.
Patient must be able to flex the knee; exercises are prescribed for ROM.
Evaluate the neurovascular status of the affected limb frequently.
Analgesics are prescribed.
Monitor for complications.
Arthroscopy
Bone scan
Gallium or thallium scanMagnetic resonance imaging
Ultrasonography
Other Tests
Mechanical inflammatory
Inherited acquiredSymmetrical asymmetrical
Poly oligo monarticulaer
E.g back pain discitis
marfan lig tearploymyosits muscle tear
RA RACTIVE arthritis septic arthritis
Types od disorders
Sign of arthritis =red warm limitation swelling
Types of arthritis=Septic
Crystal induced
Autoimmune
Para neoplastic
Reactive
Arthritis or arhtherlgia
1-what are the tissues that lead to joint pain
2-how you can differentiate between arthritis and artherlgia !!signs or symptoms2 notices